Omnichannel retail KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are essential tools for measuring the success of this integration. They help retailers understand where they excel and where there is room for improvement. From tracking sales and inventory to gauging customer satisfaction across different platforms, KPIs provide valuable insights that can drive strategic decisions and foster growth.
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the various metrics that can help retailers thrive in a marketplace that is increasingly interconnected. By understanding these indicators, businesses can refine their operations, enhance customer interactions, and achieve a competitive edge in the fast-paced world of retail. This blog post aims not only to outline the essential omnichannel retail KPIs but also to offer actionable insights on how to leverage this data effectively in the quest for omnichannel excellence.
Table of Contents
Core Omnichannel Retail KPIs
This section delves into the core omnichannel retail KPIs that are essential for a comprehensive analysis of performance as we explore Sales Metrics; assess the efficiency of marketing efforts through Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC); evaluate loyalty and engagement via Customer Retention Rates; analyze purchasing behavior through Average Order Value (AOV); and finally, gauge long-term profitability with Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV).

Each of these metrics offers valuable insights, guiding retailers towards informed decision-making and strategic planning in a multi-channel retail environment.
Sales Metrics
When considering omnichannel retail KPIs, understanding and measuring sales metrics forms the foundation of strategic decision-making. By tracking various sales metrics, businesses can assess their performance across different channels, adjust strategies in real time, and optimize customer experiences. This section will delve into the core sales metrics that are pivotal in managing and evaluating the success of omnichannel retail strategies.
Total Sales
Total sales are the most direct indicator of a retail operation’s financial performance. In an omnichannel context, this metric encompasses sales from all channels — online, offline, mobile, and any other customer touchpoints. Monitoring total sales helps retailers gauge overall market performance and understand long-term trends. To effectively analyze total sales within omnichannel retail KPIs, it is essential to segment these figures by channel, campaign, or even specific time periods to identify what drives the most revenue and why.

For a more nuanced analysis within the framework of omnichannel retail KPIs, breaking down total sales by specific channels is crucial. This segmentation allows retailers to evaluate the effectiveness of each channel independently and in correlation with others.
Further, segmenting total sales by individual marketing campaigns can reveal which promotional activities are most effective at driving revenue. This could help identify whether a recent online marketing push or an in-store discount event had a greater impact on short-term sales spikes. It also helps in understanding consumer response to different sales tactics, which is invaluable for planning future promotions.
Additionally, analyzing total sales over specific time periods can highlight seasonal trends, consumer buying patterns, and the impact of external factors such as economic shifts or changes in consumer behavior. For instance, a retailer might notice that sales peak during the holiday season and drop in the first quarter. Understanding these patterns is essential for inventory planning, staffing, and budget allocation.
Online vs. Offline Sales
This analysis is not only about counting transactions but also about understanding the deeper narrative of consumer behavior and the role of each channel in the customer journey.
- Channel Effectiveness: Analyzing the performance of sales channels in terms of revenue generation and customer engagement offers direct feedback on where investments are paying off. If online sales are accelerating more rapidly than offline sales, this could indicate a shift in consumer habits towards digital shopping, possibly driven by enhanced online user experiences or more effective digital marketing strategies. Conversely, if offline sales remain strong or experience growth, this might suggest that customers still value the tactile and personal experience offered by physical stores. This insight can be critical for deciding where to allocate resources to maximize sales and customer satisfaction.
- Customer Behavior Insights: Delving into where and how customers choose to make their purchases allows businesses to fine-tune their marketing and operational strategies. For instance, a high volume of online sales might suggest convenience is a key driver for many customers, whereas substantial in-store traffic might indicate that the sensory experience or immediate product access is highly valued. Recognizing these preferences supports strategic decisions like implementing or enhancing omnichannel services such as BOPIS (buy online, pick up in-store), which bridges the gap between online convenience and offline immediacy, potentially increasing overall sales and improving customer experience.
- Seasonal and Promotional Impact: Understanding how sales fluctuate between online and offline channels during different seasons or promotional periods can provide valuable insights for planning marketing activities and stock management. For example, if online sales typically surge during exclusive online promotions or specific eCommerce events like Cyber Monday, retailers can maximize their online marketing efforts and stock availability to capitalize on these peaks. Conversely, if offline sales increase significantly during particular times, such as the back-to-school season, it would be wise to enhance in-store promotions, staffing, and inventory to attract and manage increased foot traffic.
By meticulously analyzing online versus offline sales as one of the omnichannel retail KPIs, retailers can optimize their strategies to cater to evolving consumer preferences and maximize the effectiveness of each sales channel. This approach not only boosts sales but also enhances the overall shopping experience, encouraging customer loyalty and supporting long-term business growth in the competitive landscape of omnichannel retail.
Sales Growth Across Channels
Tracking sales growth across different channels is another critical aspect of omnichannel retail KPIs. It helps businesses understand which channels are expanding and at what rate. This metric acts as a barometer for the health and direction of each channel’s contribution to the overall business strategy.
- Strategic Resource Allocation: Sales growth metrics offer a clear perspective on where a business should focus its energies. For example, if a significant upsurge in online sales is observed, it could signal the need for enhanced IT infrastructure or more robust customer service for digital platforms. Conversely, if traditional brick-and-mortar stores are showing steady growth, it might justify further investment in physical retail space or localized marketing strategies. This strategic allocation based on channel performance ensures that resources are not just spent but invested where they can generate the highest returns.
- Scalability and Expansion Decisions: Tracking how new and existing channels grow in response to omnichannel strategies helps businesses decide when to scale operations or expand into new market areas. For instance, a consistent increase in sales from an eCommerce platform might prompt a business to expand its online inventory or explore advanced logistical solutions like automated warehousing. Additionally, if a new channel such as a mobile shopping app is attracting a growing number of users, it may be advantageous to increase functionality or integrate augmented reality features to enhance user engagement.
- New Market Penetration: Understanding sales growth in various demographics and markets is crucial for tapping into new customer segments. If data reveals that a particular channel is popular among a specific demographic — such as increased activity on social media shopping features among millennials — retailers can tailor their marketing campaigns to resonate with this group, possibly adjusting product lines to meet the unique tastes and preferences of these consumers..
- Effectiveness of Omnichannel Strategies: Observing sales growth across channels also serves as a litmus test for the effectiveness of integrated retail strategies. For instance, if the introduction of an omnichannel loyalty program correlates with higher sales volumes across both online and offline channels, it provides empirical evidence that customers value and respond to a unified shopping experience. Such insights not only validate existing strategies but also guide future enhancements and innovations in customer service and engagement.
By continuously monitoring and analyzing sales growth across different channels, retailers can fine-tune their omnichannel approaches, ensuring that they remain competitive and responsive to consumer needs and market changes. This proactive analysis helps in crafting a customer-centric, resilient, and adaptive business model that leverages strengths across all retail channels.
Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
CAC is a key performance indicator that measures the cost associated with acquiring a new customer through a specific channel or combination of channels. This metric is particularly significant in the context of omnichannel retail KPIs because it helps retailers evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of their marketing efforts across various channels.
Definition and Importance of CAC in Omnichannel Retail
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) in the context of omnichannel retail is a critical metric that quantifies the total expenses incurred in marketing and promotional activities aimed at acquiring new customers. This includes a comprehensive range of costs such as online advertising (e.g., PPC campaigns, social media ads), offline advertising (e.g., print, billboards, TV commercials), content production (e.g., blogs, videos, podcasts), staff salaries associated with marketing and sales teams, and investments in technology to enhance digital marketing efforts (e.g., CRM software, marketing automation tools). Calculating CAC in such a diverse ecosystem requires attributing these costs accurately across various channels to determine the efficiency of each in contributing to new customer acquisitions.
The significance of CAC as one of the omnichannel retail KPIs cannot be overstated. It serves not just as a measure of cost effectiveness but also as a strategic lens through which retailers can assess and refine their marketing strategies. By understanding CAC, businesses gain insight into which channels deliver the best return on investment (ROI), allowing them to allocate resources more effectively and potentially shift strategies to capitalize on the most lucrative channels. Additionally, a lower CAC typically indicates a higher efficiency of the marketing spend, which is particularly valuable in competitive retail environments where cost efficiency can significantly impact overall profitability.
Moreover, CAC is instrumental in evaluating the long-term sustainability of customer acquisition strategies in an omnichannel framework. High acquisition costs may be sustainable in the short term if the lifetime value (LTV) of customers is high, but if not, they could lead to diminishing returns. Therefore, analyzing CAC helps retailers not only to identify more cost-effective methods for customer acquisition but also to optimize their marketing mix across channels to reduce costs while maintaining or improving customer engagement and conversion rates. This strategic approach enables retailers to adapt and thrive in the evolving retail landscape, where understanding and controlling costs across multiple channels is key to maintaining a competitive edge.
Calculating CAC in an Omnichannel Environment
The calculation of Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) in an omnichannel environment poses unique challenges due to the complexity of customer interactions across multiple channels. To achieve an accurate calculation, it’s crucial to attribute customer acquisitions accurately to the specific channels that influenced or directly led to their conversion. This process typically involves a couple of key methodologies:
- Tracking Multi-Channel Interactions: In an omnichannel setting, a customer might interact with a brand in several ways before making a purchase. For example, they might see an advertisement on social media, read an email newsletter, and visit a physical store before finally making a purchase online. Advanced analytics tools are essential for tracing this multifaceted journey. These tools track and compile data from various channels, helping to map a complete picture of the customer journey. This tracking enables marketers to understand which interactions were most influential in converting browsers into buyers. It’s not just about recognizing the final touchpoint but understanding all the effective touch points along the customer journey that contribute to the decision to purchase.
- Allocation of Costs: After mapping out the customer journey, the next step is the accurate allocation of marketing costs to these various touchpoints. This can be complex, as it involves determining the influence of each interaction in the journey towards conversion. Marketers often use attribution models to assign value to each channel. These models can range from simple (such as last-click attribution, which gives all credit to the final touchpoint before purchase) to more complex (such as multi-touch attribution, which assigns a weighted value to each touchpoint based on its perceived influence on the customer’s decision). By applying these models, retailers can more accurately divide their marketing budget across channels, reflecting the true role and influence of each channel in acquiring new customers.
Effective CAC calculation in an omnichannel environment enables retailers to gauge the efficiency of their marketing efforts more accurately. It highlights which channels are most cost-effective and which may require optimization or re-evaluation in terms of strategy.
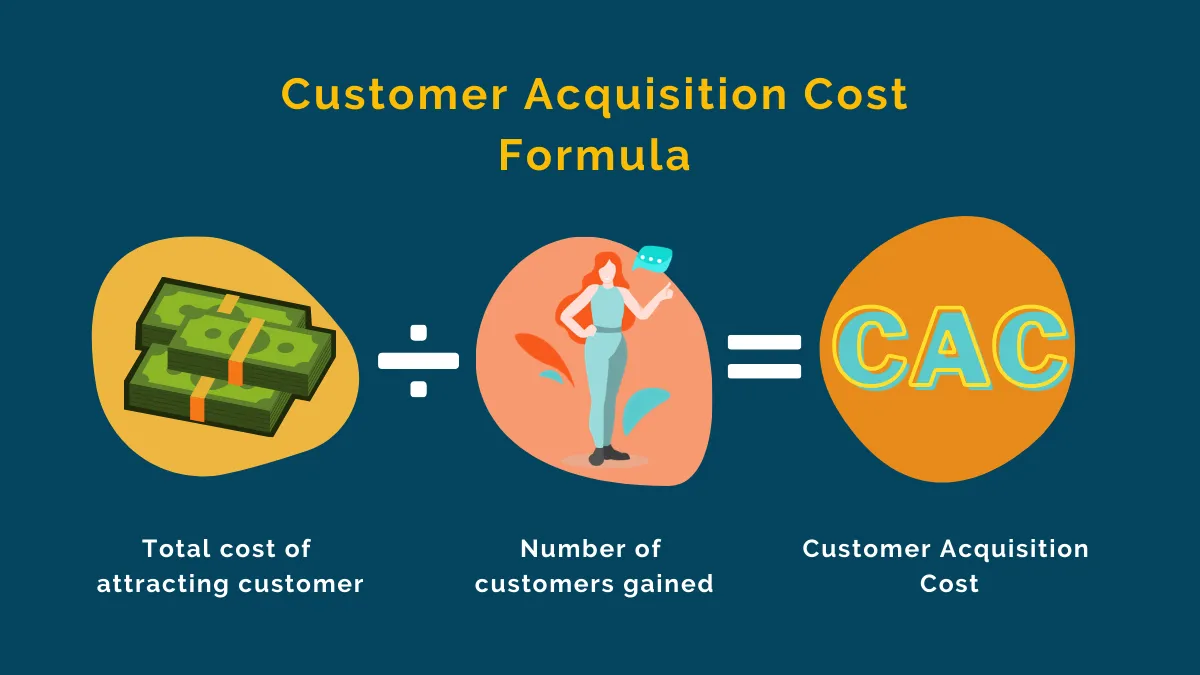
Moreover, this insight allows retailers to refine their marketing approaches continuously, ensuring resources are invested in channels that provide the best returns, enhancing overall marketing ROI and reducing wasteful spending. Through meticulous tracking and smart allocation of costs, retailers can turn the complexity of omnichannel marketing into a strategic advantage, driving more informed decisions and ultimately, more successful outcomes.
Strategies to Optimize CAC in Omnichannel Retail
Optimizing Customer Acquisition Cost in omnichannel retail involves strategic adjustments across various marketing and sales channels to enhance efficiency and effectiveness. Here, we delve deeper into the strategies that can help minimize CAC while maximizing customer engagement and conversion rates:
- Enhanced Channel Integration: The goal of enhanced channel integration is to create a seamless customer journey across all platforms, thereby increasing the likelihood of conversion at lower costs. For instance, by linking online advertisements directly to in-store promotions, retailers can bridge the gap between digital engagement and physical shopping experiences. This integration can encourage customers who engage with a brand online to visit a physical store to complete their purchase, which can lead to higher conversion rates. Additionally, integrating customer service channels so that inquiries handled via one channel (like social media) are seamlessly connected to others (such as in-store support) can enhance customer satisfaction and increase the chances of conversion without additional acquisition costs.
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns: Utilizing advanced data analytics to decipher customer preferences and behaviors allows retailers to craft highly targeted marketing campaigns. By analyzing data from various channels, retailers can identify the most effective messages and promotions for specific customer segments. This precision marketing means that resources are not wasted on broad, ineffective campaigns. Instead, by concentrating on targeted strategies where they are most likely to resonate — whether through personalized email marketing, tailored social media ads, or localized content — retailers can significantly improve conversion rates and, consequently, lower the CAC.
- Leveraging Organic Channels: Organic channels typically require lower ongoing investment compared to paid media and can be highly effective in customer acquisition. Strategies such as search engine optimization (SEO), content marketing, and leveraging social media platforms can attract customers at a lower cost than traditional paid advertising. Additionally, focusing on building a strong brand presence that encourages customer referrals and word-of-mouth can also significantly reduce CAC. For instance, creating shareable content or engaging directly with customers on social platforms can turn satisfied customers into brand advocates, who then help spread the word organically.
- Customer Retention Focus: Reducing churn by improving customer satisfaction is a strategic way to lower CAC indirectly. When customers are satisfied and engaged, they are more likely to repeat purchases and less likely to switch to competitors. Improving customer retention rates can be achieved through loyalty programs, exceptional customer service, personalized experiences, and regular engagement. By investing in customer retention strategies, the lifespan value of each customer increases, thereby spreading the acquisition cost over a longer period and more transactions, which effectively reduces the CAC.
By implementing these strategies, retailers can not only reduce their CAC but also enhance customer loyalty and brand strength in a competitive omnichannel marketplace. These efforts lead to more sustainable growth and a better return on investment from marketing expenditures.
The Impact of CAC on Omnichannel Success
CAC is one of the most important omnichannel retail KPIs because it directly impacts the profitability and scalability of marketing efforts. By regularly assessing CAC, retailers can gauge the financial efficiency of their strategies to attract new customers across various channels. This metric isn’t just a number; it’s a reflection of how well a retailer utilizes its budget and whether the allocation of resources aligns with effective customer acquisition.
A high CAC typically signals that a retailer’s marketing efforts might be costing more than they should, which can eat into profit margins and limit growth potential. This situation can arise from several factors, such as inefficient use of advertising funds, poor conversion rates, or targeting the wrong customer segments. High CAC can act as a red flag for businesses, prompting them to reevaluate their marketing strategies. It might indicate the need for optimization in areas like ad spending, channel selection, or campaign targeting. For instance, if a particular advertising channel consistently shows a high CAC, it may be beneficial to either improve the campaigns on that channel or reallocate the budget towards more effective channels.

On the other hand, a low CAC indicates that a retailer is acquiring customers cost-effectively, which is a sign of efficient marketing strategy and execution. This situation offers numerous advantages, such as increased profitability and the opportunity for scalability. Retailers with a low CAC have the potential to reinvest the savings from their acquisition costs into other areas of their business, such as enhancing customer service, expanding into new markets, or further developing omnichannel capabilities. This reinvestment can help improve the overall customer experience, foster customer loyalty, and create a more robust omnichannel presence.
Moreover, maintaining a low CAC in an omnichannel environment suggests that a retailer is successfully leveraging the strengths of various channels to complement each other, enhancing the overall efficiency of marketing efforts. For example, a retailer might use data gathered from online interactions to refine targeting in offline marketing campaigns, or vice versa, leading to more personalized and effective customer interactions that drive conversions without excessive spending.
Ultimately, the impact of CAC on omnichannel success is profound. It not only measures the cost effectiveness of customer acquisition strategies but also serves as a critical lever in managing profitability and growth. Retailers that excel in optimizing their CAC can achieve a competitive advantage by maximizing the return on their marketing investments and continuously enhancing their omnichannel strategies to meet evolving consumer demands.
Customer Retention Rates
Customer retention rates are crucial amongst omnichannel retail KPIs, serving as a barometer for measuring the success of a retailer’s ability to keep customers engaged and committed over time. They not only reflect the health of customer relationships but also directly impact the financial stability and growth potential of a retail business.

In an environment where multiple channels interact to provide a cohesive customer experience, understanding and optimizing these rates becomes essential for sustainable growth and profitability. By focusing on personalized experiences, consistency across channels, active engagement, and responsiveness to customer feedback, retailers can significantly enhance their customer retention rates and, by extension, their omnichannel success.
Importance of Customer Retention in Omnichannel Retail
Customer retention rates serve as one of the critical omnichannel retail KPIs regarding a brand’s effectiveness in sustaining and enriching its relationships with customers across multiple channels of interaction. These rates are a significant measure, often directly correlating with key aspects of business health such as customer satisfaction, loyalty, and the overall value that customers bring over their lifetime with the brand. High retention rates typically suggest that a business is successful in meeting or exceeding customer expectations in a consistent manner, which in turn fosters a strong sense of brand loyalty.
The strategic focus on customer retention, as opposed to solely acquiring new customers, involves deepening existing relationships and ensuring ongoing satisfaction and engagement. This approach is generally more cost-effective than acquisition strategies because it leverages existing relationships rather than spending resources to establish new ones. Retained customers are more likely to make repeated purchases and often at higher values, which boosts the overall profitability and stability of the business.
Moreover, a robust customer retention strategy supports the development of a loyal customer base that acts as an advocate for the brand. Satisfied, loyal customers are more inclined to share their positive experiences with others, effectively driving new customer acquisitions through powerful, organic channels such as word-of-mouth recommendations and social proof. This organic advocacy is invaluable as it comes with a high level of trust and credibility, often influencing new customers in a more profound and lasting way than traditional advertising methods.
Thus, high customer retention rates not only ensure a steady and predictable revenue stream but also play a crucial role in the organic growth of the business. They reflect a harmonious balance between meeting customer needs and successfully managing customer relationships across all channels, which is essential for long-term success in today’s competitive retail landscape.
Calculating Customer Retention Rates
Effectively measuring customer retention rates in an omnichannel environment involves a nuanced approach to data collection and analysis, as it requires a comprehensive understanding of customer interactions across various channels. Retailers must track and analyze not only the number of repeat purchases but also the ongoing engagement activities of customers over a designated period. This is compared against the total number of active customers at the beginning of the period to calculate retention rates accurately.
The inherent challenge of this measurement in an omnichannel setting is the precise attribution of customer retention to specific channels and touchpoints. This complexity arises because modern consumers often engage with a brand through multiple channels before making a repeat purchase.
For example, a customer might initially discover a product through an online ad, research it on a mobile app, and finally purchase it in a physical store. Each of these touchpoints contributes to retaining that customer, yet attributing retention to just one touchpoint would provide a skewed view of what is truly driving customer loyalty.

To address this challenge, retailers require sophisticated tracking systems capable of capturing and integrating data across all platforms. This includes CRM systems, marketing automation tools, and advanced analytics platforms that can track customer behaviors and preferences in real time. With these systems, it becomes possible to create a unified view of the customer journey, tracing all the interactions a customer has with a brand from initial contact through to repeat purchases.
For example, if a customer browses products on a mobile app, this interaction should be recorded and linked to their customer profile. If the same customer later makes a purchase online, this too is tracked, and the data is integrated to show a continuous timeline of engagement. Finally, if the customer chooses to BOPIS, this interaction is also logged, providing a full spectrum view of how omnichannel strategies are contributing to customer retention.
By recognizing and recording each of these interactions, retailers can gain a more detailed understanding of what influences customer loyalty and retention. This depth of insight allows them to refine their omnichannel strategies, ensuring they deliver personalized and cohesive experiences that encourage customers to remain engaged over time. Thus, a robust system for tracking and analyzing customer data across multiple touchpoints is crucial for measuring and enhancing customer retention rates in omnichannel retail.
Strategies to Improve Customer Retention Rates
Improving customer retention rates in an omnichannel retail environment requires a multi-faceted approach that focuses on creating personalized, consistent, and engaging customer experiences across all channels. Here’s a deeper exploration of the strategies that can significantly enhance customer retention:
- Personalized Customer Experiences: Enhancing customer retention in omnichannel retail starts with personalized experiences tailored to the customer’s preferences and previous interactions with the brand. Utilizing data analytics to understand customer behavior across channels allows retailers to deliver targeted messages, recommendations, and offers that resonate with individual customers. Personalization can manifest in various forms, from personalized emails and customized shopping recommendations to tailored in-store experiences facilitated by mobile apps or loyalty programs.
- Consistent Quality of Service Across Channels: Consistency is key in omnichannel retail. Customers expect a seamless experience, whether they are shopping online, via mobile, or in a physical store. Ensuring that service quality, brand messaging, and customer support are consistent across all platforms can significantly enhance customer satisfaction and retention. For example, a customer’s ability to return an online purchase in-store without hassle, or to receive customer support through their preferred channel at any time, can greatly influence their decision to remain with a brand.
- Engagement and Community Building: Building a community around a brand can foster a sense of belonging among customers, which is crucial for retention. Engagement can be driven through social media, exclusive members-only events, or loyalty programs that offer more than just transactional rewards. For example, offering special access to new products, or creating a platform for customers to share experiences, can strengthen the emotional connection customers feel towards the brand.
- Regular Feedback and Responsive Adjustments: Continuously gathering customer feedback across all channels and being responsive to their needs and preferences is vital for improving retention rates. This feedback should inform business decisions and prompt adjustments to products, services, or experiences. Implementing changes based on customer feedback not only improves the customer experience but also shows customers that their opinions are valued, enhancing their loyalty to the brand.
By implementing these strategies, retailers can create a holistic and attractive customer experience that spans various channels, thus significantly improving their customer retention rates. Each strategy not only strengthens the individual touchpoints but also ensures that the entire omnichannel system works effectively to keep customers returning.
Impact of High Customer Retention on Omnichannel Success
High customer retention rates are vital in omnichannel retail, serving as a robust indicator of a brand’s success across various customer interaction points. When customers return repeatedly, it demonstrates that the brand consistently meets or surpasses their expectations, whether they engage through physical stores, online platforms, or mobile apps. This consistency in fulfilling customer needs and preferences across all channels is critical in building trust and loyalty.
High retention rates contribute to lower marketing costs. It is generally more cost-effective to retain existing customers than to acquire new ones, as the former does not require the extensive use of costly acquisition tactics such as paid advertising or promotional discounts. Instead, retailers can focus on more cost-effective engagement and retention strategies like email marketing, loyalty programs, and customer appreciation events, which offer a better return on investment. This shift in focus from acquisition to retention can significantly decrease the overall marketing spend while maintaining revenue growth.

With reduced marketing expenses, overall profitability improves. Retailers can reallocate resources saved from acquisition to other areas such as product development, service enhancements, or even expansion into new markets. Furthermore, retained customers typically have better conversion rates; they are easier to sell to because they already understand and appreciate the brand value. This ease of conversion often results in a more streamlined sales process, reducing operational costs associated with sales efforts and enhancing the efficiency of the business operations.
A well-established customer base provides fertile ground for organic growth strategies such as upselling and cross-selling. These strategies are more effective with customers who have a proven interest in the brand’s offerings and a history of repeated purchases. Additionally, loyal customers often provide valuable feedback that can be instrumental in refining existing products and services or creating new ones. This continual input from loyal customers acts as a compass guiding the brand towards market trends and customer desires, fostering innovation that can keep the brand competitive and relevant. High retention rates also enable retailers to harness their customer base for insights that drive innovation and adaptation. Understanding why customers stay loyal and what they value most about the brand can help in tailoring offerings more precisely to market demands, ultimately leading to better product offerings and service improvements.
In short, high customer retention rates are more than just a metric amongst omnichannel retail KPIs; they are a comprehensive reflection of a brand’s ability to operate successfully across multiple channels in an integrated manner. This success not only boosts immediate financial performance but also establishes a foundation for sustainable growth and innovation, crucial for long-term competitiveness in the dynamic landscape of omnichannel retail.
Average Order Value (AOV)
Average Order Value (AOV) stands out as one of the critical omnichannel retail KPIs that offers insights into consumer purchasing behavior across multiple sales channels. AOV measures the average total of every order placed with a retailer over a defined period, providing key data points that help to assess the effectiveness of marketing strategies and the overall customer spending patterns. This metric is particularly valuable in an omnichannel strategy, as it helps retailers understand how different channels contribute to sales and customer engagement.
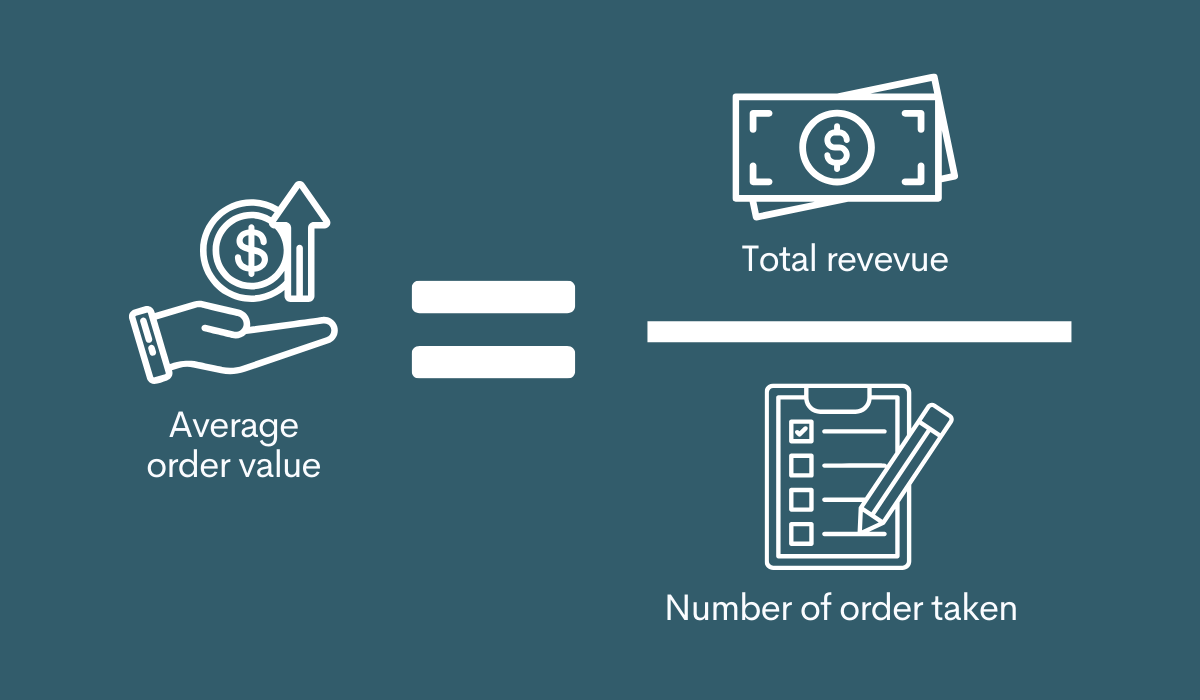
Average Order Value is calculated by dividing the total revenue by the number of orders over a specific time frame. In an omnichannel context, it’s important to segment AOV by each channel — online, in-store, mobile app, etc. — to pinpoint how each channel performs and influences shopper spending. This detailed analysis helps retailers tailor their marketing and sales strategies to boost AOV across all channels, enhancing the overall profitability of the business.
The Significance of AOV for Omnichannel Retailers
Average Order Value (AOV) is instrumental in assessing the effectiveness of various pricing strategies and promotional efforts across different sales channels. By closely analyzing changes in AOV in response to different pricing tactics and promotional activities, retailers can discern which strategies encourage higher spending.
For instance, a promotional campaign that requires a minimum spend to unlock a discount may lead to an increase in AOV. This suggests that customers are willing to add more items to their carts to meet the threshold for the discount. Understanding this behavior allows retailers to fine-tune their promotions. For example, they might increase the minimum spend threshold slightly to test if the AOV rises correspondingly, or they could apply similar promotional strategies to other product lines or channels and monitor the impact on AOV. This kind of strategic experimentation helps identify the most effective ways to boost revenue and can be a guide for deploying successful promotions across multiple retail channels.
Understanding AOV also plays a crucial role in customer segmentation and targeting. By analyzing AOV, retailers can classify their customers into segments based on their purchasing power and buying behavior. This segmentation enables more precise marketing strategies that cater to the distinct needs and preferences of each group.
For high-AOV customers, retailers might tailor their approach by offering premium products, exclusive early-access promotions, or personalized services that cater to their propensity for higher spending. Conversely, for customers with a lower AOV, retailers might focus on different incentives that encourage a higher spend per transaction, such as bundle deals, volume discounts, or loyalty points that accrue benefits over time. This targeted approach not only enhances the customer experience by aligning it with individual expectations and value perceptions but also increases the effectiveness of marketing spend by focusing efforts where they are most likely to increase AOV and overall profitability.

Further, AOV provides valuable insights into which products or categories are contributing to higher order values. This information is critical for inventory management and marketing focus. If certain products consistently contribute to a higher AOV, a retailer might decide to increase stock levels of these items or highlight them in marketing campaigns. Additionally, understanding product performance in terms of AOV can guide decisions regarding product bundling or cross-selling strategies.
For example, if high-end electronics have a high AOV, pairing them with complementary accessories in a bundled offer could further increase the AOV. Retailers can also use this data to optimize the layout of both their physical stores and online platforms, positioning high-value items in prominent locations to maximize visibility and accessibility. This strategic placement can significantly influence buying patterns, encouraging customers to purchase more or higher-value items during their shopping journey.
By leveraging AOV in these comprehensive ways—through strategic pricing and promotions, targeted customer segmentation, and optimized product mix—retailers can significantly enhance their sales effectiveness and overall financial performance in an omnichannel retail environment. Each strategy not only aims to increase AOV but also to create a more personalized and satisfying shopping experience, which in turn can drive loyalty and repeat business, key components of long-term retail success.
Strategies to Increase AOV in Omnichannel Retail
- Cross-Selling and Upselling: Effective cross-selling and upselling strategies can significantly boost AOV by encouraging customers to add additional items or upgrade to more expensive options. For instance, showing related products or accessories at checkout online, or training in-store staff to suggest complementary products, can enhance the customer’s shopping experience and increase the order value.
- Loyalty Programs: Implementing or enhancing loyalty programs to reward higher spending can also drive up AOV. These programs can offer points, discounts, or special services that incentivize higher spending, such as free shipping or a free gift with a minimum purchase amount.
- Tiered Pricing Strategies: Using tiered pricing can encourage customers to buy more to achieve a better deal, effectively increasing the AOV. For example, offering a small discount on buying two items and a larger discount for three can encourage customers to purchase more items at once.
- Technology-Driven Personalization: Leveraging data analytics and AI to offer personalized product recommendations based on customer browsing and purchase history can significantly impact AOV. By presenting customers with products that align with their interests and previous shopping behavior, retailers can increase the likelihood of a larger basket size.
In-Depth Analysis of AOV’s Impact on Omnichannel Success
The significance of Average Order Value (AOV) in shaping the success of omnichannel retail strategies is profound. A higher AOV not only reflects the economic value of transactions but also suggests that customers perceive high value in the offerings, which is crucial for sustaining long-term business growth. Here’s a deeper exploration into how AOV impacts various facets of omnichannel retailing:
- Indication of Customer Value Perception: A higher AOV typically indicates that customers perceive the products or the shopping experience as valuable enough to warrant higher spending. This is a direct reflection of customer satisfaction and the effectiveness of a retailer’s marketing and pricing strategies. In an omnichannel context, where customers interact with a brand through multiple touchpoints, a consistent or increasing AOV across these channels suggests that the brand is successfully delivering value at every point of interaction. For example, if both the online and physical store channels show a growing AOV, it implies that the integration of these channels is effectively enhancing the customer experience, leading customers to spend more.
- Strategic Decision Making: Monitoring AOV helps omnichannel retailers make informed decisions about product placement, marketing strategies, and customer engagement tactics. By analyzing AOV trends, retailers can identify which channels, products, or promotional strategies are driving higher value sales. This insight allows them to allocate resources more efficiently and focus on strategies that are likely to boost AOV further. For instance, if data shows that online promotions significantly increase AOV, retailers might invest more in digital advertising and promotional campaigns to capitalize on this trend.
- Resource Allocation and Inventory Management: Understanding AOV dynamics helps in better inventory management and resource allocation. Products that consistently contribute to a higher AOV can be stocked more aggressively, ensuring that demand is met without overstocking less popular items. Similarly, insights from AOV can guide retailers in optimizing their supply chain and logistics for maximum efficiency, ensuring that high-value products are always available across all channels without significant holding costs.
- Customer Loyalty and Retention: Efforts to increase AOV often go hand-in-hand with improving the overall customer experience, which in turn can enhance customer loyalty and retention. For instance, initiatives aimed at personalizing the shopping experience, such as tailored product recommendations or loyalty rewards, not only encourage higher spending per transaction but also enhance the overall customer relationship with the brand. Satisfied customers are more likely to return, and a focus on increasing AOV can indirectly boost retention rates by elevating the perceived value and quality of the service provided.
- Enhanced Profitability: Ultimately, the goal of increasing AOV is to enhance profitability. Higher order values mean more revenue from each transaction, which can significantly improve the financial health of a business. In an omnichannel setup, where customer acquisition can be costly and complex due to the need to maintain multiple channels, maximizing the revenue from each customer interaction becomes crucial. A higher AOV reduces the pressure on acquiring large numbers of customers by increasing the revenue generated from existing customers, thus allowing for more sustainable growth and profitability.
In summary, AOV is a critical metric in omnichannel retail KPIs, influencing not just immediate sales figures but also broader strategic decisions that dictate resource allocation, customer relationship management, and long-term business sustainability. By focusing on strategies to enhance AOV, omnichannel retailers can ensure they not only meet but exceed customer expectations, driving both revenue and loyalty in a competitive retail landscape.
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
In the landscape of omnichannel retail, Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is one of the most important omnichannel retail KPIs that provides deep insights into the long-term value of customers across multiple channels. CLV measures the total revenue a business can reasonably expect from a single customer account throughout the duration of their relationship with the company. This metric is especially critical for omnichannel retailers because it encapsulates the results of customer interactions that span digital and physical touchpoints, offering a holistic view of customer profitability over time.

CLV is integral for understanding how different customer segments contribute to the overall financial health of a retail business. In omnichannel retail, where customers engage through various channels — from online shopping to in-store purchases — the ability to track and analyze CLV across these channels helps retailers allocate marketing resources more effectively and tailor customer experiences to maximize long-term revenue. The essence of CLV in an omnichannel strategy lies in its ability to highlight the value of creating cohesive customer experiences that encourage repeat business and increase the duration of the customer relationship.
Calculating CLV in Omnichannel Environments
Calculating Customer Lifetime Value in an omnichannel setting is a critical process that integrates data across multiple customer touchpoints to predict the total value a customer will bring to a business over the entirety of their relationship. This calculation not only reflects the financial contribution of each customer but also guides strategic decision-making across the organization. Here’s a more detailed exploration of each step involved in calculating CLV in an omnichannel context:
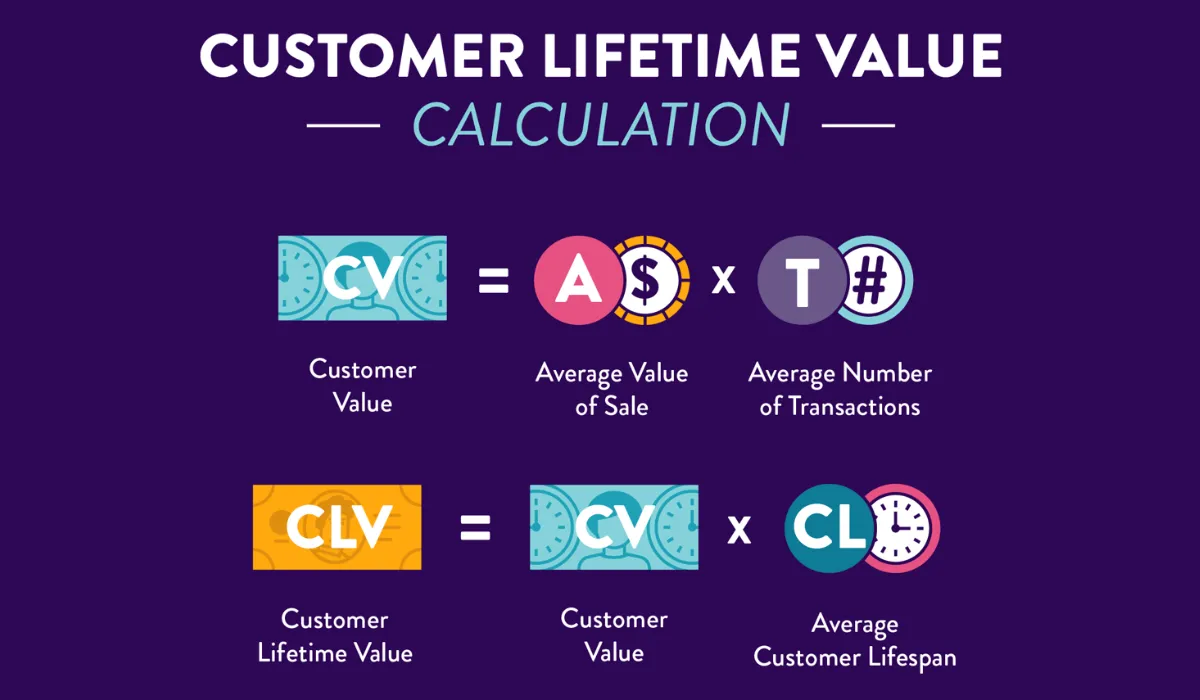
- Average Order Value (AOV): As mentioned above, to determine the Average Order Value, divide the total revenue generated from all customer purchases by the number of purchases within a specific period. This metric should be calculated separately for each channel — online, in-store, via mobile apps, etc. — to understand channel-specific spending behaviors. For omnichannel retailers, integrating data from various channels to get a unified view of AOV is crucial. For example, if a customer typically spends more in-store than online, this insight can inform personalized marketing strategies that encourage more frequent or higher-value online purchases.
- Purchase Frequency: Purchase Frequency measures how often an average customer makes a purchase within a given time frame. This calculation helps retailers understand customer engagement levels across different channels. Tracking frequency requires robust data analytics to accurately attribute purchases to individual customers across multiple platforms. Higher purchase frequency indicates stronger customer engagement, which is a positive sign for overall business health.
- Customer Value: By multiplying the Average Purchase Value by Purchase Frequency, retailers can estimate the total value a customer typically contributes within a defined period. This Customer Value is a snapshot of the immediate worth of the customer to the business, not taking into account the entire projected lifecycle. For omnichannel retailers, understanding customer value on a per-channel basis can reveal which channels are most valuable and deserve more strategic focus.
- Average Customer Lifespan: Estimating the Average Customer Lifespan involves analyzing historical data to determine how long customers typically continue to make purchases from the brand. This step is crucial and can vary significantly based on the business model, industry, and customer engagement strategies. In an omnichannel environment, it’s important to consider how different customer touchpoints contribute to retaining customers over time, potentially extending their lifespan with the brand.
- CLV: Finally, multiplying the Customer Value by the Average Customer Lifespan gives the Customer Lifetime Value. This figure represents the total revenue a retailer can expect from a typical customer throughout their relationship with the brand. In an omnichannel context, calculating CLV helps retailers gauge the long-term value of investments in customer relationship management and marketing across multiple channels.
Understanding CLV in an omnichannel environment allows retailers to refine their strategies for customer engagement and retention, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to maximize long-term returns. This metric not only helps in identifying the most profitable customer segments but also in tailoring communications, promotions, and product offerings to meet the unique needs of different customer groups, enhancing their experiences and increasing their lifetime value.
Impact of CLV on Omnichannel Success
Understanding and effectively monitoring Customer Lifetime Value as an omnichannel retail KPIs plays a pivotal role in shaping a retailer’s strategic direction. Here’s a deeper dive into how a robust CLV influences omnichannel success and supports sustainable business growth:
- Indicator of Customer Retention and Engagement: High CLV is a direct indicator of successful customer retention and engagement strategies. It suggests that customers consistently receive value from the brand’s offerings, which motivates them to maintain their relationship with the brand over time. In an omnichannel context, this implies that the integration of services and channels — from online platforms to physical stores and mobile apps — is effectively meeting or exceeding customer expectations. Customers who experience seamless interactions across multiple channels are more likely to increase their engagement, leading to higher transaction frequencies and, subsequently, greater lifetime value.
- Reduction in Acquisition Costs: By focusing on increasing the CLV, retailers can reduce their dependence on new customer acquisition strategies, which are often more costly and yield lower immediate returns compared to strategies aimed at retaining existing customers. High CLV reflects a strong base of loyal customers who contribute to a stable and predictable revenue stream. This stability allows retailers to allocate resources more effectively, not only sustaining the business with recurrent revenues but also investing in innovations and improvements that further enhance customer satisfaction and retention.
- Enhanced Profitability Through Up-Selling and Cross-Selling: A customer with a high CLV is generally more receptive to up-selling and cross-selling opportunities because of their established trust and familiarity with the brand. In an omnichannel setup, where customer data from various channels can be integrated and analyzed, personalized marketing becomes more precise and effective. Retailers can tailor their offers based on the specific buying patterns and preferences of individual customers, encouraging them to explore higher-value products or additional services that align with their interests. This strategic approach not only boosts the AOV but also reinforces the customer’s relationship with the brand, leading to sustained increases in CLV.
- Strategic Allocation of Marketing Resources:With clear insights from CLV metrics, retailers can more strategically allocate their marketing efforts and budgets across channels. Understanding which channels generate higher CLV allows businesses to optimize their spending, focusing more on these high-return channels while refining or reducing expenditure in less profitable areas. This targeted allocation helps in maximizing overall marketing ROI and ensures that each channel is leveraged to its full potential in contributing to customer value and retention.
- Long-Term Business Sustainability: Retailers that excel in maintaining high CLV are better positioned for long-term sustainability. They can rely on a loyal customer base that not only supports the business through repeated purchases but also acts as a brand advocate, attracting new customers through word-of-mouth. This organic growth is invaluable as it comes with high trust and lower cost. Furthermore, high CLV allows retailers to plan with greater confidence, investing in long-term growth initiatives such as technological advancements, market expansion, and product development with the assurance that their customer base will support these endeavors over time.
In essence, CLV is more than just a measure of customer value; it is a comprehensive indicator of how well a retailer is performing in the omnichannel landscape and a critical driver of strategic decision-making. By prioritizing the improvement of CLV, retailers not only enhance their customer relationships but also secure a robust foundation for future growth and success in the competitive retail market.
Customer Experience KPIs
Understanding customer experience is paramount for omnichannel retailers who aim to integrate and optimize interactions across multiple touchpoints. To effectively measure and enhance the customer experience, several omnichannel retail KPIs are utilized, each offering unique insights into different facets of the customer journey. This section will explore the critical customer experience KPIs, including Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), Customer Effort Score (CES), Return Rate, and Cart Abandonment Rate, and how they collectively inform omnichannel strategies.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) serves as a critical gauge of customer loyalty and brand advocacy in omnichannel retail. This straightforward metric is profoundly insightful, reflecting not just customer satisfaction but their willingness to act as brand ambassadors. Here’s a deeper exploration into how NPS functions and its strategic value in an omnichannel setting.
Calculating and Interpreting NPS
NPS is derived from customer responses to a singular, pivotal question about their likelihood to recommend the brand to others, scored on a scale from 0 to 10. Customers responding with a score of 9 or 10 are labeled as Promoters — these are highly satisfied customers who are likely to create the most value, not only through repeat business but also by attracting new customers through word-of-mouth. Those who score 7 or 8 are Passives — satisfied but unenthusiastic customers who are vulnerable to competitive offerings. Scores from 0 to 6 categorize Detractors, who are dissatisfied customers potentially detrimental to the brand through negative word-of-mouth.
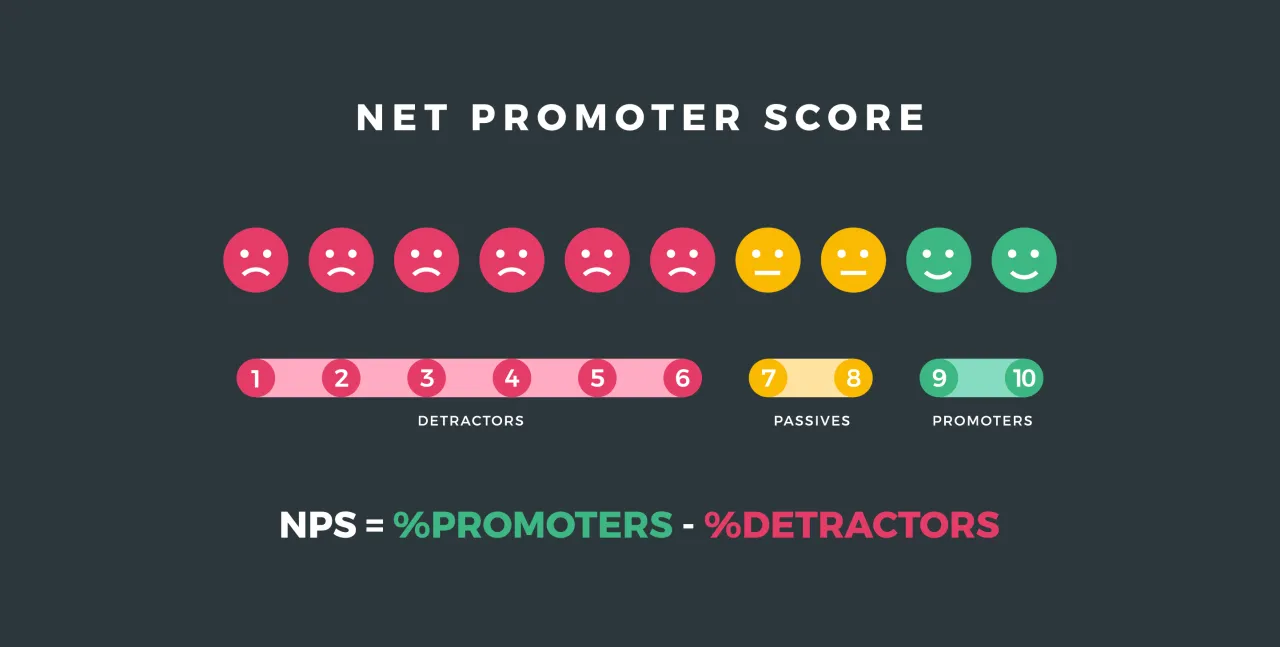
The NPS is calculated by subtracting the percentage of Detractors from the percentage of Promoters. A positive NPS (higher than zero) is generally favorable and indicates that a brand has more Promoters than Detractors. A very high NPS is a strong indicator of customer loyalty and product or service excellence.
Strategic Uses of NPS
NPS is not just a measure; it’s a tool for continuous improvement. High NPS scores across channels can reinforce a retailer’s confidence in their customer service policies and product quality, while low scores provide a clear signal that changes are needed. Omnichannel retailers can use NPS data to:
- Enhance Customer Service: Tailor training programs to address specific weaknesses in customer interactions that may be causing low NPS scores.
- Refine Product Offerings: Adjust product lines and services based on the feedback from Detractors and Passives to convert them into Promoters.
- Optimize User Experience: Improve website interfaces, mobile app usability, and in-store technology to create seamless shopping experiences that could elevate NPS.
Long-term Benefits of High NPS
In an omnichannel approach, understanding the NPS across various channels helps pinpoint strengths and weaknesses in different areas of customer interaction. For instance, an omnichannel retailer might discover that while their online platform achieves an exceptionally high NPS due to ease of use and excellent customer support, their in-store experience lags due to poor service or long wait times. This discrepancy can guide targeted improvements in customer service training, store layout adjustments, or the implementation of technology to streamline in-store processes.
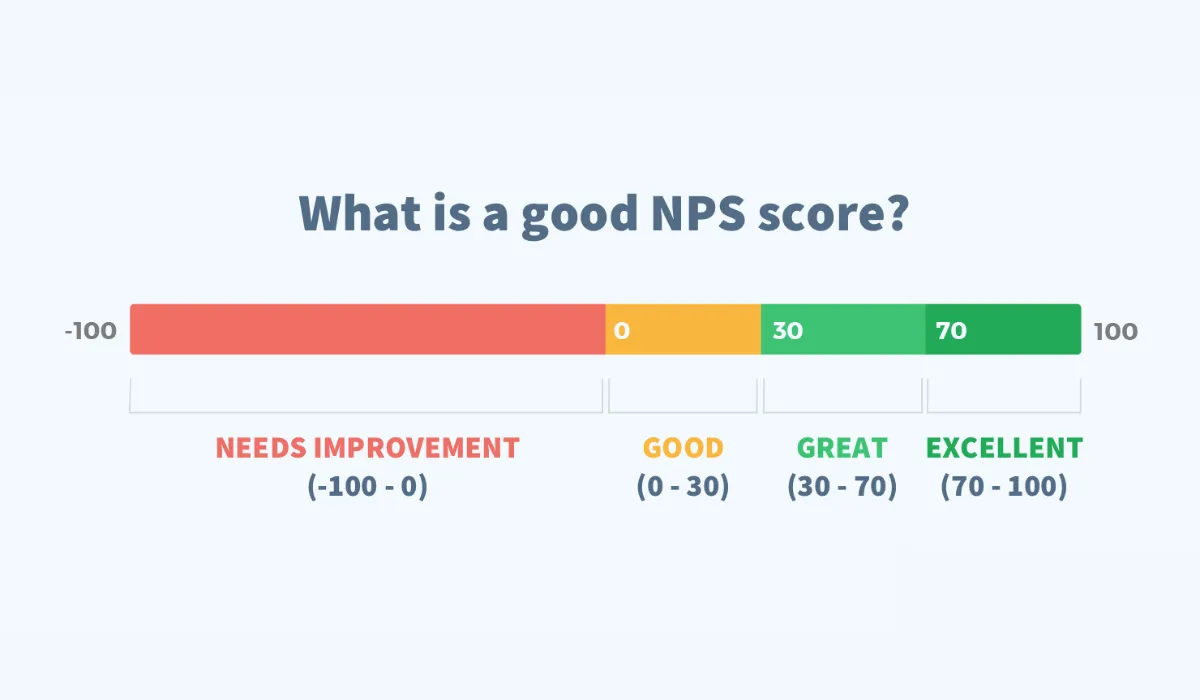
Sustaining a high NPS can lead to significant long-term benefits for omnichannel retailers. These include increased customer retention, lower marketing costs due to organic growth through recommendations, and higher overall profitability. Furthermore, a strong NPS indicates successful customer engagement strategies that can become a key competitive advantage in the retail market.
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
The Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) is a vital KPI for measuring the immediate satisfaction levels of customers within an omnichannel retail environment. As a direct reflection of how customers perceive their latest interaction or transaction, CSAT provides actionable insights that can be used to optimize customer experiences across multiple platforms and touchpoints.
Calculation and Utilization of CSAT
CSAT is calculated by soliciting customer feedback through surveys typically administered after a purchase or interaction. The survey usually asks a straightforward question such as, “How satisfied were you with your experience or purchase?” with customers providing ratings on a scale (often from 1 to 5 or 1 to 10). The responses are then converted into a percentage of customers who answered with the top-tier ratings, providing a clear measure of satisfaction levels.

To truly harness the power of CSAT in an omnichannel context, retailers should gather and analyze these scores separately for each channel—be it online, in-store, or via mobile apps. This segmented data allows retailers to identify which channels are delivering the best customer experiences and which may require immediate intervention to address specific issues.
Strategic Implications of CSAT in Omnichannel Retail
High CSAT scores generally indicate that customers are pleased with their shopping experiences and the products or services provided. In contrast, lower scores can alert retailers to problems in specific areas.
For example, low CSAT scores in an online store could indicate issues with website navigation, checkout processes, or even the quality of online customer support. Understanding these nuances allows omnichannel retailers to:
- Pinpoint Specific Areas for Improvement: Low CSAT scores can direct attention to aspects of the service or product experience that are not meeting customer expectations. Retailers can then focus on refining these areas, whether it involves streamlining a cumbersome checkout process, enhancing product quality, or improving post-purchase customer support.
- Customize Training and Development: Insights from CSAT can inform staff training programs, especially for in-store employees, to enhance direct customer interactions and ensure consistency across all physical locations.
- Adjust Product and Service Offerings: CSAT feedback can lead to adjustments in product ranges or service offerings to better align with customer expectations and demands.
Impact of CSAT
In the competitive landscape of omnichannel retail, CSAT is directly linked to customer retention and loyalty. Satisfied customers are more likely to return, make repeat purchases, and become brand advocates. Each positive experience reinforces their loyalty to the brand, which in turn contributes to a sustainable business model through repeat business and reduced customer acquisition costs.

While CSAT provides immediate insights into customer satisfaction, it is most powerful when combined with other omnichannel retail KPIs such as NPS and CES. Together, these metrics offer a comprehensive view of customer experience, from satisfaction with specific interactions (CSAT) to overall loyalty and advocacy (NPS) and the ease of interactions (CES). This integrated approach enables omnichannel retailers to develop a holistic strategy that not only addresses short-term satisfaction but also builds long-term customer relationships.
By strategically leveraging CSAT data, omnichannel retailers can make informed decisions that enhance the customer experience across all channels, driving higher levels of satisfaction and fostering a loyal customer base. The ability to quickly respond to customer feedback and make necessary adjustments ensures that the brand remains responsive and competitive in a rapidly evolving retail landscape.
Return Rate
The Return Rate is a pivotal omnichannel retail KPIs to monitor and manage, as it provides crucial insights into the reasons behind product returns and helps identify opportunities for improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiencies. Here’s an in-depth exploration of the Return Rate, its implications, and strategies for management in an omnichannel retail context.
Understanding Return Rate
Return Rate is calculated by dividing the number of returned items by the total number of items sold, typically expressed as a percentage. This metric is essential for assessing the health of product offerings and the accuracy of product descriptions across various sales channels. In an omnichannel setting, where customers may interact with products differently (e.g., seeing an item in-store vs. viewing it online), discrepancies in how products are presented can lead to higher return rates.
A high Return Rate can be symptomatic of several underlying issues:
- Product Quality Concerns: Frequent returns might indicate problems with product durability or functionality, suggesting a need for quality improvements or better quality control processes.
- Inaccurate or Misleading Product Information: If product descriptions and images are not consistent across channels or fail to accurately represent the product, customers may feel misled, leading to dissatisfaction and returns.
- Customer Expectations Not Met: Returns can also signal a mismatch between what customers expect based on the marketing materials and what the product actually offers.
By examining return rates specifically for each channel—online, in-store, mobile app, etc. — retailers can pinpoint where customers may be encountering issues.
For instance, higher return rates from online purchases could suggest that product images or descriptions may not be clear or detailed enough, causing a gap between customer expectations and the actual product. Conversely, returns in physical stores might highlight issues with the in-store experience or sales staff interactions.
Strategies to Reduce Return Rates
Minimizing the return rate involves several strategic actions that can significantly enhance customer satisfaction and reduce operational costs:
- Enhance Product Information Accuracy: Ensuring that all product information is consistent and thorough across all channels can help manage customer expectations more effectively. This includes high-quality images, detailed descriptions, and accurate sizing information for items like clothing or furniture.
- Improve Quality Control: Strengthening quality control processes to ensure that products meet the advertised standards can reduce returns due to quality issues.
- Customer Feedback Integration: Regularly collecting and analyzing customer feedback related to returns can provide insights into why returns are happening and how product offerings or descriptions can be improved.
- Flexible and Clear Return Policies: Clearly communicating return policies and making the return process as easy as possible can enhance customer satisfaction, even in situations where a return is necessary.
If you want to better your returns management, consider implementing advanced analytics and AI. It can help predict potential return patterns and identify products that might have higher return risks before they become a significant issue. Additionally, technology can streamline the returns process, making it more efficient and less costly by automating aspects like return label generation and refunds processing.
By meticulously managing and reducing the Return Rate, omnichannel retailers can not only enhance customer satisfaction but also improve their overall operational efficiency and product strategy. This focus ensures that products meet customer expectations and are presented accurately across all channels, ultimately contributing to a more successful omnichannel strategy and healthier bottom-line performance.
Cart Abandonment Rate
The Cart Abandonment Rate is a crucial omnichannel retail KPIs, reflecting the percentage of shopping carts that are initiated but not completed with a purchase. This metric is particularly important in eCommerce and can provide valuable insights into the online purchasing process and customer behavior. Below is a detailed exploration of Cart Abandonment Rate, its implications for omnichannel retail, and effective strategies to mitigate it.
Understanding Cart Abandonment Rate
The Cart Abandonment Rate is calculated by dividing the number of completed purchases by the number of shopping carts created, subtracting this from one, and then multiplying by 100 to get a percentage. This rate is indicative of how well an eCommerce platform facilitates the journey from interest to purchase. A high abandonment rate often points to friction within the checkout process that discourages customers from completing their transactions.
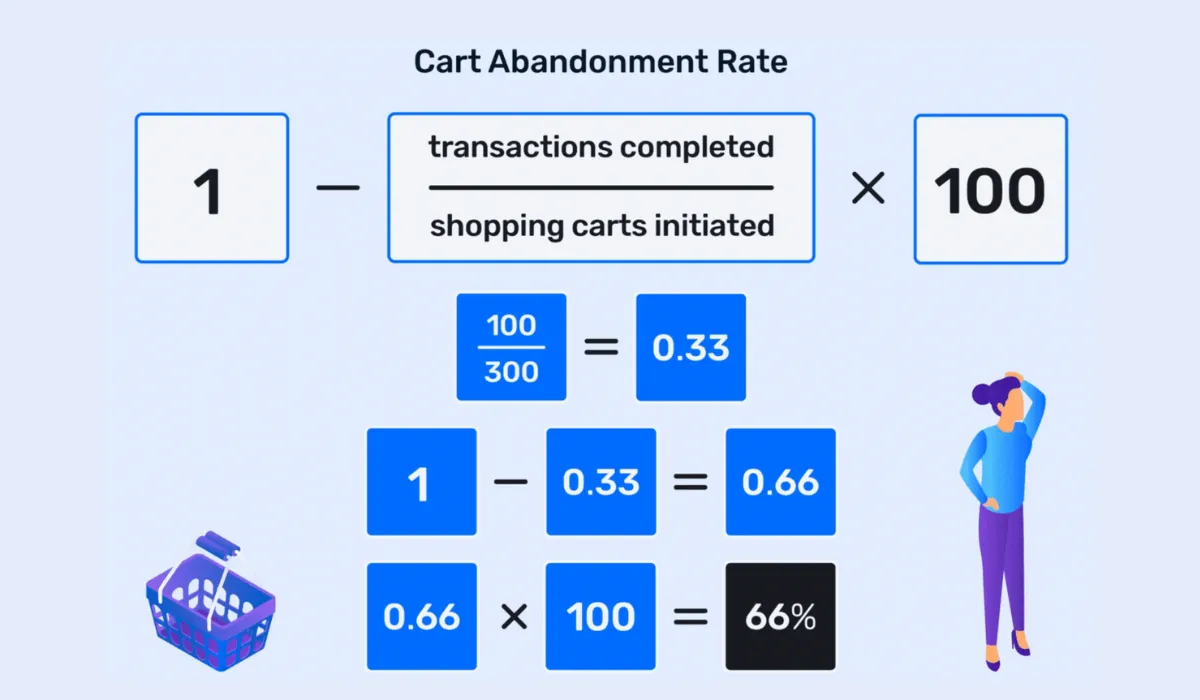
High Cart Abandonment Rates can signal several potential issues within the online shopping experience:
- Complex Checkout Processes: A lengthy or complicated checkout process can deter customers. This might include having to enter excessive information, confusing navigation, or lack of guidance on the next steps.
- Unexpected Costs: High shipping costs, taxes, or additional fees added at checkout can lead to cart abandonment. Customers prefer transparent pricing from the onset of their shopping journey.
- Limited Payment Options: Today’s consumers expect a variety of payment options, including digital wallets and alternative payment methods. A lack of these options can cause customers to abandon their carts.
- Website Performance Issues: Slow load times, crashes, or errors during the checkout process can frustrate customers and lead them to abandon their purchases.
Strategies to Reduce Cart Abandonment
Addressing cart abandonment requires a multifaceted approach to streamline the purchasing process and enhance the customer experience:
- Simplify the Checkout Process: Minimize the number of steps and amount of information required to complete a purchase. Consider features like auto-fill and guest checkout options to facilitate a quicker and smoother transaction.
- Transparent Pricing: Ensure that all costs, including shipping and taxes, are clearly disclosed early in the shopping process. Surprises at checkout can lead to distrust and lost sales.
- Diverse Payment Options: Incorporate multiple payment methods, including popular digital wallets and financing options, to accommodate a broader range of customer preferences.
- Optimize Website Performance: Regularly test and update the e-commerce platform to ensure it is fast, secure, and user-friendly. Address any bugs or glitches promptly to prevent disruptions during the checkout process.
- Retargeting Abandoned Carts: Implement strategies such as sending reminder emails or targeted ads that encourage customers to revisit their abandoned carts. Personalize these communications with details of the abandoned items and possibly include a special offer or discount to incentivize completion of the purchase.
Advanced analytics tools and AI can also help identify patterns and trends in cart abandonment, providing insights into which products are most frequently abandoned or at what stage of the checkout process customers are dropping off. This data can be instrumental in continuously refining the shopping experience to reduce abandonment rates.
By actively addressing the factors contributing to high Cart Abandonment Rates, omnichannel retailers can enhance the efficiency of their eCommerce operations and improve overall customer satisfaction. These efforts not only help convert more browsers into buyers but also build trust and loyalty among customers, encouraging repeat business and positive word-of-mouth recommendations.
Channel-Specific KPIs
To effectively manage and optimize an omnichannel retail strategy, retailers must dive deep into channel-specific KPIs. These omnichannel retail KPIs serve as metrics to provide crucial insights into how each channel contributes to the overall business and customer experience. This section explores the vital KPIs for different channels, including website traffic and conversion rates, social media engagement metrics, email marketing performance, mobile app usage and engagement, and in-store foot traffic and conversion.
Website Traffic and Conversion Rates
Website traffic and conversion rates are crucial channel-specific KPIs in omnichannel retail, offering critical insights into how effectively an online store attracts and converts potential customers into paying customers.
Understanding Website Traffic and Conversion Rates
Website traffic measures the number of users who visit the website over a specific period. It serves as a primary indicator of online presence effectiveness and initial customer interest. High traffic volumes suggest strong brand visibility and reach, potentially driven by successful marketing campaigns or strong organic search presence. However, high traffic alone doesn’t guarantee business success unless it translates into actual sales, which is where conversion rates come into play.
Conversion rates measure the percentage of website visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase. It is a direct indicator of the effectiveness of the website’s design, functionality, and overall user experience. Conversion rates help identify how well the website capitalizes on its traffic, turning visitors into customers. A low conversion rate, despite high traffic, may indicate issues with the website’s navigation, content, product offerings, pricing strategy, or checkout process.
Optimization Strategies for Website Traffic and Conversion Rates
To optimize your web traffic and conversion rate, here are the few things you can do:
Enhancing User Experience (UX):
- Simplify Navigation: Ensure that the website’s layout is intuitive and user-friendly. Simplify the navigation process to help users find products quickly and efficiently. A well-organized site structure significantly enhances the ability to browse and find information, directly impacting user satisfaction and conversion rates.
- Mobile Optimization: With a significant portion of web traffic coming from mobile devices, it’s crucial to ensure that the website is optimized for mobile. This includes fast loading times, responsive design, and accessible navigation tailored for smaller screens.
- Loading Speed: Improve site speed as delays can deter potential purchases. Faster websites provide a better user experience, encouraging visitors to stay longer and explore more products, thereby increasing the likelihood of conversion.
A/B Testing:
- Experiment with Different Elements: Regularly test different aspects of the website, such as product images, CTA buttons, layout designs, and content placements. For example, testing the color and placement of a Buy Now button may reveal preferences that lead to more conversions.
- Landing Pages: Test different versions of landing pages to determine which elements perform best in terms of visitor engagement and conversions. This could involve variations in headline text, images, or the amount of text on the page.
SEO and Retargeting Ads:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Utilize SEO strategies to increase organic traffic. This includes optimizing website content for relevant keywords, improving meta descriptions and titles for better click-through rates, and ensuring website architecture supports search engine indexing.
- Content Marketing: Develop and distribute valuable content that attracts and engages visitors, such as blogs, videos, and infographics. This not only helps improve SEO but also establishes the brand as a thought leader in its niche.
- Retargeting Campaigns: Implement retargeting strategies to bring back visitors who didn’t make a purchase on their first visit. By displaying ads to these visitors while they browse other sites, you remind them of their interest and encourage them to return, potentially increasing conversion rates.
Social Media Engagement Metrics
Social media platforms play an integral role in the omnichannel retail landscape, serving as dynamic venues for customer interaction and brand promotion. The effectiveness of a brand’s social media presence is often measured through engagement metrics, which include likes, shares, comments, and the growth of followers. These metrics are critical as they provide a quantitative look at how engaging and appealing a brand’s content is to its audience.
Engagement Metrics Explained
- Likes: This metric serves as a basic indicator of content’s immediate appeal.
- Shares: Shares and reposts indicate that the content resonates well enough that users are willing to associate it with their own profiles, expanding the content’s reach.
- Comments: Comments often provide deeper insight into how users perceive the brand or content, including constructive feedback or direct customer engagement.
- Followers: Growth in followers can signal improving brand visibility and audience interest over time.
High engagement rates typically suggest successful content strategies and effective communication channels that capture and hold the audience’s attention. Conversely, low engagement might suggest that content is not resonant or that the strategies are not effectively aligned with the audience’s preferences.
Strategies to Enhance Social Media Engagement
- Content Relevance and Value: Crafting content that is both relevant and valuable to the target audience is crucial. This involves understanding audience preferences and pain points to tailor content that speaks directly to their interests or needs. For instance, a brand can use insights from customer data to create informational content, how-to guides, or lifestyle posts that align with the audience’s interactions with the brand.
- Active Community Engagement: Brands should strive to create a community around their products or services by actively engaging with their audience. Responding to comments, participating in discussions, and even acknowledging user-generated content can foster a loyal community. This active engagement helps humanize the brand and build stronger, more personal connections with customers.
- Targeted Promotions and Contests: Social media-specific promotions, such as giveaways or contests, are excellent strategies for boosting engagement. These activities not only encourage existing followers to engage but also attract new followers. Brands can leverage these promotions to increase brand exposure and incentivize interactions by offering rewards that align with the audience’s interests.
- Regular Interaction and Consistency: Consistency in posting and interaction helps maintain brand presence and keeps the audience engaged. Setting a regular posting schedule and maintaining a consistent voice and style across all posts reinforce brand identity and help in building a dependable image.
- Utilizing Social Media Insights: Most social media platforms provide analytics tools that allow brands to track engagement metrics and audience demographics. By regularly reviewing these insights, brands can continuously refine their strategies to better meet the needs of their audience, adapting content types, posting times, and engagement tactics based on what has proven most effective.
Email Marketing Performance
Email marketing continues to be an indispensable component of omnichannel retail strategies, with open rates and click-through rates (CTR) serving as primary indicators of its effectiveness. Understanding these metrics allows retailers to gauge the impact of their email communications and refine their approaches to enhance customer engagement and drive conversions.
Understanding Email Marketing Performance
Open Rates provide insight into the percentage of recipients who open an email, which reflects the initial appeal of the email content, particularly the effectiveness of the subject line. A high open rate generally indicates that the subject line was compelling enough to catch the recipient’s attention, possibly due to effective personalization, relevance to the recipient, or timely delivery.

Click-Through Rates (CTR) measure the percentage of recipients who click on a link within the email after opening it. This metric is crucial as it reflects the effectiveness of the email content in motivating recipients to take a desired action, such as visiting a product page, reading an article, or taking advantage of a promotion. High CTRs are indicative of content that is relevant and offers perceived value to the audience, encouraging deeper engagement with the brand.
Strategies to Enhance Email Marketing Performance
In order to enhance your email marketing performance, here are a few things you can do:
- Advanced Segmentation: Going beyond basic demographic segmentation, retailers can utilize behavioral data, purchase history, and customer preferences to create highly targeted email campaigns. This advanced segmentation ensures that the content is extremely relevant to each recipient, which can significantly improve both open rates and CTRs. For example, sending a special offer on a product category that a customer has shown interest in can result in higher engagement rates compared to a generic promotional email.
- Optimizing Email Subject Lines: Crafting subject lines that resonate with the target audience is key to boosting open rates. This involves using action-oriented language, posing questions, or including intriguing teasers that pique curiosity without giving away too much. Personalizing subject lines with the recipient’s name or references to past interactions can also increase the likelihood of the email being opened. Retailers should continuously A/B test different subject lines to determine which styles and formats generate the best response.
- Compelling and Clear CTAs: Each email should include a clear and compelling call to action that guides recipients towards what they should do next. Whether it’s inviting them to learn more about a product, take advantage of a limited-time offer, or participate in a loyalty program, the CTA should be easy to find and visually distinct. Using buttons instead of hyperlinks, employing action-driven text, and placing CTAs strategically within the email can enhance visibility and improve click-through rates.
- Consistent Testing and Analytics: Continuous testing and analysis are essential to refine email strategies. This includes not only A/B testing of subject lines and CTAs but also testing different email formats, layouts, and content types. Analyzing the performance of each email campaign helps identify what resonates best with the audience and which areas might need adjustment. Metrics such as open rates, CTRs, conversion rates, and even unsubscribe rates provide a comprehensive view of campaign effectiveness.
By meticulously focusing on these strategies, omnichannel retailers can effectively utilize email marketing not only to communicate with their audience but also to drive meaningful engagement and conversion. This direct line of communication is a powerful tool for nurturing customer relationships and encouraging loyalty, ultimately contributing to sustained retail success.
Mobile App Usage and Engagement
In terms of omnichannel retail KPIs, mobile apps represent a powerful channel for cultivating customer engagement and driving sales. The performance of a mobile app can be gauged through several indicators that provide insights into how customers are interacting with the app and the value it adds to their shopping experience.
Critical KPIs for Mobile App Engagement
- App Downloads: This metric tracks the number of times the app has been downloaded. High download rates are a good initial indicator of interest in the mobile platform but need to be complemented by engagement metrics to paint a full picture of its success.
- Active Users: The number of active users (daily and monthly) is a crucial metric that helps retailers understand the actual usage of the app. High numbers of active users indicate that the app remains relevant to customers’ needs and continues to engage them effectively.
- Session Length: The average time users spend on the app during each visit reveals how engaging and compelling the app’s content is. Longer session lengths can suggest that the app offers a good user experience or valuable features that keep users interested.
- In-App Purchases: Monitoring the volume and value of purchases made directly through the app can help quantify its effectiveness in driving sales. High in-app purchase activity is a strong indicator of the app’s ability to convert engagement into revenue.
Strategies to Enhance Mobile App Engagement
- Providing Unique Value: To stand out, the app must offer features that enhance the shopping experience beyond what customers can get on other channels. This might include personalized recommendations based on user behavior, exclusive in-app discounts, or interactive features like augmented reality that allow users to see products in their home environment before purchasing.
- Continuous Improvement and Updates: Regular updates are vital to keep the app relevant and functioning smoothly. This includes both technical improvements to enhance performance and new features that respond to evolving user needs. Keeping the app updated is crucial for maintaining its security and improving user experience, which can significantly impact user retention and engagement.
- Effective Use of Push Notifications: Push notifications are a powerful tool for maintaining user engagement. They can be used to alert users to new products, special offers, and other relevant news. However, it’s important to balance frequency and relevance to avoid notification fatigue. Personalizing notifications based on user preferences and behaviors can make them more effective and less intrusive.
- Leveraging Analytics: Implementing advanced analytics to track how users interact with the app can provide valuable insights that drive further improvements. Analyzing user behavior data helps understand what features are most used, which areas of the app are underperforming, and how the app usage correlates with other customer behaviors across channels.
- Seamless Integration with Other Channels: For omnichannel success, the app should not stand alone but be seamlessly integrated with other channels. This includes syncing user profiles and shopping carts across the website, mobile app, and physical stores, as well as providing features that complement in-store experiences, such as barcode scanning for price checks and product information.

Ensuring a cohesive and unified experience across all touchpoints not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reinforces brand loyalty, ultimately driving higher engagement and conversion rates through the mobile app.
In-Store Foot Traffic and Conversion
In-store foot traffic and conversion rates are pivotal channel-specific KPIs for brick-and-mortar retailers within an omnichannel strategy. These metrics are crucial for understanding how physical locations contribute to overall business performance and customer engagement.
Understanding Foot Traffic Conversion
In-Store Foot Traffic: This KPI measures the number of customers entering a store within a given timeframe. High foot traffic is a positive sign, indicating that the store attracts a large number of visitors, which could be due to effective marketing, attractive store location, or strong brand appeal. However, high traffic doesn’t automatically translate into sales, which is where conversion rates come into play.
Conversion Rates: This metric reflects the effectiveness of the store in converting visitors into buyers. It is calculated by dividing the number of purchases by the total foot traffic. A high conversion rate suggests that the store is successful not just in attracting visitors but also in persuading them to make a purchase. This could be influenced by factors such as product availability, customer service quality, store environment, and pricing strategies.
Strategies to Enhance In-Store Performance
Leveraging In-Store Analytics Tools:
- Customer Movement Analysis: Advanced analytics tools can track where customers spend most of their time within a store. This data helps identify ‘hot spots’ which are areas of high engagement, and ‘dead zones’ which are less visited. Retailers can use this information to strategically place high-margin products in hot spots and redesign or repurpose dead zones to improve their appeal.
- Heat Maps: Creating heat maps of customer movement can further assist in visualizing the flow of traffic throughout the store, enabling more informed decisions about product placement and store layout.
Targeted In-Store Promotions:
- Exclusive Offers: Providing in-store exclusive promotions can create a unique value proposition that encourages more visits and enhances conversion rates. These could include time-sensitive discounts, loyalty program benefits for in-store purchases, or early access to new products.
- Event-Driven Marketing: Hosting in-store events or experiences can significantly boost foot traffic and conversions. These could be product launches, workshops, or holiday-themed events that provide interactive experiences for customers.

Optimizing Store Layouts and Displays:
- Customer-Friendly Layouts: Store layouts should facilitate an easy and enjoyable shopping experience. This includes clear signage, accessible pathways, strategically placed products, and well-organized sections that logically flow from one to the next.
- Dynamic Displays: Innovative and regularly updated displays can attract attention and engage customers, encouraging them to explore more products and spend more time in the store. Effective use of lighting, color, and spacing can significantly enhance product visibility and attractiveness.
Integrating Technology:
- Digital Signage and Interactive Displays: Implementing digital solutions such as interactive kiosks that provide product information, availability, or even virtual try-on options can enhance the shopping experience and assist in conversion.
- Mobile Integration: Encouraging the use of mobile devices for in-store navigation, product reviews, or even checkout can streamline the shopping process and enrich customer interactions with the brand.
Inventory and Supply Chain Metrics
Effective management of inventory and supply chain operations is fundamental in omnichannel retail. Metrics such as Inventory Turnover Rate, Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) Performance, Sell-Through Rate, and Order Fulfillment Cycle Time play critical roles in optimizing these processes. These KPIs not only help ensure product availability across all channels but also enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Inventory Turnover Rate
The Inventory Turnover Rate stands as a vital omnichannel retail KPIs,, serving as a barometer for measuring the efficiency and responsiveness of inventory management practices. By highlighting how frequently inventory is sold and replenished over a given period, this metric informs retailers about the dynamism of their stock relative to sales performance.
Understanding Inventory Turnover Rate
A high Inventory Turnover Rate generally suggests that a retailer is effective at managing inventory levels — stock is being sold and then quickly replaced, which is often indicative of good sales velocity and effective inventory management. This scenario is ideal as it minimizes holding costs, reduces the risk of obsolescence, and ensures that capital is not unnecessarily tied up in unsold stock.
On the other hand, a low Inventory Turnover Rate can be problematic. It may indicate that the inventory is stagnant, which can be due to several factors such as overstocking, poor product selection, or declining customer demand. Such situations can lead to increased storage costs, higher risks of inventory obsolescence, and the inefficient use of working capital, all of which can negatively impact the financial health of the business.
Calculating Inventory Turnover Rate
The Inventory Turnover Rate is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory during a specific period. The average inventory is typically calculated by adding the inventory levels at the beginning and end of the period and dividing by two.
For instance, if a retailer has a COGS of $1,000,000 and their average inventory value for the period is $250,000, their Inventory Turnover Rate would be 4. This means that the inventory was completely sold and replaced four times over the period.
Optimization Strategies for Improving Inventory Turnover Rate
- Enhanced Demand Forecasting: Leveraging advanced analytics and predictive modeling can enable more accurate forecasting of customer demand. By better predicting which products are likely to be in demand, retailers can optimize their stock levels to ensure they have the right products available without overstocking.
- Dynamic Product Assortment: Regularly reviewing and adjusting the product assortment based on sales performance data, market trends, and consumer preferences can help maintain the relevance and appeal of the inventory. This involves both introducing new, trending items and discontinuing underperforming ones.
- Agile Promotional Strategies: Developing flexible promotional strategies that can be quickly implemented to move excess inventory can help improve turnover rates. This may include temporary price reductions, special offers, or bundled deals, particularly for products that are overstocked or nearing the end of their product lifecycle.
- Improved Inventory Visibility Across Channels: Implementing robust inventory management systems that provide real-time visibility across all sales channels (online, in-store, mobile) enables better coordination and responsiveness. This integration ensures that inventory levels are adjusted dynamically based on sales data from all channels, which helps in maintaining optimal stock levels.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Working closely with suppliers to ensure quicker replenishment cycles and more flexible terms can also help maintain a healthier turnover rate. This could involve renegotiating delivery schedules or minimum order quantities to better align with current sales patterns and inventory needs.
Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) Performance
SKU Performance is a critical omnichannel retail KPIs that tracks and analyzes the sales effectiveness and profitability of each individual SKU (Stock Keeping Unit). This analysis is essential for understanding product dynamics across multiple sales channels and can significantly impact inventory management and marketing strategies.
Understanding SKU Performance
SKU performance provides detailed insights into how individual products contribute to overall business metrics like sales volume, revenue, and profit margins. By assessing SKU performance, retailers can pinpoint which products are driving sales and which are lagging behind. This insight is invaluable for optimizing product offerings to better align with consumer demand and market trends.

High-performing SKUs, which show strong sales or high profitability, can be prioritized within the business strategy. They might receive greater focus in terms of marketing efforts, more prominent placement in both physical and online stores, and increased stocking levels. Conversely, SKUs with poor performance may require reevaluation—this might involve price adjustments, promotional efforts to clear stock, or even discontinuation if they consistently underperform.
Advanced Analysis Techniques for SKU Performance
- Sales Volume and Revenue Tracking: Regularly monitoring the sales volume and revenue generated by each SKU provides a direct measure of its market performance. Retailers can use this data to assess consumer preference trends and adjust procurement accordingly.
- Profit Margin Analysis: Understanding the profit margins associated with each SKU helps retailers identify not just the top sellers but also the most profitable products. This can influence decisions on pricing strategies and inventory investments.
- Seasonal Performance Evaluation: Analyzing how SKUs perform in different seasons or during specific promotional periods can help in planning inventory needs and marketing strategies tailored to peak demand times.
- Market Basket Analysis: This technique involves examining the products that are frequently purchased together. Understanding these patterns can help retailers create effective cross-promotional strategies and optimize product placement both in-store and online.
Benefits of Effective SKU Performance Management
- Inventory Optimization: By identifying which SKUs are performing well and which are not, retailers can better manage their inventory levels—stocking up on the high performers and reducing or eliminating the poor performers. This leads to more efficient use of warehouse space and capital investment.
- Cost Reduction: Effective SKU management can significantly reduce costs associated with overstocking and holding unsold merchandise. By aligning inventory more closely with actual market demand, retailers can minimize markdowns and improve the turnover rate.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Focusing on SKUs that meet customer needs and preferences ensures that the most sought-after products are readily available, enhancing the customer shopping experience. It also helps retailers tailor their product assortments to better match customer expectations, which can improve loyalty and repeat business.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Robust SKU performance analysis enables retailers to make more informed decisions about product development, marketing, and sales strategies. It provides a factual basis for predicting future trends and preparing for market changes.
Sell-Through Rate
The Sell-Through Rate is a pivotal inventory and supply chain metric for omnichannel retailers, particularly in fast-moving sectors like fashion and electronics, where product life cycles are short and inventory obsolescence risks are high. This KPI provides a clear snapshot of inventory performance by showing the percentage of merchandise sold compared to the amount that was available to be sold.
Understanding the Sell-Through Rate
The Sell-Through Rate is typically calculated by taking the number of units sold during a specific time period and dividing it by the number of units that were initially available at the start of the period. The result is expressed as a percentage.
For omnichannel retailers, the Sell-Through Rate is crucial as it directly impacts how effectively a company can manage its inventory across multiple sales channels. A high Sell-Through Rate generally indicates that products are well-matched to current customer demands and that inventory levels are being managed efficiently to meet these demands without excessive surplus.
Strategies to Optimize Sell-Through Rate
- Dynamic Pricing Strategies: Retailers can implement dynamic pricing models that adjust prices based on real-time market demand, competitor pricing, and remaining inventory levels. This approach helps to maximize sales without the need for deep discounts that erode profit margins. For example, slight price adjustments downward can stimulate demand before products become outdated, particularly in fashion retail where trends can change rapidly.
- Enhanced Sales Forecasting: Utilizing advanced analytics and AI to improve sales forecasting accuracy is vital. More precise predictions about product demand help in planning the right inventory levels, thus avoiding overstock situations and ensuring popular items are sufficiently available. Forecasting tools can analyze historical sales data, seasonal trends, and consumer behavior patterns to provide insights that significantly improve inventory decisions.
- Promotional and Marketing Adjustments: Effectively aligning marketing efforts with inventory needs can drive sell-through rates. Promotions, marketing campaigns, and even in-store displays should be strategically timed to peak customer interest and move inventory efficiently. For instance, if certain items are projected to have slower sell-through, targeted promotions can help clear stock.
- Product Bundling: Combining slower-moving items with more popular products as part of a bundle offer can enhance the attractiveness of the entire package. This strategy not only helps in clearing out less popular inventory but also increases the perceived value for customers, potentially boosting overall sales.
- Feedback Loop Integration: Implementing a robust system to gather and analyze customer feedback on products can provide actionable insights that influence future buying and inventory decisions. Understanding why certain items sell well or poorly allows retailers to adjust their product offerings more effectively to meet customer expectations and market demand.
Impact of Sell-Through Rate on Omnichannel Efficiency
In an omnichannel context, maintaining an optimal sell-through rate ensures that inventory turnover remains high, reducing the costs associated with holding and managing stock. It also ensures that product offerings are fresh and relevant, which is crucial for customer retention and satisfaction. Moreover, effective management of this metric across various channels supports a cohesive retail strategy that aligns online and offline inventory, promoting a seamless customer experience.
By focusing on these strategies to maximize the sell-through rate, omnichannel retailers can not only reduce the risk of markdowns and overstock but also ensure that their inventory management practices are as profitable and responsive as possible. This proactive approach to inventory control is essential in maintaining competitive advantage in the fast-paced retail sector.
Order Fulfillment Cycle Time
Order Fulfillment Cycle Time is a crucial omnichannel retail KPIs, encapsulating the efficiency of the entire supply chain from the initial order placement to the final delivery to the customer. This metric is increasingly significant in the competitive landscape of retail, where the speed and reliability of order fulfillment are directly linked to customer satisfaction and retention.
Understanding Order Fulfillment Cycle Time
The cycle time begins when an order is placed and ends when the product is delivered to the customer. Monitoring this cycle helps identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies within the supply chain, such as delays in inventory picking, packaging, or shipping.
Understanding each component of the cycle — from order processing, inventory picking, packaging, shipment, and last-mile delivery — is vital for pinpointing specific delays and implementing focused improvements.
The Order Fulfillment Cycle Time is crucial as an omnichannel retail KPIs since modern customers expect fast and reliable delivery services. The efficiency of an omnichannel operation in meeting these expectations can significantly influence customer loyalty and brand reputation. For instance, same-day or next-day delivery options have become a benchmark in many urban markets, and meeting these expectations can set a retailer apart from competitors.
In an omnichannel environment, the ability to quickly fulfill orders from any channel—whether online, via mobile, or in-store pickup—enhances the overall customer experience. Efficient fulfillment is not just a back-end operation; it’s a crucial aspect of customer service that directly impacts sales and customer retention.
Strategies to Optimize Order Fulfillment Cycle Time
- Warehouse Automation: Implementing automation in warehouse operations, such as using robotic systems for picking and packing, can significantly speed up these processes. Automation reduces human error, increases picking accuracy, and decreases the time taken from order receipt to dispatch.
- Advanced Inventory Management Systems: Utilizing robust inventory management systems can improve the accuracy of stock levels and the speed of inventory retrieval. These systems help ensure that products are readily available when orders are placed, preventing delays caused by stock-outs or misplacement.
- Enhanced Logistics Partnerships: Collaborating closely with logistics partners can streamline the shipping and delivery process. Advanced coordination with shipping partners ensures that once orders leave the warehouse, they are delivered efficiently. Regular reviews and optimizations of shipping routes and logistics strategies can further reduce delivery times.
- Integrated Technology Solutions: Employing integrated technology solutions that connect inventory management with order processing and logistics can provide real-time data across the supply chain. This integration allows for more dynamic responses to order placement and fulfillment issues, thereby optimizing the entire cycle.
- Performance Analytics: Regular analysis of fulfillment data helps identify trends and problem areas in the order fulfillment process. This can include analyzing the time taken for each step of the fulfillment process, identifying seasonal variations in order volume, and evaluating the impact of promotional activities on fulfillment efficiency.
Analytics and Data Integration
In the increasingly complex world of omnichannel retail, leveraging advanced analytics and integrating data systems have become pivotal omnichannel retail KPIs for making informed decisions, enhancing customer experiences, and optimizing operational efficiency.

This section explores the critical role of integrated data systems, the application of real-time analytics, and the power of predictive analytics in shaping the future of retail.
Importance of Integrated Data Systems
Integrated Data Systems are essential in omnichannel retail as they consolidate data from various sources—online, in-store, mobile, and social media—into a unified platform. This integration allows retailers to have a holistic view of their operations and customer interactions across all channels.
- Holistic Customer View: By integrating data from multiple touchpoints, retailers can create comprehensive customer profiles. This unified view enables personalized marketing, tailored product recommendations, and improved customer service, all of which are essential for enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Inventory Management: Integrated systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels across all channels, helping retailers manage stock more effectively. This is crucial for fulfilling customer orders promptly and accurately, minimizing stock-outs or overstock situations.
- Consistency Across Channels: Data integration ensures consistency in customer experience across all channels. Whether a customer shops online, via a mobile app, or in a physical store, the quality of service needs to be consistent. Integrated data systems help in maintaining this consistency by synchronizing information across all points of interaction.
Real-time Analytics for Omnichannel Decisions
Real-time Analytics play a critical role in omnichannel retail by providing immediate insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and operational performance.

This instant access to data allows retailers to make swift decisions that can significantly impact their business.
- Dynamic Decision Making: With real-time analytics, retailers can quickly adjust marketing campaigns, promotions, and pricing strategies based on current market conditions and consumer behavior. For example, if a particular product is performing well in real-time analytics, a retailer might decide to run a flash sale to capitalize on this trend.
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: Real-time insights enable retailers to offer personalized experiences to customers as they interact with the brand. For instance, if analytics show that a customer is looking at a specific product online, the retailer can offer a special discount on that product as an incentive to purchase.
- Operational Efficiency: Real-time data allows for more efficient management of supply chain and inventory. Retailers can see which products are moving quickly and adjust their logistics and inventory levels accordingly to avoid sell-outs or excess stock.
Predictive Analytics in Retail
Predictive Analytics uses historical data, machine learning, and statistical algorithms to forecast future outcomes. In retail, this can transform how businesses anticipate customer needs, manage inventory, and optimize resources.
- Forecasting Customer Behavior: Predictive analytics can help retailers understand customer purchasing patterns, predict future buying behaviors, and identify potential high-value customers. This enables more effective targeting and personalization of marketing efforts.
- Inventory and Demand Forecasting: By analyzing past sales data, predictive models can forecast future product demand, helping retailers optimize their inventory levels and reduce costs associated with overstocking or understocking.
- Risk Management: Predictive analytics can also be used to assess risks in various aspects of retail operations, from supply chain disruptions to changes in consumer demand due to economic factors. This foresight allows retailers to create strategies to mitigate these risks before they impact the business.
Leveraging Technology for Omnichannel Retail KPI Measurement
In the dynamic landscape of eCommerce, leveraging technology to measure and optimize omnichannel retail KPIs is essential. Modern tools and platforms enable retailers to track performance across various channels, harnessing the power of AI and machine learning, and integrating complex systems like ERP and CRM to ensure seamless operations. This section delves into how technology is utilized to enhance KPI measurement and why it’s crucial for omnichannel success.
Tools and Platforms for Tracking KPIs
The foundation of effective omnichannel management lies in the ability to accurately measure omnichannel retail KPIs using advanced tools and platforms.
These technologies collect data from various sources and provide analytics that help retailers make informed decisions.
- Analytics Dashboards: Tools like Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, and Tableau offer comprehensive dashboards that visualize data across different retail channels. These platforms can track website traffic, conversion rates, customer engagement, and more, providing insights into how each channel contributes to overall business goals.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs create unified customer profiles by integrating data from multiple sources, including online and offline interactions. This allows retailers to track customer behavior across channels, enhancing personalized marketing efforts and improving customer service.
- Inventory Management Software: Systems like Oracle NetSuite, Shopify, and Zoho Inventory help manage stock levels by tracking product movement, order fulfillment, and restocking needs across all sales channels. These platforms are vital for maintaining optimal inventory turnover rates and minimizing costs related to overstocking or stockouts.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are transforming how omnichannel retailers measure and interpret KPIs, providing deeper insights into vast amounts of data.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms analyze historical data and predict future trends, such as customer buying behaviors or inventory demands. This helps retailers anticipate market changes, optimize inventory, and personalize marketing campaigns effectively.
- Customer Insights: Machine learning models can identify patterns in customer data, enhancing understanding of customer preferences and behaviors. This information can be used to optimize product recommendations, personalize marketing messages, and improve customer engagement strategies.
- Operational Efficiency: AI tools can optimize logistics and supply chain management by predicting the best routes, managing warehouse operations, and automating repetitive tasks, thereby reducing costs and improving order fulfillment cycle times.
Implementing ERP and CRM Systems
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are critical for integrating various aspects of an omnichannel business, from inventory management to customer interactions.
- ERP Systems: ERP systems integrate all facets of an enterprise’s operations, including inventory, order management, accounting, and human resources, into a single framework. This centralization makes it easier to track and manage business resources effectively, ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall business strategy.
- CRM Systems: CRM systems manage all relationships and interactions with customers across different channels. These systems track customer interactions, purchases, and service history, making it easier to provide consistent and personalized customer service and support.
Importance of Seamless Integration Across Channels
Seamless integration across channels is crucial for a true omnichannel experience. This integration ensures that customer interactions are consistent and personalized, regardless of the channel.

The crucial roles of Seamless Integration Across Channels you should consider:
- Data Consistency: Integrating systems and technologies ensures that data is consistent across all channels. This is crucial for maintaining accurate inventory records, providing consistent customer service, and delivering personalized shopping experiences.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Seamless integration allows customers to move fluidly between channels, from browsing online to purchasing in-store, without any disruption in service or experience. This fluidity increases customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Strategic Decision Making: With integrated data, retailers can make more strategic decisions based on comprehensive insights. This includes tailoring marketing strategies, optimizing inventory distribution, and enhancing customer engagement across all channels.
Challenges in Measuring Omnichannel Retail KPIs
Accurately measuring and managing omnichannel retail KPIs presents several unique challenges. These challenges stem from the complexity of integrating multiple sales channels, the need for consistent measurement standards, the imperative of safeguarding customer privacy, and the necessity of adapting to rapidly changing consumer behaviors.
The challenges in measuring omnichannel retail KPIs are significant but not insurmountable. By addressing data silos and integration issues, ensuring consistency in measurement, safeguarding privacy and security, and adapting to changing consumer behaviors, retailers can effectively navigate these complexities. Overcoming these challenges is essential for leveraging omnichannel retail KPIs to enhance decision-making, optimize customer experiences, and ultimately drive business success in the competitive landscape of omnichannel retail. Thus, this section delves into these core issues, highlighting the intricacies of measuring omnichannel retail KPIs effectively.
Data Silos and Integration Issues
One of the most significant hurdles in omnichannel retail is overcoming data silos. Data silos occur when information is segregated within different departments or systems, making it difficult to achieve a unified view of customer interactions and business operations.
- Impact on KPI Accuracy: Data silos can lead to inconsistent or incomplete data, which impacts the accuracy of KPIs and hinders the ability to make informed decisions based on a holistic view of customer activities and preferences.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating data across various channels, such as online stores, mobile apps, and physical retail locations, involves aligning different technology platforms and data management systems. This process can be technically complex and resource-intensive.
To mitigate these challenges, retailers must invest in robust integration technologies such as enterprise service buses (ESBs) or implement comprehensive platforms like Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) that can aggregate and normalize data across sources, providing a single source of truth for all KPI measurements.
Consistency in Measurement Across Channels
Achieving consistency in KPI measurement across diverse channels is critical to accurately assessing omnichannel performance. Each channel — from eCommerce sites and brick-and-mortar stores to mobile applications — has its unique interaction modes and data capture methods.
- Standardization of Metrics: Retailers need to establish standard definitions and consistent measurement methodologies for KPIs across all channels to ensure comparability and reliability of the data.
- Customized Metrics per Channel: While standardization is necessary, it’s also crucial to recognize that some KPIs may need to be adapted to the specificities of each channel without compromising the overall integrity of performance measurement.
For instance, conversion rates in a physical store versus an online shop might be inherently different due to varying customer behaviors and buying cycles. Retailers must develop nuanced metrics that reflect these differences while maintaining overarching KPIs for holistic performance assessment.
Privacy and Security Concerns in Data Collection
With the increase in data integration necessary for measuring omnichannel retail KPIs, privacy and security concerns become more pronounced. Retailers must navigate the complexities of data protection regulations such as GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California, which govern how customer data can be collected, stored, and used.
- Building Trust with Customers: Ensuring robust data security measures and transparent privacy policies is essential not just for compliance, but also for building and maintaining trust with customers.
- Implementing Data Protection Measures: Retailers must invest in secure data management systems and adopt best practices in data privacy, such as data anonymization and secure data access protocols, to protect sensitive customer information effectively.
Adapting to Changing Consumer Behaviors
The retail landscape is dynamic, with consumer behaviors and preferences continually evolving. This fluidity presents a challenge for maintaining relevant and effective omnichannel retail KPIs.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Retailers must continuously monitor trends and adapt their KPIs to reflect changing consumer behaviors. This might involve introducing new metrics, discarding outdated ones, or adjusting strategies to better meet consumer needs.
- Leveraging Advanced Analytics: Utilizing advanced analytics and AI can help retailers anticipate changes in consumer behavior and adapt their business strategies proactively. Predictive analytics, for instance, can forecast future trends, allowing retailers to adjust their KPIs and operations ahead of time.
Best Practices for Omnichannel Success
Omnichannel retailing represents a holistic approach to customer engagement by seamlessly integrating various shopping channels to provide a cohesive experience. As retailers navigate the complexities of this strategy, the implementation of robust omnichannel retail KPIs becomes crucial. Effective omnichannel retail KPIs help in measuring performance, guiding strategic decisions, and ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.

By embracing these best practices — setting realistic goals and fostering continuous improvement — retailers can ensure their omnichannel strategies are not only effective but also adaptable to the evolving retail landscape. This approach allows for sustained growth and success, leveraging omnichannel retail KPIs as a compass for strategic decision-making and customer satisfaction enhancement.
Setting Realistic Goals and Benchmarks
Setting realistic goals and benchmarks is fundamental for tracking the progress and effectiveness of omnichannel strategies. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Here’s how retailers can effectively set these goals:
- Understanding Customer Journeys: Begin by mapping out comprehensive customer journeys to identify all potential touchpoints across various channels. Understanding these journeys is crucial for setting relevant KPIs that reflect how customers interact with your brand, whether online, in-store, or via mobile.
- Data-Driven Insight: Utilize data analytics to gather insights from existing performance metrics. Look at historical data to set baseline values for new goals. For instance, if current data shows a 20% cart abandonment rate, setting a goal to reduce this by 5% within a quarter is realistic and measurable.
- Competitive Benchmarking: Consider industry benchmarks and standards to set realistic goals. Analyzing competitors’ performance can provide a clear view of industry standards, helping to position your goals competitively yet attainably.
- Aligning with Business Objectives: Ensure that each goal aligns with broader business objectives. For example, if the overall objective is to increase market share, relevant omnichannel retail KPIs might focus on increasing customer retention rates or improving the in-store conversion rates of online researched products.
- Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms to regularly review and adjust these goals. Feedback from various stakeholders, including sales teams, customer service, and customers themselves, can provide invaluable insights into the effectiveness of your strategies and the realism of your goals.
Continuous Improvement and Learning
For omnichannel retail to be successful, it must not be static; continuous improvement and a culture of learning are essential.

Here’s how businesses can embed these principles into their operations:
- Regular Performance Reviews: Conduct regular analyses of omnichannel retail KPIs to determine the success of various strategies and identify areas for improvement. This could be done monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the KPIs and business cycles.
- Employee Training and Development: Continuously train staff across all channels on the latest tools and strategies for customer engagement. This includes training in customer service, data analysis, and technology use, ensuring that all team members are skilled in enhancing the omnichannel experience.
- Leveraging Technology: Invest in the latest technology that can provide real-time data and analytics, facilitating immediate actions and long-term strategy adjustments. Technologies such as AI and machine learning can predict customer behaviors and preferences, offering insights into necessary adjustments in real-time.
- Customer Feedback Mechanisms: Implement robust systems for collecting and analyzing customer feedback. This feedback should be used as a learning tool to understand customer needs better and refine experiences across all channels.
- Innovation Culture: Foster a culture of innovation where new ideas are encouraged, and risks are allowed. This can be facilitated through innovation labs or cross-functional teams tasked with finding new solutions to enhance the omnichannel experience.
In Conclusion,
For retailers, the journey toward fully integrated omnichannel operations might be challenging, but it is undoubtedly rewarding. Embracing omnichannel strategies and the omnichannel retail KPIs that measure their success is not merely an option but a necessity in the modern retail landscape where customers expect seamless experiences, whether they are online, on mobile, or in-store.
Retailers should view the adoption of omnichannel strategies as a transformative process that not only enhances operational efficiency but also boosts customer satisfaction and loyalty. The ability to track, measure, and analyze performance across all channels will continue to be essential in this journey, empowering retailers to make informed decisions that align with evolving market demands and consumer expectations.
In conclusion, as we look toward the future, the role of omnichannel retail KPIs will become even more central in crafting successful retail strategies. Retailers that invest in understanding and optimizing these omnichannel retail KPIs will be well-positioned to lead the charge in the new era of retail, characterized by flexibility, efficiency, and unparalleled customer centricity. Embrace these strategies, harness the power of your data, and watch your business not only grow but also innovate and lead in the omnichannel revolution.











