Traditional retail, characterized by physical stores and face-to-face customer interactions, laid the foundation for the modern shopping experience. However, the digital transformation, fueled by the internet and technological advancements, has significantly altered how consumers shop and interact with brands. This shift has led to the emergence of multichannel retail, where businesses operate across multiple platforms such as physical stores, online websites, and mobile apps. Each channel operates independently, offering customers various touchpoints to engage with the brand.
As technology continued to advance, so did consumer expectations. The demand for a more seamless and integrated shopping experience gave birth to omnichannel retail. Unlike multichannel retail, which often operates in silos, omnichannel retail focuses on providing a unified and cohesive experience across all channels. This approach ensures that customers have a consistent and personalized journey, whether they are shopping online, in-store, or through a mobile app.
Through detailed analysis and case studies in this blog post, we aim to provide a thorough understanding of how these retail strategies impact businesses and their customers. By the end of this journey, you will have a clearer picture of which approach is best suited for your business and how to implement it effectively to achieve long-term success.
Table of Contents
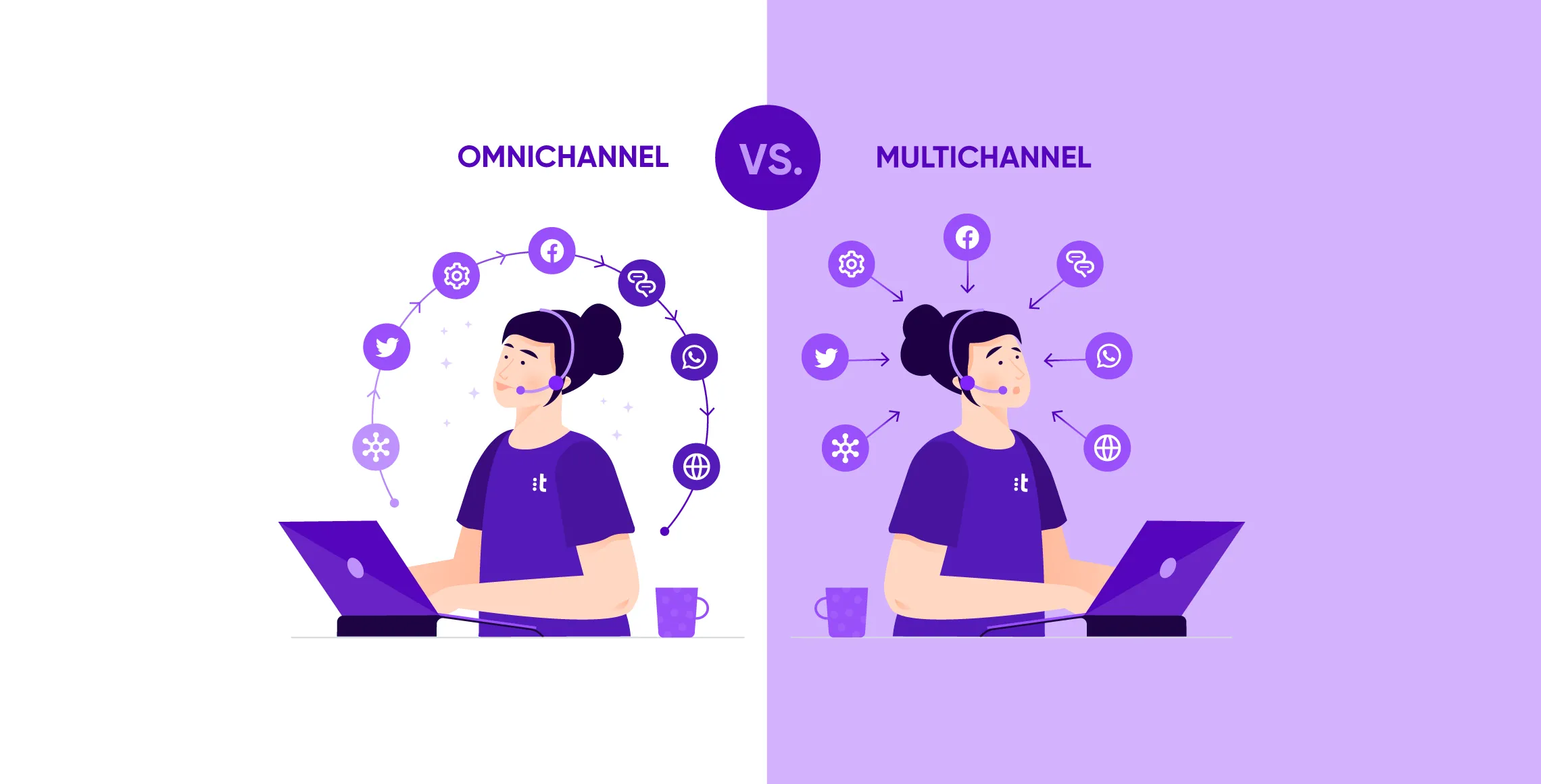
Omnichannel vs. Multichannel retail: Overview
Definition of Omnichannel and Multichannel Retail
Omnichannel Retail
Omnichannel retail is an integrated approach that seeks to provide a seamless and unified shopping experience across all customer touchpoints. This means that whether a customer interacts with a brand online, via mobile, or in a physical store, they receive a consistent and cohesive experience. Omnichannel retail is characterized by the synchronization of inventory, customer data, and communication channels to ensure that customers can effortlessly switch between different shopping mediums without experiencing any disruption or inconsistency.

Key characteristics of omnichannel retail include:
- Unified Customer Data: Customer information is centralized, allowing for personalized marketing and customer service.
- Consistent Branding and Messaging: The brand’s voice and messaging remain consistent across all channels.
- Seamless Integration: Integration of online and offline channels ensures that customers can start their shopping journey on one platform and complete it on another without any issues.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Focus on delivering a superior, personalized customer experience by leveraging data and technology.
Multichannel Retail
Multichannel retail involves using multiple channels to reach and interact with customers, but each channel operates independently. In this approach, a business may have a physical store, an online website, and a mobile app, but these channels are not integrated. Customers can choose how they want to interact with the brand, but their experience may vary significantly depending on the channel they use.

Key characteristics of multichannel retail include:
- Independent Channels: Each channel operates separately, with its own inventory, customer data, and management.
- Varied Customer Experience: The customer experience can differ across channels, potentially leading to inconsistencies.
- Flexibility for Customers: Customers have multiple options for interacting with the brand but may face challenges when switching between channels.
- Channel-Specific Strategies: Marketing and sales strategies are often tailored to each specific channel, rather than a unified approach.
Importance of Customer Experience in Retail Evolution
Customer experience has always been a cornerstone of successful retail. In the era of traditional retail, personalized service and face-to-face interactions were key to building customer loyalty and driving sales. However, the digital transformation has reshaped the landscape, making customer experience even more critical. In the omnichannel vs multichannel retail debate, the focus on customer experience is what sets these strategies apart and determines their effectiveness.
In multichannel retail, businesses aim to reach customers through various channels, each offering a distinct experience. While this approach provides flexibility and convenience, it often lacks the integration necessary to deliver a seamless journey. Customers may encounter inconsistencies when switching between channels, leading to frustration and a disjointed shopping experience. Despite these challenges, multichannel retail has been a stepping stone in the evolution of retail, paving the way for more sophisticated strategies.
Omnichannel retail, on the other hand, places customer experience at the heart of its strategy. By integrating all channels and creating a unified system, omnichannel retail ensures that customers enjoy a consistent and personalized experience, regardless of how they choose to shop. This approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also builds brand loyalty and drives repeat business. In the context of omnichannel vs multichannel retail, the emphasis on delivering a superior customer experience is a defining characteristic of omnichannel strategies.
Key Differences Between Omnichannel and Multichannel Retail
Integration and Consistency
- Omnichannel: Focuses on integrating all channels to provide a consistent and seamless customer experience. Customers can move effortlessly between different touchpoints (e.g., starting a purchase online and completing it in-store) without any disruption.
- Multichannel: Each channel functions independently, leading to potential inconsistencies in the customer experience. Customers may encounter different policies, prices, and availability depending on the channel they choose.
Customer Data Management
- Omnichannel: Utilizes a centralized database for customer information, ensuring that data is shared across all channels. This allows for personalized marketing, improved customer service, and a cohesive experience.
- Multichannel: Customer data is often siloed within each channel, which can result in fragmented and inconsistent customer profiles. This makes it challenging to provide a personalized and unified customer experience.
Marketing and Communication
- Omnichannel: Employs a unified marketing strategy that maintains consistent messaging and branding across all channels. This ensures that customers receive a coherent and recognizable brand experience.
- Multichannel: Marketing efforts are often tailored to individual channels, which can lead to varied messaging and brand perception. Customers might receive different offers and communications depending on the channel they use.
Inventory and Fulfillment
- Omnichannel: Integrates inventory management across all channels, enabling real-time visibility and flexibility in order fulfillment. Customers can choose their preferred delivery or pickup method, enhancing convenience and satisfaction.
- Multichannel: Inventory is managed separately for each channel, which can lead to inefficiencies and stock discrepancies. Customers might face limitations in product availability and fulfillment options.
Customer Experience
- Omnichannel: Prioritizes a seamless and personalized customer experience by leveraging integrated data and technology. This approach aims to exceed customer expectations and build long-term loyalty.
- Multichannel: Offers multiple touchpoints for customer interaction but may struggle to deliver a consistent and cohesive experience. Customers might face challenges when transitioning between channels, impacting their overall satisfaction.
Implications for Businesses
Technology and Infrastructure
- Omnichannel: Requires advanced technology and infrastructure to integrate and synchronize data, inventory, and communication channels. Investments in CRM, ERP, and other systems are essential to support the seamless experience.
- Multichannel: While less complex to implement initially, managing separate systems for each channel can lead to inefficiencies and higher long-term costs. Businesses may struggle to keep up with customer expectations for a unified experience.
Operational Efficiency
- Omnichannel: Streamlined operations and integrated systems enhance efficiency and reduce redundancies. Real-time data and inventory visibility allow for better decision-making and resource allocation.
- Multichannel: Independent operations can lead to duplication of efforts and resources. Inconsistencies in inventory and data management may result in operational challenges and increased costs.
Competitive Advantage
- Omnichannel: Provides a competitive edge by delivering a superior and differentiated customer experience. Businesses can leverage data to anticipate customer needs and preferences, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
- Multichannel: Offers flexibility and reach but may struggle to compete with brands that provide a more cohesive and personalized experience. Businesses need to continually innovate and adapt to stay relevant.
The debate of omnichannel vs multichannel retail is pivotal for businesses aiming to thrive in the modern retail landscape. While multichannel retail offers flexibility and reach, omnichannel retail sets the stage for a truly seamless and integrated customer experience. As businesses navigate this evolving landscape, understanding the key differences and implications of these strategies will be essential for achieving long-term success and customer satisfaction.
Importance of Understanding Omnichannel vs Multichannel
Why It’s Critical for Businesses to Differentiate and Understand These Concepts
- Strategic Decision-Making: Knowing the differences between omnichannel and multichannel retail allows businesses to make informed strategic decisions. Omnichannel retail focuses on providing a seamless, integrated customer experience across all touchpoints, whereas multichannel retail involves operating multiple independent channels. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses align their strategies with their overall goals, ensuring they invest resources effectively.
- Resource Allocation: Differentiating between the two approaches aids in proper resource allocation. Omnichannel retail requires significant investment in technology and integration to unify customer data and inventory across channels. In contrast, multichannel retail might demand less initial investment but can lead to inefficiencies and higher costs in the long run. Recognizing these needs ensures businesses allocate their budgets appropriately to maximize ROI.
- Customer Experience Management: The customer experience is a key differentiator in today’s competitive market. Omnichannel retail prioritizes a consistent and personalized experience, making it easier to meet and exceed customer expectations. By contrast, multichannel retail may result in disjointed experiences as customers switch between channels. Understanding these impacts enables businesses to choose the approach that best enhances the customer journey.
- Competitive Advantage: In an increasingly digital world, businesses that adopt a well-defined omnichannel strategy often gain a competitive edge. By offering a unified shopping experience, they can better meet the needs of modern consumers who demand flexibility and consistency. Differentiating between omnichannel vs multichannel retail helps businesses position themselves more favorably in the market.
Impact on Customer Satisfaction, Sales, and Brand Loyalty
- Customer Satisfaction: Omnichannel retail significantly enhances customer satisfaction by providing a seamless and cohesive experience across all touchpoints. When customers can interact with a brand smoothly across online and offline channels, their satisfaction levels increase. In contrast, multichannel retail can lead to inconsistencies and frustrations, such as differing policies or disjointed customer service, negatively affecting satisfaction.
- Sales: A well-executed omnichannel strategy can drive higher sales by leveraging integrated data to personalize offers and recommendations. Customers are more likely to make purchases when they receive relevant, personalized experiences. Multichannel retail, while still effective, may not achieve the same level of personalization and convenience, potentially leading to missed sales opportunities.
- Brand Loyalty: Omnichannel retail fosters greater brand loyalty by ensuring a consistent and high-quality customer experience. When customers feel recognized and valued across all interactions, their loyalty to the brand strengthens. Multichannel retail, with its potential for fragmented experiences, may struggle to build the same level of trust and loyalty. Consistent positive interactions are key to fostering long-term relationships with customers.
- Customer Retention: Omnichannel strategies are adept at retaining customers by providing continuous engagement and seamless transitions between channels. For instance, a customer might browse products on a mobile app and complete the purchase in-store, enjoying a smooth journey throughout. This continuity helps retain customers by minimizing friction points. On the other hand, multichannel retail might see higher churn rates due to inconsistent experiences and disconnected touchpoints.
- Data Utilization: Omnichannel retail’s integration of customer data across channels enables businesses to gain comprehensive insights into customer behavior and preferences. This data can be used to refine marketing strategies, optimize inventory, and enhance overall operations. Multichannel retail, with its siloed data, lacks this holistic view, making it harder to understand and respond to customer needs effectively.
- Operational Efficiency: By unifying inventory and customer data, omnichannel retail improves operational efficiency. Businesses can better manage stock levels, reduce redundancies, and streamline logistics. Multichannel retail, with its separate systems, may encounter inefficiencies and higher operational costs due to duplicated efforts and fragmented processes.
- Marketing Effectiveness: Omnichannel retail allows for more effective marketing campaigns by leveraging integrated customer data. Personalized marketing efforts, such as targeted emails or tailored advertisements, can be executed with greater precision. Multichannel retail’s segmented approach might result in less effective marketing, as it lacks the cohesive data needed to fully understand and target customers.

Understanding the differences between omnichannel vs multichannel retail is essential for businesses seeking to thrive in the modern retail environment. The choice between these approaches significantly impacts customer satisfaction, sales, and brand loyalty. By prioritizing a seamless, integrated customer experience through an omnichannel strategy, businesses can enhance their competitive advantage, foster stronger customer relationships, and drive long-term success. Conversely, while multichannel retail offers flexibility, it may fall short in delivering the consistency and personalization that today’s consumers expect.
Detailed Distinction Between Omnichannel vs Multichannel Retail
Customer Experience
The customer experience is a pivotal aspect of retail, shaping how customers interact with and perceive a brand. In the debate of omnichannel vs multichannel retail, the differences in customer experience are profound and impactful. Here, we explore how customer experience differs in both models and what customers expect from each approach.
- Seamlessness and Integration: In omnichannel retail, the customer experience is seamless and integrated across all touchpoints. Customers can start their shopping journey on one platform, such as browsing products on a mobile app, and seamlessly transition to another, like completing the purchase in a physical store, without any disruption. This integration ensures that customer data, preferences, and purchase history are synchronized across all channels, providing a fluid and uninterrupted shopping experience. In contrast, multichannel retail operates with each channel functioning independently. Customers can interact with the brand through various channels such as websites, mobile apps, and physical stores, but these channels are not integrated. This can lead to fragmented experiences where customers might need to re-enter information, face inconsistencies in product availability, or encounter different pricing and promotions across channels.
- Consistency in Branding and Messaging: Omnichannel retail ensures that branding, messaging, and promotional strategies are consistent across all channels. This consistency helps reinforce brand identity and trust among customers. Whether a customer is engaging with the brand on social media, a website, or in-store, they receive the same brand message and experience. Multichannel retail, however, may present varied branding and messaging as each channel is managed separately. This can lead to inconsistencies that may confuse customers and weaken the overall brand perception.
- Personalization: One of the hallmarks of omnichannel retail is the ability to offer highly personalized experiences. By leveraging integrated customer data, businesses can provide tailored recommendations, personalized promotions, and targeted marketing messages that resonate with individual customers. This level of personalization enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty. In multichannel retail, personalization is often limited due to siloed data and the lack of integration between channels. Customers may receive generic messages and offers that do not reflect their preferences or past interactions with the brand.
- Flexibility and Convenience: Omnichannel retail offers superior flexibility and convenience by allowing customers to choose how they interact with the brand. For instance, a customer can browse products online, check in-store availability, and opt for curbside pickup or home delivery. This flexibility caters to the diverse needs and preferences of customers, enhancing their overall shopping experience. In multichannel retail, while customers have multiple touchpoints to engage with the brand, the lack of integration can limit the flexibility and convenience they experience. Customers might find it cumbersome to switch between channels and may encounter obstacles that hinder their shopping journey.
- Customer Support and Service: Omnichannel retail excels in providing consistent and efficient customer support across all channels. Customers can reach out for assistance through various touchpoints, such as live chat on the website, social media, or in-store, and receive coherent and helpful responses. This integrated approach ensures that customer issues are resolved quickly and effectively. In multichannel retail, customer support may vary significantly across different channels, leading to inconsistent service quality. Customers might experience delays or receive conflicting information when seeking help, which can negatively impact their perception of the brand.
- Customer Loyalty and Retention: The seamless and personalized experience offered by omnichannel retail fosters strong customer loyalty and retention. When customers feel valued and recognized across all interactions, they are more likely to return and recommend the brand to others. Omnichannel strategies that reward loyalty and provide consistent positive experiences build long-term relationships with customers. In multichannel retail, the fragmented experience can make it challenging to cultivate loyalty. Customers may become frustrated with inconsistencies and choose to shop with competitors that offer a more unified and satisfying experience.
- Customer Data and Insights: Omnichannel retail leverages integrated customer data to gain comprehensive insights into customer behavior and preferences. This data-driven approach enables businesses to optimize their marketing strategies, improve product offerings, and enhance the overall customer experience. By understanding customer journeys and touchpoints, businesses can make informed decisions that drive growth and satisfaction. In multichannel retail, the lack of integrated data makes it difficult to obtain a holistic view of the customer. Insights are often limited to individual channels, hindering the ability to fully understand and address customer needs.

Understanding these key differences in customer experience between omnichannel vs multichannel retail highlights the importance of choosing the right approach for your business. While multichannel retail provides multiple avenues for customer engagement, omnichannel retail stands out for its ability to deliver a cohesive, personalized, and seamless experience that meets the evolving expectations of today’s consumers.
Data and Analytics
Data and analytics play a pivotal role in shaping the strategies and success of modern retail operations. The approaches to data collection and utilization differ significantly in omnichannel vs multichannel retail, influencing business decision-making and the ability to deliver personalized customer experiences. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their retail strategies and achieve a competitive edge.
- Data Collection: In omnichannel retail, data collection is centralized and integrated across all channels. This unified approach ensures that customer interactions, preferences, and purchase histories are captured seamlessly, providing a holistic view of the customer journey. In contrast, multichannel retail often involves siloed data collection, with each channel operating independently. This can result in fragmented and incomplete customer data, making it challenging to gain comprehensive insights.
- Data Utilization: Omnichannel retail leverages integrated data to deliver consistent and personalized customer experiences. By analyzing data from various touchpoints, businesses can create tailored marketing campaigns, recommend products based on past behavior, and provide personalized offers that resonate with individual customers. Multichannel retail, on the other hand, struggles to utilize data effectively due to the lack of integration. With data scattered across different channels, personalization efforts are often limited and less effective.
- Customer Insights: The integrated data approach in omnichannel retail enables businesses to gain deep insights into customer behavior and preferences. This comprehensive understanding allows for more accurate targeting, improved product recommendations, and better customer segmentation. In multichannel retail, insights are often limited to individual channels, providing an incomplete picture of customer behavior. This can hinder the ability to make informed decisions and optimize marketing efforts.
- Real-Time Analytics: Omnichannel retail benefits from real-time analytics that provide immediate insights into customer interactions across all channels. This enables businesses to respond quickly to customer needs, optimize inventory, and adjust marketing strategies on the fly. Multichannel retail, with its fragmented data systems, may experience delays in data processing and analysis, reducing the ability to react swiftly to market changes and customer demands.
- Business Decision-Making: The comprehensive data collected in omnichannel retail supports data-driven decision-making at all levels of the business. From inventory management to marketing strategies, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and drive growth. In multichannel retail, decision-making is often based on isolated data sets, which can lead to suboptimal strategies and missed opportunities.
- Personalization: Omnichannel retail excels in delivering personalized experiences by leveraging integrated data to understand individual customer preferences. This personalization extends across all touchpoints, ensuring that customers receive relevant and consistent messaging regardless of the channel. In multichannel retail, personalization is limited by the lack of data integration, resulting in generic marketing efforts that may not resonate with customers.
- Customer Loyalty: The ability to provide a seamless and personalized experience in omnichannel retail fosters greater customer loyalty. By understanding and anticipating customer needs, businesses can build stronger relationships and encourage repeat purchases. Multichannel retail, with its fragmented approach, may struggle to build the same level of loyalty, as customers may experience inconsistencies and feel less valued.
- Operational Efficiency: Omnichannel retail streamlines operations by integrating data across all channels, leading to more efficient inventory management, reduced redundancies, and better resource allocation. This integration supports a smoother customer experience and improves overall business performance. In multichannel retail, the lack of data integration can result in operational inefficiencies, such as overstocking or stockouts, and higher operational costs.
- Customer Experience: The data-driven approach of omnichannel retail enhances the overall customer experience by providing relevant and timely interactions at every touchpoint. Customers enjoy a consistent journey that reflects their preferences and past interactions with the brand. In multichannel retail, the disjointed data systems can lead to inconsistent customer experiences, where interactions may not align with previous engagements, reducing satisfaction.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that adopt an omnichannel approach gain a competitive advantage by leveraging data to create a superior customer experience. The ability to provide personalized and seamless interactions sets them apart from competitors who may still rely on multichannel strategies. Multichannel retail, while still valuable, may not offer the same level of differentiation and customer satisfaction, potentially leading to a competitive disadvantage.

The differences in data collection and utilization between omnichannel vs multichannel retail have profound implications for business decision-making and personalization. Omnichannel retail’s integrated approach allows for comprehensive insights, real-time analytics, and personalized customer experiences, driving operational efficiency and customer loyalty. In contrast, multichannel retail’s siloed data systems can limit the ability to fully understand and respond to customer needs, impacting overall business performance and competitive positioning. By embracing omnichannel strategies, businesses can leverage data to enhance every aspect of their operations and deliver exceptional value to their customers.
Integration and Technology
Integration and technology are foundational elements that differentiate omnichannel vs multichannel retail. The technological requirements and the role of various systems like CRM (Customer Relationship Management), ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), and others significantly impact how each retail model operates. This section delves into the specific technological needs and integration processes that define and distinguish these two approaches.
- Technological Requirements: Omnichannel retail necessitates advanced technological infrastructure to ensure seamless integration across all customer touchpoints. This includes sophisticated software solutions that can synchronize data, manage inventory in real-time, and provide consistent customer experiences. In contrast, multichannel retail requires less complex technology since each channel operates independently. However, this can lead to inefficiencies and higher costs over time due to the lack of integration.
- System Integration: In omnichannel retail, integration of various systems is crucial. This involves connecting CRM, ERP, POS (Point of Sale), eCommerce platforms, and other software to create a unified system. This integration allows for real-time data sharing and ensures that all customer interactions and transactions are seamlessly linked. Multichannel retail, however, often lacks such integration, resulting in siloed systems where data is not easily shared between channels, leading to fragmented customer experiences.
- Role of CRM Systems: CRM systems are vital in omnichannel retail, as they centralize customer data and interactions across all channels. This allows businesses to have a 360-degree view of each customer, enabling personalized marketing and improved customer service. In multichannel retail, CRM systems may only be partially utilized or used independently by each channel, limiting the ability to provide a cohesive customer experience.
- ERP Systems: ERP systems play a significant role in both omnichannel and multichannel retail, but their implementation differs. In omnichannel retail, ERP systems are integrated with other platforms to manage inventory, supply chain, finance, and human resources in a unified manner. This integration supports seamless operations and enhances efficiency. In multichannel retail, ERP systems may be used independently for each channel, leading to potential inefficiencies and data discrepancies.
- POS Systems: Omnichannel retail requires POS systems that are integrated with online and offline channels. This integration ensures that sales data is updated in real-time across all platforms, providing accurate inventory management and a unified customer profile. In multichannel retail, POS systems are typically channel-specific, which can result in inconsistent data and challenges in inventory management.
- eCommerce Platforms: In omnichannel retail, eCommerce platforms are integrated with other systems to provide a seamless online shopping experience that is connected to physical stores. This integration allows customers to check in-store availability, choose flexible delivery options, and enjoy consistent pricing and promotions. In multichannel retail, eCommerce platforms operate separately from physical stores, which can lead to discrepancies in product information, pricing, and customer experience.
- Data Synchronization: Data synchronization is a critical aspect of omnichannel retail. It ensures that customer information, inventory levels, and sales data are consistently updated across all channels. This real-time synchronization allows for accurate reporting and informed decision-making. In multichannel retail, the lack of data synchronization can lead to outdated information, inventory issues, and challenges in providing a unified customer experience.
- Customer Data Management: Omnichannel retail leverages integrated systems to manage customer data effectively. This centralized approach allows for comprehensive customer profiles that include purchase history, preferences, and interactions across all channels. Multichannel retail often struggles with fragmented customer data, making it difficult to gain a complete understanding of customer behavior and personalize interactions.
- Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management is a hallmark of omnichannel retail, enabled by integrated ERP and POS systems. This integration allows for real-time inventory tracking and seamless fulfillment options, such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS). In multichannel retail, inventory is managed separately for each channel, which can lead to overstocking, stockouts, and inefficiencies in order fulfillment.
- Customer Experience Enhancement: The technological integration in omnichannel retail enhances the overall customer experience by providing consistent and personalized interactions. Integrated CRM and ERP systems allow for targeted marketing, personalized recommendations, and efficient customer service. Multichannel retail, with its siloed systems, may find it challenging to offer the same level of personalized and seamless customer experiences.
- Operational Efficiency: Omnichannel retail’s integrated technology infrastructure supports streamlined operations, reducing redundancies and improving efficiency. Real-time data sharing and synchronized systems enable better resource allocation and faster decision-making. In multichannel retail, the lack of integration can lead to operational inefficiencies, duplicated efforts, and higher operational costs.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Omnichannel retail systems are designed to be scalable and flexible, accommodating growth and changes in customer behavior. Integrated technology allows businesses to add new channels, expand their reach, and adapt to market trends seamlessly. Multichannel retail, with its independent systems, may face challenges in scaling operations and adapting to new technologies or customer demands.

The technological requirements and integration processes in omnichannel vs multichannel retail highlight the significant differences between these two approaches. Omnichannel retail relies on advanced, integrated systems to provide a seamless and personalized customer experience, enhance operational efficiency, and support data-driven decision-making. Multichannel retail, while offering flexibility through multiple independent channels, often struggles with inefficiencies, data fragmentation, and challenges in delivering a cohesive customer experience. By understanding and leveraging the right technological infrastructure, businesses can optimize their retail strategies and achieve long-term success.
Marketing and Sales Strategies
Marketing and sales strategies are fundamental components that differentiate omnichannel vs multichannel retail. These strategies determine how businesses engage with customers, drive sales, and build brand loyalty across various channels. Understanding the distinct approaches in omnichannel and multichannel retail can help businesses tailor their efforts to maximize effectiveness and achieve their goals.
- Integrated Marketing Campaigns: In omnichannel retail, marketing campaigns are designed to be integrated across all channels. This means that a single campaign can seamlessly transition from online ads to in-store promotions, ensuring consistent messaging and branding. Customers receive a cohesive experience, whether they are interacting with the brand through social media, email, or in-store. Multichannel retail, however, often has separate marketing campaigns for each channel, which can lead to inconsistencies and fragmented customer experiences.
- Personalization: Omnichannel retail leverages integrated data to deliver highly personalized marketing messages and product recommendations. By understanding customer behavior across all touchpoints, businesses can tailor their communications to meet individual preferences and needs. In multichannel retail, personalization efforts are often limited due to the lack of integrated data. Marketing messages may be generic and less effective in engaging customers.
- Consistent Customer Experience: In omnichannel retail, the goal is to provide a consistent customer experience across all channels. Marketing and sales strategies are aligned to ensure that customers encounter the same branding, messaging, and service quality, regardless of how they interact with the brand. In multichannel retail, the customer experience can vary significantly between channels, potentially leading to confusion and dissatisfaction.
- Cross-Channel Promotions: Omnichannel retail allows for cross-channel promotions, where customers can redeem offers and discounts across different platforms. For example, a customer might receive a discount code via email that can be used both online and in-store. This flexibility enhances the shopping experience and encourages customer loyalty. In multichannel retail, promotions are typically channel-specific, which can limit their effectiveness and appeal.
- Customer Engagement: Omnichannel retail focuses on continuous and cohesive customer engagement. By integrating marketing efforts across channels, businesses can maintain an ongoing dialogue with customers, building stronger relationships and fostering loyalty. Multichannel retail, with its isolated marketing efforts, may struggle to keep customers engaged consistently.
- Sales Funnel Management: Omnichannel retail excels in managing the sales funnel by integrating data and tracking customer interactions across all touchpoints. This holistic view allows businesses to understand where customers are in their buying journey and tailor marketing efforts accordingly. Multichannel retail, lacking this integration, may find it challenging to manage the sales funnel effectively and optimize conversions.
- Channel-Specific Strategies: In multichannel retail, each channel often has its own marketing and sales strategy. This approach can lead to specialized tactics that cater to the unique characteristics of each platform. However, it can also result in silos and a lack of cohesion across the brand. Omnichannel retail, by contrast, emphasizes a unified strategy that integrates all channels, providing a seamless and consistent approach to marketing and sales.
- Data-Driven Marketing: Omnichannel retail leverages data from all customer interactions to inform marketing strategies. This data-driven approach enables precise targeting, better segmentation, and more effective campaigns. In multichannel retail, the fragmented data makes it difficult to gain comprehensive insights, leading to less informed and potentially less effective marketing efforts.
- Customer Retention: Omnichannel retail’s integrated approach helps improve customer retention by providing a consistent and personalized experience. Marketing efforts are aligned to engage customers continuously, fostering long-term loyalty. Multichannel retail may face challenges in retaining customers due to inconsistent experiences and less targeted marketing.
- Return on Investment (ROI): The integrated nature of omnichannel retail often leads to a higher ROI for marketing and sales efforts. By creating a unified strategy and leveraging data effectively, businesses can optimize their spending and achieve better results. In multichannel retail, the separate strategies and lack of integration can lead to inefficiencies and lower ROI.
- Social Media Integration: In omnichannel retail, social media is integrated into the overall marketing strategy, allowing for seamless interactions and consistent branding across platforms. Customers can engage with the brand on social media and experience the same level of service and messaging as they would through other channels. Multichannel retail may treat social media as a standalone channel, leading to disjointed experiences and less effective engagement.
- Omni-Channel Loyalty Programs: Omnichannel retail often includes integrated loyalty programs that reward customers for interactions across all channels. This encourages repeat purchases and builds a stronger connection with the brand. In multichannel retail, loyalty programs may be specific to certain channels, limiting their impact and appeal.
- Customer Feedback and Adaptation: Omnichannel retail uses integrated systems to collect and analyze customer feedback from all touchpoints. This comprehensive understanding allows businesses to adapt their marketing and sales strategies quickly to meet customer needs. In multichannel retail, feedback is often siloed, making it harder to identify trends and implement necessary changes.

The marketing and sales strategies in omnichannel vs multichannel retail highlight significant differences in how businesses engage with customers and drive growth. Omnichannel retail focuses on integration, personalization, and consistency, creating a seamless customer experience that fosters loyalty and maximizes ROI. Multichannel retail, while offering flexibility through channel-specific strategies, may struggle with fragmentation and inefficiencies.
Operational Efficiency
Operational efficiency is a critical factor that distinguishes omnichannel vs multichannel retail. The efficiency of operations impacts everything from inventory management to logistics and supply chain considerations. How businesses manage these elements can significantly influence their overall performance, cost-effectiveness, and customer satisfaction. This section explores the operational complexities and efficiencies associated with both retail models.
- Operational Complexities: Omnichannel retail involves higher operational complexities due to the need for integration across multiple channels. This includes synchronizing data, managing a unified inventory system, and ensuring consistency in customer experience. The integration of various systems and processes requires significant technological investment and continuous coordination. In contrast, multichannel retail operates with each channel independently, reducing the need for integration but leading to potential inefficiencies and duplications in operations.
- Unified Inventory Management: Omnichannel retail relies on a unified inventory management system that provides real-time visibility across all channels. This integration allows businesses to track inventory accurately, reduce stockouts, and optimize stock levels. Customers can check product availability across different touchpoints and choose their preferred method of purchase or delivery. Multichannel retail, with its separate inventory systems for each channel, often faces challenges in maintaining accurate inventory levels, leading to overstocking or stockouts and reduced operational efficiency.
- Logistics and Fulfillment: In omnichannel retail, logistics and fulfillment processes are designed to be flexible and responsive to customer demands. This includes options like buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), ship-from-store, and same-day delivery. The integrated logistics system ensures that orders can be fulfilled from any location, optimizing delivery times and reducing costs. Multichannel retail, on the other hand, has distinct logistics and fulfillment processes for each channel, which can lead to inefficiencies, higher costs, and longer delivery times.
- Supply Chain Considerations: Omnichannel retail requires a highly coordinated supply chain that supports seamless operations across all channels. This involves integrating suppliers, manufacturers, and distribution centers to ensure timely and efficient movement of goods. Real-time data sharing and collaboration are essential to maintain the flow of inventory and meet customer expectations. In multichannel retail, the lack of integration in the supply chain can result in delays, increased costs, and challenges in meeting customer demand.
- Order Management Systems (OMS): Omnichannel retail leverages advanced order management systems that centralize and streamline the order process. These systems track orders from all channels, provide real-time updates, and ensure accurate fulfillment. Customers benefit from consistent order tracking and status updates. In multichannel retail, order management systems are often channel-specific, leading to fragmented order processing and potential delays in fulfillment.
- Cost Efficiency: The integrated approach of omnichannel retail can lead to greater cost efficiency in the long run. By optimizing inventory management, logistics, and supply chain operations, businesses can reduce waste, lower operational costs, and improve profitability. In multichannel retail, the lack of integration often results in higher costs due to inefficiencies, redundancies, and the need for separate resources for each channel.
- Customer Service and Support: Omnichannel retail enhances customer service and support by providing a unified system that tracks customer interactions and transactions across all channels. This enables businesses to offer consistent and informed customer support, improving satisfaction and loyalty. Multichannel retail, with its independent systems, may struggle to provide cohesive customer service, as support teams may not have access to complete customer information.
- Scalability: Omnichannel retail systems are designed to be scalable, allowing businesses to expand and adapt to changing market conditions and customer behaviors. The integrated technology infrastructure supports growth without significant disruptions. In multichannel retail, scalability can be challenging due to the need to manage separate systems and processes for each channel, limiting the ability to quickly adapt and expand.
- Operational Agility: The integration of systems in omnichannel retail enhances operational agility, enabling businesses to respond quickly to market changes, customer demands, and supply chain disruptions. Real-time data and insights allow for proactive decision-making and adjustments. Multichannel retail, with its siloed operations, may lack the agility to respond swiftly, leading to slower reaction times and missed opportunities.
- Resource Allocation: Omnichannel retail optimizes resource allocation by leveraging integrated systems to streamline operations and reduce redundancies. This ensures that resources such as staff, inventory, and technology are used efficiently across all channels. Multichannel retail often requires separate resources for each channel, leading to potential over-allocation or under-utilization of resources.
- Performance Metrics and Analytics: Omnichannel retail benefits from comprehensive performance metrics and analytics that provide insights into operational efficiency across all channels. This data-driven approach allows businesses to identify areas for improvement, optimize processes, and enhance overall performance. In multichannel retail, the lack of integrated data can make it difficult to measure and analyze performance accurately, hindering efforts to improve efficiency.
- Customer Satisfaction: The operational efficiencies achieved in omnichannel retail contribute to higher customer satisfaction. By providing seamless experiences, timely deliveries, and consistent service, businesses can meet and exceed customer expectations. Multichannel retail, with its potential for inconsistencies and delays, may struggle to achieve the same level of customer satisfaction.

The differences in operational efficiency between omnichannel vs multichannel retail are significant and impactful. Omnichannel retail’s integrated approach enhances inventory management, logistics, and supply chain operations, leading to greater cost efficiency, scalability, and customer satisfaction. Multichannel retail, while simpler to implement initially, often faces challenges in maintaining operational efficiency due to its fragmented systems and processes. By understanding these differences, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their operations and achieve long-term success.
Customer Journey Mapping in Omnichannel vs Multichannel Retail
The process of Customer Journey Mapping provides a comprehensive view of how customers interact with a brand across various touchpoints, revealing critical insights into their behaviors, preferences, and pain points.
Understanding Customer Journey Maps
Mapping customer journeys is a critical component for businesses aiming to optimize their customer engagement strategies and enhance overall satisfaction. In the context of omnichannel vs multichannel retail, understanding how customers interact with a brand across various touchpoints can reveal significant insights into their experiences, preferences, and pain points. This comprehensive approach not only helps in improving customer satisfaction but also drives loyalty and business growth.
The importance of mapping customer journeys cannot be overstated. It provides a detailed view of the customer’s interactions with a brand, highlighting critical moments that influence their decision-making process. In omnichannel retail, where the goal is to create a seamless and integrated customer experience, journey mapping is essential to ensure that transitions between different channels, such as online and offline, are smooth and consistent. This helps in eliminating friction points and enhancing the overall customer experience. In contrast, multichannel retail often operates with independent channels, making journey mapping crucial to identify and rectify inconsistencies that could disrupt the customer’s experience.
To create an effective customer journey map, businesses should follow several key steps:
- Define Objectives: The first step is to establish clear objectives for the journey mapping process. These objectives could range from improving customer satisfaction and increasing conversion rates to identifying bottlenecks in the customer journey. Having well-defined objectives helps focus the mapping process and ensures that it aligns with the overall business goals.
- Identify Customer Personas: Understanding who the customers are is vital for accurate journey mapping. Businesses should identify and define their customer personas—semi-fictional representations of the ideal customers based on market research and real data. These personas should include detailed information about customer demographics, needs, preferences, and behaviors.
- Map Customer Touchpoints: It is essential to identify all the touchpoints where customers interact with the brand. This includes both online touchpoints, such as websites, mobile apps, and social media, and offline touchpoints, like physical stores, call centers, and print advertisements. In omnichannel vs multichannel retail, a comprehensive mapping of these touchpoints ensures that the entire customer experience is captured.
- Gather Customer Data: Collecting data on how customers move through the identified touchpoints is crucial. This can be achieved through various methods, including surveys, interviews, focus groups, and analytics tools. The data should provide insights into customer behaviors, preferences, pain points, and emotions at each stage of their journey.
- Create a Visual Representation: Developing a visual representation of the customer journey helps in understanding and communicating the journey clearly. This can be done through flowcharts, infographics, or diagrams that outline each step of the customer journey, from awareness to post-purchase, highlighting key interactions, decision points, and emotional states.
- Analyze and Identify Pain Points: Once the journey map is created, it is essential to analyze it to identify pain points and areas for improvement. Look for stages where customers experience frustration, drop off, or encounter barriers. In omnichannel retail, this analysis might reveal gaps in the integration of channels, while in multichannel retail, it could highlight inconsistencies between different touchpoints.
- Optimize the Customer Journey: Based on the analysis, develop strategies to optimize the customer journey. This could involve integrating systems to provide a seamless experience in omnichannel retail or aligning marketing and customer service efforts across channels in multichannel retail. The goal is to enhance the customer experience by addressing pain points and ensuring a smooth journey.
- Implement Changes and Monitor Results: Implement the identified changes and continuously monitor their impact on the customer journey. Use KPIs such as customer satisfaction scores, conversion rates, and customer retention rates to measure the effectiveness of the improvements. Continuous monitoring and iteration are essential to keep the customer journey optimized and aligned with evolving customer expectations.
By understanding and effectively mapping customer journeys, businesses in both omnichannel and multichannel retail can gain valuable insights into their customers’ experiences. This process helps identify areas for improvement, leading to enhanced overall satisfaction and loyalty. For omnichannel retail, it ensures a seamless and engaging customer experience across all touchpoints, while for multichannel retail, it highlights areas that need better integration and consistency. This comprehensive approach to customer journey mapping is crucial for achieving long-term success and customer loyalty in the competitive retail landscape.
Customer Journey in Multichannel Retail
In multichannel retail, customers interact with a brand through various independent channels, such as physical stores, online websites, mobile apps, and social media platforms. Each channel operates separately, offering its own unique experience. While this approach provides flexibility for customers to choose their preferred shopping method, it often leads to fragmented and inconsistent experiences. Understanding the customer journey in multichannel retail is crucial for identifying pain points and areas for improvement.
Examples of customer journeys in multichannel retail illustrate the challenges and opportunities within this model:
- Online to In-Store: A customer browses products on a retailer’s website, adds items to their cart, but decides not to complete the purchase online. Later, they visit the physical store to see the products in person and make a purchase. In this scenario, the customer might encounter different prices, product availability, or promotions, leading to confusion and frustration.
- Mobile App to Website: A customer uses the retailer’s mobile app to check for product reviews and availability. They find a product they like and switch to the desktop website to make a purchase, preferring the larger screen for detailed information. However, they may have to re-enter their search criteria and cart details, as the app and website do not share data seamlessly.
- Social Media to Online Store: A customer discovers a product on the retailer’s social media page and clicks on the link to purchase it online. The link takes them to the retailer’s website, where they have to search for the product again or navigate through several pages to find it. This disjointed experience can lead to cart abandonment.
Pain points and opportunities for improvement in multichannel retail:
- Fragmented Customer Data: Customer data is often siloed in different channels, making it difficult to provide personalized experiences. Integrating data across channels can enhance personalization and customer satisfaction.
- Inconsistent Branding and Messaging: Different channels may present varied branding, messaging, and promotions, leading to a lack of cohesive brand identity. Standardizing branding and communication can create a more unified customer experience.
- Manual Data Entry: Customers often have to re-enter information when switching between channels, causing frustration and potential abandonment. Implementing integrated systems can streamline the process and reduce friction.
- Limited Cross-Channel Promotions: Promotions are typically channel-specific, which can limit their effectiveness. Offering cross-channel promotions can increase customer engagement and loyalty.
- Inventory Discrepancies: Separate inventory systems for each channel can lead to stock discrepancies, resulting in stockouts or overstocking. Centralized inventory management can improve accuracy and efficiency.
Customer Journey in Omnichannel Retail
Omnichannel retail aims to provide a seamless and integrated customer experience across all touchpoints. By unifying online and offline channels, omnichannel retail ensures that customers can transition smoothly between different platforms without encountering disruptions or inconsistencies. This approach leverages integrated data and technology to enhance the customer journey, providing personalized and cohesive experiences.
Examples of customer journeys in omnichannel retail highlight the benefits of this integrated approach:
- Online to In-Store (BOPIS): A customer browses products on the retailer’s website, adds items to their cart, and chooses the “Buy Online, Pick Up In-Store” (BOPIS) option. They receive a notification when their order is ready for pickup, and upon visiting the store, they find a dedicated pickup area with their order ready. This seamless transition from online to in-store enhances convenience and satisfaction.
- Mobile App to In-Store: A customer uses the retailer’s mobile app to scan products and check reviews while shopping in the physical store. The app syncs with their online account, providing personalized recommendations based on their browsing history and previous purchases. This integrated experience helps the customer make informed decisions and feel valued.
- Social Media to Online Store with Personalization: A customer sees a personalized ad for a product on social media, based on their previous interactions with the brand. They click the ad and are directed to the retailer’s website, where the product is pre-populated in their cart along with related recommendations. The seamless integration of social media data with the online store enhances the shopping experience.
Enhancing the customer experience through integration in omnichannel retail involves several strategies:
- Unified Customer Data: Integrating customer data across all touchpoints allows for a 360-degree view of the customer. This enables personalized marketing, tailored recommendations, and consistent service.
- Consistent Branding and Messaging: Maintaining consistent branding and messaging across all channels reinforces brand identity and builds trust. Customers receive the same information and promotions, regardless of the channel they use.
- Real-Time Inventory Management: A centralized inventory system ensures accurate stock levels and availability across all channels. Customers can check product availability online and in-store, reducing the risk of stockouts and enhancing satisfaction.
- Flexible Fulfillment Options: Offering multiple fulfillment options, such as BOPIS, curbside pickup, and same-day delivery, provides convenience and meets diverse customer needs. Seamless integration of these options into the customer journey enhances the overall experience.
- Cross-Channel Promotions and Loyalty Programs: Implementing promotions and loyalty programs that work across all channels encourages repeat purchases and customer loyalty. Integrated systems track customer activity and rewards, providing a cohesive experience.
- Enhanced Customer Support: Integrated customer support systems enable consistent and efficient service. Customers can start a support request online and continue it in-store or vice versa, without having to repeat information.
Comparative Analysis
Understanding the key differences and similarities in the customer journeys between omnichannel vs multichannel retail is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their customer engagement strategies. Both approaches have distinct characteristics that influence customer satisfaction and loyalty, impacting how customers perceive and interact with a brand.
The customer journey in multichannel retail typically involves multiple, independent channels through which customers interact with the brand. These channels include physical stores, online websites, mobile apps, and social media platforms. While multichannel retail offers customers various ways to shop, each channel often operates in isolation, leading to fragmented experiences. For example, a customer might start their journey by browsing products on a mobile app, then visit a physical store to make a purchase, and later follow up with customer service via email. Each of these interactions may provide different information, prices, and service quality, creating inconsistencies that can frustrate customers and weaken brand loyalty.
In contrast, the customer journey in omnichannel retail is designed to be seamless and integrated across all touchpoints. Omnichannel retail leverages technology and data integration to ensure that customers can move fluidly between channels without experiencing any disruption or inconsistencies. For instance, a customer might research a product on the retailer’s website, receive personalized recommendations via email, purchase the product through a mobile app, and pick it up in-store, all while enjoying a cohesive and personalized experience. This seamless integration enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty by providing consistent and tailored interactions.
Key differences and similarities in omnichannel vs multichannel customer journeys include:
- Integration vs. Fragmentation: Omnichannel retail focuses on integrating all channels to provide a unified customer experience, while multichannel retail operates with each channel independently. This integration in omnichannel retail allows for consistent customer data, messaging, and service across all touchpoints, reducing friction and enhancing satisfaction. Multichannel retail’s fragmented approach often results in inconsistent experiences and a lack of cohesion.
- Data Utilization: In omnichannel retail, customer data is centralized and shared across all channels, enabling personalized marketing, targeted promotions, and informed customer service. This comprehensive data utilization ensures that customers receive relevant and consistent interactions, improving their overall experience. In multichannel retail, data is typically siloed within each channel, limiting the ability to personalize and optimize interactions. This can lead to generic and less effective marketing efforts.
- Customer Experience Consistency: Omnichannel retail provides a consistent customer experience by maintaining uniform branding, messaging, and service quality across all channels. Customers receive the same information and treatment, regardless of how they choose to interact with the brand. In multichannel retail, the lack of integration can lead to varied customer experiences, with different prices, promotions, and service levels across channels, which can confuse and frustrate customers.
- Flexibility and Convenience: Omnichannel retail offers greater flexibility and convenience by allowing customers to choose how they interact with the brand and providing multiple fulfillment options, such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), curbside pickup, and same-day delivery. This flexibility meets diverse customer needs and enhances satisfaction. Multichannel retail, while offering multiple touchpoints, may not provide the same level of convenience due to isolated operations and limited cross-channel integration.
- Customer Support: Omnichannel retail excels in providing integrated customer support across all channels. Customers can start a support request online and continue it in-store or vice versa, without having to repeat information or experience delays. This integrated approach ensures efficient and consistent service. In multichannel retail, customer support is often channel-specific, leading to potential inconsistencies and longer resolution times.
- Impact on Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: The seamless and personalized experience offered by omnichannel retail significantly enhances customer satisfaction and fosters loyalty. By providing a cohesive and tailored journey, businesses can build stronger relationships with customers and encourage repeat purchases. Multichannel retail, with its fragmented and inconsistent approach, may struggle to achieve the same level of satisfaction and loyalty. Customers are more likely to experience frustration and disconnects, which can lead to decreased loyalty and higher churn rates.
In summary, the comparative analysis of omnichannel vs multichannel retail highlights the importance of integration and consistency in enhancing the customer journey. Omnichannel retail’s focus on providing a seamless and personalized experience across all touchpoints leads to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty. In contrast, multichannel retail’s fragmented approach often results in inconsistent experiences and challenges in building strong customer relationships. By understanding these key differences and similarities, businesses can better tailor their strategies to meet the evolving expectations of their customers and achieve long-term success.
Technological Enablers for Omnichannel and Multichannel Retail
Technologies for Multichannel Retail
Technological advancements play a crucial role in shaping retail strategies and enhancing customer experiences. In the context of omnichannel vs multichannel retail, the technologies employed significantly influence the effectiveness and efficiency of each approach. This section provides an overview of the key technologies supporting multichannel retail strategies and identifies the technological gaps that hinder its potential compared to omnichannel retail.
Multichannel retail strategies rely on a variety of technologies to manage and optimize customer interactions across different platforms. These technologies are designed to function independently within each channel, offering distinct capabilities that cater to specific customer needs and preferences. However, the lack of integration among these technologies often limits the overall effectiveness of multichannel retail.
- eCommerce Platforms: eCommerce platforms are the backbone of online sales in multichannel retail. They enable businesses to set up and manage online stores, handle transactions, and provide various features like product catalogs, payment gateways, and customer reviews. Popular eCommerce platforms include Shopify, Magento, and WooCommerce. These platforms are essential for reaching customers online but often operate independently from other channels.
- CRM Systems: CRM systems in multichannel retail help businesses manage customer interactions, track sales, and automate marketing efforts. These systems store customer data, track purchase history, and facilitate personalized marketing campaigns. Examples of CRM systems used in multichannel retail include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM. While CRM systems are powerful tools, their data is often siloed, limiting their ability to provide a unified view of the customer across all channels.
- Point of Sale (POS) Systems: POS systems are critical for managing in-store sales and transactions. They handle payment processing, track inventory, and generate sales reports. Popular POS systems include Square, Clover, and Lightspeed. In multichannel retail, POS systems typically operate independently from online sales platforms, leading to potential discrepancies in inventory and customer data.
- Email Marketing Platforms: Email marketing platforms such as Mailchimp, Constant Contact, and Sendinblue are used to send promotional emails, newsletters, and automated messages to customers. These platforms help businesses engage with customers, promote products, and drive online traffic. However, the lack of integration with other channels can result in fragmented marketing efforts.
- Social Media Management Tools: Social media management tools like Hootsuite, Buffer, and Sprout Social enable businesses to schedule posts, monitor engagement, and analyze social media performance. These tools are essential for managing brand presence on social media platforms. In multichannel retail, social media efforts are often not integrated with other marketing channels, leading to isolated customer interactions.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile apps provide an additional channel for customer engagement, allowing businesses to offer a personalized shopping experience on smartphones and tablets. Mobile apps can feature product catalogs, exclusive offers, and in-app purchasing. While mobile apps are valuable, they often function separately from other channels, creating a disjointed customer experience.

While these technologies support multichannel retail strategies, several key elements are missing, limiting their effectiveness compared to omnichannel retail:
- Integration and Synchronization: One of the primary technological gaps in multichannel retail is the lack of integration and synchronization across different systems. Data from eCommerce platforms, CRM systems, POS systems, and other tools often remain siloed, preventing businesses from having a unified view of customer interactions and preferences. This fragmentation hinders personalized marketing and cohesive customer experiences.
- Unified Customer Data: Multichannel retail lacks a centralized database that consolidates customer information from all touchpoints. Without unified customer data, businesses struggle to provide consistent and personalized experiences across channels. Omnichannel retail addresses this gap by integrating data from all sources, enabling a comprehensive understanding of the customer journey.
- Real-Time Inventory Management: Effective inventory management is challenging in multichannel retail due to separate systems for online and offline sales. This can lead to inventory discrepancies, stockouts, or overstocking. Omnichannel retail overcomes this issue with real-time inventory management systems that provide accurate visibility and synchronization across all channels.
- Consistent Branding and Messaging: In multichannel retail, branding and messaging often vary between channels, leading to inconsistencies that can confuse customers and weaken brand identity. Omnichannel retail ensures consistent branding and messaging across all touchpoints, reinforcing a cohesive brand image and enhancing customer trust.
- Cross-Channel Customer Support: Multichannel retail typically offers channel-specific customer support, which can result in inconsistent service quality and longer resolution times. Omnichannel retail integrates customer support systems, allowing for seamless and efficient service across all channels. Customers can start a support request online and continue it in-store without repeating information.
- Personalization and Customization: The lack of integrated data in multichannel retail limits the ability to deliver personalized and customized experiences. Omnichannel retail leverages integrated data to provide tailored recommendations, personalized offers, and relevant content, enhancing customer engagement and satisfaction.
In summary, while multichannel retail relies on various key technologies to manage customer interactions across different platforms, the lack of integration and synchronization among these technologies limits its potential. The primary technological gaps in multichannel retail include the absence of unified customer data, real-time inventory management, consistent branding and messaging, cross-channel customer support, and effective personalization. Addressing these gaps through integrated systems and data consolidation can enhance the effectiveness of multichannel retail and bring it closer to the seamless experience offered by omnichannel retail.
Technologies for Omnichannel Retail
The rise of omnichannel retail has transformed the way businesses engage with customers, emphasizing the need for seamless and integrated experiences across all touchpoints. The technologies that support omnichannel strategies are critical in providing the infrastructure required to deliver consistent, personalized, and efficient interactions. This section offers an overview of the key technologies that underpin omnichannel retail and highlights how they differentiate omnichannel from multichannel retail.
In omnichannel retail, integration and real-time data synchronization are paramount. Here are the key technologies supporting omnichannel strategies:
- CRM Systems: CRM systems in omnichannel retail are designed to integrate customer data from all touchpoints into a centralized database. This integration enables businesses to gain a comprehensive view of customer interactions and preferences, facilitating personalized marketing, enhanced customer service, and informed decision-making. Systems like Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics, and HubSpot are popular choices that provide robust integration capabilities essential for omnichannel operations.
- ERP Systems: ERP systems play a crucial role in managing and automating core business processes across the entire organization. In omnichannel retail, ERP systems integrate with other platforms such as eCommerce, POS, and inventory management systems to ensure real-time data flow and operational efficiency. This integration allows businesses to manage resources effectively, optimize supply chains, and maintain accurate inventory levels. Leading ERP systems like SAP, Oracle, and Odoo offer comprehensive solutions tailored for omnichannel environments.
- POS Systems: Modern POS systems in omnichannel retail are more than just transaction processors; they are integrated hubs that connect in-store activities with online operations. These systems provide real-time sales data, customer purchase history, and inventory updates, ensuring a consistent shopping experience across all channels. Solutions like Square, Shopify POS, and Lightspeed offer the necessary integration capabilities to support seamless omnichannel retailing.
- eCommerce Platforms: eCommerce platforms are the backbone of online retail operations, providing the necessary infrastructure to manage product listings, transactions, and customer interactions. In omnichannel retail, these platforms are integrated with other systems to provide a unified shopping experience. Platforms like Shopify, Magento, and BigCommerce are equipped with APIs and integration tools that facilitate seamless connectivity with CRM, ERP, and POS systems.
- Inventory Management Systems: Effective inventory management is critical in omnichannel retail to ensure product availability and optimize fulfillment processes. Integrated inventory management systems provide real-time visibility into stock levels across all channels, reducing the risk of stockouts and overstocking. Technologies like TradeGecko, Zoho Inventory, and NetSuite offer advanced features that support centralized inventory control and multi-location management.
- Marketing Automation Tools: Marketing automation tools in omnichannel retail leverage integrated customer data to deliver personalized and targeted marketing campaigns. These tools automate email marketing, social media engagement, and other marketing activities, ensuring consistent messaging and branding across all channels. Platforms like Marketo, Pardot, and Mailchimp provide robust automation capabilities that enhance customer engagement and drive sales.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs collect and unify customer data from various sources, creating a single, comprehensive view of each customer. This integration enables businesses to deliver highly personalized experiences and targeted marketing efforts. CDPs like Segment, Tealium, and Exponea are essential for managing and analyzing customer data in omnichannel retail.
- Order Management Systems (OMS): OMS in omnichannel retail coordinate orders across all sales channels, ensuring efficient fulfillment and delivery. These systems integrate with eCommerce platforms, POS systems, and inventory management tools to provide real-time order tracking and management. Technologies like Orderhive, Brightpearl, and Shopify Plus offer advanced OMS capabilities that support omnichannel order processing.
- Customer Support and Service Platforms: Integrated customer support platforms ensure consistent and efficient service across all channels. These platforms enable seamless communication between customers and support teams, providing tools for live chat, email support, and in-store assistance. Solutions like Zendesk, Freshdesk, and Salesforce Service Cloud offer comprehensive support features that enhance the customer experience in omnichannel retail.

Technologies that define the difference between omnichannel and multichannel retail:
- Integration and Data Synchronization: The primary differentiator between omnichannel and multichannel retail is the level of integration and data synchronization across systems. Omnichannel retail relies on tightly integrated technologies that share data in real-time, ensuring a unified customer experience. Multichannel retail, on the other hand, often operates with siloed systems that do not communicate seamlessly, leading to fragmented customer interactions.
- Unified Customer Profiles: In omnichannel retail, CRM and CDP systems create unified customer profiles by consolidating data from all touchpoints. This comprehensive view allows for personalized marketing and consistent customer service. In multichannel retail, customer data is often scattered across different systems, making it challenging to provide a cohesive experience.
- Real-Time Inventory Management: Omnichannel retail benefits from integrated inventory management systems that provide real-time visibility into stock levels across all channels. This integration ensures accurate product availability and efficient fulfillment options like buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS). Multichannel retail typically lacks this level of synchronization, leading to potential inventory discrepancies and fulfillment challenges.
- Consistent Branding and Messaging: Marketing automation tools in omnichannel retail ensure that branding and messaging are consistent across all channels. This consistency reinforces brand identity and enhances customer trust. In multichannel retail, marketing efforts are often channel-specific, leading to varied messaging that can confuse customers.
- Seamless Customer Support: Integrated customer support platforms in omnichannel retail provide a seamless service experience across all channels. Customers can switch between online and offline support without losing context. In multichannel retail, support is usually handled separately for each channel, resulting in potential inconsistencies and longer resolution times.
The technologies that support omnichannel retail are designed to provide seamless integration and real-time data synchronization across all touchpoints, creating a unified and personalized customer experience. The key technological enablers include integrated CRM, ERP, POS, eCommerce platforms, inventory management systems, marketing automation tools, CDPs, OMS, and customer support platforms. These technologies differentiate omnichannel from multichannel retail by ensuring consistent branding, efficient operations, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Future Trends in Retail Technology
Emerging Technologies and Their Potential Impact
- AI and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are revolutionizing retail by enabling more personalized and efficient customer experiences. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data to predict customer preferences, optimize inventory management, and enhance marketing strategies. In omnichannel retail, AI can provide real-time personalization across all touchpoints, ensuring consistent and relevant interactions. For multichannel retail, AI can help bridge the gap between channels by providing insights that improve customer service and operational efficiency.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices are becoming increasingly prevalent in retail, offering new ways to enhance customer experience and streamline operations. Smart shelves, RFID tags, and connected devices can provide real-time inventory tracking and automated restocking, reducing out-of-stock situations. In omnichannel retail, IoT enables seamless integration of online and offline data, enhancing the overall shopping experience. In multichannel retail, IoT can improve individual channel efficiency but may face challenges in integration.
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are transforming how customers interact with products. AR allows customers to visualize products in their real-world environment through their smartphones, enhancing the online shopping experience. VR provides immersive experiences, enabling customers to explore virtual stores or try products before purchasing. These technologies are particularly beneficial for omnichannel retail, where they can provide consistent experiences across online and offline channels. In multichannel retail, AR and VR can enhance specific channels but may lack integration.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain offers significant potential for enhancing transparency and security in retail operations. It can provide immutable records of transactions, ensuring data integrity and reducing fraud. For supply chain management, blockchain can track products from origin to consumer, enhancing trust and traceability. In omnichannel retail, blockchain can facilitate secure data sharing across channels, improving customer trust and operational efficiency. In multichannel retail, blockchain can enhance individual channel security but may face integration challenges.
- Voice Commerce: The rise of voice-activated assistants like Amazon’s Alexa and Google Assistant is driving the adoption of voice commerce. Customers can use voice commands to search for products, place orders, and receive personalized recommendations. In omnichannel retail, voice commerce can provide a seamless shopping experience across devices and platforms. In multichannel retail, it can enhance individual channel interactions but may struggle with data integration.
- Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation are transforming retail operations by increasing efficiency and reducing costs. Automated warehouses, robotic process automation (RPA), and in-store robots can handle tasks like inventory management, order fulfillment, and customer assistance. In omnichannel retail, these technologies can enhance the coordination of online and offline operations, providing a consistent customer experience. In multichannel retail, robotics and automation can improve specific processes but may lack overall integration.
- 5G Technology: The rollout of 5G networks promises to revolutionize retail by enabling faster and more reliable connectivity. This technology will support real-time data transfer, enhancing the performance of IoT devices, AR/VR applications, and mobile commerce. In omnichannel retail, 5G can ensure seamless connectivity across all channels, improving customer experience and operational efficiency. In multichannel retail, 5G can enhance the performance of individual channels but may face challenges in achieving full integration.
Predictions for the Future of Retail Technology
- Enhanced Personalization and Customer Experience: As AI and ML technologies advance, the level of personalization in retail will continue to improve. Omnichannel retail will see even more sophisticated personalization across all touchpoints, providing highly tailored experiences that drive customer loyalty. Multichannel retail will also benefit from enhanced personalization, though the impact may be more fragmented.
- Greater Integration of Online and Offline Channels: The future of retail will likely see a convergence of online and offline channels, driven by technologies like IoT, AR/VR, and 5G. Omnichannel retail will lead this integration, offering a seamless and cohesive shopping experience. Multichannel retail will need to adopt integrated technologies to stay competitive and meet customer expectations.
- Increased Adoption of Blockchain for Transparency and Security: Blockchain technology will become more prevalent in retail, providing enhanced security, transparency, and traceability. Omnichannel retail will benefit from secure data sharing and trusted transactions across all channels. Multichannel retail will also adopt blockchain, though the impact may vary depending on the level of integration.
- Rise of Voice Commerce and Conversational AI: Voice commerce will continue to grow, with more customers using voice-activated assistants for shopping. Omnichannel retail will leverage voice commerce to provide a seamless experience across devices and platforms. Multichannel retail will need to integrate voice commerce into their strategy to remain competitive.
- Automation and Robotics Revolutionizing Operations: The adoption of robotics and automation will increase, transforming various aspects of retail operations. Omnichannel retail will benefit from improved coordination of online and offline processes, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction. Multichannel retail will also see improvements, though the benefits may be more isolated.
- Accelerated Digital Transformation with 5G: The deployment of 5G networks will accelerate digital transformation in retail, enabling faster and more reliable connectivity. Omnichannel retail will leverage 5G to enhance real-time data transfer and improve the overall customer experience. Multichannel retail will also benefit, though the extent of the impact will depend on the level of integration.
The future of retail technology promises significant advancements that will further differentiate omnichannel vs multichannel retail. Emerging technologies like AI, IoT, AR/VR, blockchain, voice commerce, robotics, and 5G will shape the retail landscape, enhancing personalization, integration, and operational efficiency. Omnichannel retail, with its focus on seamless integration and real-time data synchronization, will continue to lead the way in delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Measuring Success in Omnichannel and Multichannel Retail
For both omnichannel and multichannel retail, KPIs provide critical insights into operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall performance. By systematically tracking and analyzing these KPIs, businesses can identify strengths and weaknesses, drive continuous improvement, and enhance the customer experience.
KPIs
Understanding and analyzing the necessary KPIs is essential for identifying strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. This section explores the KPIs specific to omnichannel vs multichannel retail and discusses how to measure and analyze these indicators effectively.
What are the KPIs for Multichannel and Omnichannel Retail?
KPIs are metrics used to evaluate the effectiveness and success of retail strategies. While many KPIs are relevant to both omnichannel and multichannel retail, their application and importance can vary depending on the approach.

Here are some critical KPIs for each model:
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT): Customer satisfaction scores measure how satisfied customers are with their shopping experience. This KPI is vital for both omnichannel and multichannel retail, as it directly impacts customer loyalty and retention. High CSAT scores indicate a positive customer experience, while low scores highlight areas needing improvement.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS measures customer loyalty and their likelihood to recommend the brand to others. It is a crucial KPI for understanding overall customer sentiment and predicting future growth. In omnichannel retail, a high NPS suggests that customers appreciate the seamless and integrated experience, while in multichannel retail, it reflects satisfaction with individual channel interactions.
- Customer Retention Rate: This KPI measures the percentage of customers who continue to shop with the brand over a specific period. High retention rates indicate strong customer loyalty and satisfaction. Omnichannel retail typically aims for higher retention by providing a consistent experience across all channels, while multichannel retail focuses on retaining customers within each channel.
- Average Order Value (AOV): AOV tracks the average amount spent by customers per transaction. This KPI helps businesses understand spending patterns and identify opportunities to increase sales through upselling and cross-selling. Omnichannel strategies often aim to increase AOV by leveraging personalized recommendations across all touchpoints.
- Conversion Rate: Conversion rate measures the percentage of visitors who make a purchase. This KPI is essential for both omnichannel and multichannel retail, indicating the effectiveness of the sales funnel. Omnichannel retail typically achieves higher conversion rates by providing a cohesive and streamlined shopping experience.
- Cart Abandonment Rate: This KPI tracks the percentage of online shopping carts that are abandoned before completion. High cart abandonment rates indicate potential issues in the checkout process or lack of trust. Reducing this rate is crucial for improving sales and customer satisfaction in both omnichannel and multichannel retail.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): CLV estimates the total revenue a business can expect from a customer over their entire relationship with the brand. This KPI is vital for understanding long-term profitability and the effectiveness of retention strategies. Omnichannel retail often aims to increase CLV by enhancing customer loyalty through integrated experiences.
- Channel Performance: Measuring the performance of individual channels is crucial in multichannel retail. KPIs such as sales per channel, traffic per channel, and channel-specific conversion rates provide insights into the effectiveness of each channel. In omnichannel retail, these KPIs help understand how each channel contributes to the overall customer journey.
- Inventory Turnover: This KPI measures how often inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period. High inventory turnover indicates efficient inventory management and strong sales. Omnichannel retail relies on real-time inventory tracking to optimize turnover, while multichannel retail may face challenges with inventory discrepancies across channels.
- Fulfillment and Delivery Times: These KPIs measure the efficiency of order processing and delivery. Fast and reliable fulfillment is crucial for customer satisfaction. Omnichannel retail aims for quick and seamless fulfillment through integrated logistics, while multichannel retail must ensure efficient operations within each channel.
How to Measure and Analyze These KPIs
Measuring and analyzing KPIs requires a systematic approach to gather accurate data and derive actionable insights. Here are steps to effectively measure and analyze KPIs for omnichannel and multichannel retail:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish clear business objectives that align with your overall strategy. Determine which KPIs are most relevant to achieving these objectives. For example, if the goal is to increase customer loyalty, focus on KPIs like NPS, retention rate, and CLV.
- Collect Accurate Data: Use reliable tools and systems to collect data across all channels. For omnichannel retail, ensure data integration across CRM, ERP, POS, and eCommerce platforms to get a unified view. In multichannel retail, gather data from each channel independently but strive for consistency in data collection methods.
- Use Advanced Analytics Tools: Employ advanced analytics tools and software to process and analyze data. Tools like Google Analytics, Adobe Analytics, and CRM analytics platforms can provide in-depth insights into customer behavior and performance metrics. These tools are essential for both omnichannel and multichannel retail to track and analyze KPIs effectively.
- Regular Monitoring and Reporting: Establish a regular monitoring and reporting schedule to track KPI performance. Weekly, monthly, or quarterly reports can help identify trends, detect issues early, and measure progress towards goals. Consistent monitoring is crucial for making data-driven decisions in both omnichannel and multichannel retail.
- Segment Data for Detailed Insights: Segment data by customer demographics, purchase behavior, and channel interactions to gain deeper insights. For omnichannel retail, analyze how different segments move across channels and their impact on overall performance. In multichannel retail, evaluate the performance of each segment within individual channels.
- Benchmark Against Industry Standards: Compare your KPIs against industry benchmarks to understand your competitive position. Identifying areas where you lag behind can help prioritize improvement efforts. Both omnichannel and multichannel retailers should regularly benchmark their performance to stay competitive.
- Identify and Address Pain Points: Use KPI analysis to identify pain points in the customer journey. For example, a high cart abandonment rate might indicate issues with the checkout process. Once identified, take corrective actions to address these pain points and improve the overall customer experience.
- Implement Continuous Improvement: Continuously refine and improve your strategies based on KPI insights. For omnichannel retail, focus on enhancing integration and personalization across channels. In multichannel retail, aim to optimize the performance of each channel while exploring opportunities for better integration.
- Communicate Insights Across the Organization: Share KPI insights with relevant stakeholders across the organization. Ensuring that all departments understand performance metrics and their implications helps align efforts towards common goals. Regular communication fosters a data-driven culture and supports continuous improvement.
Understanding and effectively measuring KPIs is crucial for assessing the success of omnichannel vs multichannel retail strategies. By focusing on relevant KPIs such as customer satisfaction, NPS, retention rates, AOV, and conversion rates, businesses can gain valuable insights into their performance and identify areas for improvement. Employing advanced analytics tools, regularly monitoring performance, and implementing continuous improvement strategies will help businesses optimize their retail operations and achieve long-term success.
Sales and Revenue Metrics
This section explores the methods for tracking sales and revenue across various channels and provides a comparative analysis of sales performance between omnichannel and multichannel retail.
Tracking Sales and Revenue in Different Channels
Accurate tracking of sales and revenue is fundamental for assessing the performance of retail channels. In omnichannel retail, where the aim is to provide a seamless and integrated customer experience, tracking involves consolidating data from all touchpoints to get a holistic view of sales performance.

This integrated approach ensures that sales data from physical stores, online platforms, mobile apps, and other channels are combined into a single system, providing a comprehensive picture of overall performance.
- POS Systems: Modern POS systems in physical stores track sales transactions, inventory levels, and customer interactions. These systems are crucial for capturing real-time data on in-store sales and integrating it with online sales data to provide a unified view.
- eCommerce Platforms: Online sales data is tracked through eCommerce platforms like Shopify, Magento, and WooCommerce. These platforms offer detailed analytics on website traffic, conversion rates, and revenue, enabling businesses to monitor the performance of their online channels.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile apps provide a direct channel for sales and customer engagement. Tracking sales through mobile apps involves analyzing in-app purchases, user behavior, and engagement metrics to understand the effectiveness of this channel.
- Social Media and Marketplaces: Sales data from social media platforms and online marketplaces (such as Amazon and eBay) is tracked using specific tools and integrations. These platforms provide insights into customer interactions, product performance, and revenue generated through social channels.
In multichannel retail, tracking sales and revenue is often done independently for each channel. This approach can lead to fragmented data, making it challenging to get a unified view of overall performance. Businesses typically rely on individual systems for each channel, such as separate POS systems for physical stores and different analytics tools for online platforms. While this method allows for detailed analysis of each channel, it lacks the integration needed to understand cross-channel interactions and customer journeys fully.
Comparative Analysis of Sales Performance
Comparing sales performance between omnichannel and multichannel retail provides valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of each approach. This comparative analysis helps businesses identify opportunities for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance overall performance.
- Total Sales and Revenue: In omnichannel retail, the integration of sales data from all channels often leads to higher total sales and revenue. The seamless customer experience encourages repeat purchases and higher average order values (AOV). Multichannel retail, with its independent channels, may struggle to achieve the same level of performance due to fragmented customer journeys and inconsistencies.
- Sales by Channel: Omnichannel retail allows businesses to track and analyze sales performance across different channels comprehensively. This holistic view helps identify which channels are performing well and which need improvement. In multichannel retail, sales by channel are tracked separately, providing detailed insights into each channel’s performance but lacking a unified perspective.
- Cross-Channel Sales: Omnichannel retail excels in leveraging cross-channel sales opportunities. For example, customers may browse products online and purchase them in-store, or vice versa. Tracking these cross-channel interactions helps businesses understand how different channels complement each other and drive overall sales. Multichannel retail often misses these insights due to the lack of integration.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Omnichannel retail typically sees higher CLV as customers who experience a seamless and personalized journey are more likely to become loyal and repeat buyers. Multichannel retail may face challenges in building long-term customer relationships due to inconsistent experiences across channels.
- Conversion Rates: Conversion rates tend to be higher in omnichannel retail, where the customer journey is optimized for seamless transitions between channels. The consistent experience reduces friction and encourages conversions. In multichannel retail, conversion rates may vary significantly between channels, reflecting the inconsistencies and potential barriers in the customer journey.
- Customer Retention and Loyalty: Omnichannel retail strategies are designed to enhance customer retention and loyalty by providing a unified experience. The ability to track customer interactions across channels helps businesses tailor their strategies to meet customer needs. Multichannel retail, with its independent channels, may struggle to retain customers who expect a cohesive and personalized experience.
Tracking sales and revenue metrics in omnichannel vs multichannel retail is crucial for understanding performance and driving growth. Omnichannel retail benefits from integrated systems that provide a comprehensive view of sales across all channels, leading to higher total sales, better customer retention, and increased lifetime value. Multichannel retail, while offering detailed insights into individual channel performance, often faces challenges due to fragmented data and inconsistent customer experiences.
Operational Metrics
For both omnichannel and multichannel retail strategies, Operational metrics provide valuable insights into the performance of various processes, helping businesses identify areas for improvement and optimize their operations.
By understanding and tracking key operational metrics, businesses can ensure they are running smoothly and meeting customer expectations. This section explores the key operational metrics to track and their impact on overall success in the context of omnichannel vs multichannel retail.
Key Operational Metrics to Track Efficiency
- Order Fulfillment Time: This metric measures the time taken from when a customer places an order to when it is shipped. In omnichannel retail, where seamless and quick fulfillment is crucial, tracking this metric helps ensure that orders are processed efficiently across all channels. For multichannel retail, it’s essential to monitor fulfillment times for each channel to identify bottlenecks and improve service levels.
- Inventory Turnover Rate: Inventory turnover rate indicates how often inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period. A high turnover rate signifies efficient inventory management and strong sales. In omnichannel retail, integrated inventory systems help maintain optimal stock levels across all channels, reducing excess inventory and stockouts. Multichannel retail must track this metric separately for each channel, which can reveal disparities in inventory management practices.
- Return Rate: Return rate measures the percentage of products returned by customers. High return rates can indicate issues with product quality, descriptions, or fulfillment processes. In omnichannel retail, tracking return rates across all channels helps identify specific problems and streamline the returns process. For multichannel retail, analyzing return rates by channel can highlight inconsistencies in product offerings or customer expectations.
- Shipping Accuracy: Shipping accuracy measures the percentage of orders shipped correctly without errors. High accuracy is critical for customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. In omnichannel retail, integrated systems ensure consistent and accurate order processing across all channels. In multichannel retail, monitoring shipping accuracy for each channel helps pinpoint and address specific issues.
- Customer Service Response Time: This metric tracks the average time taken to respond to customer inquiries and resolve issues. Quick and efficient customer service is vital for maintaining customer satisfaction. Omnichannel retail benefits from integrated customer support systems that provide consistent service across all touchpoints. In multichannel retail, response times can vary by channel, making it important to monitor and improve service levels individually.
- Cost per Order (CPO): CPO measures the total cost associated with processing and fulfilling each order, including labor, packaging, and shipping costs. Lowering CPO is crucial for maintaining profitability. In omnichannel retail, integrated operations can optimize costs by leveraging shared resources and streamlined processes. Multichannel retail must track CPO separately for each channel to identify opportunities for cost reduction.
- Store Traffic and Online Traffic Metrics: Tracking the number of visitors to physical stores and online platforms provides insights into customer behavior and channel performance. In omnichannel retail, understanding traffic patterns helps optimize the overall customer journey. Multichannel retail must analyze these metrics separately to understand the effectiveness of each channel in attracting and retaining customers.
- Fulfillment Costs: This metric tracks the costs associated with fulfilling orders, including warehousing, picking, packing, and shipping expenses. In omnichannel retail, integrated systems help minimize fulfillment costs by optimizing inventory placement and leveraging economies of scale. Multichannel retail needs to monitor these costs for each channel to ensure efficiency and profitability.
Impact of Operational Metrics on Overall Success
Operational metrics play a vital role in determining the overall success of retail strategies by providing actionable insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of various processes. The impact of these metrics on omnichannel vs multichannel retail can be significant:
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: Efficient operations directly contribute to higher customer satisfaction. Metrics such as order fulfillment time, shipping accuracy, and customer service response time ensure that customers receive their orders promptly and accurately, leading to positive experiences and increased loyalty. Omnichannel retail, with its integrated approach, often excels in maintaining high customer satisfaction across all touchpoints. Multichannel retail can improve satisfaction by addressing inefficiencies within each channel.
- Cost Management and Profitability: Operational metrics like inventory turnover rate, cost per order, and fulfillment costs are crucial for managing expenses and maintaining profitability. By optimizing these metrics, businesses can reduce waste, lower operational costs, and improve their bottom line. Omnichannel retail benefits from economies of scale and integrated processes, which help streamline costs. Multichannel retail needs to carefully manage each channel’s expenses to ensure overall profitability.
- Operational Efficiency: Tracking metrics such as return rate and inventory turnover rate helps businesses identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. Efficient inventory management and accurate order processing reduce the likelihood of stockouts, overstocking, and returns, leading to smoother operations. Omnichannel retail’s integrated systems enhance overall efficiency, while multichannel retail must focus on optimizing each channel individually.
- Competitive Advantage: Superior operational performance provides a competitive edge by enabling businesses to deliver consistent and reliable service. Metrics like customer service response time and shipping accuracy ensure that customers have positive experiences, which can differentiate a brand from its competitors. Omnichannel retail’s ability to provide a seamless experience across all channels often leads to higher customer loyalty and market share. Multichannel retail can gain an advantage by excelling in specific channels and gradually integrating processes to enhance overall performance.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Operational metrics provide the data needed for informed decision-making. By continuously monitoring and analyzing these metrics, businesses can identify trends, predict future needs, and make strategic adjustments to improve performance. Omnichannel retail’s integrated data approach allows for comprehensive insights and more effective decisions. Multichannel retail can benefit from detailed analysis within each channel and work towards greater integration for holistic insights.
Operational metrics are critical for tracking efficiency and ensuring the overall success of retail strategies. The impact of these metrics on omnichannel vs multichannel retail highlights the advantages of integrated systems and the importance of addressing inefficiencies within each channel.
Conclusion
Throughout this comprehensive exploration of omnichannel vs multichannel retail, we have highlighted the distinct characteristics, advantages, and challenges associated with each approach. Omnichannel retail has emerged as the next evolutionary step beyond multichannel retail, emphasizing seamless integration and a unified customer experience across all touchpoints. This approach leverages advanced technologies such as CRM, ERP, POS, and marketing automation tools to provide consistent, personalized, and efficient interactions, driving higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In contrast, multichannel retail, while offering multiple avenues for customer interaction, often faces challenges related to fragmentation and inconsistency. Each channel operates independently, leading to data silos and varied customer experiences. Despite these challenges, multichannel retail excels in providing detailed insights into the performance of individual channels, allowing businesses to optimize their strategies for each specific platform.
The progression from multichannel to omnichannel retail represents a significant advancement in how businesses interact with their customers. Looking beyond omnichannel, the future may bring even more sophisticated and integrated retail strategies that leverage emerging technologies to create a truly seamless and personalized customer journey. This could involve further integration of physical and digital experiences, hyper-personalization driven by AI, and the adoption of new immersive technologies.
All in all, the detailed examination of omnichannel vs multichannel retail reveals that while both strategies offer unique benefits, omnichannel retail stands out as the next level of retail evolution. By continuously innovating and adapting to emerging trends, retailers can create a robust and future-proof strategy that meets the ever-changing demands of their customers, ensuring success in the competitive retail landscape.