The concept of omnichannel logistics has evolved significantly over the years. Historically, businesses operated in silos, with separate channels for in-store and online sales. This often led to inefficiencies and inconsistencies in inventory management and customer service. However, with the advent of advanced technologies and the growing expectation for instant gratification, companies began to realize the importance of a unified approach.
Key milestones in the evolution of omnichannel logistics include the integration of real-time inventory tracking systems, the development of sophisticated order management software, and the rise of innovative delivery solutions such as same-day delivery and buy-online-pick-up-in-store (BOPIS) options.
Today, omnichannel logistics is a necessity for businesses aiming to thrive in the digital age. The ability to provide a seamless and efficient shopping experience across all channels is crucial for retaining customer loyalty and driving growth. As we delve deeper into the intricacies of omnichannel logistics, we will explore its core components, strategies, challenges, and future trends, offering a comprehensive guide to mastering this essential aspect of supply chain management.
Table of Contents
Understanding Omnichannel Logistics
Core Concepts and Principles
Integration of Multiple Channels
The primary principle of omnichannel logistics is the integration of multiple distribution channels to create a unified and coherent system. This integration ensures that customers have a consistent experience regardless of the platform they use to interact with a brand. Omnichannel logistics necessitates a centralized inventory management system that provides real-time visibility across all channels. This means that whether a product is available in a physical store, an online shop, or a mobile app, the inventory data is synchronized to reflect accurate stock levels. This unified approach helps prevent issues like stockouts and overstocking, ensuring that customers can always find the products they need.
With omnichannel logistics, order fulfillment is no longer confined to a single channel. Customers can place an order online and choose to pick it up in-store (BOPIS), or they can return online purchases to a physical location (BORIS). This flexibility requires a robust logistics network capable of coordinating orders across multiple fulfillment centers and retail locations. Effective coordination reduces delivery times and enhances the overall customer experience. Data integration is at the heart of omnichannel logistics. By consolidating data from various channels, businesses gain valuable insights into customer preferences and purchasing behaviors. This data-driven approach allows companies to personalize their offerings and tailor marketing strategies to meet the specific needs of their customers.
Effective communication between different channels is essential for the success of omnichannel logistics. This involves not only the technical integration of systems but also the alignment of business processes and teams. Streamlined communication ensures that all stakeholders, from warehouse managers to customer service representatives, have access to the same information, enabling them to provide consistent and accurate service.
Seamless Customer Experience
The ultimate goal of omnichannel logistics is to provide a seamless customer experience. This means that customers should be able to transition effortlessly between different channels without any disruption or inconsistency. Omnichannel logistics ensures that the brand experience remains consistent across all touchpoints. Whether a customer is browsing a website, visiting a physical store, or using a mobile app, the brand’s messaging, visual identity, and service quality should be uniform. Consistency builds trust and reinforces brand loyalty, making customers more likely to return for future purchases.
By leveraging data from various channels, omnichannel logistics enables businesses to offer personalized interactions. For example, if a customer frequently purchases a particular product online, the system can recommend complementary items or notify them of related promotions when they visit a store. Personalization enhances the customer experience by making it more relevant and engaging, ultimately driving higher conversion rates. Flexibility is a cornerstone of the seamless experience offered by omnichannel logistics. Customers should have the option to choose how and where they want to shop, pay, and receive their orders. Offering various fulfillment options, such as home delivery, in-store pickup, and same-day shipping, caters to the diverse preferences of customers and enhances their convenience.
Returns are an inevitable part of retail, and omnichannel logistics makes the process more convenient for customers. By allowing returns across different channels, businesses can improve customer satisfaction and loyalty. An efficient returns management system not only simplifies the process for customers but also helps businesses manage inventory more effectively by quickly reintegrating returned items into the supply chain. Providing real-time support is critical for maintaining a seamless customer experience. With omnichannel logistics, customer service teams have access to comprehensive data from all channels, enabling them to resolve issues quickly and accurately. Whether through chatbots, phone support, or in-store assistance, prompt and effective customer support enhances the overall shopping experience and fosters positive relationships.
Key Components
Inventory Management
Inventory management is the backbone of omnichannel logistics. It involves the processes and systems used to track and manage stock levels across multiple channels. Effective inventory management ensures that customers can access the products they want, whether they are shopping online, in-store, or through a mobile app. One of the essential elements of omnichannel logistics is real-time inventory tracking. This involves using advanced technologies such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and IoT (Internet of Things) devices to monitor stock levels continuously. Real-time tracking provides accurate and up-to-date information on inventory levels across all channels, reducing the risk of stockouts and overstocking.
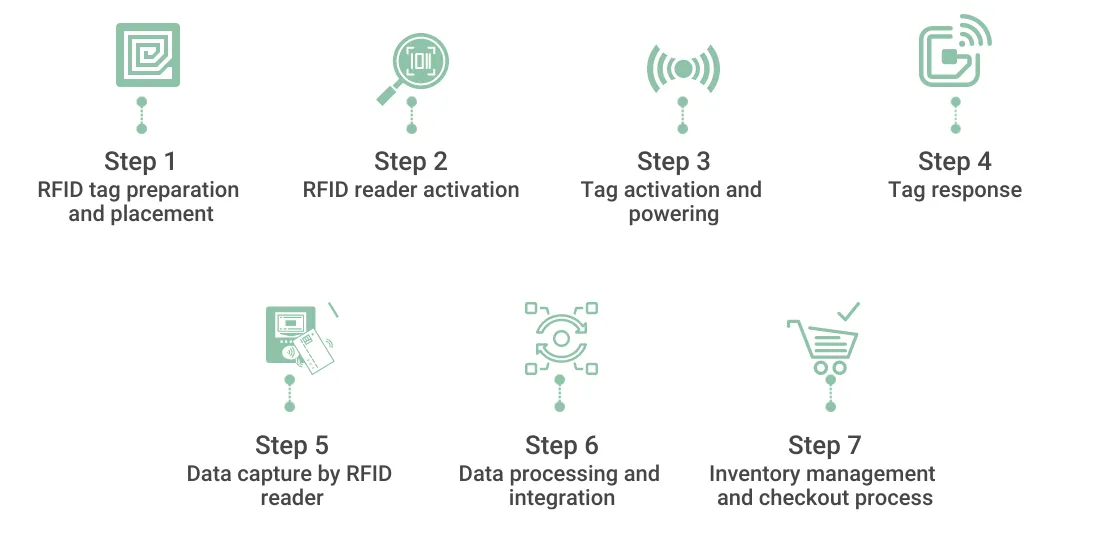
In omnichannel logistics, inventory is often distributed across multiple locations, including warehouses, distribution centers, and retail stores. This distribution helps to shorten delivery times and improve the overall customer experience. A distributed inventory system requires sophisticated software that can manage and optimize stock levels at each location, ensuring that products are available where they are most needed. Inventory optimization involves balancing stock levels to meet customer demand while minimizing holding costs. Techniques such as demand forecasting, safety stock calculation, and just-in-time inventory are used to achieve this balance. Effective inventory optimization in omnichannel logistics helps to reduce excess inventory, lower costs, and improve cash flow.
Handling returns efficiently is a critical part of inventory management in omnichannel logistics. Returns must be processed quickly and accurately to ensure that returned products are reintegrated into the inventory system and made available for resale as soon as possible. A robust returns management process enhances customer satisfaction and helps to maintain accurate inventory levels.
Transportation and Distribution
Transportation and distribution are vital components of omnichannel logistics, as they determine how products move from suppliers to warehouses, and ultimately to customers. Efficient transportation and distribution networks are essential for meeting customer expectations for fast and reliable delivery. Omnichannel logistics often involves the use of multiple transportation modes, such as trucks, trains, ships, and airplanes, to move products efficiently. Multi-modal transportation allows companies to choose the most cost-effective and timely shipping methods based on the specific needs of each order. This flexibility helps to reduce shipping costs and improve delivery times.
Many companies leverage third-party logistics providers (3PLs) to handle transportation and distribution tasks. 3PLs offer expertise, technology, and infrastructure that can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of omnichannel logistics. By outsourcing logistics functions to 3PLs, companies can focus on their core business activities while benefiting from the scale and capabilities of specialized logistics providers.
Distribution centers play a crucial role in omnichannel logistics by serving as hubs for storing and dispatching products. The layout, processes, and technologies used in distribution centers can significantly impact business efficiency. Technologies such as automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), conveyor belts, and warehouse management systems (WMS) help to streamline operations and reduce order processing times.
IT Systems
IT systems are the foundation of omnichannel logistics, enabling the integration and coordination of various components within the supply chain. These systems provide the tools and data needed to manage inventory, transportation, and distribution effectively. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate all aspects of a business’s operations, including inventory management, order processing, and financial management. In omnichannel logistics, ERP systems provide a unified platform for managing and optimizing the entire supply chain. By consolidating data from various channels, ERP systems enable real-time decision-making and improve overall efficiency.
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is specialized software designed to manage and optimize warehouse operations. In omnichannel logistics, WMS systems track inventory, manage order fulfillment, and coordinate the movement of goods within the warehouse. Advanced WMS features, such as real-time inventory tracking, automated picking and packing, and integration with other supply chain systems, enhance operational efficiency and accuracy. An Order Management System (OMS) is crucial for managing orders across multiple channels in omnichannel logistics. It ensures that orders are processed accurately and efficiently, regardless of the channel through which they are placed. OMS systems provide real-time visibility into order status, inventory levels, and customer information, enabling companies to fulfill orders quickly and accurately.

A Transportation Management System (TMS) is used to plan, execute, and optimize the transportation of goods. In omnichannel logistics, TMS systems help to manage shipping routes, carrier selection, and freight costs. By providing real-time tracking and analytics, TMS systems enable companies to improve delivery performance and reduce transportation costs. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are essential for managing customer interactions and data. In omnichannel logistics, CRM systems provide insights into customer preferences and behaviors, enabling companies to offer personalized experiences and improve customer satisfaction. Integrating CRM systems with other logistics systems ensures that customer data is consistent and accessible across all channels.
Omnichannel Logistics Strategies
Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is a cornerstone of omnichannel logistics, enabling retailers to maintain optimal stock levels, reduce costs, and enhance the customer experience.
Real-Time Inventory Tracking
Real-time inventory tracking is essential for the success of omnichannel logistics. It involves continuously monitoring and updating inventory levels across all sales channels and fulfillment locations. This strategy ensures that inventory data is always accurate and up-to-date, providing numerous benefits.
Real-time inventory tracking provides enhanced accuracy and visibility across the entire supply chain. By continuously updating inventory levels, retailers can avoid stockouts and overstock situations, which can lead to lost sales and increased holding costs. This level of accuracy is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction, as it ensures that products are available when and where customers need them. Real-time visibility allows retailers to quickly identify inventory discrepancies and take corrective actions, ensuring a smooth and efficient supply chain.
Moreover, real-time inventory tracking significantly improves the customer experience. Accurate inventory information allows customers to see real-time product availability when shopping online or in-store, building trust and enhancing the shopping experience. Customers can confidently make purchasing decisions knowing that the products they want are in stock. This transparency also supports features like Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store (BOPIS) and Buy Online, Return In-Store (BORIS), which offer added convenience and flexibility. Real-time tracking also enables better management of promotional activities, ensuring that advertised products are available and reducing the risk of customer disappointment.
Additionally, real-time inventory tracking enhances operational efficiency. By providing a continuous flow of accurate data, retailers can optimize their replenishment processes, ensuring that inventory levels are maintained at optimal levels without overstocking. This efficiency extends to order fulfillment, where real-time tracking enables quicker response times and more accurate order picking, packing, and shipping. Ultimately, real-time inventory tracking is a critical component of omnichannel logistics, driving accuracy, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
Distributed Inventory Systems
Distributed inventory systems are another vital element of omnichannel logistics, allowing retailers to strategically position their inventory across multiple locations to meet customer demand efficiently. This approach involves managing inventory in various warehouses, distribution centers, and even retail stores, rather than relying on a central warehouse. The benefits of distributed inventory systems are numerous and significant:
One of the primary advantages of distributed inventory systems is the ability to reduce delivery times and costs. By positioning inventory closer to the end customer, retailers can offer faster delivery options and reduce shipping costs. This proximity is particularly important in the context of omnichannel logistics, where customers expect quick and reliable delivery. Distributed inventory systems enable retailers to fulfill orders from the nearest location, whether it’s a warehouse or a physical store, enhancing delivery speed and efficiency.
Furthermore, distributed inventory systems improve stock availability and reduce the risk of stockouts. By spreading inventory across multiple locations, retailers can better balance stock levels and ensure that products are available where they are needed most. This distribution helps to mitigate the impact of supply chain disruptions, as inventory can be rerouted from one location to another to meet demand. In omnichannel logistics, this flexibility is crucial for maintaining a consistent customer experience across all channels.

In addition to enhancing delivery speed and stock availability, distributed inventory systems support advanced fulfillment strategies such as ship-from-store and in-store pickup. These strategies leverage the physical retail network to fulfill online orders, providing customers with more options and improving the utilization of store inventory. For example, ship-from-store allows retailers to use their stores as mini-distribution centers, reducing the reliance on centralized warehouses and speeding up delivery times. In-store pickup, on the other hand, offers customers the convenience of picking up their online orders at a nearby store, further enhancing the omnichannel experience.
Distributed inventory systems also contribute to better demand forecasting and inventory planning. By analyzing data from multiple locations, retailers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of customer demand patterns and adjust their inventory strategies accordingly. This data-driven approach enables more accurate forecasting, optimized stock levels, and reduced excess inventory. In the context of omnichannel logistics, effective demand forecasting and inventory planning are essential for meeting customer expectations and maintaining operational efficiency.
Order Fulfillment
Order fulfillment is a critical aspect of omnichannel logistics, encompassing all the processes involved in receiving, processing, and delivering customer orders. Effective order fulfillment strategies ensure that customers receive their purchases promptly and accurately, regardless of the sales channel they use. Two key strategies in omnichannel order fulfillment are cross-channel order management and flexible fulfillment options like BOPIS (Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store) and BORIS (Buy Online, Return In-Store).
Cross-Channel Order Management
Cross-channel order management is a vital component of omnichannel logistics, as it integrates orders from various sales channels into a single, cohesive system. This integration allows retailers to manage orders efficiently, ensuring that customers receive a consistent experience no matter where they shop. Cross-channel order management involves several critical elements:
First, it provides a unified view of all customer orders, regardless of the channel through which they are placed. This means that orders from the online store, mobile app, and physical stores are consolidated into a single system. This unified view allows retailers to track and manage orders more effectively, ensuring that each order is processed promptly and accurately. By having a centralized order management system, retailers can minimize errors, reduce delays, and improve overall efficiency.
Second, cross-channel order management enables seamless inventory synchronization. Accurate inventory data is crucial for fulfilling orders correctly and preventing stockouts or overselling. By synchronizing inventory across all channels, retailers can ensure that the products listed as available online are truly in stock. This synchronization also supports more efficient inventory allocation, allowing retailers to fulfill orders from the most appropriate location, whether it’s a warehouse, distribution center, or retail store.
Third, cross-channel order management enhances customer service by providing comprehensive order visibility. Customer service representatives can access detailed information about order status, history, and any issues that may arise. This visibility allows them to assist customers more effectively, providing real-time updates and resolving problems quickly. Improved customer service leads to higher satisfaction levels and increased loyalty, which are critical for long-term business success.
Finally, cross-channel order management supports advanced fulfillment options, such as drop shipping and ship-from-store. Drop shipping allows retailers to fulfill orders directly from the supplier, reducing the need for inventory storage and handling. Ship-from-store leverages the existing retail network to fulfill online orders from nearby stores, reducing delivery times and costs. These advanced fulfillment options enhance flexibility and responsiveness, key attributes of effective omnichannel logistics.
BOPIS and BORIS
BOPIS and BORIS are innovative fulfillment options that exemplify the flexibility and customer-centric nature of omnichannel logistics. These options provide customers with greater convenience and choice, enhancing their overall shopping experience.
BOPIS is a popular fulfillment method that allows customers to purchase products online and pick them up at a physical store. This option offers several benefits for both retailers and customers. For customers, BOPIS provides the convenience of shopping online without the wait for shipping. They can pick up their purchases at a time that suits them, often on the same day. This immediacy is particularly appealing for urgent or last-minute purchases. For retailers, BOPIS drives foot traffic to physical stores, creating opportunities for additional sales. Customers who come to pick up their orders may browse the store and make additional purchases, increasing the overall transaction value.
Implementing BOPIS requires seamless integration between online and in-store systems. Retailers must ensure that their inventory is accurately reflected across all channels and that the store staff can quickly locate and prepare the items for pickup. Clear communication with customers is also essential, providing them with precise instructions on where and how to pick up their orders. A well-executed BOPIS program enhances customer satisfaction by combining the convenience of online shopping with the immediacy of in-store pickup.
BORIS is another valuable fulfillment option that supports the flexibility of omnichannel logistics. It allows customers to return online purchases to a physical store, simplifying the returns process. This option offers significant convenience, as customers can avoid the hassle of shipping returns and waiting for refunds. For retailers, BORIS reduces the costs associated with handling returns and restocking inventory. It also provides an opportunity to engage with customers in-store, potentially converting a return into an exchange or additional purchase.

Effective implementation of BORIS requires robust systems to manage returns and reintegrate them into the inventory. Retailers must ensure that their return policies are clearly communicated and that the in-store staff is trained to handle returns efficiently. A smooth returns process enhances customer trust and loyalty, as it demonstrates the retailer’s commitment to customer satisfaction.
Warehousing Solutions
Warehousing solutions are a critical aspect of omnichannel logistics, ensuring that products are stored, managed, and dispatched efficiently to meet the demands of various sales channels. In the context of omnichannel logistics, warehousing must be flexible, responsive, and technologically advanced to handle the complexities of modern supply chains. Two key strategies in warehousing solutions include multi-purpose fulfillment centers and advanced warehousing technologies such as robotics and automation.
Multi-Purpose Fulfillment Centers
Multi-purpose fulfillment centers are essential for supporting the diverse requirements of omnichannel logistics. These centers are designed to handle a variety of tasks, including storing inventory, processing orders, and managing returns for multiple sales channels. By consolidating these functions into a single facility, retailers can achieve greater efficiency and flexibility in their operations.
One of the primary benefits of multi-purpose fulfillment centers is their ability to support multiple channels seamlessly. In traditional logistics models, separate facilities often handle different types of orders, such as online versus in-store purchases. However, in an omnichannel logistics framework, a multi-purpose fulfillment center can process orders from various channels simultaneously. This integration reduces the need for redundant infrastructure and streamlines operations, leading to cost savings and improved service levels.
Moreover, multi-purpose fulfillment centers enhance inventory management by providing a centralized location for stock. This centralization allows for better inventory visibility and control, enabling retailers to optimize stock levels and reduce the risk of overstocking or stockouts. Accurate inventory data is crucial for fulfilling orders promptly and accurately, which is a fundamental requirement of omnichannel logistics.
Additionally, these fulfillment centers are strategically located to minimize delivery times and costs. By placing fulfillment centers closer to major markets and customer hubs, retailers can reduce the distance products need to travel, enhancing delivery speed and reducing shipping expenses. This strategic placement is particularly important in omnichannel logistics, where customers expect rapid and reliable delivery options.
Multi-purpose fulfillment centers also facilitate efficient returns management, an essential aspect of omnichannel logistics. Handling returns in the same facility where orders are processed allows for quicker restocking and resale of returned items. This efficiency helps maintain accurate inventory levels and reduces the impact of returns on overall operations.
Advanced Warehousing Technologies
Advanced warehousing technologies, such as robotics and automation, play a pivotal role in optimizing omnichannel logistics. These technologies enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and speed of warehouse operations, enabling retailers to meet the high demands of modern consumers.
Robotics is transforming warehousing by automating repetitive and labor-intensive tasks. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are used to transport goods within the warehouse, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing throughput. These robots can navigate complex environments, avoid obstacles, and follow optimized paths, ensuring that products are moved quickly and efficiently from storage to picking areas.
Automation extends to various aspects of warehousing, including picking and packing processes. Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) use robotics to store and retrieve items from high-density storage racks, maximizing space utilization and minimizing retrieval times. These systems are particularly valuable in omnichannel logistics, where the rapid fulfillment of orders is crucial. Automated picking systems, such as robotic arms and conveyor belts, further enhance efficiency by accurately selecting and transporting items to packing stations.
Advanced warehousing technologies also include the use of AI and machine learning to optimize operations. AI-driven algorithms can analyze large volumes of data to forecast demand, optimize inventory placement, and improve order routing. In the context of omnichannel logistics, AI helps ensure that inventory is positioned in the most strategic locations, reducing delivery times and costs.
Another significant advancement is the implementation of warehouse management systems (WMS) that integrate with other supply chain systems. A WMS provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, order statuses, and warehouse activities, enabling better decision-making and coordination. In omnichannel logistics, a WMS ensures that all channels have accurate and up-to-date information, supporting seamless operations and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Automation also improves the accuracy and reliability of warehouse operations. Automated systems reduce the risk of human error in picking, packing, and shipping processes, ensuring that orders are fulfilled correctly and efficiently. This accuracy is vital in omnichannel logistics, where customer expectations for fast and flawless service are high.
Furthermore, advanced warehousing technologies contribute to better resource utilization and labor management. By automating routine tasks, warehouses can allocate human resources to more strategic and value-added activities, such as quality control and customer service. This shift enhances overall productivity and supports the scalability of omnichannel logistics operations.
Transportation and Delivery
Transportation and delivery are pivotal components of omnichannel logistics, ensuring that products reach customers efficiently and reliably across multiple channels. Effective transportation strategies enhance the overall customer experience, reduce costs, and address the complexities inherent in omnichannel logistics. This section explores two critical strategies: last-mile delivery innovations and the use of third-party logistics providers (3PLs).
Last-Mile Delivery Innovations
Last-mile delivery, the final step in the transportation process where products are delivered to the customer’s doorstep, is a crucial aspect of omnichannel logistics. Innovations in this area are essential to meet the increasing demands for speed, reliability, and flexibility. Last-mile delivery innovations include a range of technologies and approaches designed to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction.
One significant innovation in last-mile delivery is the use of autonomous delivery vehicles, such as drones and self-driving cars. These technologies can dramatically reduce delivery times, especially in urban areas with high traffic congestion. For example, companies like Amazon and UPS are experimenting with drone deliveries to provide rapid and cost-effective service for smaller packages. This approach not only speeds up the delivery process but also reduces the environmental impact by minimizing the need for traditional delivery vehicles.
Another key development is the implementation of smart lockers and pickup points. Retailers and logistics providers are increasingly using smart lockers, located in convenient locations like shopping centers and transportation hubs, to facilitate easy and secure package pickups. Customers receive a code to access their lockers and retrieve their orders at their convenience, eliminating the need to wait at home for deliveries. This innovation is particularly useful in omnichannel retail logistics, where customers expect flexible and convenient delivery options.
Real-time tracking and delivery updates are also crucial for improving last-mile delivery. Advanced GPS and mobile technology allow customers to track their packages in real-time, providing greater transparency and reducing anxiety about delivery times. Retailers can send automated notifications to keep customers informed about the status of their deliveries, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Crowdsourced delivery is another innovative approach gaining traction in omnichannel logistics. Companies like Uber and Postmates utilize a network of independent drivers to perform deliveries. This model leverages existing transportation infrastructure and provides a scalable solution to meet fluctuating delivery demands. Crowdsourced delivery can be particularly effective during peak shopping periods, such as holidays and sales events, when traditional logistics networks may be overwhelmed.
However, last-mile delivery innovations also present several omnichannel logistics challenges. Integrating these new technologies with existing logistics systems can be complex and costly. Ensuring the reliability and safety of autonomous vehicles and drones requires significant investment in infrastructure and regulatory compliance. Additionally, managing crowdsourced delivery networks poses challenges related to consistency and quality control.
Use of Third-Party Logistics Providers (3PLs)
The use of 3PLs is a strategic approach to enhancing omnichannel logistics. 3PLs offer specialized expertise, advanced technology, and scalable solutions that can help retailers manage the complexities of transportation and delivery more effectively. Partnering with 3PLs provides several benefits and addresses key challenges in omnichannel logistics.
One of the primary advantages of using 3PLs is their ability to offer comprehensive logistics services, including warehousing, transportation, and distribution. By outsourcing these functions to 3PLs, retailers can focus on their core business activities while leveraging the expertise and infrastructure of their logistics partners. This partnership is particularly beneficial in omnichannel logistics, where the integration of multiple channels requires sophisticated logistics capabilities.
3PLs provide access to advanced technology and systems that enhance transportation efficiency. For example, 3PLs often use state-of-the-art transportation management systems (TMS) to optimize routing, track shipments, and manage carrier relationships. These systems enable real-time visibility into the transportation network, allowing retailers to monitor deliveries, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions. The use of such technology is essential for meeting the demands of omnichannel retail logistics, where timely and accurate deliveries are crucial.
Another significant benefit of 3PLs is their ability to scale operations based on demand fluctuations. During peak seasons or promotional events, retailers may experience a surge in order volumes that can strain their logistics capabilities. 3PLs have the resources and flexibility to scale up their operations quickly, ensuring that customer orders are fulfilled without delays. This scalability is a key advantage in omnichannel logistics, where customer expectations for fast and reliable delivery are high.
3PLs also bring extensive industry knowledge and experience, helping retailers navigate the challenges of omnichannel logistics. For example, 3PLs can provide insights into the best practices for managing cross-border shipments, handling customs regulations, and optimizing last-mile delivery. Their expertise can help retailers improve their logistics processes, reduce costs, and enhance overall efficiency.
However, partnering with 3PLs also presents certain challenges in omnichannel logistics. One of the main concerns is the potential loss of control over the logistics process. Retailers must ensure that their 3PL partners adhere to their service standards and deliver a consistent customer experience. Effective communication and collaboration are essential to maintaining alignment between the retailer and the 3PL. Additionally, integrating the systems and processes of the retailer with those of the 3PL can be complex and require significant effort and coordination.
Technology and Integration
Technology and integration are the backbone of effective omnichannel logistics, ensuring that all aspects of the supply chain work seamlessly together. The role of big data and analytics and the integration of ERP and CRM systems are pivotal in creating a responsive and efficient logistics framework. This section explores how these technologies drive the success of omnichannel logistics.
Role of Big Data and Analytics
Big data and analytics play a crucial role in omnichannel logistics by providing the insights needed to optimize operations, improve customer experiences, and make informed decisions. In the context of what is omnichannel logistics, big data helps to answer this by offering a detailed understanding of customer behavior, supply chain performance, and market trends.
One of the primary applications of big data in omnichannel logistics is demand forecasting. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and customer preferences, retailers can predict future demand more accurately. This predictive capability allows for better inventory management, ensuring that the right products are available at the right time and place. For example, a retailer using big data analytics might identify an upcoming surge in demand for specific products during a holiday season and adjust their inventory levels accordingly, thus avoiding stockouts and overstock situations.
Another significant benefit of big data in omnichannel logistics is enhancing customer segmentation and personalization. Retailers can use data analytics to segment their customer base into distinct groups based on purchasing behavior, preferences, and demographics. This segmentation enables more targeted marketing efforts and personalized shopping experiences. For instance, a retailer might use data to identify customers who frequently purchase a particular type of product and offer them personalized promotions or recommendations, thereby increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Operational efficiency is also greatly improved through the application of big data analytics in omnichannel logistics. By monitoring and analyzing supply chain data in real time, retailers can identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in their operations. For example, analytics can reveal patterns in delivery delays, prompting investigations and solutions to improve delivery times. Additionally, big data can help optimize routing and transportation logistics, reducing costs and enhancing delivery speed.
Big data also plays a role in risk management within omnichannel logistics. By analyzing data from various sources, including weather forecasts, geopolitical events, and supplier performance, retailers can anticipate potential disruptions and develop contingency plans. For example, if analytics indicate a high risk of supply chain disruption due to an approaching storm, a retailer can proactively adjust their logistics strategy to mitigate the impact, such as rerouting shipments or increasing inventory levels in affected areas.
However, leveraging big data in omnichannel logistics comes with challenges. The vast amount of data generated by various channels and touchpoints can be overwhelming and requires robust data management and analysis tools. Additionally, ensuring data accuracy and consistency across the supply chain is critical for making reliable decisions. Data privacy and security are also major concerns, as retailers must protect sensitive customer and business information from breaches and misuse.
Integration of ERP and CRM Systems
The integration of ERP and CRM systems is fundamental to the success of omnichannel logistics. These systems provide a unified platform for managing various aspects of the supply chain and customer interactions, ensuring a seamless and efficient operation.
ERP systems are designed to manage and integrate core business processes, including inventory management, order processing, financial accounting, and human resources. In the context of omnichannel logistics, ERP systems play a vital role in coordinating and optimizing these processes across multiple channels. For instance, an ERP system can provide real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing retailers to manage stock more effectively and fulfill orders promptly. By integrating inventory data from online stores, physical stores, and distribution centers, ERP systems ensure that products are available where and when they are needed.
CRM systems, on the other hand, focus on managing customer relationships and interactions. In omnichannel logistics, CRM systems capture and analyze customer data from various touchpoints, such as online purchases, in-store transactions, and customer service interactions. This comprehensive view of customer behavior and preferences enables retailers to offer personalized experiences and improve customer satisfaction. For example, a CRM system might identify a customer who frequently buys certain products and automatically suggest related items or offer loyalty rewards.
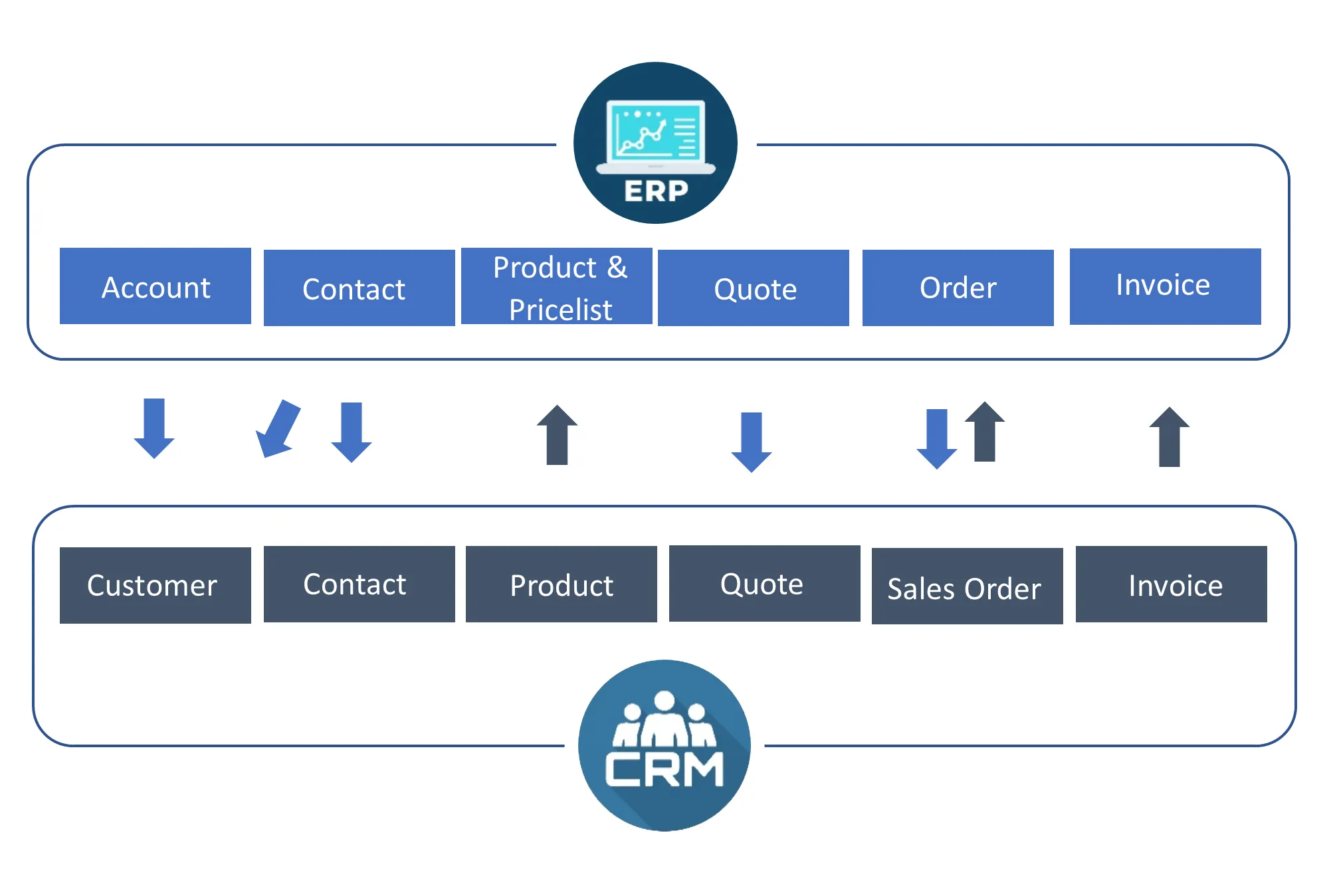
The integration of ERP and CRM systems is crucial for achieving a seamless omnichannel experience. When these systems are connected, data flows smoothly between them, providing a holistic view of both operations and customer interactions. This integration enables more efficient order management, as customer orders can be processed and tracked in real-time, regardless of the channel through which they are placed. For example, a customer might place an order online and choose to pick it up in-store (BOPIS). An integrated ERP and CRM system ensures that the order is processed accurately, the inventory is updated in real-time, and the customer receives timely notifications about the status of their order.
Moreover, the integration of ERP and CRM systems enhances decision-making capabilities in omnichannel logistics. By combining operational data from the ERP system with customer insights from the CRM system, retailers can make more informed decisions about inventory management, marketing strategies, and customer service. For instance, data from an ERP system might indicate a high demand for a particular product, while CRM data reveals that certain customer segments are most interested in this product. Retailers can use this combined information to adjust their inventory levels and tailor their marketing efforts to target the right customers.
However, integrating ERP and CRM systems presents several challenges in omnichannel logistics. Ensuring data consistency and accuracy across systems is critical, as discrepancies can lead to inefficiencies and errors. The integration process itself can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and execution. Additionally, retailers must address data privacy and security concerns, as integrating systems increases the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Challenges in Omnichannel Logistics
Businesses venturing into omnichannel retail must navigate significant challenges, especially in omnichannel logistics. From ensuring accurate inventory visibility and maintaining order accuracy to managing costs and integrating advanced technologies, these omnichannel logistics challenges must be addressed to achieve a seamless and efficient logistics operation.
Inventory Visibility
The ability to maintain accurate inventory levels and synchronize data across channels presents significant challenges that retailers must address to achieve a seamless omnichannel experience. Understanding these omnichannel logistics challenges and implementing effective solutions is crucial for the success of omnichannel logistics.
Maintaining Accurate Inventory Levels
Maintaining accurate inventory levels is one of the primary omnichannel logistics challenges. Accurate inventory data is essential for meeting customer demands, optimizing stock levels, and preventing both stockouts and overstock situations. However, achieving this accuracy is complex due to the multiple channels and touchpoints involved in omnichannel retail logistics.
One of the main difficulties in maintaining accurate inventory levels is the dynamic nature of customer orders. In an omnichannel environment, customers can place orders through various channels, such as online stores, physical stores, mobile apps, and social media platforms. Each of these channels draws from the same inventory pool, which can lead to discrepancies if the inventory data is not updated in real-time. For example, a customer might purchase the last available item online while another customer is purchasing the same item in-store, leading to overselling and customer dissatisfaction.
Another challenge is the variability in lead times and supply chain disruptions. Factors such as supplier delays, transportation issues, and seasonal demand fluctuations can affect inventory levels. Inaccurate forecasting and planning can exacerbate these issues, resulting in either excess inventory or stock shortages. For instance, during peak shopping periods like holidays, retailers might struggle to keep up with demand, leading to stockouts of popular items.
To address these challenges, retailers must implement robust inventory management systems that provide real-time visibility into stock levels across all channels. Advanced inventory management solutions, such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and IoT sensors, can track inventory movements accurately and provide up-to-the-minute data. These technologies enable retailers to monitor inventory levels continuously, reducing the risk of discrepancies and ensuring that the available stock reflects the actual inventory.
Additionally, demand forecasting tools that leverage big data and analytics can help retailers predict future inventory needs more accurately. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and customer behavior, these tools can generate reliable forecasts, allowing retailers to adjust their inventory levels proactively. For example, a retailer might use predictive analytics to anticipate increased demand for certain products during a seasonal promotion and adjust their stock levels accordingly.
Synchronizing Data Across Channels
Synchronizing data across channels is another significant challenge in omnichannel logistics. Effective synchronization ensures that inventory data, customer information, and order details are consistent and accurate across all platforms. This consistency is crucial for providing a seamless customer experience and maintaining operational efficiency.
One of the main obstacles to data synchronization is the integration of disparate systems. In many cases, retailers use different systems for managing their online stores, physical stores, warehouses, and distribution centers. These systems often operate independently, making it difficult to achieve real-time synchronization. For example, an order placed online might not immediately reflect in the inventory system used by physical stores, leading to discrepancies and potential overselling.
Another challenge is the complexity of managing returns and exchanges across multiple channels. In an omnichannel environment, customers expect to be able to return or exchange products through any channel, regardless of where the original purchase was made. This flexibility requires seamless data synchronization to ensure that inventory levels are updated accurately and returns are processed efficiently. For instance, a customer might purchase an item online and return it in-store, requiring real-time updates to the inventory and order management systems.
To overcome these challenges, retailers need to invest in integrated systems that facilitate seamless data synchronization. ERP systems and centralized inventory management platforms can consolidate data from various channels, providing a unified view of inventory, orders, and customer information. These systems ensure that all channels have access to the same accurate and up-to-date data, reducing the risk of discrepancies and improving overall efficiency.
Implementing middleware solutions that enable data integration between different systems is another effective strategy. Middleware acts as a bridge, allowing disparate systems to communicate and share data in real-time. For example, a middleware solution can integrate the inventory management system with the e-commerce platform, ensuring that inventory updates are reflected immediately across all channels.
Cloud-based solutions also offer significant advantages for data synchronization in omnichannel logistics. Cloud platforms provide a scalable and flexible infrastructure that supports real-time data sharing and collaboration. Retailers can leverage cloud-based inventory management systems to synchronize data across all channels, ensuring that inventory levels, order statuses, and customer information are always accurate and consistent. For instance, a cloud-based system can update inventory levels in real-time as orders are placed, reducing the risk of overselling and improving customer satisfaction.
Moreover, adopting standardized data formats and communication protocols can enhance data synchronization. Standardization ensures that data can be easily shared and interpreted across different systems, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies. For example, using standardized barcodes and product identifiers can streamline the process of updating inventory levels and tracking orders across multiple channels.
Order Accuracy
Order accuracy is a critical aspect of omnichannel logistics, directly impacting customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. Ensuring that orders are fulfilled correctly and delivered on time is paramount in a retail environment where customers expect seamless and error-free experiences. However, achieving high order accuracy in omnichannel logistics presents several challenges that retailers must navigate effectively.
Reducing Errors in Order Fulfillment
One of the significant omnichannel logistics challenges is reducing errors in order fulfillment. Errors can occur at various stages of the fulfillment process, including picking, packing, and shipping. These errors can lead to incorrect or incomplete orders, resulting in customer dissatisfaction and increased return rates. Understanding what is omnichannel logistics and the complexities involved is essential for implementing strategies to minimize these errors.
To reduce errors in order fulfillment, retailers need to invest in advanced technologies and automation. Automated picking systems, such as robotic pickers and conveyor belts, can significantly enhance accuracy by reducing human error. These systems are designed to select and move items efficiently, ensuring that the correct products are picked for each order. For example, Amazon’s fulfillment centers use a combination of robots and human workers to optimize the picking process, achieving high levels of accuracy and efficiency.
Another effective strategy is the implementation of barcode scanning and RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology. These technologies provide real-time tracking and verification of items throughout the fulfillment process. For instance, workers can use barcode scanners to verify that the correct items are being picked and packed, reducing the likelihood of errors. RFID tags can track items automatically, providing an additional layer of accuracy and ensuring that each order contains the correct products.
Training and process optimization are also crucial for reducing errors in order fulfillment. Retailers must train their staff on best practices and standard operating procedures to minimize mistakes. Regular audits and quality checks can help identify and address any issues in the fulfillment process. For example, implementing a double-check system where two workers verify the contents of an order before it is shipped can significantly reduce errors.
Additionally, leveraging data analytics can help identify patterns and root causes of fulfillment errors. By analyzing data on order accuracy and fulfillment processes, retailers can pinpoint areas for improvement and implement targeted solutions. For instance, if data analysis reveals that a particular product category has a higher error rate, retailers can investigate and address the specific issues contributing to these errors.
Ensuring Timely Deliveries
Ensuring timely deliveries is another one of critical omnichannel logistics challenges. Customers increasingly expect fast and reliable delivery options, and delays can lead to dissatisfaction and lost sales. Meeting these expectations requires efficient coordination and execution across the entire supply chain.
One of the primary strategies for ensuring timely deliveries is optimizing transportation and distribution networks. Retailers must strategically locate warehouses and distribution centers close to major markets to reduce transit times. For example, retailers like Walmart and Target have invested in regional distribution centers to facilitate faster deliveries and support their omnichannel retail logistics strategies.
Investing in advanced transportation management systems (TMS) is also essential for ensuring timely deliveries. A TMS provides real-time visibility into the transportation network, enabling retailers to monitor shipments, optimize routes, and manage carrier relationships. This visibility allows for proactive management of potential delays and disruptions, ensuring that deliveries remain on schedule. For instance, a TMS can reroute shipments in real-time to avoid traffic congestion or adverse weather conditions, minimizing delays.
Collaboration with reliable logistics partners is another crucial factor in ensuring timely deliveries. Third-party logistics providers (3PLs) can offer expertise, infrastructure, and flexibility to support timely fulfillment and delivery. By partnering with 3PLs, retailers can leverage their established networks and capabilities to meet customer delivery expectations. For example, collaborating with a 3PL that specializes in last-mile delivery can enhance delivery speed and reliability, particularly in urban areas.
Implementing dynamic delivery options, such as same-day or next-day delivery, is also becoming increasingly important in omnichannel logistics. Retailers can use advanced algorithms and data analytics to optimize these delivery options, balancing speed and cost. For instance, offering same-day delivery for high-priority items or leveraging local inventory to fulfill orders quickly can improve delivery performance and customer satisfaction.
Another key aspect of ensuring timely deliveries is effective communication with customers. Providing real-time tracking and delivery updates keeps customers informed about the status of their orders and helps manage expectations. For example, sending automated notifications at key stages of the delivery process, such as when the order is shipped and when it is out for delivery, can enhance the customer experience and reduce anxiety about potential delays.
However, ensuring timely deliveries also presents challenges in omnichannel logistics. Balancing cost and speed is a constant challenge, as faster delivery options often come with higher costs. Retailers must find a balance that meets customer expectations without eroding profit margins. Additionally, managing peak demand periods, such as holidays and promotional events, requires careful planning and resource allocation to maintain delivery performance.
Technology Integration
Technology integration is one of the fundamental omnichannel logistics challenges, where the goal is to create a seamless and efficient operation by integrating various systems and technologies. This integration is essential for achieving the synchronization and coordination necessary for omnichannel retail logistics. However, it presents significant challenges, particularly in terms of the compatibility of legacy systems with new technologies and ensuring data security and privacy.
Compatibility of Legacy Systems with New Technologies
One of the most significant omnichannel logistics challenges is ensuring the compatibility of legacy systems with new technologies. Many retailers operate with a mix of older, legacy systems and newer, advanced technologies. These legacy systems, which may include outdated inventory management, order processing, and warehouse management systems, often lack the flexibility and interoperability needed to integrate with modern solutions.
The challenge begins with understanding what is omnichannel logistics and the need for a unified approach across all channels. For instance, a retailer with an established brick-and-mortar presence might have used a traditional inventory system for years. When the retailer expands into e-commerce, they need a system that can handle online orders, real-time inventory updates, and multi-channel fulfillment. However, integrating a modern e-commerce platform with a legacy inventory system can be complex and costly.
Legacy systems are typically not designed to communicate with newer technologies, leading to data silos and inefficiencies. For example, a retailer might face difficulties synchronizing inventory levels between their online store and physical locations if the systems do not share data seamlessly. This lack of integration can result in inaccurate inventory levels, overselling, and poor customer experiences.
To overcome these challenges, retailers need to invest in middleware solutions that facilitate communication between legacy systems and new technologies. Middleware acts as a bridge, enabling data to flow seamlessly between different systems. For example, a middleware solution can connect an old inventory management system with a new order management platform, ensuring that inventory levels are updated in real-time as orders are placed and fulfilled.
Another approach is to gradually upgrade or replace legacy systems with more flexible and scalable solutions. This process, known as system modernization, involves transitioning from outdated systems to modern, cloud-based platforms that can easily integrate with other technologies. For instance, a retailer might move from a traditional on-premise inventory system to a cloud-based ERP system that offers real-time data synchronization and advanced analytics.
Despite these solutions, the transition from legacy systems to new technologies is not without its challenges. The process can be time-consuming and expensive, requiring significant investment in technology and training. Additionally, there is a risk of disruption during the transition period, as employees and processes adjust to new systems. Retailers must carefully plan and manage the integration process to minimize these risks and ensure a smooth transition.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Data security and privacy concerns are paramount in omnichannel logistics, where the integration of various systems and technologies involves the handling of vast amounts of sensitive data. Retailers must ensure that customer data, transaction details, and business information are protected from breaches and unauthorized access. This challenge is compounded by the need to comply with various data protection regulations and standards.
Understanding the omnichannel logistics definition includes recognizing the importance of secure data management across all channels. As retailers collect and store data from online purchases, in-store transactions, mobile apps, and other sources, they must implement robust security measures to protect this information. For example, an e-commerce platform must safeguard customer payment details, while a CRM system must secure personal information such as names, addresses, and purchase histories.
One of the main challenges in data security is protecting against cyber threats. Retailers are prime targets for cyberattacks, including data breaches, ransomware, and phishing attacks. These threats can compromise sensitive data, disrupt operations, and damage the retailer’s reputation. To mitigate these risks, retailers must implement comprehensive cybersecurity strategies, including firewalls, encryption, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.
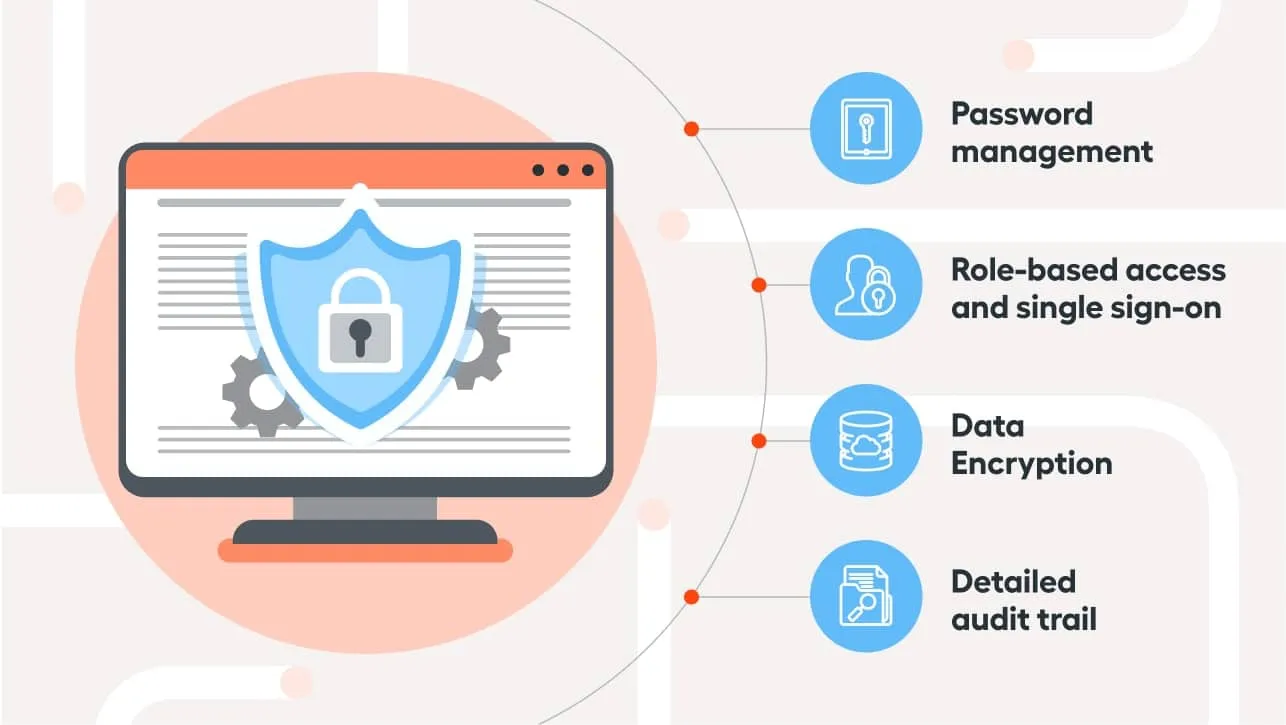
Data privacy concerns are also critical in omnichannel logistics. Retailers must comply with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. These regulations impose strict requirements on how retailers collect, store, and use personal data. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal repercussions.
To address data privacy concerns, retailers must implement policies and practices that ensure the responsible handling of customer data. This includes obtaining explicit consent from customers for data collection, providing transparency about data usage, and allowing customers to access and delete their data upon request. For example, a retailer should clearly inform customers how their data will be used when they sign up for a loyalty program or make an online purchase.
Another key aspect of data security and privacy is ensuring that all integrated systems comply with security standards. When integrating legacy systems with new technologies, retailers must ensure that data transferred between systems is encrypted and secure. For example, data transmitted between an online store and a warehouse management system should be encrypted to prevent interception by malicious actors.
Retailers must also consider the security of third-party vendors involved in their omnichannel logistics. Many retailers rely on third-party logistics providers, payment processors, and technology vendors to support their operations. It is crucial to ensure that these partners adhere to stringent security standards and practices. Retailers should conduct regular audits and assessments of their third-party vendors to identify and address potential security vulnerabilities.
Cost Management
Cost management is a critical challenge in omnichannel logistics, where retailers must balance costs with service quality and manage returns and reverse logistics effectively. As customers increasingly expect fast, reliable, and flexible delivery options, retailers face the daunting task of controlling expenses while maintaining high service standards. Understanding the nuances of cost management in omnichannel logistics is essential for achieving operational efficiency and profitability.
Balancing Costs with Service Quality
One of the primary challenges in omnichannel logistics is balancing costs with service quality. Retailers must offer superior customer service, including fast shipping, flexible delivery options, and excellent customer support, without incurring prohibitive costs. This balancing act is crucial to remain competitive in the retail market and retain customer loyalty.
To understand what omnichannel logistics is and its implications, it is essential to recognize that omnichannel logistics involves integrating multiple sales channels and optimizing the supply chain to provide a seamless customer experience. This integration often leads to increased complexity and higher costs. For example, offering same-day delivery or multiple delivery windows can significantly increase operational expenses due to the need for expedited shipping and additional resources.
One effective strategy for balancing costs with service quality is leveraging technology and automation. Automated systems, such as warehouse management systems (WMS) and transportation management systems (TMS), can streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve efficiency. For instance, a TMS can optimize delivery routes, reducing fuel consumption and labor costs while ensuring timely deliveries. Similarly, automation in warehousing, such as robotic picking and packing, can enhance productivity and reduce labor costs.
Another approach is to implement dynamic pricing and cost allocation models. Retailers can use data analytics to understand the cost implications of various delivery options and adjust pricing accordingly. For example, offering free shipping for standard delivery while charging a premium for expedited shipping can help balance service quality with cost management. Additionally, cost allocation models that distribute expenses across different sales channels based on their usage can provide more accurate cost control.
Collaborating with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) is also a viable strategy for managing costs. 3PLs offer expertise, infrastructure, and scalability that can help retailers manage logistics more cost-effectively. By outsourcing logistics functions to 3PLs, retailers can benefit from economies of scale and access advanced technologies without significant capital investment. For example, partnering with a 3PL for last-mile delivery can reduce delivery costs while maintaining high service standards.
Managing Returns and Reverse Logistics
Returns and reverse logistics are significant challenges in omnichannel logistics, often leading to increased costs and operational complexities. Efficiently managing returns is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and controlling expenses associated with reverse logistics.
Returns are an inevitable part of retail, particularly in omnichannel retail logistics where customers expect the flexibility to return products through any channel. The omnichannel logistics definition includes the seamless integration of returns management across all channels, ensuring that customers can return online purchases in-store or vice versa. This flexibility, while beneficial for customer experience, adds complexity to the logistics process.
One of the main challenges in managing returns is the cost associated with processing and handling returned items. Returns involve multiple steps, including receiving, inspecting, restocking, and potentially refurbishing or disposing of products. Each step incurs costs, such as labor, transportation, and inventory management. For example, a returned item purchased online might need to be shipped back to a central warehouse, inspected for damage, and then either restocked or discarded, all of which add to the overall cost.
To manage returns and reverse logistics effectively, retailers can implement several strategies. First, developing a robust returns management system (RMS) can streamline the process and reduce costs. An RMS can automate return authorizations, track return shipments, and manage inventory updates, ensuring that returned items are processed quickly and efficiently. For instance, an RMS can automatically generate return labels for customers, reducing the time and effort required for returns.
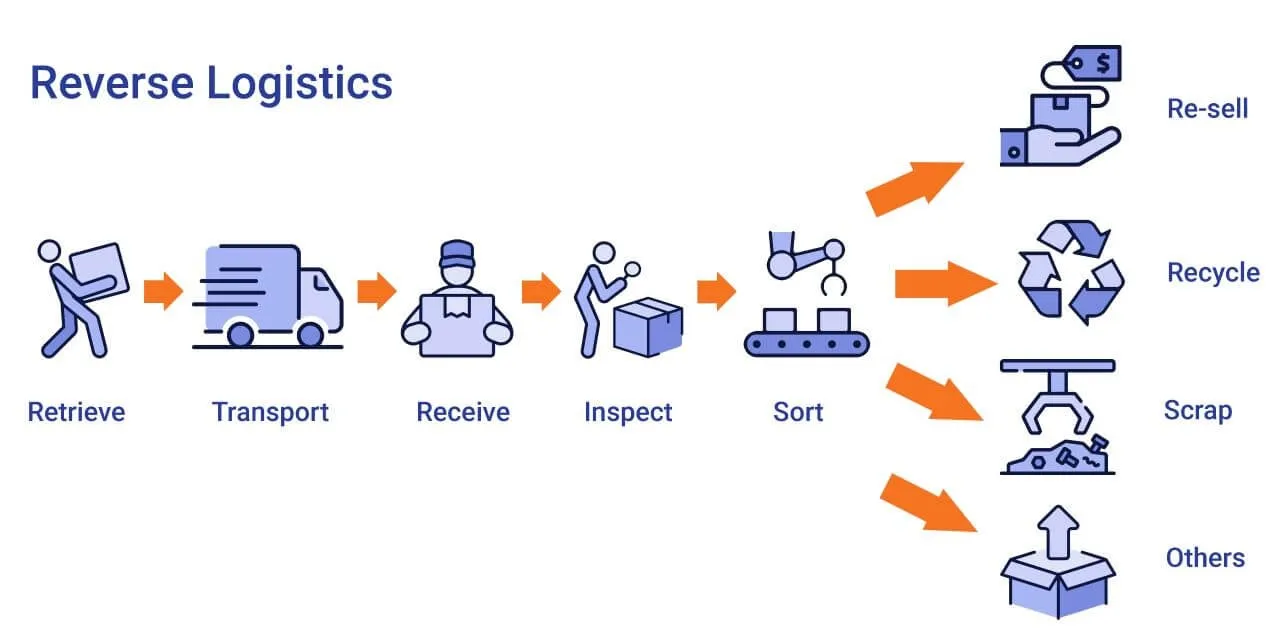
Second, optimizing the reverse logistics network is essential for minimizing costs. Retailers can strategically locate return processing centers close to major customer bases to reduce transportation costs and speed up the returns process. Additionally, leveraging 3PLs for reverse logistics can provide cost-effective solutions and expertise in handling returns. For example, a 3PL with specialized facilities for processing returns can manage the entire reverse logistics process, from receiving and inspecting returns to restocking and refurbishing products.
Third, implementing return reduction strategies can help manage costs by minimizing the volume of returns. Retailers can provide detailed product information, customer reviews, and virtual try-on solutions to help customers make informed purchasing decisions, reducing the likelihood of returns. Additionally, offering incentives for in-store returns can encourage customers to return items to physical locations, reducing transportation costs and enabling quicker restocking.
Data analytics plays a crucial role in managing returns and reverse logistics. By analyzing return patterns and customer behavior, retailers can identify common reasons for returns and address underlying issues. For example, if data reveals that a particular product has a high return rate due to sizing issues, retailers can adjust product descriptions or provide more accurate sizing information to reduce returns. Additionally, predictive analytics can help forecast return volumes, enabling retailers to allocate resources and plan for peak return periods effectively.
Omnichannel Logistics Examples: Case Studies
Examining successful omnichannel logistics implementations provides valuable insights into effective strategies and best practices. Companies like Zara, Amazon, and Walmart have set industry benchmarks by integrating advanced technologies, optimizing supply chains, and enhancing customer experiences. This section explores how these retail giants serve as omnichannel logistics examples to businesses that want to achieve operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Amazon
Amazon is a prime example of successful omnichannel logistics, setting the gold standard in the industry with its innovative approaches to warehousing, fulfillment, and data analytics. By understanding what is omnichannel logistics and leveraging its extensive resources, Amazon has managed to create a seamless, efficient, and customer-centric logistics network. This section provides an in-depth look at Amazon’s strategies and practices that exemplify successful omnichannel logistics.
Overview
Amazon, founded in 1994 by Jeff Bezos, started as an online bookstore but quickly diversified into a wide array of product categories. Today, it is one of the world’s largest e-commerce companies, renowned for its vast product selection, fast delivery times, and customer-centric approach. Central to Amazon’s success is its sophisticated omnichannel logistics network, which integrates various sales channels and optimizes supply chain operations to meet the high expectations of modern consumers.
Amazon’s omnichannel logistics includes a robust infrastructure comprising advanced warehousing technologies, an extensive distribution network, and cutting-edge data analytics. These components work together to provide a seamless shopping experience, whether customers are purchasing products online, through the mobile app, or via voice-enabled devices like Amazon Echo.
Innovations in Warehousing and Fulfillment
Amazon’s innovations in warehousing and fulfillment are key drivers of its success in omnichannel logistics. The company has revolutionized traditional warehousing practices by implementing advanced technologies and automation to enhance efficiency and accuracy.
One of the most notable innovations is the use of robotics in Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon acquired Kiva Systems (now Amazon Robotics) in 2012, integrating robotic technology into its warehousing operations. These robots, also known as drive units, move products around the warehouse, bringing shelves directly to human workers who then pick and pack the items. This automation significantly reduces the time required to process orders and minimizes the risk of errors, exemplifying a critical aspect of omnichannel logistics.
Another innovation is the use of automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS). These systems enable Amazon to maximize storage space and improve inventory management. By utilizing vertical storage racks and robotic cranes, AS/RS can quickly and accurately retrieve items, further speeding up the order fulfillment process. This technology is particularly beneficial for managing the vast inventory required to support Amazon’s diverse product offerings.
Amazon’s fulfillment network also includes strategically located fulfillment centers, sortation centers, and delivery stations. This extensive network allows Amazon to offer fast and reliable delivery options, such as same-day and two-hour delivery through Amazon Prime Now. By positioning fulfillment centers close to major customer hubs, Amazon reduces transportation times and costs, enhancing its omnichannel retail logistics capabilities.
Use of Data Analytics for Inventory Management
Data analytics plays a crucial role in Amazon’s omnichannel logistics strategy, providing valuable insights that drive decision-making and optimize inventory management. By harnessing the power of big data, Amazon can predict customer demand, streamline operations, and enhance the overall efficiency of its supply chain.
One of the key applications of data analytics in Amazon’s logistics is demand forecasting. Amazon uses sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models to analyze historical sales data, customer behavior, and market trends. This predictive analytics capability enables Amazon to anticipate fluctuations in demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly. For instance, during the holiday season, Amazon can predict which products will be in high demand and ensure adequate stock to meet customer needs.
Real-time inventory tracking is another critical aspect of Amazon’s data-driven approach. Using advanced tracking technologies, Amazon monitors inventory levels across its entire fulfillment network. This real-time visibility allows Amazon to quickly identify and address potential stock-outs or overstock situations, ensuring that products are always available for customers. For example, if a particular item is selling faster than expected, Amazon can quickly replenish stock from nearby fulfillment centers or suppliers.
Amazon also leverages data analytics to optimize its supply chain operations. By analyzing data on shipping routes, delivery times, and transportation costs, Amazon can identify inefficiencies and implement improvements. For example, Amazon uses route optimization algorithms to determine the most efficient delivery routes, reducing fuel consumption and delivery times. Additionally, data-driven insights enable Amazon to negotiate better rates with shipping carriers, further reducing logistics costs.
Personalization is another area where Amazon excels, thanks to its use of data analytics. By analyzing customer purchase history and browsing behavior, Amazon can provide personalized product recommendations and targeted marketing. This personalized approach not only enhances the customer experience but also drives sales and increases customer loyalty. For instance, customers might receive tailored recommendations for products they are likely to be interested in, based on their previous purchases and searches.
Final Evaluation
Amazon’s success in omnichannel logistics can be attributed to its relentless focus on innovation, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. By understanding and implementing the principles of what is omnichannel logistics, Amazon has created a seamless and integrated logistics network that sets the standard for the industry.
The company’s innovations in warehousing and fulfillment, such as the use of robotics and automated storage systems, have revolutionized traditional logistics practices. These technologies enable Amazon to process orders quickly and accurately, reducing the time it takes for products to reach customers. The strategic placement of fulfillment centers and the extensive distribution network further enhance Amazon’s ability to offer fast and reliable delivery options.
Amazon’s use of data analytics for inventory management and supply chain optimization is another critical factor in its success. Predictive analytics, real-time tracking, and personalized marketing all contribute to a more efficient and customer-centric logistics operation. By leveraging big data, Amazon can anticipate demand, manage inventory levels effectively, and provide a personalized shopping experience.
However, Amazon’s approach to omnichannel logistics is not without its challenges. The company must continuously invest in technology and infrastructure to maintain its competitive edge. Additionally, managing the complexities of a global supply chain and ensuring data security and privacy are ongoing concerns.
In conclusion, Amazon’s omnichannel logistics strategy exemplifies the successful integration of advanced technologies, innovative practices, and data-driven decision-making. By focusing on efficiency and customer satisfaction, Amazon has set a benchmark for omnichannel retail logistics. Retailers looking to improve their logistics operations can learn valuable lessons from Amazon’s approach, from embracing automation and data analytics to optimizing supply chain networks and enhancing the customer experience.
Walmart
Walmart is a leading example of successful omnichannel logistics, demonstrating how a traditional brick-and-mortar retailer can effectively integrate physical and online stores to provide a seamless customer experience. By leveraging its extensive network of physical locations, investing in technology, and optimizing last-mile delivery, Walmart has become a formidable player in the omnichannel retail logistics landscape. This section explores Walmart’s strategies and innovations in omnichannel logistics.
Overview
Walmart, founded in 1962 by Sam Walton, is one of the world’s largest retailers with thousands of stores worldwide. Known for its commitment to low prices and wide product selection, Walmart has embraced omnichannel logistics to meet the evolving demands of its customers. Understanding what is omnichannel logistics, Walmart has developed a comprehensive strategy that integrates its physical stores with its online presence, offering customers a seamless shopping experience across all channels.
The omnichannel logistics at Walmart involves using its vast network of physical stores as hubs for online orders, leveraging advanced technologies for inventory management and fulfillment, and implementing efficient last-mile delivery solutions. This approach allows Walmart to provide fast and convenient service to its customers while maintaining operational efficiency.
Integration of Physical and Online Stores
One of the key components of Walmart’s omnichannel logistics strategy is the integration of its physical and online stores. This integration allows Walmart to utilize its extensive network of brick-and-mortar locations to support its e-commerce operations, creating a seamless shopping experience for customers.
Walmart’s stores serve as both retail locations and fulfillment centers for online orders. This dual role enables Walmart to offer convenient services such as Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store (BOPIS) and curbside pickup. Customers can place orders online and choose to pick them up at a nearby store, often on the same day. This service not only provides convenience for customers but also drives foot traffic to physical stores, potentially leading to additional in-store purchases.
To facilitate the integration of physical and online stores, Walmart has invested in advanced inventory management systems. These systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels across all locations, ensuring that products are available where and when they are needed. For example, if a customer orders a product online for in-store pickup, the system can quickly locate the item in the nearest store and reserve it for the customer. This real-time inventory tracking is crucial for maintaining accuracy and preventing stockouts.
Another important aspect of Walmart’s integration strategy is the use of technology to enhance the in-store shopping experience. Walmart has introduced features such as mobile apps that allow customers to scan and pay for items using their smartphones, reducing checkout times and improving convenience. Additionally, Walmart’s app provides personalized recommendations and promotions based on customer preferences and purchase history, bridging the gap between online and in-store shopping.
Efficient Last-Mile Delivery Solutions
Efficient last-mile delivery is a critical component of Walmart’s omnichannel logistics strategy. The last mile, or the final step in the delivery process where products are transported to the customer’s doorstep, is often the most challenging and costly part of logistics. Walmart has implemented several innovative solutions to address these challenges and provide fast, reliable delivery options.
One of the key strategies Walmart employs is leveraging its network of physical stores as fulfillment centers for online orders. By shipping products from the nearest store rather than a central warehouse, Walmart can reduce delivery times and costs. This ship-from-store model allows Walmart to offer same-day and next-day delivery options, meeting customer expectations for speed and convenience.
Walmart has also invested in advanced technologies to optimize its last-mile delivery operations. For example, the company uses route optimization software to determine the most efficient delivery routes, reducing fuel consumption and delivery times. Additionally, Walmart has experimented with autonomous delivery vehicles and drones to further enhance its delivery capabilities. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize last-mile delivery by reducing reliance on traditional delivery methods and improving efficiency.
Collaboration with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) is another important aspect of Walmart’s last-mile delivery strategy. Walmart partners with various 3PLs to expand its delivery network and provide flexible delivery options. For instance, Walmart has collaborated with companies like DoorDash and Postmates to offer same-day grocery delivery. These partnerships enable Walmart to scale its delivery operations and reach more customers without significant capital investment.
Walmart’s delivery subscription service, Walmart+, is another innovative solution aimed at enhancing last-mile delivery. For a monthly or annual fee, customers can enjoy unlimited free delivery on eligible items, along with other benefits such as fuel discounts and mobile scan-and-go. This subscription model not only provides value to customers but also fosters loyalty and encourages repeat purchases.
Final Evaluation
Walmart’s success in omnichannel logistics can be attributed to its strategic integration of physical and online stores, investment in advanced technologies, and implementation of efficient last-mile delivery solutions. By understanding and applying the principles of what is omnichannel logistics, Walmart has created a seamless and customer-centric logistics network that enhances the shopping experience and drives operational efficiency.
The integration of physical and online stores allows Walmart to leverage its vast network of brick-and-mortar locations to support e-commerce operations, providing convenient services like BOPIS and curbside pickup. Advanced inventory management systems ensure real-time visibility and accuracy, preventing stockouts and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Walmart’s innovative approach to last-mile delivery, including the use of ship-from-store models, route optimization software, and autonomous delivery technologies, enables the company to offer fast and reliable delivery options. Collaborations with 3PLs and the introduction of the Walmart+ subscription service further strengthen Walmart’s delivery capabilities and customer loyalty.
However, Walmart’s omnichannel logistics strategy is not without challenges. The company must continuously invest in technology and infrastructure to maintain its competitive edge. Additionally, managing the complexities of a global supply chain and ensuring data security and privacy are ongoing concerns.
Walmart’s omnichannel logistics strategy exemplifies the successful integration of physical and online stores, advanced technologies, and efficient delivery solutions. By focusing on customer convenience and operational efficiency, Walmart has set a benchmark for omnichannel retail logistics. Retailers looking to enhance their logistics operations can learn valuable lessons from Walmart’s approach, from leveraging existing assets and investing in technology to optimizing last-mile delivery and fostering customer loyalty.
Zara
Zara, one of the world’s leading fashion retailers, has effectively leveraged omnichannel logistics to support its fast fashion business model. Through real-time inventory tracking and a highly responsive supply chain, Zara ensures that it can meet customer demands quickly and efficiently. This section explores how Zara has implemented omnichannel logistics to enhance its operations and maintain a competitive edge in the fashion industry.
Overview
Zara, founded in 1975 by Amancio Ortega in Spain, is a flagship brand of the Inditex Group. Known for its fast fashion approach, Zara rapidly designs, manufactures, and delivers new clothing styles to stores worldwide. Understanding what is omnichannel logistics and integrating its principles into their operations, Zara has developed a robust logistics framework that supports its business model, ensuring that it can respond swiftly to the latest fashion trends and consumer preferences.

Zara’s omnichannel logistics involves integrating various sales and distribution channels to provide a seamless shopping experience for customers. This includes maintaining real-time visibility of inventory levels, optimizing supply chain processes, and leveraging advanced technologies to support rapid product turnover. Zara’s approach to omnichannel retail logistics is a key factor in its ability to deliver new fashion collections to stores and online platforms quickly and efficiently.
Real-Time Inventory Tracking
Real-time inventory tracking is a critical component of Zara’s omnichannel logistics strategy. By maintaining up-to-the-minute visibility of inventory levels across its entire supply chain, Zara can ensure that products are available where and when they are needed, minimizing stockouts and overstock situations.
Zara uses sophisticated inventory management systems that provide real-time data on stock levels in its stores, warehouses, and distribution centers. These systems are integrated with POS terminals, enabling Zara to monitor sales and inventory movements continuously. For example, when an item is sold in a store, the inventory system updates automatically, reflecting the new stock level in real time. This information is then used to make replenishment decisions, ensuring that popular items are restocked quickly.
The use of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology further enhances Zara’s real-time inventory tracking capabilities. RFID tags are attached to individual items, allowing Zara to track products throughout the supply chain accurately. RFID readers placed in stores and warehouses can instantly identify the location and status of tagged items, providing detailed insights into inventory levels and movements. This technology reduces the time and labor required for manual inventory checks and improves overall accuracy.
Real-time inventory tracking also supports Zara’s omnichannel retail logistics by enabling efficient order fulfillment for online and in-store purchases. For instance, if a customer orders a product online, the system can quickly determine the nearest location with available stock and arrange for shipping or in-store pickup. This capability ensures that customers receive their orders promptly, enhancing their shopping experience and satisfaction.
Fast Fashion Logistics Model
Zara’s fast fashion logistics model is designed to support its business strategy of rapidly bringing new styles to market. This model relies on a highly responsive supply chain that can quickly adapt to changing fashion trends and consumer demands. Key elements of Zara’s fast fashion logistics model include agile production processes, strategic sourcing, and efficient distribution.
Zara’s production process is characterized by its flexibility and speed. Unlike traditional fashion retailers that plan collections months in advance, Zara designs and produces new styles in response to current trends and customer feedback. This approach, known as “just-in-time” production, allows Zara to introduce new collections every few weeks, keeping its inventory fresh and appealing to fashion-conscious consumers. By producing smaller batches and replenishing stock based on actual sales data, Zara minimizes the risk of overproduction and excess inventory.
Strategic sourcing is another critical aspect of Zara’s fast fashion logistics model. Zara maintains close relationships with its suppliers, many of which are located near its headquarters in Spain. This proximity allows for shorter lead times and greater control over the production process. Additionally, Zara uses a combination of in-house manufacturing and outsourcing to balance cost and flexibility. For example, basic items may be produced in lower-cost regions, while more complex or trendy items are manufactured in-house or by local suppliers to ensure quick turnaround times.
Efficient distribution is essential for Zara’s fast fashion logistics model. Zara operates a centralized distribution system, with major distribution centers located in Spain. From these hubs, products are shipped to stores worldwide using a combination of air and ground transportation. This centralized approach allows Zara to maintain tight control over its inventory and ensure that new collections reach stores quickly. For example, Zara’s distribution centers can process and dispatch orders within hours of receiving them, enabling rapid replenishment of stock in stores.
Zara’s logistics model also incorporates advanced technology and data analytics to optimize supply chain operations. By analyzing sales data, customer feedback, and market trends, Zara can make informed decisions about product design, production, and distribution. This data-driven approach ensures that Zara remains responsive to changing consumer preferences and market conditions.
Final Evaluation
Zara’s success in omnichannel logistics is a testament to its innovative and responsive approach to supply chain management. By understanding and applying the principles of what is omnichannel logistics, Zara has created a logistics framework that supports its fast fashion business model and enhances customer satisfaction.
The integration of real-time inventory tracking into Zara’s operations ensures that the company can maintain accurate stock levels and respond quickly to customer demands. Advanced technologies such as RFID and automated inventory management systems provide the visibility and accuracy needed to support efficient order fulfillment and replenishment.
Zara’s fast fashion logistics model, characterized by agile production processes, strategic sourcing, and efficient distribution, enables the company to bring new styles to market rapidly. This model minimizes the risk of overproduction and excess inventory, ensuring that Zara can maintain a fresh and appealing product offering.
Despite its success, Zara’s omnichannel logistics strategy is not without challenges. The company must continuously invest in technology and infrastructure to maintain its competitive edge. Additionally, managing a complex global supply chain and ensuring data security and privacy are ongoing concerns.
All in all, Zara serves as one of the omnichannel logistics examples that highlight the successful integration of advanced technologies, responsive supply chain processes, and data-driven decision-making. By focusing on speed, flexibility, and customer satisfaction, Zara has set a benchmark for omnichannel retail logistics. Retailers looking to enhance their logistics operations can learn valuable lessons from Zara’s approach, from implementing real-time inventory tracking and leveraging advanced technologies to optimizing production and distribution processes.
Implementing Omnichannel Logistics in Your Business
Assessment and Planning
Implementing omnichannel logistics in your business requires a thorough assessment and strategic planning to ensure seamless integration and operational efficiency. This process begins with evaluating your current logistics capabilities and setting clear goals and KPIs.
Evaluating Current Logistics Capabilities
Understanding what is omnichannel logistics and how it applies to your business is the first step in the assessment process. Omnichannel logistics involves integrating various sales channels, such as online stores, physical retail locations, and mobile platforms into a cohesive system that provides a seamless customer experience. To effectively implement this, you need to evaluate your existing logistics infrastructure and processes.
Start by conducting a comprehensive audit of your current logistics capabilities. This audit should cover all aspects of your supply chain, including inventory management, warehousing, order fulfillment, and transportation. Assess the efficiency and effectiveness of each component to identify strengths and weaknesses. For example, if your current inventory management system is unable to provide real-time updates across all channels, this could lead to stockouts or overstock situations, negatively impacting customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Examine your technology stack to determine if your current systems can support omnichannel logistics. This includes evaluating your warehouse management systems (WMS), transportation management systems (TMS), and any other relevant software. Integration capabilities are crucial; your systems must communicate effectively to provide accurate, real-time data. If you identify gaps in your technology, consider upgrading to more advanced, integrated solutions that can handle the complexities of omnichannel retail logistics.
Another critical area to assess is your workforce. Ensure that your team has the necessary skills and knowledge to manage an omnichannel logistics operation. This might involve additional training or hiring new personnel with expertise in logistics and supply chain management. For instance, your staff should be proficient in using advanced inventory management systems and understand the importance of synchronizing data across channels to maintain accurate stock levels.
Setting Clear Goals and KPIs
Once you have a clear understanding of your current logistics capabilities, the next step is to set clear goals and KPIs for your omnichannel logistics strategy. These goals should align with your overall business objectives and address the specific challenges and opportunities identified during the assessment phase. Additionally, incorporating omnichannel retail KPIs, such as customer satisfaction, sales growth across channels, and the effectiveness of marketing strategies, will help ensure a comprehensive approach to measuring and achieving success.
Start by defining what success looks like for your omnichannel logistics implementation. This might include goals such as reducing order fulfillment times, increasing inventory accuracy, improving customer satisfaction, and lowering logistics costs. Each goal should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to ensure clarity and focus.
For example, a goal might be to achieve 99% inventory accuracy across all channels within six months. This goal addresses the challenge of maintaining accurate stock levels, which is critical for providing a seamless customer experience. Another goal might be to reduce order fulfillment times to less than 24 hours, enhancing customer satisfaction and competitive advantage in the market.
Once you have defined your goals, establish KPIs to measure your progress. KPIs are quantifiable metrics that provide insights into the performance of your logistics operations. Common KPIs for omnichannel logistics include order accuracy rate, inventory turnover rate, order fulfillment time, return rate, and customer satisfaction score.
For instance, to measure order accuracy, you can track the percentage of orders fulfilled without errors over a specific period. An improvement in this KPI would indicate that your efforts to reduce fulfillment errors are effective. Similarly, tracking the inventory turnover rate can help you understand how efficiently your inventory is being managed and identify opportunities for optimization.
In addition to setting KPIs, establish regular review processes to monitor and analyze your performance. Use data analytics to gain insights into your logistics operations and identify areas for improvement. For example, if you notice a high return rate, analyze the reasons behind the returns and implement strategies to address the underlying issues, such as improving product descriptions or offering better customer support.
Choosing the Right Technologies
Choosing the right technologies is a critical step in implementing omnichannel logistics effectively. The technologies you select must support seamless integration across various channels, optimize logistics operations, and enhance customer experiences. This involves identifying suitable software and tools that align with your business needs and ensuring scalability and flexibility to accommodate future growth and changes.
Identifying Suitable Software and Tools
To effectively implement omnichannel logistics, you must first identify the right software and tools that align with your business needs. This process involves evaluating your current technological infrastructure, understanding the specific requirements of omnichannel logistics, and selecting solutions that can support your goals.
One of the fundamental technologies for omnichannel logistics is an integrated Warehouse Management System (WMS). A robust WMS helps manage and optimize warehouse operations, including inventory management, order fulfillment, and shipping. When selecting a WMS, look for features such as real-time inventory tracking, automated replenishment, and integration capabilities with other systems. For instance, a WMS that provides real-time inventory visibility across all channels can help prevent stockouts and overstock situations, ensuring that products are available when and where customers need them.
Another essential tool is a Transportation Management System (TMS), which helps streamline and optimize transportation and delivery operations. A TMS can manage carrier relationships, optimize shipping routes, and provide real-time tracking of shipments. Features to look for in a TMS include route optimization, load planning, and integration with warehouse and order management systems. An effective TMS can reduce shipping costs, improve delivery times, and enhance customer satisfaction by providing accurate and timely delivery information.
Order Management Systems (OMS) are also crucial for omnichannel logistics. An OMS coordinates order processing across multiple sales channels, ensuring that orders are fulfilled efficiently and accurately. Key features to consider in an OMS include centralized order processing, real-time inventory visibility, and integration with WMS and TMS. A robust OMS enables seamless order management, reducing the risk of errors and delays in order fulfillment.
Additionally, CRM systems play a significant role in omnichannel logistics by managing customer interactions and data. A CRM system can provide insights into customer preferences and behaviors, enabling personalized marketing and customer service. When selecting a CRM, look for features such as customer segmentation, data analytics, and integration with other logistics systems. A well-integrated CRM can enhance the customer experience by providing personalized recommendations and support.
Lastly, consider leveraging advanced technologies such as AI and Machine Learning to optimize your logistics operations. AI and ML can provide predictive analytics for demand forecasting, optimize inventory levels, and enhance decision-making processes. For example, AI-powered demand forecasting can help predict future sales trends, enabling you to adjust inventory levels proactively and reduce the risk of stockouts or overstock situations.
Ensuring Scalability and Flexibility
Ensuring scalability and flexibility in your chosen technologies is essential for the long-term success of your omnichannel logistics strategy. As your business grows and market conditions change, your logistics systems must be able to adapt and scale to meet new demands.
Scalability refers to the ability of your logistics systems to handle increased volumes of transactions, inventory, and customer interactions without compromising performance. When evaluating software and tools, consider their scalability features, such as cloud-based infrastructure, modular design, and capacity for handling large datasets. For example, cloud-based WMS and TMS solutions can easily scale up to accommodate higher volumes of orders and inventory, ensuring that your logistics operations remain efficient during peak periods.
Flexibility, on the other hand, involves the capability of your systems to adapt to changing business requirements and market conditions. This includes integrating new sales channels, accommodating different fulfillment models, and supporting various delivery options. When selecting technologies, prioritize those that offer flexible integration capabilities, customizable workflows, and support for multiple channels. For instance, an OMS that can seamlessly integrate with new e-commerce platforms or third-party logistics providers (3PLs) can help you expand your reach and adapt to evolving customer expectations.
Additionally, look for technologies that support agile development and continuous improvement. Agile methodologies allow for iterative development and deployment, enabling you to quickly respond to changes and implement new features or enhancements. For example, a TMS that supports agile development can quickly incorporate new shipping carriers or optimize routes based on real-time traffic data, ensuring that your delivery operations remain efficient and responsive.
Another aspect of flexibility is the ability to support various fulfillment models, such as ship-from-store, buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), and same-day delivery. Your logistics systems should be able to handle these different models seamlessly, providing customers with a consistent and convenient shopping experience. For example, a WMS that supports multiple fulfillment options can dynamically allocate inventory and resources based on the chosen fulfillment method, ensuring timely and accurate order processing.
Training and Development
Implementing omnichannel logistics effectively requires not only the right technology and infrastructure but also a skilled and adaptable workforce. Training and development are crucial components of this process, ensuring that your team is equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to manage the complexities of omnichannel logistics. This section explores strategies for building a skilled workforce and fostering a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
Building a Skilled Workforce
Building a skilled workforce is foundational to the success of any omnichannel logistics strategy. Understanding what is omnichannel logistics and its implications for your business operations helps in defining the necessary skill sets required for your team. The goal is to create a workforce capable of navigating the integrated and dynamic nature of omnichannel retail logistics.
Start by identifying the key roles and responsibilities within your logistics operations. These roles may include inventory managers, warehouse operators, logistics coordinators, data analysts, and customer service representatives. Each role requires specific skills and expertise to ensure efficient and accurate handling of logistics tasks. For instance, inventory managers need to be proficient in real-time inventory tracking and management systems, while data analysts must be skilled in interpreting logistics data to inform decision-making.
Develop comprehensive training programs tailored to the needs of each role. These programs should cover both technical and soft skills, ensuring that employees are well-rounded and capable of handling various aspects of omnichannel logistics. Technical training might include the use of warehouse management systems (WMS), transportation management systems (TMS), and order management systems (OMS). For example, training warehouse operators on the use of automated picking systems and RFID technology can improve efficiency and accuracy in order fulfillment.

In addition to technical skills, emphasize the importance of soft skills such as communication, problem-solving, and teamwork. Effective communication is vital in coordinating across different channels and departments, while strong problem-solving skills enable employees to address logistics challenges proactively. For instance, logistics coordinators must be able to communicate effectively with suppliers, carriers, and other stakeholders to ensure smooth operations.
Implement hands-on training and real-world simulations to provide practical experience. This approach helps employees apply their knowledge in realistic scenarios, enhancing their ability to manage actual logistics challenges. For example, conducting simulation exercises that mimic peak shopping periods can prepare employees for handling high volumes of orders efficiently.
Encourage cross-training and role rotation to build a versatile workforce. Cross-training allows employees to gain experience in different roles, increasing their understanding of the entire logistics process. This versatility is particularly valuable in omnichannel logistics, where flexibility and adaptability are crucial. For example, cross-training inventory managers and warehouse operators can improve coordination and efficiency in inventory management and order fulfillment.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation
In the rapidly evolving landscape of omnichannel logistics, continuous learning and adaptation are essential for maintaining a competitive edge. The logistics environment is constantly changing, driven by advancements in technology, shifts in consumer behavior, and emerging market trends. Fostering a culture of continuous learning ensures that your workforce remains up-to-date with the latest developments and can adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
Promote a learning culture within your organization by encouraging employees to pursue ongoing education and professional development. Offer access to online courses, workshops, certifications, and industry conferences that cover the latest trends and best practices in omnichannel logistics. For example, providing training on new logistics technologies such as AI and machine learning can help employees leverage these tools to optimize operations.
Implement regular training updates to keep employees informed about new technologies, systems, and processes. As your business adopts new tools and strategies, ensure that your workforce receives timely training to maximize the benefits of these innovations. For instance, if you introduce a new inventory management system, provide comprehensive training sessions to ensure that employees can use the system effectively.
Encourage knowledge sharing and collaboration among employees. Create platforms and opportunities for employees to share their experiences, insights, and best practices with their colleagues. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of community and collective learning within the organization. For example, establish regular team meetings or knowledge-sharing sessions where employees can discuss their experiences and challenges in managing omnichannel logistics.
Leverage data and feedback to drive continuous improvement. Use performance metrics and employee feedback to identify areas for improvement in your training programs and logistics operations. For example, if data analysis reveals a high error rate in order fulfillment, investigate the underlying causes and implement targeted training to address these issues. Continuously refining your training programs based on data and feedback ensures that they remain relevant and effective.
Stay informed about industry trends and innovations by engaging with professional networks and industry associations. Participate in logistics forums, webinars, and conferences to stay updated on the latest developments in omnichannel logistics. This engagement helps your organization anticipate changes and adapt proactively. For example, learning about emerging technologies such as blockchain or autonomous delivery vehicles can help you prepare for their potential impact on your logistics operations.
Monitoring and Optimization
Implementing omnichannel logistics effectively requires ongoing monitoring and optimization to ensure that operations remain efficient and responsive to changing demands. Regular performance reviews and continuous improvement strategies are essential components of this process. These practices help identify areas of improvement, optimize processes, and maintain a high level of service quality.
Regular Performance Reviews
Regular performance reviews are crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of omnichannel logistics. These reviews involve systematically evaluating the performance of various logistics operations, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing corrective measures. The goal is to ensure that all aspects of the supply chain are functioning optimally and contributing to a seamless customer experience.
Start by establishing clear performance metrics and KPIs that align with your business goals. Common KPIs for omnichannel logistics include order accuracy rate, inventory turnover rate, order fulfillment time, delivery time, return rate, and customer satisfaction score. For example, tracking order accuracy can help you identify issues in the fulfillment process that may lead to incorrect shipments and customer dissatisfaction.
Conduct regular performance reviews using these KPIs to assess the efficiency and effectiveness of your logistics operations. These reviews should be scheduled at consistent intervals, such as weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending on the complexity and scale of your operations. During these reviews, analyze performance data to identify trends, patterns, and areas of concern. For instance, if you notice an increase in order fulfillment times, investigate the root causes and develop strategies to address them.

Utilize advanced analytics tools to gain deeper insights into your logistics performance. Data analytics can help you identify correlations and causations that might not be immediately apparent. For example, analytics might reveal that certain products consistently experience delays due to supplier issues, allowing you to address these problems proactively. Additionally, predictive analytics can forecast potential future challenges, enabling you to take preventive measures.
Involve key stakeholders from various departments, including supply chain, warehousing, transportation, and customer service, in the performance review process. This collaborative approach ensures that different perspectives are considered and that solutions are comprehensive. For instance, input from the customer service team can provide valuable insights into recurring customer complaints related to logistics, helping you identify and address systemic issues.
Document the findings from each performance review and track the progress of implemented improvements. Maintaining a record of performance data and action plans allows you to measure the impact of your optimization efforts over time. For example, if you implement a new routing optimization tool to improve delivery times, track its effectiveness by comparing delivery performance before and after its implementation.
Continuous Improvement Strategies
Continuous improvement is a fundamental principle of successful omnichannel logistics. It involves systematically and incrementally enhancing logistics processes to achieve better performance, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Implementing continuous improvement strategies ensures that your logistics operations remain adaptable and responsive to evolving business needs and market conditions.
One effective continuous improvement strategy is the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle. This iterative process involves four steps:
- Plan: Identify areas for improvement and develop a detailed plan to address them. For example, if you identify that order picking errors are a significant issue, plan a strategy to improve the picking process, such as implementing new training programs or upgrading picking technology.
- Do: Implement the plan on a small scale to test its effectiveness. For instance, pilot the new picking technology in one warehouse to assess its impact on order accuracy and efficiency.
- Check: Monitor the results of the implementation and compare them against the desired outcomes. Use performance metrics and data analysis to evaluate the effectiveness of the changes. For example, analyze order accuracy rates and fulfillment times before and after the implementation of the new picking technology.
- Act: Based on the results, decide whether to scale up the implementation, make further adjustments, or abandon the plan if it did not produce the expected outcomes. If the new technology proves effective, roll it out across all warehouses and continue to monitor its performance.
Another continuous improvement strategy is Lean Six Sigma, which combines lean manufacturing principles with Six Sigma methodologies to eliminate waste and reduce variability in processes. Applying Lean Six Sigma to omnichannel logistics can help streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance service quality. For example, use value stream mapping to identify and eliminate non-value-added activities in your logistics processes, such as excessive handling or unnecessary inventory movements.
Encourage a culture of innovation and continuous improvement within your organization. Empower employees at all levels to identify and suggest improvements to logistics processes. Create platforms for employees to share their ideas and recognize and reward those who contribute valuable insights. For example, establish a suggestion program where warehouse staff can propose process improvements, and reward those whose ideas lead to significant efficiency gains.
Leverage technology to support continuous improvement efforts. Advanced logistics software and automation tools can provide real-time data and analytics to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. For example, using machine learning algorithms to analyze delivery data can help optimize routing and reduce delivery times. Implementing IoT devices in warehouses can provide real-time visibility into inventory levels and movements, enabling more accurate and efficient inventory management.
Finally, stay informed about industry trends and best practices. Engage with professional networks, attend industry conferences, and participate in webinars to learn about the latest developments in omnichannel logistics. Adopting proven best practices and emerging technologies can provide new opportunities for continuous improvement. For instance, learning about the latest advancements in autonomous delivery vehicles or blockchain technology can help you identify new ways to enhance your logistics operations.
In conclusion,
Adopting and innovating in omnichannel logistics is essential for businesses seeking to meet the evolving demands of today’s consumers. Investing in the right technologies, building a skilled workforce, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement are vital steps in this journey. As retail omnichannel trends continue to evolve, companies must stay ahead by integrating advanced logistics solutions. As demonstrated by the case studies of successful companies like Amazon, Walmart, and Zara, effective omnichannel logistics can drive significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and customer loyalty. Businesses are encouraged to evaluate their current logistics capabilities, set clear goals, and implement integrated systems to fully realize the benefits of omnichannel logistics.
Looking ahead, the potential for businesses embracing omnichannel logistics is vast. The ongoing advancements in technology, such as AI, machine learning, and automation, will continue to revolutionize supply chain management. Companies that stay ahead of these trends and continually refine their logistics strategies will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape. By leveraging the power of omnichannel logistics, businesses can enhance their agility, responsiveness, and overall performance, ultimately driving long-term success and growth. Embracing this approach not only meets the current needs of the market but also prepares businesses for future opportunities and challenges in the dynamic world of retail.