There is a typical misunderstanding that mobile application vs web application are two very similar things, however, the two are very different. Not only are there contrasts for the client, but they are additionally evolved and sent unexpectedly, so it is significant not to confuse the two.
Before ultimately putting resources into your application, you will need to choose which sort of application will best suit your spending plan, prerequisites, and objectives.
Would it be a good idea for you to put resources into building up a mobile application, or would it be a good idea for you to zero in on your assets on building a portable responsive web application? In this article, you will get familiar with the distinction between mobile application vs web application and gain bits of knowledge that will educate your choice to create one sort of application over the other.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Mobile Application?
- What Is a Web Application?
- Mobile Application and Web Application: The Big Difference
- Advantages of Web Application over Mobile Application
- Immediacy: Mobile Websites Are Instantly Available
- Compatibility: Mobile Websites Are Compatible Across Devices
- Upgradability: Mobile Websites Can be Updated Instantly
- Findability: Mobile Websites Can be Found Easily
- Shareability: Mobile Websites Can be Shared Easily by Publishers and between Users
- LifeCycle: Mobile Websites Cannot be Deleted
- A Mobile Website Can be an App
- Time and Cost: Mobile Websites Are Easier and Less Expensive
- Support and Maintenance
- Advantages of the Mobile Application over Web Application
- Mobile Application vs. Web Application: Which One Is for You?
What Is a Mobile Application?
Mobile applications are built for a particular stage, for example, IOS for the Apple iPhone or Android for probably all other smartphones. They are downloaded and introduced through an application store and approach framework assets, for example, GPS and the camera work.
Mobile applications live and run on the actual gadget. Snapchat, Instagram, Google Maps, and Facebook Messenger are a few instances of famous versatile applications.

Mobile applications are more costly to create than web applications. Because they are stage explicit, dispatching an application across various locations essentially implies beginning without any preparation regarding plan and improvement. Notwithstanding, they are a lot quicker, and will in general, be further developed regarding highlights and usefulness.
How Does a Mobile Application Work?
Mobile applications are known for their speed and a more sophisticated browsing experience for users. They are also advantageous in terms of consuming less internet data. Here’s a brief overview of how a mobile application works:
- Downloading the Application: The process begins with the user downloading the application from a digital distribution platform, such as the App Store for iPhone users or Google Play Store for Android users.
- Data and Storage Requirements: To download the application, a certain amount of data and storage space is required. The user must ensure that their mobile device has sufficient space to accommodate the application. Once this is verified, the download process commences.
- Initial Setup: After the application is downloaded, the user typically needs to provide login details or sign up to create a new account. This step is crucial for personalizing the user experience and often involves setting preferences or granting necessary permissions for the application to function properly.
- Usage and User Experience: Once the setup is complete, the application is ready to be used. Mobile applications are designed to display content and deliver services effectively. They often provide an enhanced user experience compared to their web counterparts, offering smoother navigation, faster loading times, and tailored features that leverage the capabilities of mobile devices.
How Is a Mobile App Developed?
Developing a mobile app can be undertaken by companies recruiting professional developers, or by individuals with programming skills. The approach to mobile app development has evolved over time.
In the past, developers needed to use specific software development kits (SDKs) for Android, iOS, or Windows Phone to build apps for these platforms. However, modern development practices also allow the use of intermediary languages like JavaScript.

Native Mobile Apps: These apps are constructed using the designated programming languages specific to their intended platform. Once downloaded from an app store, a native app is stored in the device’s memory and can be accessed by clicking on its icon. Many native apps are designed to function without an internet connection. They offer the advantage of accessing various hardware and features on the device, such as the camera, GPS, sensors, address book, and calendar.
Hybrid Mobile Apps: Hybrid apps, on the other hand, provide more flexibility in their construction. They are typically built using a combination of HTML5, CSS, and JavaScript. Essentially, hybrid apps are web apps that are designed to look and function like native apps. This approach is often faster and easier for developers. While hybrid apps can also utilize various features of a mobile device, they are powered by an internet browser, which differentiates them from native apps.
In summary, the choice between developing a native or hybrid mobile app depends on various factors, including the desired user experience, the specific functionalities required, and the developer’s proficiency in different programming languages and frameworks.
What Is a Web Application?
Web applications are accessed via the internet browser and adjust to whichever device you view them on. They are not native to a specific framework and should not be downloaded or introduced. Because of their responsive nature, they look and function a lot like mobile applications, and this is where the disarray emerges.

Web applications will, in general, be fabricated utilizing JavaScript, CSS, and HTML5. Dissimilar to mobile applications, there is no standard programming advancement pack for building web applications. Nonetheless, engineers do approach layouts.
Contrasted with mobile applications, web applications are typically speedier and more straightforward to assemble, yet they are a lot less complicated regarding highlights. In case you are keen on learning HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, investigate this free arrangement of web development tutorials.
How Does a Web Application Work?
Web applications offer a distinct advantage over mobile applications in that they do not require installation as separate applications on a desktop. Instead, they are accessible through a web browser, making them a convenient choice for users. The process begins when a user initiates a query through their browser over the internet, reaching out to a web server.
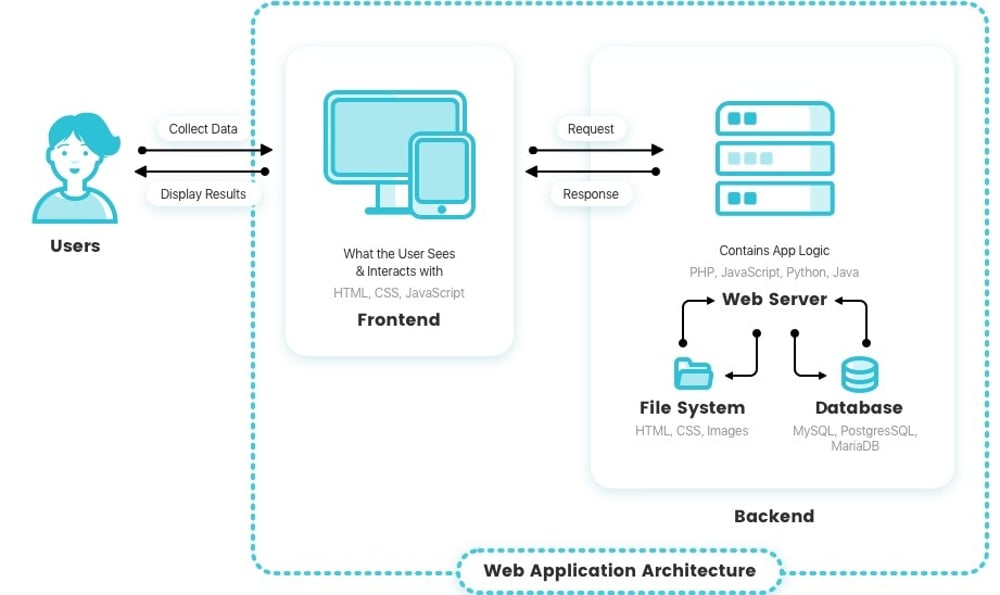
Upon receiving this request, the web server prepares to respond to it. This involves interacting with a web application server, which is a critical component in this process.
The web application server processes the user’s request, fetching and organizing the necessary information or performing the required computations.
Once the web application server has processed the request, it sends the results back to the web server. This is a crucial step as it involves transferring the processed data, which might include various forms of content such as text, images, or other data types, depending on the nature of the user’s request.
Finally, the web server takes this information and presents it to the user through their web browser. This display of information is what the user ultimately sees and interacts with on their device.
The entire process, from the user’s initial query to the display of information, is typically swift, making web applications an efficient tool for accessing and interacting with a variety of services and information over the internet.
How Is a Web App Developed?
Developing a mobile web app involves a blend of client-side and server-side scripting languages. Client-side languages, such as JavaScript and CSS, are executed by the user’s web browser. These languages are responsible for the look and feel of the web app, handling tasks like page layout, user interface interactions, and dynamic content display.

On the other hand, server-side scripting involves languages like Python, Objective-C, or Java. This aspect of the code deals with the backend operations, such as receiving, processing, storing, and sending information between the browser and the server. This is where the web app’s logic and data management occurs, ensuring that user requests are appropriately handled.
HTML is also a crucial component, used as the markup language that structures and organizes the content on the web page, forming the skeleton of the web app.
The development process can be undertaken by an individual developer or a team led by a software engineer, depending on the complexity of the project. The functioning of a web app centers around user interaction, typically via a web form. When a user inputs data into the form, this information is sent to the app server. The server then executes the necessary task based on the user’s request and sends the results back to the user’s browser. This process is designed to work seamlessly both on desktop and mobile devices, offering a versatile and efficient user experience.
Mobile Application and Web Application: The Big Difference
A mobile website is like some other site. It comprises program-based HTML pages connected and accessed over the Internet (for portable ordinarily WiFi or 3G or 4G organizations). The conspicuous trademark that distinguishes a mobile website from a standard site is the way that it is intended for the more modest handheld presentation and contact screen interface.
Progressively, responsive website design has turned into the new norm for mobile well-disposed websites, yet that can scale to any measured gadget – from work areas down to tablets and handheld cell phones.

Like any website, mobile websites/responsive sites can show text content, information, pictures, and video. They can likewise get too explicit mobile highlights like snap-to-call (to dial a telephone number) or area-based planning.
Applications are simple applications downloaded and introduced on your cell phone instead of being delivered inside a program. Clients visit explicit device gateways like Apple’s App Store, Android Market, or Blackberry App World to discover and download applications for a given working framework. The application may pull substance and information from the Internet, incomparable style to a site, or it might download the importance, so it tends to be accessed without an Internet association.
Advantages of Web Application over Mobile Application
If your objectives are fundamentally identified with marketing or public communications, a mobile/responsive website is quite often going to make sense as a practical initial step in your mobile effort strategy. This is because a mobile website has various intrinsic benefits over applications, including more extensive availability, similarity, and cost-effectiveness.
Immediacy: Mobile Websites Are Instantly Available
A mobile website is instantly open to clients through a program across various devices (iPhone, Android, BlackBerry, and so on). Applications then again require the client to initially download and introduce the application from a commercial application center before the substance or application can be seen – a significant boundary between beginning engagement and activity/transformation.
Compatibility: Mobile Websites Are Compatible Across Devices
A single mobile website can approach customers across various kinds of cell phones, while native mobile applications require a different adaptation to be produced for each device.

Moreover, mobile website URLs are effectively coordinated inside other mobile advances like SMS, and QR Codes, and close to handling correspondence (NFC).
Upgradability: Mobile Websites Can be Updated Instantly
A mobile website is considerably more potent than an application and unadulterated adaptable capacity to refresh content. If you want to change the design or content of a mobile website, you just publish the modification once and the changes are immediately visible.
Findability: Mobile Websites Can be Found Easily
Mobile websites are a lot simpler for customers to discover because their pages can be shown in list items and recorded in industry-explicit registries, making it simple for qualified guests to locate you. Above all, visitors to your standard website can be shipped off your mobile website when they are on a handheld (utilizing device location). Conversely, the visibility of applications is to a great extent limited to maker application stores.
Shareability: Mobile Websites Can be Shared Easily by Publishers and between Users
Mobile website URLs are effortlessly divided among clients through an essential link (for example, inside an email or text message, Facebook, or Twitter post). Publishers can easily direct clients to a mobile website from a blog or site or even on paper. An application just can not be partaken in this design.
LifeCycle: Mobile Websites Cannot be Deleted
The average age of an application is relatively short, under 30 days, according to some research. Unless your application is genuinely remarkable and helpful (in a perfect world, both), it is sketchy how long it will keep going on a client’s device. Mobile websites, then again, are consistently accessible for customers to get back to them.
A Mobile Website Can be an App
Like a standard website, mobile websites can be developed as data set-driven web applications that act like native applications. A mobile web application can be a practical option in contrast to local application development.
Time and Cost: Mobile Websites Are Easier and Less Expensive
Finally, mobile website improvement is impressively more time and financially savvy than the development of a local application, particularly if you need to have a presence at various stages (requiring advancement of different applications).
Support and Maintenance
The mobile application vs web application considerations do not end with the underlying launch; appropriately supporting and keeping an application (updates, testing, similarity issues, and continuous turn of events) is considerably more expensive and included than supporting a website over time.
Advantages of the Mobile Application over Web Application
While businesses with enormous wallets can utilize both mobile application vs web application, different companies may need to pick one. The decision between mobile application vs web application relies upon their expense, ease of use, required highlights, and the crowd they serve.
That being said, research show that clients prefer mobile application vs web application. This makes for a solid motivation to create mobile applications for contacting potential (and existing) customers.
Mobile Apps Offer Better Personalization
Personalization is tied in with offering custom-made correspondence to clients depending on their interests, location, and usage behavior, and that is just the beginning. With mobile applications, it is not difficult to treat clients with customized insight. Utilizing a mobile application A/B testing tool, you can likewise try out various experiences for your clients.
Mobile applications can allow clients to set up their preferences toward the beginning, based on which clients can be presented with modified substances. Applications can likewise follow and notice client engagement and submit custom suggestions and updates to the customers. Moreover, they can similarly distinguish the area of the clients progressively to give topography explicit substance.
Ease of Sending Notifications
For the last few decades, email has been the most generally utilized specialized business tool. Organizations have widely used email (some nearly engaged with it) to contact their clients. Therefore, email has lost the adequacy it once had; it’s open rates and snap rates have continually dropped.
Making Use of Smartphone’s Utilities
Mobile applications have the upside of using highlights of a cell phone like a camera, contact list, GPS, calls, accelerometer, compass, and so forth. Such device features, when utilized inside an application, can make the client experience intuitive and fun.

Additionally, these features can likewise diminish the efforts customers would need to make in any case. For example, clients finishing a banking application structure may have to present their photos to complete the process. The application can allow clients to take their cell phone camera to catch and submit a photo. The device features can essentially shorten the time customers take to play out a specific task in an application and even boost conversions.
Ability to Work Offline
It is presumably the most fundamental difference between a mobile application vs web application. Although applications also may require web availability to perform a large portion of their assignments, they can, in any case, offer essential substance and usefulness to clients in disconnected mode.
How about we take the case of a banking application once more? The application can give highlights like duty estimation, portion computation, and assurance of credit limit. These features can work even without the assistance of a web association.
Freedom in Designing
Indeed, even with every one of the mechanical progressions in web planning, versatile sites need to depend a great deal on programs to perform even the most rudimentary capacities. Mobile sites rely upon program highlights like the back button, refresh button, and address bar to work. Mobile Apps do not have any of these limitations.
New Branding Experience
Since a mobile application is unmistakable from an organization’s website, it has the freedom to offer another marketing experience to clients. It implies that the organization can try different things with new marking styles for the application, which can be not quite the same as the normal brand style of the organization’s site (or the organization altogether).
Going a step further, businesses can assemble portable applications explicitly to progress into another brand style for themselves. Furthermore, a mobile application can likewise permit clients to customize its appearance, as customers would prefer. This can additionally help in the personalization front of the application.
Mobile Application vs. Web Application: Which One Is for You?
When deciding between a mobile application and a web application, it’s important to consider your specific needs, target audience, and the functionality you require. Here’s a comparison to help you make an informed decision.
User Context and Purposes
Understanding the context and purpose of users is crucial in deciding between a web and a mobile application. Web resources provide a wealth of information, typically accessed from a stationary, seated position. This environment is conducive to longer user sessions and detailed interactions. Conversely, mobile devices cater to on-the-go access, offering quick information retrieval and shorter usage periods.
In mobile UX design, the focus is on simplicity and intuitiveness. The navigation should be straightforward, with concise, well-structured code and a clear visual hierarchy. Design elements like natural gestures for small screens, simplified menu options, clear visual pathways, consistent UI elements like fonts and colors, and easily accessible buttons and links are key. These elements should be aligned with accessibility standards to ensure the app’s functionality is available to all users.
The choice between a web or mobile app hinges on the user’s context. Web apps excel in environments suited for longer engagement, like research or extensive reading.
On the other hand, a mobile app is more appropriate for products requiring regular, brief interactions, such as habit tracking, mobile eCommerce, or social media apps. This distinction is pivotal in ensuring that the chosen platform aligns with the users’ needs and the intended purpose of the app.
Screen Size Requirements
The assessment of screen size requirements for your product or service, especially in the context of B2B tools, plays a pivotal role in determining whether a web-based platform is more suitable than a mobile application. The growing trend of web-based B2B tools accessible via various devices, including phones, tablets, and desktop computers, brings several advantages:
- Accessibility Across Devices: Web-based tools allow users to access information quickly and conveniently, regardless of the device they are using. This flexibility ensures that users are not limited to a particular device, enhancing the overall accessibility of the tool.
- Advantage of Larger Screens: On larger screens, such as those of desktop computers, content can be viewed more clearly and in greater detail. This is particularly beneficial for B2B applications where complex data and visuals are common. The clarity and space offered by larger screens enhance the user experience, especially when dealing with detailed information.
- Efficiency in Handling Data-Intensive Tasks: For tasks like downloading or exporting PDFs, a desktop environment is more efficient. PDFs can consume significant data space on mobile devices, and frequent downloads could lead to storage issues. Additionally, viewing and interacting with PDFs is often more convenient on a larger screen.
- Centralized Data Storage: Users may prefer to keep their files on a single machine rather than having them spread across multiple devices. This preference for centralized data storage is catered to effectively by web-based applications.
- Enhancing User Experience: By allowing access to larger screens, companies can ensure a consistently positive user experience. Mobile screens may not always be the best medium for displaying complex content clearly, which is crucial in B2B interactions involving charts, analytical data, and frequent navigation between screens.
In conclusion, web apps are particularly suitable for complex, work-related applications that require detailed data analysis and frequent interaction with substantial content. The flexibility and efficiency offered by web apps in handling such tasks make them a preferred choice in the B2B domain.
Features of Used Devices
For businesses like beauty product sales, developing a mobile app is particularly beneficial due to the extensive time people spend on their mobile devices. This platform not only provides a larger audience but also allows for the utilization of features unique to mobile devices, such as high-resolution cameras. In the beauty industry, the quality of images is crucial for market success, and mobile devices excel in providing superior camera quality.
While a web-based application accessible on mobile can use the device’s camera, it doesn’t fully leverage other mobile-specific hardware and functionalities. Features like a phone’s built-in gyroscope or GPS, which could be critical for apps in other sectors like fitness or navigation, are more effectively integrated into mobile apps.

In designing a mobile app, especially for a visually-driven industry, incorporating device-specific elements in the UX/UI design is key. This includes larger interactive buttons and streamlined navigation suited for smaller screens.
Collaboration with your software development team is crucial to ensure seamless integration with third-party apps, which could include social media, online payment methods, and push notifications, depending on your product’s needs.
In essence, mobile apps offer the significant advantage of tapping into device-specific hardware and features, like GPS and high-resolution cameras, enhancing the user experience and potentially contributing to the success of the product.
Research Your Competitor
Analyzing the competitive landscape is a vital step for businesses planning to launch a new product or app. This analysis helps in making an informed decision about the development platform – whether to opt for a mobile or web-based application.
If the majority of top players in your market are utilizing web-based solutions, it often indicates that this platform meets the users’ needs effectively. These competitors have likely tailored their user experience (UX) to enable users to achieve their goals efficiently, contributing to their market success. The popularity and widespread adoption of their platforms suggest that users find them convenient and user-friendly.
It’s important to remember that users often appreciate familiarity, especially within the same product category. If potential users are already accustomed to web-based solutions from your competitors, introducing a similar platform can ease their transition to your app. This familiarity can be a significant advantage in encouraging users to switch to your product.
Conducting thorough research on competitors not only identifies what’s working well in the market but also highlights potential opportunities and risks. This insight is crucial before investing in the development of a new app.
Final thought
As mobile use keeps on rising worldwide, the “mobile application vs web application” question will remain an undeniable thought for associations looking to build up a mobile presence. If your mobile objectives are essentially promoting driven, or if your goal is to communicate information and establish a large mobile firm that can be easily maintained. Such a thing is divided among clients and found on web indexes. At that point, a mobile-friendly, responsive site is a sensible decision.
If you’re interested in mobile app development, you should Check out our Mininest module, which is a free mobile app builder that allows you to quickly and easily transform your whole eCommerce website into a native mobile app. Mininest will provide you with the most comprehensive option for developing your own Magento 2 mobile application in only a few hours!
Contact us now to have more information about this excellent module!