At its core, an omnichannel warehouse bridges the gap between online and offline operations by providing real-time visibility into inventory across multiple channels. This ensures that customers can access accurate stock information whether they are shopping online or in-store. Additionally, omnichannel warehouses support a variety of fulfillment strategies, from same-day delivery to click-and-collect, allowing businesses to offer faster and more flexible delivery options.
This blog post will explore the transformative impact of omnichannel warehousing on supply chain operations and customer satisfaction, while diving deep into the strategies, technologies, and best practices that businesses can adopt to stay ahead in today’s omnichannel-driven marketplace.
Table of Contents
Understanding Omnichannel Warehouse
Omnichannel Warehousing And Its Role In Modern Supply Chains
Definition of Omnichannel Warehousing
Omnichannel warehousing refers to the integration and coordination of a company’s inventory, order management, and fulfillment processes across all sales channels, both online and offline. Unlike traditional warehousing models, where products are stored and distributed based on singular or limited channels (such as a single eCommerce platform or brick-and-mortar stores), an omnichannel warehouse facilitates the flow of goods across all retail and distribution points. This system ensures that products are available to customers regardless of where they choose to shop, whether it be online, in-store, or through mobile apps.
The omnichannel warehouse plays a pivotal role in modern supply chains by ensuring real-time inventory visibility, flexible fulfillment options, and optimized delivery speed. This type of warehousing is designed to handle the complexities of multiple channels, providing a cohesive system where orders from eCommerce platforms, retail stores, and third-party marketplaces are processed efficiently within the same facility. It centralizes all aspects of warehousing, from storage and picking to packing and shipping, allowing businesses to manage all customer orders from a unified system. This centralization not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances the customer experience by ensuring that inventory is accurately reflected across all sales channels.
Differences Between Traditional and Omnichannel Warehousing
The differences between traditional warehousing and omnichannel warehousing are stark and reflect the broader shift in the retail and eCommerce industries. A traditional warehouse typically supports single-channel distribution, meaning it is often siloed in its approach. For example, a traditional warehouse may be dedicated solely to storing goods for physical retail stores or fulfilling orders from an eCommerce platform. In this model, there is minimal interaction between the systems managing in-store inventory and those handling online sales. This often results in inefficiencies, such as stockouts or overstocks, where products may be unavailable in one channel despite being overstocked in another.
In contrast, the omnichannel warehouse breaks down these silos by centralizing inventory management and distribution for all sales channels. With real-time visibility, an omnichannel system allows businesses to use a single pool of inventory for multiple channels, ensuring better stock utilization. For example, if an item is low in stock for an online order, it can be sourced from a nearby retail store or fulfillment center to avoid a delay. This flexibility is essential for meeting customer expectations, particularly in terms of delivery speed and convenience.
Additionally, traditional warehouses tend to operate in a more static and reactive manner, relying on bulk shipments and scheduled deliveries. However, an omnichannel warehouse is far more dynamic, capable of processing individual orders, managing same-day deliveries, and offering flexible fulfillment options such as in-store pickup (click-and-collect) or curbside delivery. This adaptability allows businesses to cater to customer preferences more effectively while streamlining operations to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
The omnichannel warehouse represents a transformative shift from the rigid, single-channel focus of traditional warehousing to a more fluid, integrated system that supports the complexities of modern retail. By embracing this model, businesses can improve their supply chain efficiency, enhance the customer experience, and better manage the challenges of today’s multi-channel retail environment.
Importance in the Retail Landscape
The Rise of eCommerce and the Need for Seamless Integration
In recent years, eCommerce has become a dominant force in the global retail industry, changing the way businesses operate and how customers interact with brands. The shift towards digital retail has necessitated the evolution of traditional supply chains and warehousing models. The omnichannel warehouse emerges as a direct response to these changes, enabling businesses to manage and integrate multiple sales channels, including online marketplaces, physical stores, and direct-to-consumer platforms, within a unified operational framework.

As customers engage with brands through various channels, businesses can no longer afford to operate in silos. An omnichannel warehouse ensures that inventory is centrally managed and that orders from any sales channel can be fulfilled efficiently. Whether a customer places an order online, via mobile, or at a physical store, the omnichannel warehouse integrates all these touchpoints to streamline operations. This seamless integration allows for real-time synchronization of stock levels, which is essential for providing accurate product availability information across all channels. Without the implementation of an omnichannel warehouse, businesses may struggle to meet the growing demands of a digitally-driven marketplace, leading to delays, stock discrepancies, and dissatisfied customers.
Moreover, the omnichannel warehouse supports businesses in scaling their operations to meet the increased volume of online orders, particularly during peak seasons. As eCommerce continues to grow, having a warehousing system that can dynamically adjust to handle surges in demand becomes essential. The omnichannel warehouse offers the flexibility and scalability that modern retailers need to remain competitive in this fast-paced environment.
Customer Expectations
Today’s consumers expect more from the brands they interact with, and this extends to how products are delivered and managed. One of the most significant changes in consumer behavior is the demand for faster deliveries. With the rise of same-day or even one-hour delivery services offered by major retailers, the omnichannel warehouse must be equipped to handle such expectations. By integrating various fulfillment models—such as ship-from-store, click-and-collect, or direct delivery—the omnichannel warehouse enables businesses to offer a range of delivery options that meet the specific needs of their customers.

Real-time stock availability is another critical factor driving the importance of omnichannel warehouses. Customers expect the information they see online or in-store to reflect the actual availability of products. An omnichannel warehouse provides real-time updates on stock levels across multiple channels, preventing situations where customers place orders for items that are out of stock. This transparency helps build trust with customers and ensures a more reliable shopping experience.
Furthermore, consumers today seek flexibility in how and when they receive their orders. With options like curbside pickup, in-store pickup, or home delivery, customers now have more control over their purchasing experience. The omnichannel warehouse plays a vital role in offering these choices by ensuring that all fulfillment methods are seamlessly coordinated. Whether it’s preparing an order for in-store pickup or shipping it directly from a warehouse, the omnichannel warehouse manages these processes to ensure fast, accurate, and convenient service for the customer.
Key Components of Omnichannel Warehousing
Inventory Visibility
Real-time Inventory Tracking and Management Across All Sales Channels
One of the main challenges in managing an omnichannel warehouse is ensuring that inventory levels are accurately tracked and updated in real time across all sales platforms. In a traditional warehouse, stock might only be updated at certain intervals, creating discrepancies between what is available and what is displayed to customers. However, in an omnichannel warehouse, real-time inventory tracking is essential to avoid issues such as selling out-of-stock items online or holding excess inventory in one location while other channels face shortages.
Real-time inventory visibility allows businesses to synchronize their stock levels across all sales channels, from eCommerce platforms to physical retail locations. This means that when a customer makes a purchase online, the system immediately updates the available stock, reducing the risk of overselling. Similarly, if inventory is low at one location, the omnichannel warehouse system can automatically source products from another warehouse or store, ensuring that customer orders can be fulfilled without delay. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also improves the customer experience, as shoppers are less likely to encounter unavailable items or shipping delays.
In addition to improving fulfillment speed, real-time inventory tracking helps businesses optimize their stock levels across various locations. By having a clear, centralized view of inventory, companies can make informed decisions about where to allocate products based on demand, minimizing the costs associated with excess stock or emergency restocking. This ability to dynamically manage inventory in response to real-time data is a key advantage of the omnichannel warehouse model.
Technologies Supporting Inventory Visibility in Omnichannel Warehousing
To achieve real-time inventory visibility in an omnichannel warehouse, businesses rely on several advanced technologies that help track, manage, and update stock levels with precision. Among these technologies, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) play a pivotal role in ensuring that inventory is monitored accurately across all channels.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification)
RFID technology is a game-changer for inventory management in the omnichannel warehouse. It uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to products, allowing for seamless stock monitoring without manual intervention. RFID tags can be scanned from a distance, which makes it significantly easier for warehouse workers to track large volumes of items in real time. This technology eliminates human error in inventory counting and ensures that stock levels are updated instantaneously across all platforms. As a result, the omnichannel warehouse benefits from faster and more accurate inventory tracking, reducing the risk of discrepancies between physical stock and what is displayed online or in stores.
RFID also enhances the ability of the omnichannel warehouse to handle multiple fulfillment methods. For example, when a product is purchased through click-and-collect, the RFID system can quickly locate the item in-store, ensuring that the order is ready for pickup without delay. This level of automation streamlines the entire fulfillment process, making the omnichannel warehouse more efficient and responsive to customer needs.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) further enhances inventory visibility by connecting physical devices—such as sensors, RFID readers, and inventory management systems—into a unified network. In an omnichannel warehouse, IoT devices can monitor various aspects of inventory in real time, from stock levels to the movement of goods within the warehouse. For example, IoT-enabled sensors can track when products are moved from one location to another or when they are picked for fulfillment, ensuring that the system is always up to date.
IoT plays a crucial role in ensuring that all locations within the omnichannel warehouse network are synchronized. Whether inventory is stored in a central distribution center or a local store, IoT technology ensures that any changes in stock levels are communicated to the central system, allowing for accurate real-time visibility. This level of transparency is especially important in a complex omnichannel environment, where inventory can be distributed across multiple fulfillment centers, stores, and even third-party logistics providers.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Advanced Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are the backbone of any omnichannel warehouse. These systems provide comprehensive oversight of inventory levels, order management, and fulfillment processes, enabling businesses to track stock in real time across all channels. A WMS integrates with other systems, such as eCommerce platforms, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and transportation management systems (TMS), creating a cohesive network that ensures inventory is updated and orders are fulfilled efficiently.
A WMS in an omnichannel warehouse can automatically allocate inventory based on demand, ensuring that products are sourced from the most optimal location for fulfillment. For example, if a customer orders a product online, the WMS can determine whether to ship from a warehouse, a store, or a fulfillment center based on proximity, stock levels, and delivery speed. This level of automation reduces manual intervention, streamlines operations, and enhances the customer experience by ensuring faster and more accurate deliveries.
Moreover, WMS systems can generate real-time reports and analytics, providing businesses with valuable insights into inventory performance. This data-driven approach allows companies to make informed decisions about stock allocation, replenishment, and demand forecasting, further optimizing the omnichannel warehouse for efficiency and profitability.
Seamless Order Fulfillment
Efficient Processing of Orders from Different Sales Platforms
One of the key challenges of managing an omnichannel warehouse is the ability to handle orders from various sales platforms in a cohesive manner. Traditional warehousing models often struggle with siloed operations, where orders from different channels (such as online and in-store) are processed separately, leading to inefficiencies and delays. However, in an omnichannel warehouse, all orders are funneled into a centralized system that coordinates the fulfillment process across all channels.
The omnichannel warehouse operates with a unified view of inventory and order data, enabling it to streamline the fulfillment process. For example, when an online order is placed, the warehouse management system (WMS) in the omnichannel warehouse can automatically identify the best location to fulfill the order, whether it is from a central distribution center, a local store, or another fulfillment hub. This flexibility ensures that the order is processed and shipped as quickly as possible, reducing delivery times and minimizing the risk of delays or stock shortages.
By integrating sales channels, the omnichannel warehouse also supports cross-channel fulfillment, where products purchased through one channel can be fulfilled by another. This level of integration is essential for meeting customer expectations for convenience, especially when they choose to buy online and pick up in-store or return items purchased online at a physical location. The ability of the omnichannel warehouse to facilitate these processes ensures a seamless experience for the customer, regardless of how they interact with the brand.
Various Omnichannel Fulfillment Models
A major strength of the omnichannel warehouse is its ability to support various fulfillment models, allowing businesses to offer flexible options to their customers. These fulfillment models, which include ship-from-store, click-and-collect, and same-day delivery, are designed to meet different customer needs, from fast delivery to convenience. By incorporating multiple fulfillment strategies into the omnichannel warehouse, businesses can improve the customer experience and stay competitive in an increasingly demanding market.
Ship-from-Store Fulfillment
Ship-from-store is one of the most effective omnichannel fulfillment models, allowing businesses to leverage their physical retail locations as fulfillment centers. In this model, an order placed online or through a mobile app is fulfilled using inventory from a nearby store rather than a central warehouse or distribution center. This strategy offers several advantages. First, it reduces delivery times by shipping from a location that is geographically closer to the customer. Second, it helps optimize inventory usage by utilizing stock from stores that may have excess inventory. Finally, it helps reduce shipping costs, as products are shipped from local stores rather than from a single central location.
For example, a customer in a major metropolitan area might place an order online for an item that is available in a nearby store. Instead of the order being fulfilled by a warehouse hundreds of miles away, the omnichannel warehouse system identifies the store with available stock and routes the order to be picked, packed, and shipped from that location. This not only speeds up the delivery process but also frees up capacity in the central warehouse for handling other orders.
Click-and-Collect (Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store)
Click-and-collect, also known as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), is another popular omnichannel fulfillment model that is widely used in today’s retail environment. This model allows customers to place orders online and then pick them up at a physical store, providing a convenient option for those who prefer not to wait for shipping or who want to avoid delivery fees.
In an omnichannel warehouse, the click-and-collect process is seamlessly integrated with the overall inventory and fulfillment system. When an online order is placed for in-store pickup, the omnichannel warehouse identifies the nearest store with the required inventory and ensures that the item is reserved for the customer. The store is then notified to prepare the order for pickup, streamlining the process and reducing the time it takes for the customer to collect their purchase.
Click-and-collect is a highly effective model for improving customer convenience, as it allows shoppers to browse and purchase items online while still enjoying the immediate gratification of in-store pickup. This model also helps reduce the strain on the central omnichannel warehouse by distributing fulfillment tasks to individual stores, making it an ideal strategy for businesses with multiple retail locations.
Same-Day Delivery
Same-day delivery is one of the most sought-after fulfillment options in the modern retail landscape. As customers become increasingly accustomed to fast shipping speeds, businesses are under pressure to provide same-day or next-day delivery services. The omnichannel warehouse plays a crucial role in facilitating these expedited deliveries by optimizing the fulfillment process and ensuring that orders are picked, packed, and shipped as quickly as possible.
In an omnichannel warehouse, same-day delivery is made possible through a combination of advanced inventory management, real-time data tracking, and strategic fulfillment location optimization. When a same-day delivery order is placed, the omnichannel warehouse system immediately identifies the closest fulfillment center or store with the necessary stock, ensuring that the order is fulfilled and shipped in the shortest possible timeframe. This process is highly automated, reducing the time and effort required to process same-day delivery orders.
By supporting same-day delivery, the omnichannel warehouse allows businesses to stay competitive in an environment where fast shipping is a key differentiator. Moreover, this fulfillment model enhances customer satisfaction by providing a level of service that meets the increasing demands for speed and convenience.
Flexible and Scalable Storage
The Importance of Adaptable Storage Solutions for Fluctuating Inventory Levels
One of the primary challenges faced by an omnichannel warehouse is managing fluctuating inventory levels across multiple sales channels. In today’s retail environment, demand can change rapidly due to factors such as holiday shopping seasons, promotional events like Black Friday or Cyber Monday, or sudden shifts in consumer preferences. To accommodate these fluctuations, the omnichannel warehouse must be equipped with adaptable storage solutions that allow for the seamless expansion or contraction of storage space.
During peak demand periods, such as the holiday season, an omnichannel warehouse may experience significant increases in order volume. In these situations, traditional static storage solutions can become a bottleneck, leading to inefficiencies such as overcrowded aisles, delayed order picking, or even stockouts. By implementing flexible storage systems, the omnichannel warehouse can quickly adjust its layout to accommodate additional inventory without sacrificing operational efficiency. For example, adjustable shelving systems or mobile storage units can be reconfigured to create more space for high-demand products, allowing for quicker access and faster fulfillment times.
Conversely, when demand decreases, such as during off-peak seasons, the omnichannel warehouse must be able to scale down its storage operations to avoid wasting space and resources. In this scenario, flexible storage solutions allow the warehouse to consolidate inventory into a smaller footprint, reducing overhead costs such as heating, lighting, and labor associated with maintaining unnecessary space. The ability to scale storage space in response to fluctuating demand ensures that the omnichannel warehouse operates efficiently year-round, regardless of market conditions.
In addition to seasonal fluctuations, omnichannel warehouses must also be prepared for demand surges driven by unexpected events, such as viral product trends or supply chain disruptions. By utilizing scalable storage solutions, an omnichannel warehouse can respond quickly to these changes, ensuring that inventory is properly managed and customer orders are fulfilled without delay.
Techniques for Optimizing Warehouse Space
To achieve flexible and scalable storage, an omnichannel warehouse must employ a range of techniques designed to optimize space utilization and accommodate different inventory levels. These techniques not only enhance the warehouse’s ability to scale operations but also improve overall efficiency by ensuring that products are stored and retrieved in the most effective manner possible. Two of the most important techniques for optimizing space in an omnichannel warehouse are the use of dynamic storage layouts and modular systems.
Dynamic Storage Layouts
Dynamic storage layouts are a key strategy for optimizing space in an omnichannel warehouse. Unlike static layouts, where storage locations are fixed and unchanging, dynamic layouts allow for the reconfiguration of storage zones based on current inventory needs. This flexibility is essential in an omnichannel environment, where different products may require different storage solutions depending on factors such as demand, size, and picking frequency.
One common approach to dynamic storage is the use of zone-based storage systems, where the warehouse is divided into different zones that can be adjusted to accommodate various types of products. For example, fast-moving items that are frequently ordered online may be stored in a high-access zone near the packing and shipping areas, while slower-moving products may be placed in a less accessible zone. During peak seasons or promotional periods, the layout can be adjusted to expand the storage capacity of high-demand zones, ensuring that frequently ordered products are easily accessible.
Another technique used in dynamic layouts is slotting optimization, which involves organizing products within the warehouse based on factors such as size, weight, and order frequency. By analyzing historical sales data, the omnichannel warehouse can determine which products are likely to be ordered together and place them in proximity to one another. This reduces the time and effort required for picking and packing, ultimately improving fulfillment speed and efficiency. Slotting optimization also allows the warehouse to reorganize its layout based on changing product demand, ensuring that space is used effectively as inventory levels fluctuate.
Modular Storage Systems
Modular storage systems are another critical component of scalable and flexible storage in an omnichannel warehouse. These systems are designed to be easily reconfigured, allowing the warehouse to quickly adapt to changes in inventory size, product type, or order volume. Modular storage units can be adjusted in height, width, or depth, providing a customizable solution for storing a wide range of products.
One of the most common types of modular storage used in omnichannel warehouses is adjustable shelving. These shelving units can be expanded or contracted to fit different product sizes, ensuring that storage space is maximized without wasting vertical or horizontal space. For example, during a peak season, the warehouse can expand its shelving units to accommodate larger volumes of products, while during off-peak periods, the shelves can be adjusted to store smaller amounts of inventory more efficiently.
Another example of modular storage is the use of mobile racking systems, which allow for the movement of entire storage units to create additional space when needed. These systems operate on tracks or wheels, enabling warehouse workers to move racks as inventory levels change. This flexibility is particularly useful in omnichannel warehouses with fluctuating demand, as it allows for the quick creation of additional storage space without the need for costly renovations or expansions.
Vertical Storage Solutions are also a popular modular system used in omnichannel warehouses, especially those with limited floor space. By utilizing the vertical height of the warehouse, these systems maximize storage capacity without taking up additional square footage. Vertical lift modules (VLMs) and automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) are examples of vertical storage solutions that can significantly increase the efficiency of an omnichannel warehouse by automating the storage and retrieval process.
Automated Solutions
The Role of Robotics and Drones in Automating Warehouse Tasks
In an omnichannel warehouse, robotics play a crucial role in automating tasks that would traditionally require significant manual labor, such as picking and packing products for shipment. The implementation of robots in the warehouse can significantly improve both the speed and accuracy of these tasks, allowing the warehouse to keep pace with high volumes of orders, especially during peak periods.
Robotic Picking and Packing
Robotic picking systems are designed to automate the process of selecting items from shelves and preparing them for shipping. In a traditional warehouse, human workers would need to navigate large aisles, manually locate items, and bring them to packing stations. This process can be slow and prone to errors, especially in large warehouses with thousands of products. In contrast, robotic systems in an omnichannel warehouse are capable of locating, retrieving, and delivering products to designated packing stations with remarkable speed and precision.
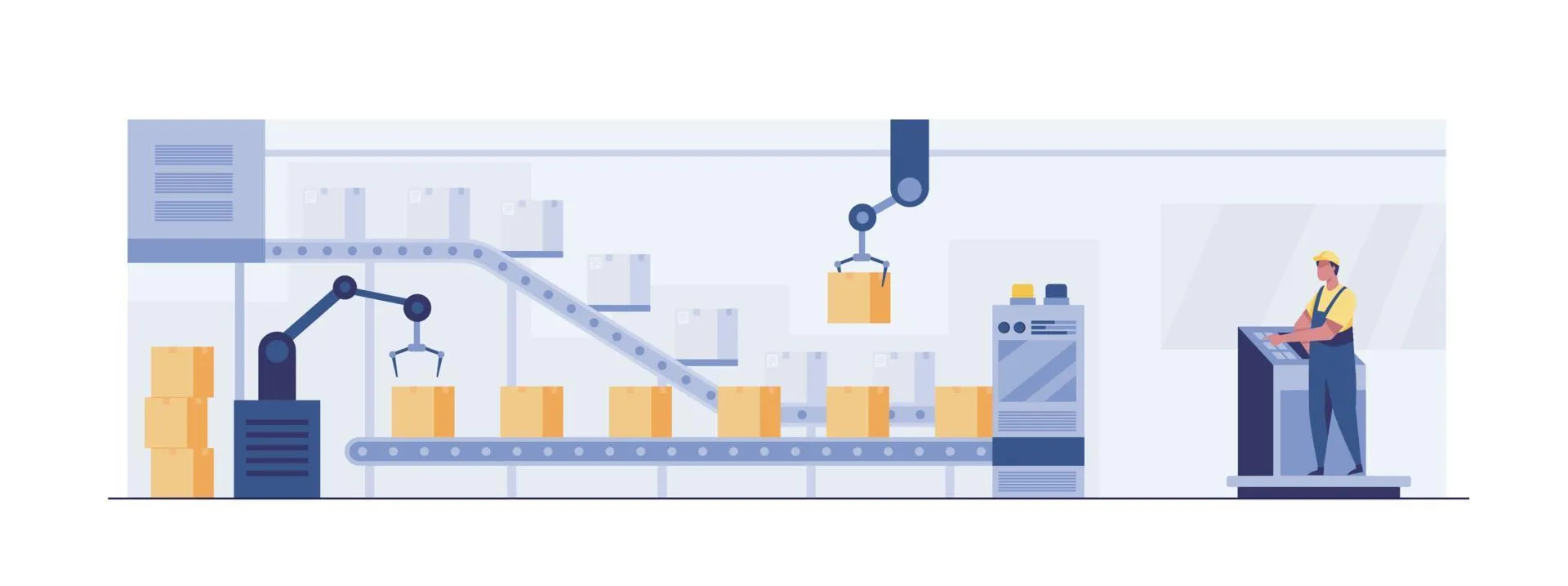
These robots, often referred to as automated guided vehicles (AGVs) or autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), can be programmed to travel specific routes or navigate the warehouse using advanced sensors and mapping technologies. This automation drastically reduces the time it takes to pick and pack orders, enabling the omnichannel warehouse to fulfill customer orders more quickly. Moreover, robotic systems are able to operate 24/7, allowing warehouses to handle a higher volume of orders without the limitations of human labor, such as fatigue or shift changes.
The omnichannel warehouse also benefits from robotic packing solutions, which automate the process of boxing and labeling items for shipment. This not only speeds up the packing process but also ensures consistent packaging quality, reducing the risk of damaged items during transit. Additionally, robotic packing systems can be integrated with warehouse management software to automatically print and apply shipping labels, further streamlining the process.
Drones for Inventory Checks
In addition to robotics, drones are becoming an increasingly important tool in the omnichannel warehouse, particularly for conducting inventory checks. In a large warehouse, manually counting and verifying inventory can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can fly through the warehouse, scanning inventory in real time and feeding data back to the warehouse management system. This ensures that stock levels are always up to date across all channels, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
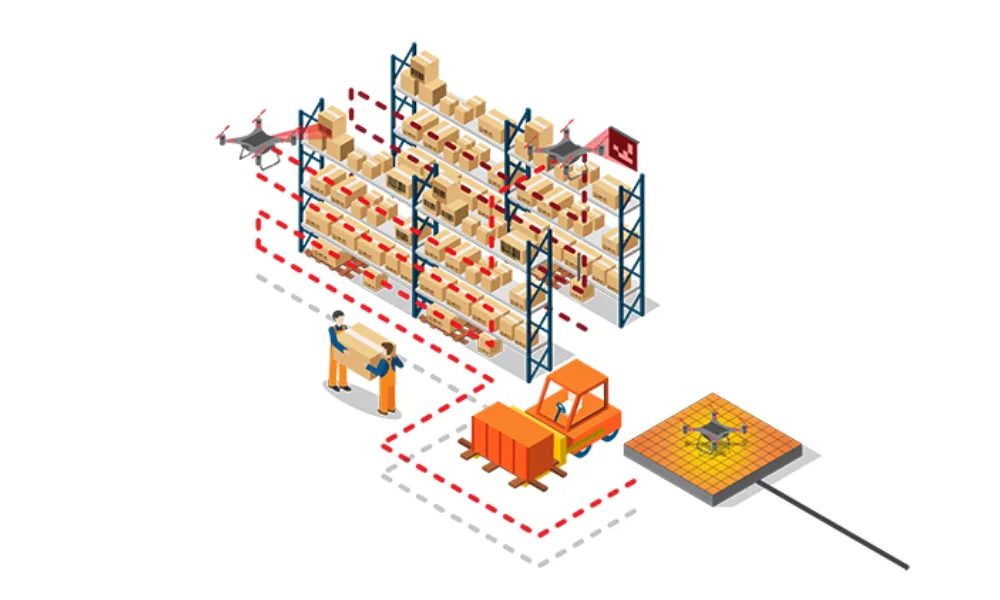
Drones are particularly useful for accessing hard-to-reach areas in the warehouse, such as high shelves or narrow aisles, where manual inventory checks would be difficult or dangerous. By automating this process, the omnichannel warehouse can maintain accurate inventory records without the need for regular physical audits, saving both time and labor costs. The use of drones for inventory management is a key example of how automation is improving operational efficiency in the omnichannel warehouse.
AI-Powered Automation Solutions for Predicting Demand and Optimizing Routes
While robotics and drones automate physical tasks within the omnichannel warehouse, AI-powered systems play a critical role in optimizing the decision-making processes that drive warehouse efficiency. AI-powered automation helps the omnichannel warehouse predict demand, optimize routes for picking and delivery, and manage inventory more effectively.
Predicting Demand with AI
One of the most significant benefits of AI in the omnichannel warehouse is its ability to predict demand with a high degree of accuracy. AI algorithms analyze large datasets from various sources, such as historical sales data, seasonal trends, and even external factors like weather patterns or social media activity. By identifying patterns and trends in this data, AI-powered systems can forecast future demand for specific products, allowing the warehouse to adjust its inventory levels accordingly.

For example, if an AI system predicts a surge in demand for certain products due to an upcoming holiday or promotional event, the omnichannel warehouse can preemptively stock more of those items to ensure they are readily available for fulfillment. This reduces the risk of stockouts and improves customer satisfaction by ensuring that products are always in stock when needed. Additionally, accurate demand forecasting helps the omnichannel warehouse avoid overstocking, which can tie up valuable storage space and increase holding costs.
Optimizing Routes for Picking and Delivery
AI-powered systems also play a crucial role in optimizing the routes used for picking items within the warehouse and delivering orders to customers. In the context of an omnichannel warehouse, where orders may be fulfilled from various locations (such as central distribution centers, local stores, or micro-fulfillment centers), efficient route planning is essential to minimize delivery times and reduce operational costs.
AI systems analyze real-time data to determine the most efficient routes for picking items within the warehouse. For example, if multiple orders contain similar products, the AI system can group these orders together and create an optimized picking route that minimizes travel time between different storage locations. This not only speeds up the picking process but also reduces labor costs by minimizing the distance that workers or robots need to travel within the warehouse.

For last-mile delivery, AI-powered automation systems can optimize delivery routes based on factors such as traffic conditions, weather, and proximity to the customer. By selecting the most efficient routes, the omnichannel warehouse can reduce delivery times and lower fuel costs, all while improving the customer experience by ensuring timely deliveries. This level of optimization is particularly important in an omnichannel environment, where customers expect fast and flexible delivery options such as same-day or next-day shipping.
Enhancing Overall Warehouse Efficiency
In addition to predicting demand and optimizing routes, AI-powered automation enhances the overall efficiency of the omnichannel warehouse by continuously monitoring and analyzing warehouse operations. AI systems can detect inefficiencies in real time, such as bottlenecks in the fulfillment process or underutilized storage space, and suggest corrective actions to improve productivity. For example, if an AI system identifies that certain products are frequently ordered together, it can recommend changes to the warehouse layout to place these products closer to one another, reducing picking times and improving order fulfillment speed.
By automating decision-making processes and providing actionable insights, AI-powered systems enable the omnichannel warehouse to operate more efficiently, reduce operational costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Multi-location Synchronization
Synchronization of Data Across Multiple Warehouse Locations
In an omnichannel warehouse setup, inventory is distributed across various locations to optimize order fulfillment speed and cost-efficiency. However, to effectively manage this distributed inventory, it is essential to synchronize data across all these warehouse locations. Data synchronization refers to the process of continuously updating and sharing inventory information in real time between different warehouses, retail outlets, and fulfillment centers.
For example, when a customer places an online order, the omnichannel warehouse management system (WMS) must immediately check inventory availability across multiple locations. If the item is available at a nearby warehouse or store, the system can route the order to the closest location for faster fulfillment. This decision-making process relies on real-time data synchronization between all locations to ensure that inventory levels are up-to-date and accurate.
Without proper synchronization, an omnichannel warehouse risks facing challenges such as discrepancies between physical and virtual stock levels. For instance, one warehouse might show items in stock even though they have already been sold through another sales channel, leading to delays in fulfillment and customer dissatisfaction. By maintaining accurate, real-time inventory data across all locations, the omnichannel warehouse ensures that customers receive reliable information about product availability, no matter which sales channel they use.
Moreover, data synchronization plays a critical role in ensuring that the omnichannel warehouse can quickly respond to shifts in demand. For example, during peak shopping seasons or special promotions, certain products may experience a sudden surge in demand. With multi-location synchronization, the omnichannel warehouse can identify which locations have surplus inventory and redistribute stock to areas with higher demand, preventing stockouts and improving overall efficiency.
The synchronization of data across multiple warehouse locations also enables businesses to optimize their order fulfillment strategies. In an omnichannel warehouse, orders can be fulfilled from a variety of locations, such as a central distribution center, a regional warehouse, or even a retail store. By having real-time visibility into inventory levels at each location, the warehouse management system can choose the most efficient fulfillment point, minimizing shipping times and reducing costs.
Ensuring Seamless Coordination Between Various Fulfillment Centers and Retail Outlets
The complexity of an omnichannel warehouse lies not only in managing inventory across multiple locations but also in ensuring seamless coordination between various fulfillment centers and retail outlets. The ability to synchronize operations across these diverse fulfillment points is essential for creating a unified and efficient supply chain. Seamless coordination ensures that all parts of the omnichannel warehouse network work together to meet customer expectations for fast, flexible, and accurate order fulfillment.
In an omnichannel warehouse, seamless coordination between different fulfillment centers and retail outlets means that the entire network operates as a cohesive system rather than as independent units. For example, if an item is out of stock at a central warehouse but available at a retail store, the omnichannel warehouse system can automatically redirect the order to be fulfilled from the store. Similarly, if a customer chooses to buy online and pick up in-store (BOPIS), the system must synchronize inventory data between the online platform and the store’s inventory system to ensure that the item is available for pickup when the customer arrives.
The coordination between fulfillment centers and retail outlets also extends to managing reverse logistics, which is the process of handling returns. In an omnichannel warehouse, customers may choose to return items to a store, even if they purchased the product online. Seamless coordination ensures that returned items are quickly reintegrated into the inventory system, making them available for resale across all channels. This reduces the time it takes to process returns and restock items, improving overall efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Furthermore, seamless coordination allows the omnichannel warehouse to respond to changes in demand by redistributing inventory across different locations. For example, if a certain product is selling quickly in one region but slowly in another, the omnichannel warehouse system can automatically trigger a stock transfer to balance inventory levels. This level of flexibility is essential for maintaining optimal stock levels and preventing overstocking or understocking at specific locations.
Technology plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless coordination in an omnichannel warehouse. Advanced warehouse management systems (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software provide the real-time data synchronization and communication tools necessary to manage inventory and fulfillment operations across multiple locations. These systems integrate data from all sales channels, warehouses, and retail outlets, ensuring that every part of the omnichannel warehouse network is working with accurate, up-to-date information.
Additionally, automated systems and AI-powered tools can help streamline coordination by predicting demand fluctuations, optimizing stock levels, and suggesting the most efficient fulfillment strategies. These technologies enable the omnichannel warehouse to respond quickly to changes in demand, ensuring that customers receive their orders on time, regardless of the fulfillment location.
Challenges in Managing an Omnichannel Warehouse
Inventory Management
Managing Multi-channel Inventory
One of the greatest challenges of managing an omnichannel warehouse is handling inventory across multiple sales channels. In a traditional warehouse, inventory might be stored in one central location and used to fulfill orders for a specific sales channel, such as a physical store or an eCommerce platform. In an omnichannel warehouse, however, inventory must be distributed and managed across a range of locations, including physical stores, regional distribution centers, and even external marketplaces like Amazon or eBay. Each of these channels has different requirements for inventory management, fulfillment, and customer service, making it essential to have a unified system in place that can handle the complexity of multi-channel operations.
In an omnichannel warehouse, it is crucial to have real-time visibility into inventory levels across all channels. This means that whether a customer is shopping online, in-store, or through a mobile app, they should always have access to accurate product availability information. Without this real-time visibility, businesses risk overselling items that are no longer in stock or missing out on sales because products are incorrectly listed as unavailable. This can lead to customer dissatisfaction and lost revenue.

To effectively manage multi-channel inventory, businesses must implement advanced warehouse management systems (WMS) that allow for centralized inventory control and real-time updates across all sales platforms. These systems integrate with various sales channels, ensuring that inventory is synchronized and accurately reflected across the entire omnichannel network. When an order is placed, the system updates stock levels in real time, regardless of where the inventory is stored or where the order was placed. This integration helps eliminate discrepancies between sales channels, reduces the risk of errors, and enables businesses to fulfill orders quickly and accurately.
Moreover, managing multi-channel inventory in an omnichannel warehouse requires sophisticated logistics and fulfillment strategies. For instance, businesses must determine how best to allocate inventory across different locations to ensure that orders can be fulfilled as quickly and cost-effectively as possible. This might involve shipping products from a central warehouse, fulfilling orders from a local store, or using a combination of fulfillment centers depending on customer location and inventory availability. Balancing these logistics is essential for optimizing both inventory levels and fulfillment speed in an omnichannel warehouse environment.
Avoiding Stockouts and Overstocking
Stockouts occur when an item is unavailable at the time of purchase, causing missed sales opportunities and customer frustration. Overstocking, on the other hand, occurs when too much inventory is held in the warehouse, tying up capital and consuming valuable storage space. Both scenarios can have a detrimental impact on business operations, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
Avoiding Stockouts
Stockouts are particularly damaging in an omnichannel warehouse because they affect not only one sales channel but the entire network. If a customer is unable to find a product online, in-store, or on a third-party platform, the business risks losing that sale to a competitor. In addition, stockouts can lead to delays in order fulfillment, especially if inventory needs to be transferred from one location to another to fulfill an order. To avoid stockouts, businesses must have real-time visibility into inventory levels and the ability to anticipate demand accurately across all channels.
Demand forecasting plays a critical role in preventing stockouts. In an omnichannel warehouse, demand forecasting involves analyzing historical sales data, customer behavior, and market trends to predict future demand for products across various channels. By forecasting demand accurately, businesses can ensure that the right amount of inventory is available in each location to meet customer needs without running out of stock. For example, if a particular product is known to sell well during certain seasons or promotional periods, the omnichannel warehouse can preemptively stock more of that item to avoid stockouts during peak demand.
Another strategy for avoiding stockouts is maintaining safety stock, which serves as a buffer to protect against unexpected demand spikes or supply chain disruptions. In an omnichannel warehouse, safety stock can be distributed across various locations to ensure that even if one warehouse runs low on a particular item, other locations can step in to fulfill orders. This decentralized approach to inventory management helps minimize the risk of stockouts and ensures that customer orders can be fulfilled on time, even during high-demand periods.
Avoiding Overstocking
While stockouts can lead to lost sales, overstocking can result in financial losses by tying up capital in excess inventory and increasing storage costs. Overstocking is especially problematic in an omnichannel warehouse because the inventory is spread across multiple locations, making it more difficult to track and manage effectively. Excess inventory can also lead to markdowns and discounts, which erode profit margins and reduce the overall profitability of the business.
To avoid overstocking, businesses must balance inventory levels with actual demand. This requires careful planning and the use of data analytics to monitor sales trends and adjust inventory levels accordingly. In an omnichannel warehouse, it is important to avoid holding too much inventory in one location while other locations remain understocked. By distributing inventory more evenly across the omnichannel network, businesses can reduce the risk of overstocking in any single location and ensure that products are available where they are most likely to sell.

Advanced inventory management systems can help businesses avoid overstocking by automating the process of reordering and replenishing inventory based on real-time data. For example, if inventory levels in one location are higher than expected, the system can automatically adjust future orders to prevent overstocking. Similarly, if a product is selling more slowly than anticipated, the system can reduce the amount of stock ordered for that location in the next replenishment cycle. This level of automation and data-driven decision-making helps optimize inventory levels across the omnichannel warehouse and minimizes the risk of overstocking.
Balancing Inventory Across Channels
To successfully avoid stockouts and overstocking, businesses must focus on balancing inventory levels across all sales channels and fulfillment locations. This involves distributing inventory based on demand forecasts, sales patterns, and customer behavior across online platforms, physical stores, and other channels. By strategically positioning inventory across the omnichannel warehouse network, businesses can ensure that stock levels are optimized for each location and that customer orders can be fulfilled quickly and accurately.
Inventory management is a critical challenge for any omnichannel warehouse. Managing multi-channel inventory requires real-time visibility and centralized control to ensure that inventory levels are accurate and consistent across all locations. Avoiding stockouts and overstocking is essential for maintaining smooth operations, minimizing costs, and meeting customer expectations. By using advanced technology and data-driven strategies, businesses can effectively manage inventory in an omnichannel warehouse and achieve the right balance between supply and demand.
Complexity in Order Fulfillment
Balancing Cost and Speed
One of the most significant challenges faced by omnichannel warehouses is balancing the cost of order fulfillment with the speed at which customers expect their orders to arrive. Consumers are increasingly accustomed to fast or even same-day delivery, especially as eCommerce giants like Amazon set new benchmarks for fulfillment speed. However, meeting these expectations can be costly, particularly for businesses that do not have the infrastructure to support rapid delivery across multiple locations.
In an omnichannel warehouse, order fulfillment costs can vary greatly depending on the strategy employed. For instance, ship-from-store is a popular fulfillment method where orders placed online are fulfilled from a nearby retail location rather than a central warehouse. This strategy can reduce delivery times, as items are shipped from the closest store to the customer’s location, which also helps reduce shipping costs. However, while ship-from-store can improve delivery speed, it can be more expensive to operate in the long run, as retail stores may not be optimized for efficient picking, packing, and shipping like a dedicated warehouse.

Another fulfillment strategy used in omnichannel warehouses is direct-to-consumer shipping from a central warehouse or distribution center. This model allows businesses to leverage their warehouse infrastructure to manage inventory, process orders, and ship directly to customers. While this method is more cost-effective than ship-from-store in terms of operational efficiency, it may not be as fast, particularly if the warehouse is located far from the customer. This creates a tension between cost and speed that businesses must navigate when selecting the most appropriate fulfillment strategy for their omnichannel warehouse.
To balance cost and speed effectively, many businesses adopt a hybrid fulfillment approach in their omnichannel warehouse. This strategy involves using multiple fulfillment methods depending on the proximity of inventory to the customer, the urgency of the delivery, and the associated costs. For instance, a business might use ship-from-store for local, high-priority orders, while relying on direct-to-consumer shipping for orders that are less time-sensitive or for customers located farther away from retail locations.
Optimizing fulfillment strategies in an omnichannel warehouse requires real-time visibility into inventory levels across all locations. This visibility allows businesses to choose the most cost-effective and timely fulfillment option for each order. Advanced warehouse management systems (WMS) and AI-driven automation tools can analyze factors such as product availability, customer location, and shipping costs to determine the optimal fulfillment strategy for each order, reducing both costs and delivery times.
Handling Reverse Logistics
Another key challenge in managing an omnichannel warehouse is efficiently handling reverse logistics, which involves processing returns, exchanges, and refunds. With the growth of eCommerce, customers have become accustomed to flexible return policies and the ability to return products purchased online to physical stores or through mail-in options. While these options enhance the customer experience, they significantly complicate the operations of an omnichannel warehouse.
In an omnichannel warehouse, reverse logistics is more complex than in a traditional warehouse environment due to the multiple sales and return points involved. Customers may purchase an item online and return it to a store, or they may purchase an item in-store and initiate a return through a different online platform. Managing these diverse return scenarios requires a seamless integration of systems that can track and process returns from all channels while ensuring that inventory is updated accordingly.
One of the main challenges in reverse logistics for omnichannel warehouses is the cost associated with processing returns. Returns involve multiple touchpoints, including inspection, repackaging, restocking, and sometimes refurbishing. This process can be labor-intensive and costly, especially if the product needs to be shipped back to a central warehouse from a retail store or customer’s home. To mitigate these costs, omnichannel warehouses must implement efficient return processing systems that streamline the flow of returned goods and minimize the time products spend in the reverse logistics loop.
Inventory management is also a critical aspect of handling reverse logistics in an omnichannel warehouse. When a product is returned, it needs to be quickly reintegrated into the inventory system so that it can be resold. This requires real-time updates across all sales channels to ensure that the returned item is available for purchase as soon as it is restocked. Failing to do so can result in lost sales opportunities or excess stock sitting idle in the warehouse.
To manage reverse logistics more effectively, many omnichannel warehouses leverage automated return systems. These systems use AI and machine learning algorithms to streamline the return process by categorizing returned products, determining whether they can be resold, and automatically updating inventory systems. Automated systems can also help reduce the time it takes to process refunds or exchanges, improving customer satisfaction and reducing the operational burden on the warehouse.
Additionally, the omnichannel warehouse must ensure that the return policies are consistent across all channels. Whether a customer is returning a product in-store or by mail, the process should be straightforward, and the same level of service should be provided. This consistency enhances the customer experience and strengthens brand loyalty, but it requires seamless coordination between the warehouse, retail outlets, and online platforms.
Data Integration and Synchronization
Maintaining Real-time Data Synchronization
One of the key challenges of managing an omnichannel warehouse is maintaining real-time data synchronization across all connected systems. With multiple sales channels, warehouses, and fulfillment centers involved, the need for accurate and up-to-date data is paramount. Real-time synchronization ensures that all inventory, sales, and customer data are aligned, regardless of whether the transaction happens in-store, online, or through a third-party marketplace.
In an omnichannel warehouse, real-time synchronization allows businesses to track and manage inventory levels across all channels, preventing stock discrepancies and ensuring that orders are fulfilled accurately and on time. For instance, when a customer places an order online, the warehouse management system must immediately update the stock levels across all platforms—eCommerce websites, in-store point-of-sale systems, and third-party sellers—to reflect the new inventory status. This real-time update helps prevent the problem of overselling, where customers may be able to purchase items that are no longer available due to a lag in data updates.
Moreover, real-time synchronization helps optimize the order fulfillment process by ensuring that orders are directed to the most appropriate warehouse or fulfillment center based on current inventory levels. For example, if a customer orders a product online and it is available at a nearby store, real-time data synchronization enables the system to route the order to that location for faster fulfillment through a ship-from-store model. Without real-time data, this type of dynamic decision-making would not be possible, and businesses risk delays, inefficiencies, and unhappy customers.
In addition to inventory management, real-time data synchronization also impacts customer experience. Customers expect accurate and up-to-date information on product availability, delivery times, and order status. With real-time synchronization between systems, businesses can provide customers with real-time order tracking, ensuring that they are kept informed about the status of their purchase. This transparency builds trust and enhances customer satisfaction, which is especially important in an omnichannel retail environment.
To achieve real-time data synchronization, businesses must invest in integrated technology solutions that connect their warehouse management system (WMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, and eCommerce platforms. These systems must be able to communicate and share data in real-time, providing a unified view of inventory, sales, and customer interactions. Additionally, advanced technologies such as cloud-based platforms and the Internet of Things (IoT) can play a key role in facilitating real-time data updates across an omnichannel warehouse.
Integration Challenges
While real-time data synchronization is essential for the smooth operation of an omnichannel warehouse, integrating legacy systems with new omnichannel technologies presents a significant challenge for many businesses. Legacy systems are often outdated, rigid, and lack the flexibility needed to handle the complexities of an omnichannel environment. These older systems were not designed to support the integration required for modern omnichannel operations, leading to data inconsistencies, delays in processing, and even system failures.
One of the primary difficulties in integrating legacy systems with modern omnichannel technologies is the lack of compatibility between different platforms. For example, a legacy warehouse management system may not be able to communicate effectively with a new eCommerce platform or ERP system, resulting in a disjointed flow of data. This lack of integration can cause serious problems, such as delayed order processing, inaccurate inventory levels, and misaligned sales data. When inventory, sales, and customer data are not properly integrated, it becomes difficult to maintain a consistent and accurate view of the business across all sales channels.
Another major challenge businesses face when integrating legacy systems into an omnichannel warehouse is the high cost and complexity of the integration process. Many legacy systems were built on outdated technology frameworks, making it difficult to connect them with modern cloud-based platforms or advanced data analytics tools. As a result, businesses must often invest significant time and resources into custom development, middleware solutions, or third-party integration services to bridge the gap between legacy systems and new omnichannel technologies.
Data migration is another hurdle businesses must overcome during the integration process. Legacy systems often contain large volumes of historical data, such as customer information, sales records, and inventory details, which must be transferred to the new omnichannel platforms. Ensuring that this data is accurately migrated without any loss or corruption is critical, as incomplete or inaccurate data can lead to operational inefficiencies and poor decision-making in the omnichannel warehouse. Moreover, data migration must be conducted in a way that minimizes disruption to the ongoing operations of the warehouse, making it a complex and time-sensitive task.
The lack of real-time capabilities in many legacy systems also poses a significant challenge. Traditional systems may rely on batch processing or periodic updates, which means that inventory and sales data may not be updated in real-time. In an omnichannel warehouse, where orders and inventory levels are constantly changing across multiple platforms, these delays can result in stock discrepancies, overselling, or understocking. To address this issue, businesses must either upgrade their legacy systems to support real-time data processing or replace them with modern, cloud-based systems that are designed for omnichannel operations.
To overcome these integration challenges, many businesses are turning to cloud-based solutions that provide greater flexibility, scalability, and real-time data synchronization capabilities. Cloud-based platforms enable seamless integration between different systems, allowing businesses to connect their WMS, ERP, and eCommerce platforms in real-time. Additionally, cloud-based systems can be easily updated and expanded to accommodate new sales channels, making them ideal for the dynamic nature of omnichannel warehouses.
Businesses must also adopt a phased approach to integration, gradually replacing or upgrading legacy systems over time while ensuring that critical operations are not disrupted. By prioritizing the integration of key systems, such as inventory management and order fulfillment, businesses can begin to experience the benefits of real-time data synchronization while minimizing the risk of costly system failures.
Demand Fluctuations
Handling Seasonal Peaks
Seasonal peaks, such as the holiday shopping season, Black Friday, and back-to-school periods, are some of the most challenging times for an omnichannel warehouse. These peak seasons can see a massive increase in order volumes across all sales channels, placing enormous strain on inventory levels, order processing times, and shipping logistics. Customers expect fast delivery and seamless service during these high-demand periods, so any delays or stock shortages can lead to dissatisfied customers, lost sales, and damage to the brand’s reputation.
In an omnichannel warehouse, managing seasonal peaks requires careful planning and preparation well in advance. One of the key strategies is forecasting demand based on historical data from previous peak seasons, sales trends, and market analysis. By analyzing this data, businesses can better predict which products will be in high demand and ensure that they have sufficient stock to meet customer needs. However, forecasting alone is not enough. The omnichannel warehouse must also implement a flexible inventory management system that allows it to scale operations quickly in response to changing demand patterns.
Another strategy for handling seasonal peaks in an omnichannel warehouse is inventory distribution across multiple locations. Instead of relying on a central warehouse to fulfill all orders, businesses can spread inventory across regional warehouses, fulfillment centers, and even retail stores. This approach reduces the risk of stock shortages in any one location and helps expedite delivery times by ensuring that products are closer to customers. For example, a business might use a ship-from-store model to fulfill online orders during peak seasons, leveraging the inventory in physical stores to reduce the strain on central warehouses.
Automating warehouse operations is another critical aspect of managing seasonal demand surges. Automation technologies, such as robotics, conveyor systems, and automated picking tools, can significantly improve the speed and accuracy of order fulfillment. By automating repetitive tasks like picking, packing, and sorting, the omnichannel warehouse can handle larger volumes of orders without requiring a proportional increase in labor. This is particularly important during seasonal peaks when hiring and training temporary workers may not be feasible or cost-effective.
In addition to automation, flexible staffing models can help businesses handle increased demand during peak seasons. Many omnichannel warehouses use temporary or seasonal workers to supplement their regular workforce during high-demand periods. However, the key to success lies in having an efficient training program that enables temporary workers to quickly adapt to the warehouse’s processes and technologies. Some warehouses also use flexible shift scheduling to ensure that they have enough labor during the busiest times of the day, while avoiding overstaffing during slower periods.
Despite careful planning and preparation, bottlenecks can still occur during seasonal peaks. To mitigate these risks, omnichannel warehouses should implement contingency plans that address potential challenges such as supplier delays, transportation issues, or equipment failures. For instance, having backup suppliers or alternative shipping routes can prevent disruptions in the supply chain and ensure that customer orders are fulfilled on time, even when unexpected challenges arise.
Managing Flash Sales and Unexpected Demand
Flash sales, promotional events, and viral marketing campaigns can lead to sudden and dramatic spikes in demand that are difficult to predict. These events often generate excitement among customers, resulting in a flood of orders within a short time frame. For an omnichannel warehouse, handling these sudden surges in demand can be extremely challenging, as they put pressure on both inventory levels and fulfillment systems. If not managed effectively, flash sales can lead to stock shortages, delayed shipments, and customer dissatisfaction.
To successfully manage flash sales and unexpected demand surges, omnichannel warehouses must be agile and responsive. One of the most important strategies is real-time inventory tracking. Real-time visibility into inventory levels across all sales channels ensures that businesses can quickly identify when stock is running low and take corrective action. For example, if a product becomes a bestseller during a flash sale, the warehouse management system can automatically adjust inventory levels, trigger reorders, and reallocate stock from other locations to prevent stockouts.

Another key to managing flash sales in an omnichannel warehouse is dynamic order prioritization. During periods of high demand, not all orders are equally urgent. By using real-time data and predictive analytics, the warehouse can prioritize orders based on factors such as customer location, shipping speed, and product availability. For instance, orders for high-demand items that are in limited supply might be fulfilled from multiple locations to ensure fast delivery, while less urgent orders can be processed later. This approach helps balance the workload and prevents the fulfillment system from becoming overwhelmed.
Scalability is another critical component of managing unexpected demand surges in an omnichannel warehouse. Scalability refers to the ability of the warehouse to quickly expand its operations to meet higher demand without sacrificing efficiency. Cloud-based warehouse management systems (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms enable businesses to scale their operations by providing real-time data, automation tools, and seamless integration across sales channels. These systems can automatically adjust fulfillment processes, allocate resources, and update inventory data in real time, allowing the warehouse to handle sudden spikes in demand with minimal disruption.
In addition to scalable technology solutions, omnichannel warehouses can implement just-in-time inventory practices to manage unexpected demand surges. Just-in-time inventory management involves keeping minimal stock on hand and relying on frequent replenishment to meet demand. While this strategy carries some risks, such as potential delays from suppliers, it can be effective in managing flash sales by ensuring that inventory is constantly replenished without the need for excessive stockpiling. By working closely with suppliers and maintaining strong communication channels, the omnichannel warehouse can respond quickly to demand fluctuations and keep inventory levels aligned with customer orders.
Finally, effective communication with customers is essential when managing flash sales and unexpected demand surges in an omnichannel warehouse. Customers need to be informed about product availability, estimated delivery times, and any potential delays due to high order volumes. Transparency in communication helps set realistic expectations and reduces the likelihood of negative feedback or order cancellations. Automated notification systems can be used to keep customers updated on the status of their orders, while customer service teams can provide real-time support for any questions or concerns.
Labor Shortages and Skills Gaps
Addressing Workforce Shortages
Labor shortages have become a significant challenge for omnichannel warehouses, especially during periods of high demand such as holiday seasons, Black Friday, or flash sales. The shortage of skilled warehouse workers can lead to delays in order fulfillment, increased operational costs, and ultimately, a decline in customer satisfaction. As omnichannel warehouses continue to expand their operations to meet the demands of multi-channel retail, the need for a reliable and scalable workforce becomes increasingly critical.
One of the primary causes of labor shortages in omnichannel warehouses is the fluctuating nature of demand. During peak seasons, warehouses often experience a sharp increase in order volumes, requiring a larger workforce to handle the surge in activity. However, hiring and training temporary workers to manage these short-term spikes in demand can be costly and inefficient. In addition, the demand for warehouse workers often outpaces supply, making it difficult for businesses to find and retain skilled employees when they need them most.

To address these workforce shortages, omnichannel warehouses are increasingly turning to automation and robotics to fill the gaps. By automating repetitive tasks such as picking, packing, and sorting, warehouses can reduce their reliance on manual labor and improve efficiency. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs), robotic picking systems, and conveyor belts are just a few examples of how automation can help omnichannel warehouses cope with labor shortages. While automation may not entirely replace the need for human workers, it can significantly reduce the burden on the workforce during peak demand periods and help ensure that orders are fulfilled on time.
Another strategy for addressing labor shortages in omnichannel warehouses is the use of temporary or seasonal workers. Many warehouses hire additional staff during busy periods to handle the increased workload. However, to be effective, this approach requires efficient training programs that can quickly onboard temporary workers and get them up to speed on warehouse processes and technologies. Cross-training permanent employees in multiple roles can also help alleviate workforce shortages by providing more flexibility in staffing. For example, employees trained in both order picking and packing can be shifted between roles as needed, allowing the warehouse to adapt to changing demands more efficiently.
Partnerships with staffing agencies can also be an effective way to address workforce shortages. Staffing agencies can provide omnichannel warehouses with access to a pool of pre-screened and trained workers who can be deployed quickly during peak demand periods. This can save time and resources, as the warehouse does not need to handle the recruitment and training process internally. In addition, working with staffing agencies can provide greater flexibility in scaling the workforce up or down based on real-time demand fluctuations.
Training and Retaining Skilled Workers
While automation can alleviate some of the pressure caused by labor shortages, there is still a strong need for skilled workers who can manage, operate, and maintain the technology that powers an omnichannel warehouse. The increasing reliance on automation, robotics, and warehouse management software (WMS) means that warehouse employees must possess a higher level of technical knowledge than ever before. However, the rapid pace of technological advancement often leaves warehouses facing a skills gap, where employees may not have the necessary training to use these systems effectively.
One of the most important strategies for addressing skills gaps in an omnichannel warehouse is to implement comprehensive training programs that upskill the workforce in new technologies and processes. These training programs should focus on teaching employees how to operate and troubleshoot automation systems, use WMS effectively, and optimize warehouse workflows. For example, workers should be trained on how to manage automated picking systems, monitor real-time inventory data, and utilize data analytics tools to improve operational efficiency. By equipping employees with the skills they need to work with advanced technology, omnichannel warehouses can improve productivity and reduce the likelihood of errors or delays in the fulfillment process.

Training programs should also emphasize cross-functional skills to increase workforce flexibility. In an omnichannel warehouse, employees may be required to perform multiple tasks, such as managing inventory, picking and packing orders, and operating machinery. By cross-training employees in different roles, warehouses can ensure that their workforce is adaptable and capable of shifting between tasks as needed. This flexibility is particularly valuable during peak demand periods when certain areas of the warehouse may require more resources than others.
In addition to upskilling the workforce, retaining skilled employees is critical for the long-term success of an omnichannel warehouse. High employee turnover can lead to increased recruitment and training costs, as well as disruptions in operations. To reduce turnover, warehouses must focus on creating a positive work environment, offering competitive wages, and providing opportunities for career growth and advancement.
One of the most effective ways to retain skilled workers in an omnichannel warehouse is to invest in employee development programs. These programs can provide workers with ongoing training and development opportunities, helping them to build their skills and advance their careers within the company. By offering opportunities for professional growth, warehouses can increase employee engagement and job satisfaction, making it less likely that workers will seek employment elsewhere. For example, employees who show an interest in technology can be offered additional training in warehouse automation systems or given the chance to take on leadership roles in managing new technologies.
Employee recognition and reward programs can also play a key role in improving retention. Recognizing and rewarding employees for their hard work, particularly during peak demand periods, can boost morale and encourage loyalty. This can be as simple as offering bonuses or incentives for meeting performance targets or providing recognition through employee of the month programs. Creating a culture of appreciation helps employees feel valued and motivates them to stay with the company.
Finally, offering flexible work schedules can help omnichannel warehouses attract and retain skilled workers, particularly during peak demand periods. Many workers, especially those in the gig economy, value flexibility in their work schedules. By offering options such as part-time shifts, flexible hours, or remote work for administrative roles, warehouses can appeal to a broader pool of workers and improve employee satisfaction.
Strategies for Implementing Omnichannel Warehousing
Assessing Business Needs
Identifying Current Pain Points
Before transitioning to an omnichannel warehouse, it is important to evaluate the inefficiencies and challenges within existing warehouse operations. Many businesses experience pain points related to stockouts, slow fulfillment times, or difficulties in integrating inventory and sales data across multiple sales channels. These issues not only impact operational efficiency but also affect customer satisfaction, as delays in fulfillment or inaccurate stock levels can lead to lost sales and frustrated customers.
One of the most common pain points in traditional warehouse operations is inventory management, particularly in managing stock across multiple sales channels. Businesses that rely on separate systems for online orders, in-store purchases, and third-party marketplaces often struggle to keep track of inventory in real time. As a result, they may face stockouts in one channel while carrying excess inventory in another. This leads to inefficiencies, such as missed sales opportunities due to unavailable products or increased holding costs for overstocked items. Implementing an omnichannel warehouse allows for centralized inventory management, ensuring that stock levels are synchronized across all channels and that products are allocated more efficiently to meet demand.
Another significant pain point is slow fulfillment caused by inefficient warehouse processes. Traditional warehouses may not be optimized to handle the high volume of orders generated by eCommerce platforms or the fast fulfillment speeds demanded by modern customers. For instance, a warehouse designed to serve brick-and-mortar stores may not have the systems in place to manage online orders efficiently. By transitioning to an omnichannel warehouse, businesses can streamline fulfillment processes, such as by implementing ship-from-store or click-and-collect options that reduce shipping times and improve customer satisfaction.
In addition to inventory and fulfillment challenges, businesses often face integration issues when managing multiple sales channels. For example, legacy systems used to manage physical store inventory may not integrate well with eCommerce platforms or third-party marketplaces, leading to data discrepancies and delays in updating stock levels. This lack of integration creates confusion for both the warehouse and the customer, as products may be shown as available online when they are actually out of stock. Implementing an omnichannel warehouse involves integrating these systems to ensure that inventory data is consistent and updated in real time, regardless of the sales channel.
By identifying these pain points, businesses can better understand where omnichannel warehouse strategies can make the greatest impact. Whether it’s improving inventory management, speeding up fulfillment, or integrating sales platforms, omnichannel warehousing offers solutions to common operational challenges.
Understanding Customer Expectations
A successful omnichannel warehouse strategy must also be built around a deep understanding of customer expectations. In today’s competitive retail environment, customers expect more from businesses, including faster shipping, real-time access to product availability, and flexible fulfillment options such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS). Failing to meet these expectations can lead to lost customers, negative reviews, and damage to a brand’s reputation. Therefore, businesses must align their warehouse processes with customer preferences to deliver a seamless and satisfying shopping experience.
One of the most significant expectations customers have today is for fast shipping. With the rise of eCommerce giants offering same-day or next-day delivery, customers now expect their orders to be processed and delivered quickly, regardless of the sales channel. For businesses operating an omnichannel warehouse, meeting these expectations requires optimizing fulfillment processes and leveraging multiple fulfillment methods, such as ship-from-store. This approach allows businesses to fulfill orders from the closest available location, reducing delivery times and ensuring that customers receive their products as quickly as possible.

Customers also expect real-time stock updates across all channels, including online platforms, mobile apps, and physical stores. When browsing a retailer’s website or app, customers want to know immediately if an item is available for purchase and when it can be delivered. Inconsistent or outdated stock information can lead to disappointment and abandoned carts if customers discover that an item is unavailable after placing an order. An omnichannel warehouse with real-time inventory visibility ensures that stock levels are accurately reflected across all platforms, giving customers confidence that the products they see online are available and ready to ship.
In addition to fast shipping and accurate stock information, customers value flexible fulfillment options. Many customers now prefer the convenience of buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS) or curbside pickup, which allows them to order products online and collect them at a nearby location without waiting for shipping. This is particularly appealing for customers who want the convenience of online shopping combined with the immediacy of in-store pickup. To meet this expectation, an omnichannel warehouse must be able to manage and fulfill orders across different locations, including both warehouses and retail stores. Integrating these fulfillment methods into the warehouse strategy not only enhances the customer experience but also helps reduce shipping costs and delivery times.
Finally, personalized shopping experiences are becoming increasingly important to customers. An omnichannel warehouse can support personalization by leveraging customer data to tailor product recommendations, offer targeted promotions, and create a more customized shopping experience. For instance, by analyzing customer purchase history, businesses can ensure that frequently purchased items are always in stock or offer faster delivery options for preferred customers. Personalization can help build stronger relationships with customers and encourage repeat purchases.
By understanding and addressing these customer expectations, businesses can implement omnichannel warehouse strategies that improve operational efficiency while delivering a superior customer experience. Meeting the demands for faster shipping, real-time stock visibility, and flexible fulfillment options requires a well-coordinated warehouse operation that is capable of handling orders from multiple channels seamlessly.
Technology Integration
Essential Technology for Omnichannel Success
The foundation of any omnichannel warehouse lies in the implementation of core technologies that are designed to handle the complexities of modern supply chains. These systems enable businesses to manage inventory, process orders efficiently, and coordinate shipping logistics across multiple channels. Three of the most essential technologies for omnichannel success include Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, and Transportation Management Systems (TMS). Together, these systems ensure that the omnichannel warehouse operates efficiently, from receiving and storing goods to shipping orders and managing returns.
- WMS: is a critical tool for any omnichannel warehouse, as it provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, tracks the movement of products within the warehouse, and automates the picking and packing process. WMS technology ensures that inventory is accurately tracked across all channels, reducing the risk of stockouts or overstocking, and helps businesses optimize the use of warehouse space. In an omnichannel environment, where orders can come from multiple sales channels simultaneously, a WMS allows businesses to efficiently manage orders by automating key processes like order picking, packing, and shipping. One of the key benefits of using a WMS in an omnichannel warehouse is the ability to prioritize orders based on factors such as delivery time, customer location, or product availability. This ensures that urgent orders are fulfilled first, while less time-sensitive orders are processed later. A WMS also enables businesses to implement different fulfillment methods, such as ship-from-store, click-and-collect, or direct-to-consumer shipping, by seamlessly coordinating inventory and order fulfillment across multiple locations.
- ERP: are another essential technology for omnichannel warehouse success, providing a centralized platform for managing all aspects of the business, including inventory, sales, finance, and supply chain operations. ERP systems are especially valuable in an omnichannel environment because they allow businesses to integrate data from multiple departments and sales channels into a single system. This integration enables real-time visibility into inventory levels, order status, and customer data, ensuring that all departments are working with the same accurate information. By using an ERP system, businesses can streamline their order management processes by automating tasks such as invoicing, payment processing, and financial reporting. In an omnichannel warehouse, ERP systems also help manage demand forecasting and inventory planning, ensuring that the warehouse has the right amount of stock to meet customer demand across all channels. Additionally, ERP systems can integrate with other technologies, such as WMS and TMS, to provide a complete solution for managing warehouse operations, logistics, and customer orders.
- TMS: helps businesses optimize their shipping processes by managing the movement of goods between warehouses, distribution centers, and customers. TMS technology can track shipments in real-time, manage delivery routes, and analyze shipping costs, enabling businesses to choose the most cost-effective and efficient delivery options. For omnichannel warehouses that offer multiple fulfillment methods, such as same-day delivery, next-day shipping, or buy-online-pickup-in-store (BOPIS), a TMS is invaluable in coordinating these services. TMS systems can analyze factors such as shipping costs, customer location, and delivery times to determine the best fulfillment option for each order. By integrating TMS with WMS and ERP systems, businesses can create a seamless logistics network that improves delivery speed and reduces costs.
Best Practices for Integrating Systems
Without proper integration, businesses risk data silos, inefficiencies in order processing, and miscommunication between systems. When these technologies are fully integrated, however, businesses can achieve synchronized inventory management, efficient order fulfillment, and real-time customer data updates. The following best practices can help ensure the successful integration of WMS, ERP, and eCommerce platforms within an omnichannel warehouse.
- Streamline Data Synchronization: One of the most important best practices for integrating WMS, ERP, and eCommerce platforms is to ensure that data synchronization happens in real-time across all systems. Real-time data synchronization is critical for providing accurate inventory levels, processing orders quickly, and ensuring that customer information is up to date. By integrating these systems into a single platform, businesses can eliminate data silos and improve communication between departments. For example, when an order is placed on an eCommerce platform, the WMS should automatically update the inventory levels, and the ERP should generate the invoice and initiate the fulfillment process. This level of automation ensures that the omnichannel warehouse operates efficiently and that customers receive accurate information about their orders.
- Use APIs for Seamless Integration: Another best practice for integrating systems in an omnichannel warehouse is to leverage Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to connect different platforms. APIs allow for seamless communication between systems such as WMS, ERP, and TMS, enabling them to share data in real-time. By using APIs, businesses can ensure that inventory data, order information, and shipping details are consistently updated across all channels. APIs also provide flexibility in integrating third-party platforms, such as eCommerce marketplaces or CRM systems, into the omnichannel warehouse. This level of integration allows businesses to scale their operations as they add new sales channels or fulfillment centers.
- Implement a Centralized Data Hub: A centralized data hub can be a powerful tool for integrating WMS, ERP, and eCommerce platforms in an omnichannel warehouse. A centralized data hub serves as the single source of truth for all inventory, sales, and customer data, ensuring that all systems are working with the same information. By consolidating data into a central location, businesses can streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve decision-making. For example, a centralized data hub can provide real-time insights into inventory availability, order status, and shipping timelines, allowing warehouse managers to make informed decisions about resource allocation and order prioritization.
- Test Integration Thoroughly: Before fully implementing system integration in an omnichannel warehouse, it is important to thoroughly test the integration to ensure that all systems are working correctly. Testing should include verifying that data is being shared accurately between WMS, ERP, and eCommerce platforms, as well as checking for any potential issues with order processing or inventory management. By conducting rigorous testing, businesses can identify and resolve any integration problems before they impact warehouse operations.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Maintenance: Even after systems are successfully integrated, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are essential for ensuring that the omnichannel warehouse continues to operate smoothly. Regularly monitoring the performance of integrated systems can help businesses identify potential issues, such as data discrepancies or system outages, before they affect operations. Additionally, businesses should invest in ongoing system maintenance to ensure that all platforms are up to date and functioning properly. This can include updating APIs, performing software patches, and conducting regular system audits to ensure data accuracy.
Optimizing Warehouse Layout
Designing an Omnichannel-friendly Layout
The primary goal when designing an omnichannel-friendly warehouse layout is to create a space that accommodates the diverse needs of multiple sales channels. Unlike traditional warehouses that might focus on fulfilling orders for either eCommerce or physical stores, an omnichannel warehouse must handle a variety of order types, each with its own requirements for picking, packing, and shipping. To ensure smooth operations, businesses must create distinct zones within the warehouse that are flexible enough to handle different activities, such as online order processing, in-store order fulfillment, and returns management.
One of the key strategies for designing an omnichannel-friendly layout is to create flexible zones for different types of orders. For instance, a warehouse might have dedicated zones for processing online orders, including picking and packing areas designed for high-speed fulfillment. Another zone might be reserved for handling in-store orders, where items are picked and packed for delivery to a retail location or for customers using buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS) services. By separating these areas, the warehouse can ensure that each type of order is processed efficiently without interfering with other operations.
In addition to separating zones for different order types, an omnichannel warehouse should also have a dedicated returns management area. Returns are a common feature of omnichannel operations, particularly for eCommerce orders, where customers may return items via mail or in-store. A well-designed returns area allows warehouse staff to quickly inspect, restock, or process returned items, ensuring that they are re-entered into inventory as quickly as possible. This reduces delays in making returned products available for resale and helps maintain accurate stock levels across all channels.
Another important aspect of designing an omnichannel-friendly layout is optimizing the flow of goods within the warehouse. For example, products that are frequently ordered together should be stored near each other to minimize the time and effort required for picking. Additionally, placing fast-moving items closer to packing and shipping areas can help speed up order fulfillment. By carefully analyzing order patterns and customer behaviors, businesses can design a layout that minimizes unnecessary movement and improves the overall efficiency of the warehouse.
Finally, an omnichannel-friendly layout must be scalable and adaptable. As customer preferences and market conditions change, the warehouse layout should be flexible enough to accommodate new sales channels, fulfillment methods, or product categories. For instance, if a business decides to expand its BOPIS services or introduce same-day delivery, the warehouse should be able to adapt by reallocating space or adjusting workflows to meet these new demands. This level of flexibility ensures that the warehouse remains responsive to changing market conditions and customer needs.
Space Optimization Techniques
In addition to creating a layout that supports the efficient handling of omnichannel orders, businesses must also focus on optimizing the use of available warehouse space. Space is one of the most valuable resources in any warehouse, and maximizing its use is essential for improving operational efficiency and reducing costs. In an omnichannel warehouse, where products must be managed and fulfilled across multiple sales channels, optimizing space becomes even more important. Several techniques can be used to maximize space, including vertical racking, cross-docking, and the creation of dedicated fast-moving goods sections.
- Vertical Racking: One of the most effective ways to optimize space in an omnichannel warehouse is through the use of vertical racking. Vertical racking allows businesses to make better use of the height of the warehouse by stacking products vertically, rather than relying solely on floor space. This is particularly useful in warehouses with high ceilings, where vertical storage can significantly increase the amount of usable space. By storing items vertically, warehouses can accommodate more inventory without needing to expand their physical footprint, which is especially valuable during peak demand periods or when inventory levels fluctuate. In an omnichannel warehouse, vertical racking can be used to store products that are not needed immediately but still need to be easily accessible when required. For instance, slow-moving items can be placed on higher shelves, while fast-moving products are stored on lower shelves for quicker access. Vertical racking systems can also be integrated with automated picking technologies, such as automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS), to improve the efficiency of picking items from higher shelves. This reduces the need for manual labor and helps speed up order fulfillment.
- Cross-docking: Another space optimization technique that can enhance efficiency in an omnichannel warehouse is cross-docking. Cross-docking involves the direct transfer of products from inbound shipments to outbound shipments, without the need for long-term storage. This technique is particularly useful for fast-moving goods, as it reduces the time products spend in the warehouse and frees up valuable storage space for other inventory. In an omnichannel warehouse, cross-docking can be used to quickly process orders that require same-day or next-day delivery, as products can be shipped directly to customers or retail locations without the need for additional handling. Cross-docking is also beneficial for managing high-demand products during peak seasons or promotional events. Instead of storing large quantities of these items in the warehouse, businesses can use cross-docking to move products quickly from suppliers to customers, reducing congestion in the warehouse and ensuring faster fulfillment. By minimizing the amount of time products spend in the warehouse, cross-docking helps improve order turnaround times and optimizes the use of available space.
- Dedicated Fast-moving Goods Sections: In any warehouse, certain products are in higher demand and move more quickly than others. In an omnichannel warehouse, it’s essential to create dedicated sections for fast-moving goods to ensure that these items can be picked and packed quickly. These fast-moving goods sections should be located close to packing and shipping areas to reduce the time it takes to process orders and get them out the door. By dedicating specific zones to fast-moving items, businesses can improve the efficiency of order fulfillment and reduce the risk of bottlenecks in the warehouse. For example, during peak shopping periods like Black Friday or the holiday season, having a dedicated area for high-demand products allows the warehouse to process orders more quickly and keep up with increased demand. Additionally, businesses can adjust the location of fast-moving sections based on real-time sales data, ensuring that the warehouse layout remains responsive to changing customer preferences and market trends.
Collaboration with Third-Party Logistics Providers (3PLs)
Role of 3PLs in Omnichannel Warehousing
In the context of an omnichannel warehouse, 3PLs serve as strategic partners that help businesses expand their fulfillment capabilities and improve operational efficiency. With the growing demand for faster shipping, flexible delivery options, and seamless returns, many businesses find it difficult to meet customer expectations on their own. By collaborating with 3PLs, businesses can tap into a wide range of services that enhance their ability to fulfill orders quickly and accurately while also managing the complexities of reverse logistics and international shipments.
One of the key roles 3PLs play in an omnichannel warehouse is supporting last-mile delivery. Last-mile delivery refers to the final leg of the fulfillment process, where a product is delivered from a distribution center or retail location to the customer’s doorstep. This stage is often the most time-consuming and expensive part of the delivery process, particularly in an omnichannel environment where customers expect fast and flexible delivery options. 3PLs specialize in last-mile logistics, offering businesses access to vast delivery networks, advanced routing technologies, and localized fulfillment centers that can reduce delivery times and costs. By leveraging a 3PL’s last-mile capabilities, businesses can offer services such as same-day or next-day delivery, improving customer satisfaction and staying competitive in the market.

In addition to last-mile delivery, 3PLs also provide critical support in reverse logistics, which is the process of managing returns, exchanges, and refunds. Returns are an inevitable part of eCommerce and omnichannel retail, especially as customers expect flexible return options across both online and in-store channels. Managing returns can be resource-intensive, involving tasks such as product inspections, repackaging, restocking, and refund processing. By partnering with a 3PL, businesses can outsource these tasks to experts who have the infrastructure and technology to handle reverse logistics efficiently. This not only reduces the burden on the omnichannel warehouse but also ensures that returned products are quickly re-entered into the inventory system, improving stock availability and minimizing losses.
Another significant role 3PLs play in omnichannel warehousing is cross-border fulfillment. As businesses expand their reach to international markets, managing cross-border logistics becomes increasingly complex, involving customs regulations, international shipping, and local delivery networks. 3PLs with expertise in cross-border fulfillment can help businesses navigate these challenges, ensuring that international orders are processed, shipped, and delivered efficiently. By outsourcing cross-border logistics to a 3PL, businesses can offer international customers the same seamless shopping experience as domestic customers, without having to invest in the infrastructure or expertise required for global fulfillment.
Overall, 3PLs offer a wide range of services that help businesses optimize their omnichannel warehouse operations. From enhancing last-mile delivery and managing returns to facilitating cross-border fulfillment, 3PLs provide the specialized capabilities that enable businesses to meet customer expectations for speed, convenience, and flexibility.
Key Considerations for 3PL Partnerships
While partnering with 3PLs offers many advantages, selecting the right provider is critical to ensuring the success of an omnichannel warehouse. Not all 3PLs are equipped to handle the unique demands of omnichannel fulfillment, so businesses must carefully evaluate potential partners based on their ability to integrate with existing systems, scale operations, and provide the level of service needed to meet customer expectations.
One of the most important considerations when choosing a 3PL is system integration. In an omnichannel warehouse, seamless communication between different platforms—such as Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, and eCommerce platforms—is essential for real-time inventory tracking, order processing, and customer data management. The 3PL you partner with must have the technological capabilities to integrate smoothly with your existing systems. This includes the ability to share data in real-time, ensuring that orders are processed efficiently, inventory levels are updated accurately, and customers receive timely information about their purchases. Without proper integration, data silos can form, leading to inefficiencies, delays, and customer dissatisfaction.
Another critical factor is the scalability of the 3PL’s operations. As businesses grow, their fulfillment needs may change—especially during peak seasons or periods of rapid expansion. The ideal 3PL partner should be able to scale its operations to accommodate these changes without sacrificing service quality. For example, during the holiday shopping season or a major promotional event, businesses may experience a surge in order volumes that exceeds their normal capacity. A scalable 3PL can quickly ramp up resources, such as warehouse space, labor, and transportation, to handle the increased demand. Scalability is essential for ensuring that the omnichannel warehouse can meet customer expectations for fast and accurate fulfillment, even during periods of high demand.
The ability to provide multi-channel delivery options is another key consideration when evaluating 3PL partnerships. In an omnichannel environment, customers expect a range of delivery options, from standard shipping to same-day delivery or in-store pickup. The 3PL you choose should offer flexible fulfillment methods that cater to these diverse customer preferences. This includes having a network of localized fulfillment centers that can support fast shipping, as well as the ability to coordinate with retail locations for services such as buy-online-pick-up-in-store (BOPIS). A 3PL with strong multi-channel delivery capabilities can enhance the overall customer experience by offering convenient and flexible shipping options that align with their needs.
Additionally, businesses should assess the 3PL’s expertise in specific services relevant to their operations. For example, if a business is heavily involved in international trade, it will need a 3PL with strong capabilities in cross-border fulfillment, including knowledge of customs regulations, international shipping standards, and local delivery networks. Similarly, if returns management is a significant part of the business model, the 3PL should have robust reverse logistics processes in place to handle product inspections, restocking, and refunds efficiently.
Finally, businesses should consider the service level agreements (SLAs) offered by the 3PL. SLAs define the level of service the 3PL is committed to providing, including metrics such as order accuracy, shipping times, and return processing speeds. Clear SLAs help ensure that the 3PL meets the business’s fulfillment requirements and provides the level of service needed to maintain customer satisfaction. Businesses should look for 3PLs that are willing to customize SLAs based on specific omnichannel needs, ensuring that the partnership aligns with their operational goals and customer expectations.
Case Studies of Successful Omnichannel Warehouses
Amazon
Amazon is widely recognized as one of the most successful companies in eCommerce and logistics, and its omnichannel warehousing strategy plays a crucial role in its ability to deliver on its promises of fast, reliable, and convenient service. Founded in 1994 by Jeff Bezos as an online bookstore, Amazon quickly expanded into a multi-category retail giant, offering everything from electronics and apparel to groceries and cloud computing services. With a customer base that spans the globe and millions of orders processed daily, Amazon has become synonymous with speed and efficiency in order fulfillment.
Amazon’s omnichannel warehouse operations are among the most sophisticated in the world, integrating a vast network of fulfillment centers, transportation hubs, and delivery stations. These warehouses are strategically located around the globe to ensure that Amazon can meet its ambitious delivery targets, such as same-day, next-day, or two-day shipping through its Amazon Prime service. Central to Amazon’s success is its ability to effectively manage inventory across multiple channels—including its own eCommerce platform, physical retail locations (such as Amazon Go and Whole Foods), and third-party sellers who use Amazon’s logistics infrastructure via the Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program.
How Amazon Leverages Omnichannel Warehousing to Meet Customer Expectations
Amazon’s omnichannel warehouse strategy is built around a single goal: meeting customer expectations for fast, convenient, and reliable delivery. To achieve this, Amazon has developed a highly responsive and flexible omnichannel fulfillment system that integrates its global network of warehouses with cutting-edge technologies, real-time inventory tracking, and advanced data analytics.
One of the key ways Amazon leverages its omnichannel warehouse is by using multi-channel fulfillment options to ensure that customers receive their orders as quickly as possible. Amazon’s fulfillment centers process orders not only for its own online store but also for physical retail locations and third-party sellers. This integration allows Amazon to dynamically allocate inventory and route orders through the most efficient fulfillment channel. For example, if a customer orders a product that is available at a nearby Amazon fulfillment center, the system will automatically select that location for fulfillment to reduce shipping time. Similarly, for grocery items ordered through Amazon Fresh or Whole Foods, products may be sourced from local retail stores or dedicated grocery fulfillment centers, ensuring that fresh goods reach customers in a timely manner.
Amazon’s omnichannel warehouse also enables real-time inventory visibility across all sales channels, which is crucial for maintaining accurate stock levels and preventing issues like stockouts or overstocking. Using sophisticated warehouse management systems (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, Amazon’s fulfillment centers track inventory as it moves through the supply chain—from receiving goods from suppliers to packing and shipping orders. This real-time data allows Amazon to make instant decisions about where to source products, how to optimize warehouse space, and when to reorder stock, ensuring that customers always have access to the products they want.
Fulfillment Center Automation and Inventory Management
Amazon is a leader in the use of automation and robotics to streamline operations in its omnichannel warehouses. Over the years, the company has invested heavily in advanced technologies that improve efficiency, reduce operational costs, and increase the speed of order fulfillment. One of the most significant innovations in Amazon’s warehouses is the use of Amazon Robotics, a fleet of autonomous robots that assist with picking, packing, and moving inventory within the fulfillment centers.
Amazon’s robots are designed to reduce the time it takes for workers to retrieve products by bringing shelves of goods directly to human packers. This system, known as goods-to-person automation, dramatically reduces walking time for warehouse workers, allowing them to fulfill more orders in less time. The robots are equipped with sensors and advanced navigation systems that enable them to move through the warehouse safely, avoiding collisions and optimizing routes for maximum efficiency. By automating the most labor-intensive tasks, Amazon’s omnichannel warehouse can process orders faster and with greater accuracy than traditional warehouses.
In addition to robotics, Amazon uses machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize its inventory management processes. AI-powered algorithms analyze historical sales data, customer behavior, and seasonal trends to predict demand and ensure that the right products are available in the right locations. For example, Amazon’s inventory management system can anticipate increased demand for certain products during peak shopping seasons, such as Black Friday or the holiday period, and proactively stock fulfillment centers accordingly. This predictive approach helps Amazon maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing the risk of stockouts while minimizing excess inventory.
Amazon’s omnichannel warehouses also employ real-time data analytics to monitor the performance of its fulfillment centers and identify areas for improvement. Using data from its warehouse management systems, Amazon tracks key performance indicators (KPIs) such as order processing times, inventory turnover rates, and delivery accuracy. This data-driven approach allows Amazon to continuously refine its omnichannel warehousing operations, improving efficiency and ensuring that customers receive their orders on time.
Analysis and Evaluation
Amazon’s omnichannel warehouse strategy is widely regarded as one of the most effective in the world, driven by its use of automation, real-time inventory management, and multi-channel fulfillment. By integrating these advanced technologies and processes, Amazon has been able to meet the demands of a global customer base while maintaining the flexibility to scale its operations rapidly.
One of the key strengths of Amazon’s approach is its ability to adapt to fluctuations in demand. Whether during peak shopping seasons or flash sales, Amazon’s omnichannel warehouses can quickly scale up operations to handle increased order volumes, ensuring that customers receive their products on time. This flexibility is supported by Amazon’s robust technology infrastructure, which enables real-time data analysis and predictive inventory management.
Another notable strength is Amazon’s use of automation to drive efficiency. By deploying robots and machine learning algorithms in its fulfillment centers, Amazon has reduced labor costs and improved order accuracy, which in turn enhances customer satisfaction. The combination of automation and human labor allows Amazon to fulfill orders faster than many competitors, setting the standard for speed in the industry.
However, one of the potential challenges Amazon faces with its omnichannel warehouse strategy is the high capital investment required to maintain its extensive automation infrastructure. The cost of developing, implementing, and maintaining robotic systems, AI algorithms, and advanced data analytics can be substantial, making it difficult for smaller businesses to replicate Amazon’s model. Despite this, Amazon’s continued investment in innovation has helped it stay ahead of the competition and solidify its position as a leader in omnichannel warehousing.
Walmart
Walmart is one of the largest and most successful retailers in the world, with over 11,000 stores in 27 countries. Founded in 1962 by Sam Walton, Walmart initially grew by focusing on offering low prices and a wide range of products in physical stores. However, as consumer shopping habits began to shift toward eCommerce, Walmart recognized the need to adapt its traditional retail model to include online sales and more flexible fulfillment options. Today, Walmart is not only a leader in physical retail but also one of the largest eCommerce retailers, consistently ranking alongside Amazon.
To support this massive transition and the demand for seamless shopping experiences across multiple channels, Walmart has implemented a robust omnichannel warehouse strategy. This strategy is designed to optimize inventory management, speed up order fulfillment, and integrate the company’s physical and digital operations. By leveraging both its extensive network of stores and its growing eCommerce infrastructure, Walmart aims to offer customers the convenience of online shopping combined with the immediacy of in-store services.
Walmart’s Omnichannel Strategy and its Integration of Stores and Warehouses
A key component of Walmart’s omnichannel warehouse strategy is its integration of stores and warehouses. Unlike traditional retailers that keep their physical stores and eCommerce operations separate, Walmart has developed a strategy that turns its stores into mini-warehouses, enhancing fulfillment capabilities and reducing delivery times. This approach allows Walmart to blur the lines between its online and offline operations, creating a unified system where inventory is managed holistically across all sales channels.
One of the most significant ways Walmart achieves this integration is through its ship-from-store model. In this system, Walmart leverages its vast network of physical stores to fulfill online orders. When a customer places an order online, Walmart’s system identifies the store closest to the customer that has the item in stock and ships it directly from that location. This approach significantly reduces shipping times and costs, as products are often already located near the customer. By using stores as fulfillment centers, Walmart maximizes its existing infrastructure, allowing it to compete more effectively with eCommerce giants like Amazon.
Walmart’s omnichannel warehouse strategy also includes the use of regional distribution centers (RDCs) and fulfillment centers dedicated to eCommerce. These warehouses are strategically located across the country to ensure that high-demand products are readily available for online orders. Walmart’s RDCs primarily handle the distribution of products to stores, while the eCommerce fulfillment centers are designed to process online orders exclusively. By maintaining this balance between store-based fulfillment and centralized eCommerce operations, Walmart can provide a variety of delivery options to customers, including same-day, next-day, and two-day shipping.
Additionally, Walmart’s buy online, pick up in-store service is a crucial element of its omnichannel warehouse strategy. BOPIS allows customers to shop online and pick up their orders at a nearby Walmart store, providing the convenience of eCommerce without the wait for shipping. This service is particularly appealing to customers who want to avoid delivery fees or need items quickly. Walmart’s ability to integrate its store inventory with its online platform ensures that BOPIS orders are fulfilled promptly, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Innovations in Order Fulfillment and Delivery
Walmart has also invested heavily in innovations in order fulfillment and delivery to enhance its omnichannel warehouse strategy. One of the most notable innovations is the use of automated fulfillment systems in its warehouses. To improve the speed and accuracy of order processing, Walmart has adopted advanced technologies such as robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) to automate key aspects of its fulfillment operations. These systems help streamline the picking, packing, and sorting of products, allowing Walmart to process higher volumes of orders more efficiently than traditional manual methods.
For example, Walmart has implemented automated picking systems in some of its fulfillment centers, where robots retrieve products from shelves and bring them to human packers. This reduces the time it takes to fulfill an order and minimizes the risk of errors, such as selecting the wrong product or shipping to the incorrect address. Automation also allows Walmart to scale its operations during peak shopping periods, such as the holiday season or Black Friday, without requiring a proportional increase in labor costs.
In addition to warehouse automation, Walmart has introduced innovations in last-mile delivery, the final stage of the fulfillment process where orders are delivered to customers. One of the key challenges in last-mile delivery is reducing the time and cost associated with transporting goods from the fulfillment center to the customer’s doorstep. To address this, Walmart has explored several delivery models, including crowdsourced delivery through its Spark Delivery program. This service uses independent drivers, similar to the gig economy model employed by companies like Uber and DoorDash, to deliver orders from stores to customers’ homes. By utilizing local drivers, Walmart can offer faster delivery times, particularly for same-day and next-day orders, while keeping delivery costs competitive.
Walmart has also invested in grocery delivery innovations, including the expansion of its online grocery pickup and delivery services. Customers can order groceries online and choose between home delivery or curbside pickup at their local store. To support this service, Walmart has built out specialized grocery fulfillment centers that are equipped with cold storage and other features necessary for handling fresh and frozen products. Walmart is also experimenting with autonomous vehicle delivery and drone delivery, aiming to further reduce delivery times and enhance the efficiency of its last-mile logistics.
Analysis and Evaluation
Walmart’s omnichannel warehouse strategy has positioned the company as a formidable player in both the physical retail and eCommerce markets. One of the key strengths of Walmart’s approach is its ability to leverage its existing infrastructure—specifically its vast network of physical stores—to fulfill online orders and offer flexible delivery options. By turning stores into mini-warehouses and integrating them with regional distribution centers and dedicated eCommerce fulfillment centers, Walmart can serve customers faster than many of its competitors. This hybrid model allows Walmart to capitalize on the strengths of both traditional retail and eCommerce, creating a seamless shopping experience across all channels.
Another strength of Walmart’s omnichannel warehouse strategy is its focus on innovation in order fulfillment. By investing in automation, AI, and advanced warehouse technologies, Walmart has been able to streamline its fulfillment processes, reduce labor costs, and increase order accuracy. These innovations are particularly important in the highly competitive eCommerce landscape, where speed and efficiency are critical to maintaining customer loyalty.
However, Walmart’s omnichannel strategy is not without its challenges. One potential weakness is the complexity of integrating physical and digital operations. Managing inventory, orders, and logistics across thousands of stores and multiple fulfillment centers requires sophisticated systems and careful coordination. While Walmart has made significant progress in this area, the complexity of its operations increases the risk of inefficiencies, such as stock discrepancies or delays in order processing. Additionally, Walmart faces stiff competition from eCommerce-focused companies like Amazon, which have built their operations entirely around online fulfillment and may have a technological edge in certain areas, such as automation and data analytics.
Walmart’s omnichannel warehouse strategy represents a successful integration of its brick-and-mortar and eCommerce operations, allowing the company to meet the evolving needs of its customers. By leveraging its store network, investing in innovative technologies, and offering flexible fulfillment options, Walmart has created a highly efficient and scalable system for handling omnichannel orders. While there are challenges associated with managing such a complex operation, Walmart’s continued focus on innovation and customer satisfaction ensures that it remains a leader in the retail and eCommerce space.
Zara
Zara is one of the largest and most successful fast fashion retailers in the world, operating over 2,000 stores in 96 countries. Founded in 1974 in Spain by Amancio Ortega, Zara is known for its ability to quickly bring the latest fashion trends from the runway to store shelves. Central to Zara’s business model is its fast fashion supply chain, which emphasizes speed and flexibility in design, production, and distribution. Unlike traditional fashion retailers that release seasonal collections months in advance, Zara introduces new collections every few weeks, responding quickly to changing consumer preferences.
A key element of Zara’s success is its highly efficient supply chain, which relies on a carefully coordinated network of production facilities, warehouses, and stores. Zara’s omnichannel warehouse strategy plays a critical role in ensuring that inventory moves seamlessly between these nodes, allowing the company to restock stores quickly, fulfill online orders, and manage returns effectively. By integrating its physical and digital channels, Zara has created a supply chain that is not only responsive to market demand but also capable of delivering a consistent customer experience across all platforms.
The Role of Omnichannel Warehousing in Zara’s Fast Fashion Supply Chain
Omnichannel warehousing is at the heart of Zara’s fast fashion supply chain, enabling the company to maintain its competitive edge by delivering new products to stores and customers faster than its competitors. Unlike traditional warehouses that focus on storing large quantities of inventory, Zara’s omnichannel warehouses are designed to support just-in-time inventory management. This approach minimizes the amount of stock held at any given time, allowing Zara to quickly respond to changes in consumer demand while reducing the costs associated with excess inventory.
One of the key functions of Zara’s omnichannel warehouse is cross-channel inventory management, which ensures that products are available where they are needed most, whether in stores or for online orders. Zara operates a centralized warehousing system, with distribution centers strategically located near its manufacturing hubs in Spain and other countries. These distribution centers act as the primary nodes in Zara’s supply chain, receiving finished goods from production facilities and distributing them to stores and fulfillment centers around the world. By using a centralized approach, Zara can maintain tight control over its inventory, ensuring that products are distributed efficiently based on real-time demand data from both its physical stores and eCommerce platforms.
Zara’s omnichannel warehouses also play a crucial role in supporting multi-channel fulfillment, enabling the company to offer a seamless shopping experience across its online and offline channels. For example, Zara uses its stores as mini-fulfillment centers, allowing customers to place online orders and pick them up in-store, or have products shipped directly to their homes from the nearest warehouse. This level of integration between Zara’s warehouses and its retail stores ensures that inventory is utilized optimally, reducing the risk of stockouts in stores while also speeding up delivery times for online orders.
Zara’s omnichannel warehouse strategy also supports its global distribution network, ensuring that new collections are available in stores across the world within a matter of days. Once products are shipped from Zara’s distribution centers, they are delivered to stores within 24-48 hours, ensuring that customers always have access to the latest trends. This fast turnaround time is made possible by Zara’s efficient warehousing operations, which prioritize speed and flexibility in order fulfillment.
How Zara Uses Real-Time Inventory and AI to Manage Its Warehouse Operations
To maintain its fast-paced supply chain, Zara relies heavily on real-time inventory management and artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize its warehouse operations. Real-time inventory tracking is essential for Zara, as it allows the company to maintain visibility into stock levels across all of its warehouses and stores. By using advanced warehouse management systems (WMS), Zara can monitor inventory movements in real time, ensuring that products are always available where they are needed most.
Zara’s use of real-time inventory data extends beyond basic stock tracking. The company also uses this data to make dynamic inventory allocation decisions. For example, if a particular product is selling faster than expected in a certain region, Zara’s system can automatically reallocate inventory from other warehouses or stores to meet the demand. This level of agility is critical in the fast fashion industry, where trends can shift rapidly, and product availability can make or break a sale. Real-time inventory management also allows Zara to avoid the costs associated with overstocking or understocking, ensuring that the right amount of inventory is available at all times.
In addition to real-time inventory management, Zara has embraced artificial intelligence and machine learning to further enhance its warehouse operations. AI plays a key role in Zara’s demand forecasting and inventory planning processes, enabling the company to predict customer demand more accurately and adjust its supply chain accordingly. By analyzing vast amounts of data, including historical sales trends, customer preferences, and external factors such as weather and economic conditions, Zara’s AI-driven systems can anticipate which products will be in high demand and ensure that they are available in the right quantities at the right time.
AI is also used in warehouse automation, helping to streamline processes such as order picking, packing, and shipping. For instance, Zara uses robotic systems in its warehouses to automate the retrieval and sorting of products, reducing the time it takes to process orders and ensuring that products are shipped to stores and customers quickly. This use of AI and robotics not only improves the efficiency of Zara’s warehouse operations but also allows the company to scale its operations during peak periods, such as during new product launches or seasonal sales.
Furthermore, Zara’s AI-powered systems help optimize the placement of products within its warehouses, ensuring that fast-moving items are stored in easily accessible locations, while slower-moving products are stored in less prime areas. This level of smart inventory placement reduces the time spent retrieving products and increases the overall efficiency of Zara’s warehouse operations.
Analysis and Evaluation
Zara’s omnichannel warehouse strategy has played a pivotal role in the company’s success in the fast fashion industry. By integrating real-time inventory management with AI-driven systems, Zara has created a highly efficient and responsive supply chain that allows it to meet the ever-changing demands of the fashion market. One of the key strengths of Zara’s approach is its ability to leverage real-time data to make informed decisions about inventory allocation and fulfillment. This level of visibility and agility ensures that products are always available where they are needed most, whether in stores or for online orders.
Another strength of Zara’s omnichannel warehouse strategy is its focus on speed and flexibility. By using just-in-time inventory management and maintaining a centralized distribution system, Zara is able to quickly respond to changes in demand, reducing the time it takes to bring new products to market. This fast turnaround time is one of the factors that sets Zara apart from its competitors in the fast fashion industry, allowing the company to capitalize on emerging trends and provide customers with the latest styles.
However, one potential challenge for Zara is the complexity of managing a global supply chain. While Zara’s centralized warehousing model allows for greater control over inventory, it also requires a high level of coordination between its warehouses, stores, and production facilities. As Zara continues to expand its global presence, maintaining this level of coordination could become increasingly difficult, particularly as new markets and sales channels are added to the mix. To mitigate this risk, Zara will need to continue investing in advanced technologies, such as AI and automation, to ensure that its omnichannel warehouse operations remain efficient and scalable.
Zara’s omnichannel warehouse strategy has been instrumental in supporting its fast fashion business model, allowing the company to deliver new products to market quickly while maintaining tight control over its inventory. By leveraging real-time inventory management, AI, and warehouse automation, Zara has created a supply chain that is both agile and efficient, ensuring that it can meet the demands of its global customer base. As Zara continues to innovate and expand, its omnichannel warehouse strategy will remain a key driver of its success in the fast fashion industry.
Best Practices for Optimizing Omnichannel Warehouse Efficiency
Real-time Inventory Management
Implementing Advanced Inventory Systems
To effectively manage inventory in an omnichannel warehouse, businesses must implement advanced inventory systems that provide real-time visibility and control over stock levels. A robust WMS is central to this effort, as it helps manage the movement, storage, and tracking of inventory within the warehouse. However, in an omnichannel environment, where orders may come from multiple sales channels—such as online platforms, brick-and-mortar stores, and third-party marketplaces—traditional WMS solutions are no longer sufficient. To ensure real-time inventory management, businesses must integrate their WMS with IoT technology and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems.
IoT technology plays a critical role in enabling real-time inventory tracking within an omnichannel warehouse. IoT devices, such as smart sensors and connected tags, can be attached to individual products, pallets, or containers, providing real-time data on the location, condition, and movement of inventory. These devices communicate directly with the WMS, ensuring that inventory data is continuously updated as products are moved, picked, or packed. For example, IoT sensors can track temperature-sensitive goods, ensuring that perishable products remain within safe storage conditions, while also alerting warehouse managers if there is any deviation from required temperature levels. By integrating IoT devices into the warehouse, businesses can monitor stock levels across all channels with greater accuracy, reducing the likelihood of stockouts or overstocking and ensuring that products are readily available when customers place their orders.
RFID technology further enhances the real-time visibility of inventory by enabling businesses to track products as they move through the warehouse, from receiving to shipping. RFID tags, which are embedded in products or packaging, use radio waves to transmit data to RFID readers positioned throughout the warehouse. Unlike traditional barcode scanning, RFID does not require direct line-of-sight, allowing for faster and more efficient tracking of goods. As a result, warehouse staff can quickly and accurately locate items, speeding up order picking and fulfillment processes. The combination of RFID and IoT technologies ensures that inventory data is consistently updated in real time, providing businesses with a complete, real-time view of their stock levels across all channels.
In addition to improving inventory visibility, advanced WMS solutions can be integrated with eCommerce platforms, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and ERP systems to ensure that inventory data is synchronized across the entire supply chain. This integration enables businesses to manage their inventory holistically, balancing stock levels across multiple sales channels and fulfillment centers. For example, when a product is sold in a physical store, the WMS can automatically update the inventory levels in the eCommerce platform, ensuring that online shoppers are not shown out-of-date stock information. By implementing an integrated, real-time inventory system, businesses can improve their omnichannel warehouse efficiency, reduce order errors, and enhance the customer experience.
Automating Stock Replenishment
Another key strategy for optimizing omnichannel warehouse efficiency is automating the stock replenishment process. In an omnichannel environment, where demand can fluctuate rapidly across different sales channels, it is essential to maintain optimal stock levels to meet customer needs without overstocking. Manual stock replenishment processes can be time-consuming and error-prone, leading to stockouts or excess inventory. By automating stock replenishment with AI-driven demand forecasting tools, businesses can ensure that their inventory levels are always aligned with customer demand, minimizing disruptions to the supply chain and reducing the costs associated with holding excess inventory.
AI-powered demand forecasting leverages historical sales data, market trends, and real-time sales data to predict future demand for products. These tools use machine learning algorithms to analyze patterns in customer behavior, seasonality, and external factors such as promotions or economic conditions. By accurately forecasting demand, AI-driven systems can automate the stock replenishment process, ensuring that products are reordered and restocked as needed to meet anticipated customer demand. This eliminates the guesswork involved in manual inventory management, allowing businesses to avoid the risks of stockouts or overstocking.
For example, in a fashion retail omnichannel warehouse, AI-powered forecasting tools can analyze sales data from previous seasons, combined with current sales trends, to predict which products are likely to be in high demand during an upcoming holiday season. Based on this data, the system can automatically trigger stock replenishment orders for these products, ensuring that the warehouse is well-prepared to meet customer demand during the peak shopping period. Similarly, in a grocery omnichannel warehouse, the system can monitor real-time sales data and automatically reorder perishable items based on expiration dates and consumption rates, reducing food waste and ensuring product freshness.
Automating stock replenishment with AI-driven tools also helps businesses manage just-in-time inventory practices, which are critical for reducing the amount of capital tied up in excess stock. With just-in-time inventory management, products are ordered and restocked as needed, minimizing the time they spend in storage. This not only reduces storage costs but also helps businesses respond more quickly to changes in customer demand. For example, if a particular product experiences a sudden spike in demand due to a viral marketing campaign, the AI-driven system can automatically adjust the replenishment schedule to ensure that the warehouse maintains adequate stock levels without over-ordering.
By automating the stock replenishment process, businesses can also reduce lead times and improve order fulfillment speed. AI-driven systems can identify the most efficient suppliers, optimize order quantities, and select the best delivery schedules based on real-time demand data. This enables businesses to restock products more quickly and efficiently, reducing the time it takes for new inventory to arrive at the warehouse. With faster stock replenishment, omnichannel warehouses can maintain a continuous flow of inventory, ensuring that products are always available for fulfillment and minimizing delays in the order fulfillment process.
Efficient Order Picking and Packing
Zone and Batch Picking Strategies
Order picking is one of the most time-consuming and labor-intensive tasks in any warehouse. In an omnichannel warehouse, where orders may come from multiple sales channels and involve a wide variety of products, optimizing the picking process is essential to maintaining high levels of efficiency. Two key strategies that have proven effective in reducing travel time and increasing productivity are zone picking and batch picking. These methods enable warehouse staff to pick orders more quickly and accurately, leading to faster fulfillment times and improved overall warehouse performance.
Zone picking is a strategy that divides the warehouse into specific zones, with each zone assigned to a team of pickers. Rather than having a single picker travel across the entire warehouse to collect all items for an order, the order is divided into smaller tasks based on the location of the items. Each picker is responsible for gathering products from their designated zone, and the items are later consolidated at a packing station. This method significantly reduces the time spent walking through the warehouse, as pickers only need to focus on their assigned area. Zone picking is particularly effective in large omnichannel warehouses where products are stored across vast areas, and minimizing travel time is crucial for maintaining efficiency.
For example, in an omnichannel warehouse handling a mix of eCommerce and in-store orders, zone picking can be used to optimize the fulfillment of large, multi-item orders. One picker may be assigned to the zone containing apparel, while another handles electronics. By distributing the workload across multiple pickers, the warehouse can process orders more quickly, reducing the time it takes for products to be picked, packed, and shipped.
Batch picking, on the other hand, involves grouping multiple orders together and picking items for those orders in one trip. Instead of picking items for a single order at a time, pickers gather items for several orders simultaneously, reducing the number of trips needed to fulfill multiple orders. This method is particularly useful for warehouses that handle a high volume of small, single-item orders, as it allows pickers to maximize their efficiency by consolidating their movements and minimizing downtime between picks.
In an omnichannel warehouse, batch picking is especially valuable when fulfilling orders from different channels that have similar products. For instance, if several online customers have ordered the same product, the warehouse staff can use batch picking to collect multiple units of the product in one go, rather than making separate trips for each order. By grouping orders together and picking items in bulk, batch picking helps streamline the fulfillment process, reducing both travel time and labor costs.
Both zone picking and batch picking can be enhanced through the use of pick-to-light and voice-picking technologies. Pick-to-light systems use illuminated indicators to guide pickers to the correct product location, speeding up the picking process and reducing errors. Similarly, voice-picking systems provide pickers with audio instructions via a headset, allowing them to keep their hands free while navigating the warehouse. These technologies further improve the efficiency of zone and batch picking by ensuring that pickers can quickly locate and retrieve the correct items with minimal mistakes.
Automation in Packing Processes
While optimizing order picking is essential for improving warehouse efficiency, the packing process is equally important in ensuring that orders are fulfilled quickly and accurately. As customer expectations for fast and error-free deliveries continue to rise, omnichannel warehouses are increasingly turning to automated packing systems to enhance productivity and reduce manual errors. Automated packing technologies, such as conveyor belts, automated sorting machines, and robotic packing systems, can significantly speed up the packing process, allowing warehouses to handle larger order volumes with greater efficiency.
One of the most common forms of automation in the packing process is the use of conveyor belts to move items from the picking area to the packing station. In traditional warehouses, pickers often have to manually transport items to the packing area, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. By implementing conveyor belts, warehouses can automate this task, allowing items to be transported quickly and efficiently without requiring human intervention. This not only speeds up the packing process but also frees up warehouse staff to focus on more value-added tasks, such as quality control or managing high-priority orders.
Automated sorting machines are another critical component of automated packing systems in omnichannel warehouses. These machines use sensors and AI-powered algorithms to automatically sort items based on factors such as size, weight, and destination. Once items are picked and placed on the conveyor belt, the sorting machine directs them to the appropriate packing station, where they are packaged and prepared for shipping. By automating the sorting process, warehouses can reduce the risk of errors, such as sending items to the wrong packing station or mislabeling packages. This ensures that orders are packed accurately and efficiently, minimizing the likelihood of delays or returns due to packing mistakes.
In addition to conveyor belts and sorting machines, some omnichannel warehouses are implementing robotic packing systems, which can automatically package items without the need for manual labor. These systems use robotic arms and AI-driven software to pick items from the conveyor belt, place them into packaging, and seal the package for shipping. Robotic packing systems are particularly useful in high-volume warehouses that need to process large numbers of orders quickly, as they can operate continuously without fatigue, reducing bottlenecks in the packing process. Moreover, robotic systems can be programmed to handle various types of packaging, from standard boxes to custom-sized containers, allowing warehouses to optimize packaging based on the size and shape of the items being shipped.
One of the key benefits of automating the packing process is the reduction in manual errors. Human error is a common issue in manual packing operations, leading to mistakes such as incorrect item counts, mislabeled packages, or damaged goods due to improper packing. By automating these tasks, warehouses can minimize the risk of such errors, ensuring that orders are packed accurately and consistently. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also reduces the costs associated with returns, re-shipping, and customer service inquiries.
Additionally, automation in packing can contribute to more sustainable warehousing practices by optimizing the use of packaging materials. AI-powered systems can analyze the dimensions of each item and select the most appropriate packaging size, reducing the use of excess materials and minimizing waste. By using the right amount of packaging for each order, omnichannel warehouses can lower their environmental footprint while also reducing shipping costs, as smaller, lighter packages are less expensive to transport.
Effective Workforce Management
In an omnichannel warehouse, efficient workforce management is essential for maintaining high levels of productivity, reducing operational costs, and ensuring that orders are processed and fulfilled quickly. As the demand for faster, more accurate order fulfillment continues to grow, the ability to effectively manage and optimize the workforce becomes even more critical. With the rise of automation and technology in warehouse operations, ensuring that employees are well-trained and optimally allocated is key to maintaining a competitive edge. In this section, we explore two essential components of effective workforce management: optimizing workforce allocation and training and upskilling workers to handle modern omnichannel warehouse demands.
Optimizing Workforce Allocation
The performance of an omnichannel warehouse is heavily influenced by how well the workforce is allocated. Peak demand periods, such as holiday shopping seasons, flash sales, and promotional events, can lead to a significant increase in order volumes, requiring businesses to strategically allocate their workforce to handle the surge in activity. Conversely, during low-activity periods, warehouses must avoid overstaffing, which can lead to unnecessary labor costs. To balance these fluctuations, it is essential to use labor management software to monitor workforce performance, analyze activity levels, and make data-driven decisions about staff allocation.
Labor management software provides omnichannel warehouses with the tools they need to optimize workforce allocation in real-time. By tracking metrics such as individual worker performance, task completion rates, and overall warehouse activity, LMS enables managers to gain insights into how labor is being utilized and where improvements can be made. For example, if a certain section of the warehouse is experiencing bottlenecks due to an influx of orders, managers can use labor management software to reallocate workers from less busy areas to help alleviate the pressure. This level of flexibility ensures that the workforce is being deployed where it is most needed, improving overall efficiency and preventing delays in order fulfillment.
In addition to real-time workforce management, labor management software can help omnichannel warehouses predict and plan for peak demand periods. By analyzing historical data on order volumes, seasonal trends, and promotional schedules, the software can forecast when and where additional labor will be needed. This allows warehouse managers to adjust staffing levels in advance, ensuring that there are enough workers on hand to handle increased order volumes without overwhelming existing staff. During periods of low demand, the software can also identify opportunities to reduce labor costs by scaling back workforce numbers, either by adjusting work schedules or reallocating staff to other areas of the business.
Another key benefit of using labor management software is its ability to track worker productivity. By monitoring KPIs such as pick rates, packing times, and accuracy levels, warehouse managers can identify top-performing employees and areas where additional training or support may be needed. This data-driven approach to workforce management ensures that each worker is contributing to the overall efficiency of the warehouse and helps managers make informed decisions about staffing and scheduling. By optimizing workforce allocation based on real-time data, omnichannel warehouses can ensure that labor is being used efficiently, even during periods of fluctuating demand.
Additionally, labor management software can support automated scheduling, which further improves workforce allocation. Automated scheduling tools can create dynamic work schedules that align with warehouse activity levels, ensuring that workers are assigned to shifts based on real-time demand. This reduces the administrative burden on managers and helps prevent labor shortages or overstaffing. By automating workforce scheduling, omnichannel warehouses can improve labor utilization and ensure that staff are always available to meet customer needs.
Training and Upskilling Workers
As omnichannel warehouses become increasingly reliant on automation and advanced technology, the need for a well-trained and skilled workforce becomes more important than ever. Training and upskilling workers on new technologies, systems, and best practices is crucial for maintaining high levels of productivity, particularly when managing complex orders or interacting with automated systems. Regular training programs not only improve employee performance but also help workers adapt to the changing demands of an omnichannel warehouse environment.
One of the key areas where training is essential is in the use of automated systems. As more warehouses adopt technologies such as robotics, conveyor belts, automated sorting machines, and AI-powered inventory management systems, it is critical that employees understand how to operate and interact with these tools effectively. Workers who are unfamiliar with automated systems may struggle to keep up with the pace of operations, leading to delays, errors, and reduced efficiency. By providing comprehensive training on how to use these systems, omnichannel warehouses can ensure that their workforce is capable of maximizing the benefits of automation and improving overall productivity.
In addition to training on automated systems, omnichannel warehouses must also focus on training workers to manage complex orders that span multiple channels. Omnichannel warehouses often deal with a wide variety of orders, including those from eCommerce platforms, physical stores, and third-party marketplaces. Handling these orders requires employees to be proficient in managing different order types, shipping requirements, and customer expectations. For example, workers may need to learn how to prioritize orders for same-day delivery or process BOPIS orders alongside standard eCommerce shipments. Training workers to navigate these complexities ensures that orders are processed accurately and efficiently, regardless of the channel through which they were placed.

Upskilling workers on emerging technologies and best practices also helps future-proof the workforce, allowing employees to take on new roles as the warehouse evolves. For example, as more warehouses adopt AI-powered systems for demand forecasting, inventory management, and predictive maintenance, workers will need to understand how to interpret and act on the insights generated by these systems. By providing training on AI-driven technologies, warehouses can equip their employees with the skills needed to manage more advanced systems, reduce reliance on manual processes, and contribute to the overall efficiency of the warehouse.
Training and upskilling are not limited to technical skills; they also encompass soft skills such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving, which are essential for maintaining a collaborative and efficient workforce. In an omnichannel warehouse, workers must be able to communicate effectively with one another, especially when coordinating tasks such as order picking, packing, and shipping. Regular training on soft skills can help workers improve their ability to collaborate, resolve issues quickly, and maintain a positive working environment, all of which contribute to the overall success of the warehouse.
Furthermore, continuous training helps improve employee retention and job satisfaction. In a competitive job market, employees are more likely to stay with a company that invests in their professional development and offers opportunities for growth. By providing ongoing training and upskilling programs, omnichannel warehouses can create a more engaged and motivated workforce, reducing turnover and ensuring that experienced employees remain on the team. This is particularly important in an industry where high employee turnover can lead to operational disruptions and increased hiring costs.
Reducing Operational Costs
Energy Efficiency and Resource Optimization
One of the most impactful ways to reduce operational costs in an omnichannel warehouse is by adopting energy efficiency and resource optimization strategies. Warehouses consume significant amounts of energy to power lighting, heating, cooling, and automated systems. By implementing energy-saving initiatives, warehouses can reduce their utility bills and overall operational expenses while contributing to a more sustainable operation.
A key area where warehouses can achieve immediate cost savings is through LED lighting systems. Traditional incandescent and fluorescent lighting consume more energy and require frequent maintenance due to their shorter lifespan. In contrast, LED lighting is much more energy-efficient, using up to 80% less energy than traditional lighting and lasting significantly longer. Many warehouses are now switching to LED lighting, which not only reduces energy consumption but also lowers maintenance costs due to the longer lifespan of these bulbs. Additionally, LED lighting provides brighter and more uniform illumination, improving visibility for warehouse workers and enhancing overall safety and productivity.
In conjunction with energy-efficient lighting, omnichannel warehouses can implement automated climate control systems to regulate heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) based on real-time data. Warehouses often require climate control to maintain optimal conditions for products, especially for temperature-sensitive goods such as food or pharmaceuticals. However, traditional HVAC systems can lead to energy wastage if they operate continuously, even when not necessary. By installing automated climate control systems, warehouses can monitor temperature and humidity levels and adjust them automatically based on the needs of the environment. For example, during periods of low activity, the system can reduce heating or cooling in areas that are not in use, saving energy and lowering utility costs. These smart systems ensure that climate control is only activated when necessary, leading to more efficient resource usage.
Another important aspect of reducing energy costs is the integration of renewable energy sources. Warehouses with large roof spaces can install solar panels to generate electricity, reducing their reliance on traditional energy sources and cutting down on utility expenses. Solar power is a sustainable, long-term solution that can significantly lower energy costs while also reducing the warehouse’s carbon footprint. In addition to solar energy, some warehouses are experimenting with wind energy or using geothermal systems to further enhance energy efficiency. By investing in renewable energy, warehouses not only reduce their operational costs but also contribute to environmental sustainability, which is becoming increasingly important to consumers and stakeholders alike.
In terms of resource optimization, water management systems can also be implemented to reduce water consumption in the warehouse. Automated water-saving technologies, such as low-flow faucets and water recycling systems, can help warehouses minimize water usage, particularly in areas such as restrooms and cleaning operations. By optimizing water consumption, warehouses can further reduce operational costs and contribute to overall resource conservation efforts.
Cross-Docking and Just-in-Time Inventory
Beyond energy efficiency, optimizing inventory management is another crucial strategy for reducing operational costs in an omnichannel warehouse. Two key practices that help minimize storage costs and reduce inventory holding expenses are cross-docking and just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems. By adopting these practices, warehouses can reduce the need for long-term storage, improve the flow of goods, and minimize inventory waste, leading to substantial cost savings.
Cross-docking is a logistics strategy where incoming goods are unloaded from inbound transportation and directly transferred to outbound transportation, with little or no storage in between. In a cross-docking system, products move through the warehouse quickly and are shipped to their destination as soon as they arrive. This eliminates the need for long-term storage, reducing the space required for inventory and minimizing associated costs such as rent, utilities, and labor. For omnichannel warehouses, cross-docking is particularly effective for handling fast-moving consumer goods, seasonal items, and products with high turnover rates.
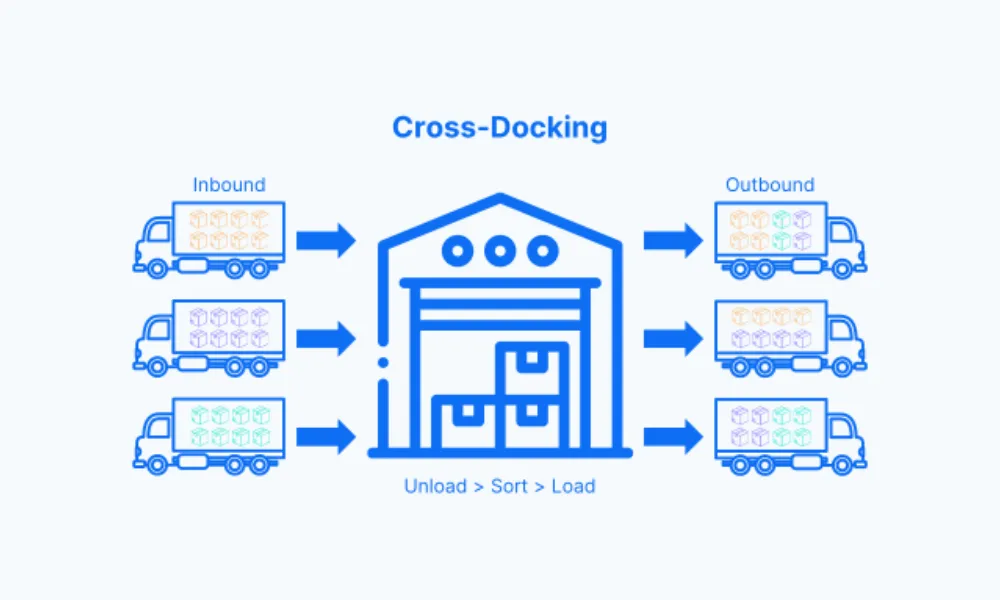
For example, a retail business may receive shipments of popular products such as electronics or fashion items, which are immediately transferred to outbound trucks for delivery to stores or customers. Instead of placing these items in storage, cross-docking ensures they are quickly distributed to where they are needed, reducing inventory handling time and lowering storage costs. Cross-docking also improves order fulfillment speed, which is essential in an omnichannel environment where customers expect fast deliveries.
In addition to cross-docking, implementing a just-in-time (JIT) inventory system can further reduce operational costs by minimizing the amount of inventory held in the warehouse. With JIT inventory management, products are ordered and delivered to the warehouse just in time to meet customer demand, rather than being stocked in large quantities. This reduces the need for excess inventory, which can lead to waste and higher holding costs. By keeping inventory levels low and ordering products based on real-time demand, warehouses can reduce storage costs, avoid overstocking, and improve cash flow.
For example, an omnichannel warehouse managing inventory for an eCommerce retailer can use JIT to ensure that products are only restocked when they are needed to fulfill specific orders. By using demand forecasting tools and real-time sales data, the warehouse can predict when products will be needed and schedule deliveries accordingly. This reduces the risk of holding excess inventory, which not only ties up capital but also takes up valuable warehouse space.
However, for JIT inventory to be successful, warehouses must have strong relationships with their suppliers and reliable transportation networks to ensure that products are delivered on time. Delays in receiving inventory can lead to stockouts and customer dissatisfaction, so omnichannel warehouses must invest in robust demand forecasting tools and supply chain management systems to ensure that products are replenished efficiently and consistently.
By combining cross-docking with JIT inventory practices, omnichannel warehouses can significantly reduce their operational costs by minimizing storage needs, improving the flow of goods, and reducing the risk of inventory waste. These strategies also improve the overall efficiency of the warehouse, allowing businesses to better respond to fluctuating demand and deliver products more quickly to customers.
Conclusion
As we have explored throughout this comprehensive guide, omnichannel warehousing is a critical component of modern supply chains, driven by the growing complexity of managing multiple sales channels and the increasing expectations of consumers. From understanding the shift to omnichannel warehousing in the context of evolving eCommerce trends to examining its key components—such as real-time inventory visibility, seamless order fulfillment, and automated solutions—it is clear that omnichannel warehouses offer unparalleled advantages in terms of flexibility, scalability, and efficiency.
For businesses seeking to stay competitive in this rapidly evolving landscape, adopting omnichannel warehousing is no longer an option—it’s a necessity. By leveraging the best practices, tools, and strategies outlined in this post, companies can position themselves to thrive in the fast-paced world of omnichannel retail, ensuring they meet customer expectations and remain agile in the face of future challenges. The path forward lies in embracing omnichannel warehousing to create more efficient, sustainable, and customer-centric operations that drive long-term success.