A business plan serves as the role of a roadmap guiding and showing related parties in an organization where a business is headed. A well-thought-out business planning will pave the way for the success of a firm’s operation. This ultimate guide will show you how to get your plan done step-by-step without any complexity or frustration.
Table of Contents
Basic concepts about business planning
What is business planning?
A business planning process can play out in various ways. If you have ever jotted down just some business ideas with a few tasks to be accomplished, that means you’ve written a business plan—or at least some basic components of it. Another example is when the upper managers come together to make a plan for the company’s success. Therefore, in its simplest form, a business plan is a plan that demonstrates how your business is going to operate, and how you’re going to make it succeed.
In detail, business planning commonly involves certain sections such as collecting ideas that outlines a summary of the business’ current state, the state of the broader market, as well as detailed steps the business will take to improve its performance in the coming period.
Why do we need business planning? First and foremost, the purpose of a business plan is to describe, analyze a business opportunity and/or examine the current situation of a firm. In addition, it can be used as a source of reference for partners, investors, or any other related parties to have an overview of your company before making any investment decision. A structured and comprehensive business plan will play an important role in persuading potential investors to offer financial support to help you expand your business.
>> Read more: 6 Big project implementation steps to start an e-Commerce website
Common types of business planning
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is basically a quick summary of a business delivered on a single page. In this format, the business situation and plan are described in concise, direct, and to-the-point language.
This type of business planning normally serves two purposes. Firstly, it can be a great tool to introduce the business to outsiders who expose themselves to the company in the first place. Due to time limitation, a simple one-page plan is often a better approach compared to a long and detailed one. Secondly, a one-page plan is more suitable for early-stage companies. This is because keeping the business idea on one-page size can make it easier to oversee the entire concept at a glance and quickly refine any part when new ideas come up.
Lean business plan
Lean business planning is a commonly-used format among enterprises. Basically, it is more detailed than the first type with some additional information about finance. However, it’s not as long as the third type. Therefore, lean plans are preferred to be used internally by both start-up and mature companies for strategic planning and growth.
Specifically, lean business planning includes loan/ investment sections and focuses almost exclusively on business strategy, milestones, tactics, metrics, budgets, and forecasts. This type of business plan omits some sections such as the company’s history, organization, and management as company’s employees certainly should be aware of these information.
Traditional business plan
Traditional business plan, also known as an external business plan, is the formal document to provide information about a business to outsiders. Compared to a lean plan, this type of business planning is more well-presented, with more attention to detail in the language and format.
In addition, an external plan demonstrates how potential funds are going to be used and what are the expected return on the investment. Furthermore, it puts a strong emphasis on the upper management team. Thus, it’s critical to include key team members’ biographies and how their background experience can help the company grow.
8 Major components of business planning
When you map out a business plan, it is not necessary to stick to the exact traditional business planning process or outline. Instead, you can choose the most suitable sections for your business and needs, and omit those that are not relevant. A common business planning skeleton consists of 8 fundamental sections as below.
Executive summary
The first step in business planning is to create an effective and concise executive summary. Normally, the executive summary will be the first chapter in your plan and ideally take up one or two pages. This section is an overview of your company and your plans, containing information about what your business does, what its current position is, where you want to take your business in a certain period of time, and why it will be successful.
The role of an effective executive summary in business planning should not be underestimated. In fact, it is an important part that investors solely ask for when deciding whether to work with your business or not. You can simplify this step of your business planning by drawing out some pieces of information as following:
- Mission statement: Your mission statement should briefly explain your business and the set goals.
- General information: Including the company’s history and development, its organizational structure and locations – make sure to keep it short and straightforward.
- Highlights: Key milestones of the business can be evidence supporting why the company will be successful in the future.
- Products and services: Briefly describe what your company sells and your customers.
- Financial information: You can include this information in your business planning if you plan to ask for financing support from investors.
- Future plans: Summarize where you plan to take your business in the future.
Company description
The second step in business planning is adding a company description. Compared to the brief information you provide in the executive summary, the company description is a top-level look into the company’s current situation.
You can break down this section into some specific bullets to better describe your business operations and boast about your strengths.
- What your business does: You should start this section by describing the purpose of your business, your target customers, budget, along with service or product lines. These pieces of information will give readers and investors a general sense of your firm.
- Specific information about the industry and marketplace of your business: In this part, you should give all related parties insight into the nature of the industry and marketplace that your company operates in. You can also highlight the competitive edge and your value proposition that the firm offers to the market as supporting details for further business planning.
- The legal structure of your business: This is when you explain what kind of business entity of your company (Sole Proprietorship, Limited Partnership, General Partnership, C-Corporation, S-Corporation or Limited Liability Company). Besides, you need to describe briefly the overview of your own structure as well.
Essentially, the company description section should be precise and informative, and at the same time, gives a catchy pitch about your firm to win over potential investors.
Market research
In the next step of business planning, you have to perform a comprehensive analysis of your industry, market, and competitors.
The purpose of the market research is to convince prospective investors that you, as the business owner, have a solid understanding of the industry outlook, target market, and your business’ role. To effectively shed light on this analysis, your business planning should include the following sections:
- Industry description: In this part, you might want to dive into details about the size of your industry, its development scenarios over the years, list out and explain important trends and characteristics. Some major players in the industry should be mentioned as well.
- Target market overview: Describe your target market, audience, and customers in a high-level overview.
- Target market characteristics: You want to give readers feasible answers to their questions regarding your customers, their needs, the location of your target market, the type of your business’ target market, the key demographic that your company is serving. This way, you can ensure readers in-depth information on your target market.
- Target market size and growth: You should include specific and updated data about the market size in the overall industry over time, and then a sense of the predicted growth of your market.
- Your market share potential: Once you are equipped with an in-depth analysis of your target market’s current state, you need to estimate the proportion of market share your firm expects to gain in the targeted geographic area.
- Market pricing: Thanks to market research, you can give the most suitable estimated pricing for your products and propose proper distribution and promotional strategies.
- Barriers: It’s important to include barriers to market entry that your business may confront in your business planning. Some sources of market barriers could be policies and regulations, lack of personnel, changing technology, or high investment outlays, etc.
- Competitor research: Last but not least, you have to perform a competitor analysis to propose strategic business planning for your company’s growth. Consider your target market as a whole, now you can narrow your top competitors into these main types: direct, indirect, and replacement. Then, you can choose to apply the most suitable competitor research to develop an impactful marketing strategy for your brand. These five frameworks are respectively: SWOT, Porter’s five forces, strategic group analysis, growth-share matrix, and perceptual mapping. Regardless of whatever competitor research you stick to, you need to complete some major tasks namely: identify competitors, compare marketing indexes (including marketing positioning, site traffic and performance keywords, the share of voice, backlinks, and SEO effectiveness).
Organization and management
Defining your company’s organization and management structure is one of the crucial stages in business planning. This section lays out who is in charge of certain responsibilities in your company as well as their background and contribution to the success of your business.
At this point, you need to break down some concepts:
- Organizational structure: An organizational chart showing how your firm is structured could be an excellent choice to clarify each position.
- Ownership structure: You have scratched the surface of your business’ ownership structure in the company description. However, in this stage of business planning, you need to dive deeper into how your firm is legally structured by explaining who owns what and providing data on how much they own.
- Background information of owners and board of directors: This is your chance to present your company’s competitive edge – quality leadership.
- Hiring need: You can also list out any key talent acquisition strategies in order to achieve your business goals in the future.
>> Read more: Digital transformation for retail: 5 Consumer shopping trends 2020
Products and services
Now, it’s time to thoroughly explain the products or services your business offers. This practice will help you lay out your business planning for product positioning.
You can start off by adding some bullet points as follows:
- A description of your business’ products or services: You need to give details about your offerings and highlight what makes them stand out.
- Current status of products: You should give a realistic and honest picture explaining the development of your offerings. If you’re conducting research and development of a product or service, explain it in detail.
- Intellectual property: A patent can provide your business with a competitive edge over your competitors in the marketplace. Therefore, if you need to grant patents for your offerings, you should jot that down in your business planning.
- Sourcing and fulfillment: It is necessary to include information about your sourcing practice and fulfillment status in business planning. This data will be evidence of your strategic path in the future.
Marketing and sales
After giving all the essential details regarding your market offerings, you will jump into explaining your marketing and sales strategies. Your ultimate goal in this section is to describe and explain how you will attract and retain customers.
Let’s kick off with the marketing strategy. In fact, there is no single way to approach a marketing plan. Your strategy should be able to generate quality leads in accordance with the growing needs of customers. Basically, you need to pay attention to two core marketing aspects namely:
- Positioning: Brand positioning can determine where your brand stands in the mind of your customers, and decide how they find and interact with your firm. Thus, you need to explain how unique your positioning strategy is in order to appeal to investors.
- Promotion: Next, you need to frame the plans you build for product packaging and advertising (both online or traditional approaches), public relations, or your content marketing practices.
Once you have your marketing framework explained, you need to include your sales plan in business planning. At this point, you come to describe and project your salesforce and selling strategy:
- Salesforce: Describe your sales team regarding the size, training process, and vision of the department.
- Selling strategy: You’d better give your readers an overview of how you will start and close the deal. Besides, you can also demonstrate your understanding by engaging a detailed description of the sales funnels for your business.
Financial projections
Last but not least, you should supplement your strategic funding request with financial projections. At this step, your aim is to create a positive image of your firm’s stability, thus proving that your business will be worth the capital investment of potential investors.
If your firm is already established, you should include some document as below in your business planning:
- Income statements.
- Balance sheets.
- Cash flow statements.
- Accounts receivable statements/ Accounts payable statements/ Documentation of debt obligations (if applicable).
At the same time, you also want to create a positive outlook for the next coming years. To achieve that, you should include the forecasted version of these above documents, then clearly explain your financial projections, and finally match them to your funding requests.
In case your business is a startup firm without any previous financial data, you need to drop out financial projections in this section. Research and analysis of the industry and your top competitors in previous steps will assist you during this journey. You might want to include:
- Statements of projected income.
- Balance statements.
- Capital expenditure budgets.
- Cash flow forecasts.
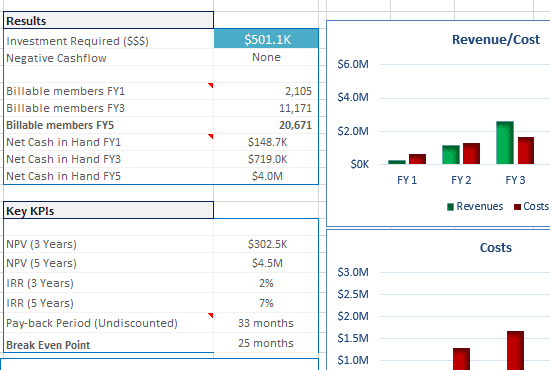
To get into detail regarding a financial projection, consulting with a business accountant or financial advisor might be a wise choice to minimize any future mistakes. Besides, to better demonstrate the projections, charts or graphs are commonly-used tools.
In addition, an optional part you might want to include in your financial business planning could be funding requests. Here, you need to prepare a detailed plan that contains:
- The amount of funding you need right now.
- Any funding you will need in the future.
- The purpose and the possible impact of the funds (it could be working capital, franchising fees, equipment purchases, or even acquiring a business, etc.).
Appendix
The appendix appears at the end of your business planning, holding all of the supporting information for your claims in the document.
With the appendix, you can cite any additional data points, footnotes, charts, further explanations, or even some legal documents, contracts, and product pictures. Other than that, the appendix is also a great place to include resumes of your staff for better references.
3 Must-read tips to make business planning easier
Keep it short and straightforward
An effective business planning should be short and straight to the point. This can be explained by two reasons. First, concise business planning is more appealing to the reader compared to the prolonged and off-topic one. Second, your business planning is the guidance for a firm in its development journey. Therefore, an excessively long business planning can be a certain deterrent for you to revise and base on when needed.
Know your audience
Another useful tip concerns the use of language in business planning. Ideally, you should write the plan with proper language so that your audience will fully understand the message.
In detail, successful business planning should provide simple and direct explanations, use easy-to-understand terminologies, and include a detailed appendix for further references.
Revise and update it regularly
Normally, the most important section of business planning is the review schedule in which you set specific times to review your progress toward set goals. As a guide map for your business development, business planning can bring long-term benefits. Therefore, rather than a one-off event, it should be an ongoing practice of self-assessment and planning with regular revision and update.
The takeaway
There you have it – as we’ve broken down step-by-step on how to write business planning effectively for your company development. It’s time to jump into action to guide your business on the right track.
If you stumble upon any problems during the process, let us know by leaving a comment belo. We will come back to you with a rational explanation.