In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the definitions, components, benefits, and challenges between omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, providing a clear understanding of how businesses can best utilize them to achieve their marketing goals.
Table of Contents
Omnichannel vs. Multichannel Marketing: Overview
Definition of Omnichannel Marketing
Omnichannel marketing is a strategic approach that seeks to provide customers with a seamless and integrated experience across all communication channels, whether online or offline. The key principle behind omnichannel marketing is that every channel, whether it’s a physical store, a website, a social media platform, or a mobile app, works together to create a unified and consistent experience for the customer.
In an omnichannel strategy, the customer is at the center of the marketing efforts. All channels are interconnected, allowing customers to move from one touchpoint to another without any disruption in their journey. For example, a customer might browse products on a mobile app, add items to their cart, and then complete the purchase later on a desktop computer or in a physical store. The customer’s data and interactions are synchronized across all channels, ensuring that their experience is consistent and personalized.
This level of integration is made possible through advanced data analytics and technology that allow businesses to track customer behavior and preferences across all channels. By analyzing this data, businesses can tailor their marketing messages and offers to each customer, creating a more relevant and engaging experience. For instance, a customer who frequently shops online may receive personalized emails with product recommendations based on their browsing history, or they may see targeted ads on social media featuring items they’ve shown interest in.

The benefits of omnichannel marketing extend beyond just enhancing the customer experience. By providing a consistent and personalized experience, businesses can build stronger relationships with their customers, increase brand loyalty, and ultimately drive higher conversion rates. Additionally, omnichannel marketing allows businesses to gather more comprehensive insights into customer behavior, enabling them to optimize their marketing strategies and make more informed decisions.
In the context of omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, the omnichannel approach is often viewed as a more advanced and customer-centric strategy. While both strategies involve the use of multiple channels, omnichannel marketing differentiates itself by focusing on the integration and coordination of these channels to create a seamless and cohesive customer journey. This integration is what sets omnichannel marketing apart, making it an essential strategy for businesses looking to meet the demands of today’s connected and digitally savvy consumers.
Definition of Multichannel Marketing
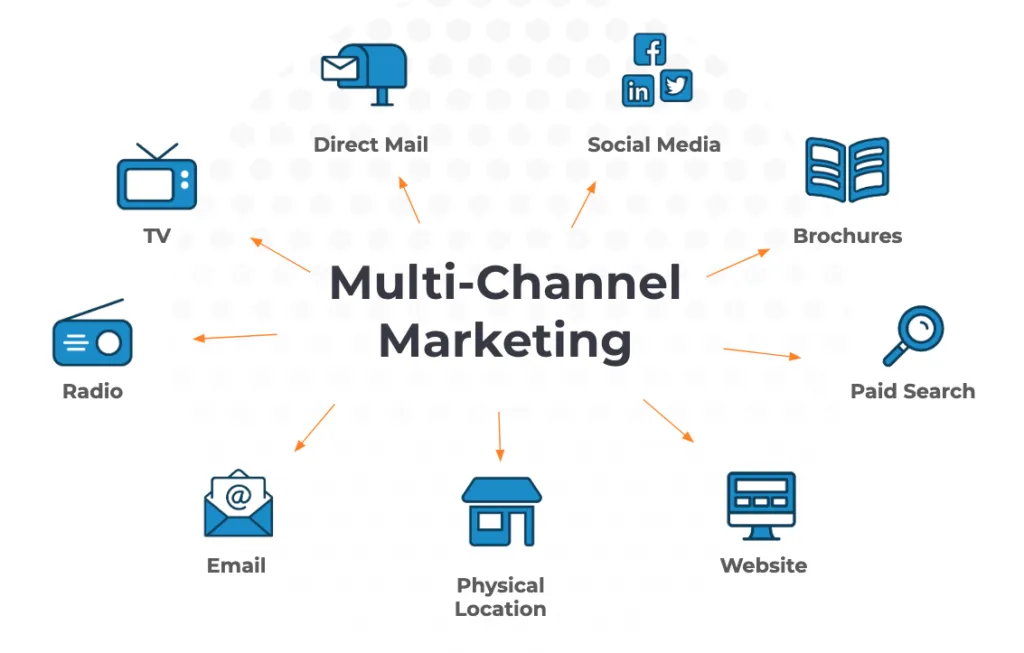
Multichannel marketing refers to a strategy that utilizes multiple channels to reach and engage customers. Each channel in a multichannel marketing strategy operates independently, allowing businesses to connect with customers through various touchpoints such as social media, email, websites, physical stores, and more. The primary focus of multichannel marketing is on the presence across numerous platforms, ensuring that customers can interact with the brand through their preferred channel.
In multichannel marketing, each platform or channel has its own set of goals, messaging, and strategies, which means that the customer experience can vary depending on the channel they are interacting with. For example, the messaging on a brand’s Instagram account may be tailored to engage a younger audience, while email campaigns might focus on a different demographic or customer segment. This flexibility allows businesses to target specific groups of customers more effectively, leveraging the strengths of each channel to meet their marketing objectives.
One of the key advantages of multichannel marketing is the ability to reach a broader audience. By being present on multiple platforms, businesses can increase their visibility and touch base with customers who may prefer one channel over another. For instance, a customer who frequently checks emails might not be as active on social media, but multichannel marketing ensures that they still receive relevant information and offers through their preferred medium.
However, while multichannel marketing allows for extensive reach, it does not necessarily integrate these channels to provide a unified customer experience. Each channel may operate in a silo, leading to potential inconsistencies in messaging and customer experience. This lack of integration can sometimes result in a fragmented customer journey, where interactions with the brand on different platforms feel disconnected.
In the debate of omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, the primary distinction lies in how customer interactions are managed across channels. While omnichannel marketing emphasizes a seamless, integrated experience across all touchpoints, multichannel marketing focuses on maximizing presence and reach across diverse platforms, often without the same level of cohesion. Despite this, multichannel marketing remains a valuable approach for businesses looking to expand their reach and cater to the preferences of different customer segments.
Brief Overview of Differences and Similarities between omnichannel vs multichannel marketing
When exploring omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, it’s essential to understand both the similarities and differences between these two strategies. While they share some common ground in their approach to customer engagement, they diverge significantly in execution and impact on the customer experience.
Similarities
- Use of Multiple Channels: Both omnichannel and multichannel marketing strategies utilize multiple channels to reach and engage customers. These channels can include social media, email, websites, physical stores, mobile apps, and more. The goal in both approaches is to maximize the brand’s presence and ensure that customers can interact with the brand through their preferred platforms.
- Customer Engagement Focus: At the heart of both strategies is the goal of enhancing customer engagement. By leveraging various touchpoints, both omnichannel and multichannel marketing aim to increase customer interactions, drive sales, and build brand loyalty. They recognize that customers today are active on more than one platform, and both strategies seek to meet customers where they are.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Both omnichannel and multichannel marketing rely on data to make informed decisions about customer preferences, behaviors, and trends. This data is used to tailor marketing efforts, optimize campaigns, and improve customer targeting across different channels. Whether it’s through personalized emails, targeted social media ads, or location-based promotions, data plays a crucial role in both approaches.
Differences
- Integration vs. Independence: The most significant difference between omnichannel and multichannel marketing lies in their approach to channel integration. Omnichannel marketing focuses on creating a unified customer experience across all channels, ensuring that each interaction complements the others. Multichannel marketing, however, treats each channel as a separate entity, often resulting in isolated customer experiences.
- Customer Experience: Omnichannel marketing prioritizes the customer journey, aiming to provide a seamless, personalized experience across all channels. In contrast, multichannel marketing emphasizes reaching customers on multiple platforms, sometimes at the expense of consistency and integration. For example, a customer might start their shopping journey on a mobile app, receive a personalized email with product recommendations, and then complete their purchase in a physical store, all with the same level of personalization and consistency. On the other hand, in multichannel marketing, the customer experience can vary between channels, as each channel operates independently, leading to potential inconsistencies in messaging and branding.
- Data Usage: Omnichannel marketing heavily relies on data integration to tailor customer experiences across channels. Multichannel marketing, while data-driven, may not connect data across channels in the same way, leading to varied messaging and experiences. In omnichannel marketing, data and analytics are integrated across all channels to provide a comprehensive view of the customer journey. This integration allows for more accurate and personalized marketing efforts, as data from one channel can inform strategies on another. For example, a customer’s online browsing history can influence the in-store promotions they receive. In multichannel marketing, data is often siloed within each channel, making it challenging to create a unified view of the customer or to personalize the experience based on cross-channel interactions.
- Strategic Focus: Omnichannel marketing is a more customer-centric approach that focuses on delivering a cohesive and personalized experience throughout the customer journey. It requires significant coordination and investment in technology to ensure that all channels work together seamlessly. Multichannel marketing, while still customer-focused, is more concerned with maximizing reach and engagement across individual channels. It often involves less complexity in terms of integration but may not offer the same level of personalization and consistency as omnichannel marketing
Understanding Multichannel Marketing
As businesses navigate an increasingly complex digital landscape, understanding multichannel marketing is essential for creating effective strategies that reach diverse customer segments. This approach involves engaging customers through multiple, often independent, platforms, enabling brands to connect with their audience wherever they are active.
Definition
Multichannel marketing is a strategy that involves engaging customers through multiple channels, such as social media, email, websites, physical stores, and more. The core idea of multichannel marketing is to maximize brand presence and reach by allowing customers to interact with the brand on their preferred platforms. However, in multichannel marketing, each channel often operates independently, with its own distinct strategy, goals, and messaging. This means that while customers can access the brand through various touchpoints, their experiences may vary depending on the channel they are using.
The independence of each channel in multichannel marketing allows businesses to tailor their approach to suit the strengths of each platform. For example, social media might be used to generate brand awareness and engagement, while email campaigns are designed to drive conversions. This flexibility is one of the main advantages of multichannel marketing, as it enables businesses to optimize their efforts across different platforms to reach a broader audience.

However, the lack of integration between channels can sometimes lead to a fragmented customer experience. Since each channel operates in its own silo, there is often little to no coordination between the different touchpoints. This can result in inconsistent messaging and a disjointed customer journey, where interactions on one channel do not inform or enhance the experience on another.
Components of Multichannel Marketing
Multichannel marketing is a strategy that leverages various channels to connect with customers and drive engagement. Each channel serves a unique purpose and reaches different segments of the audience, contributing to a comprehensive marketing approach. Understanding the components of multichannel marketing involves recognizing the various channels involved and how they can be strategically integrated to create an effective marketing ecosystem.
Various Channels Involved
- Social Media: Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn play a crucial role in multichannel marketing. They are used to build brand awareness, engage with customers, and drive traffic to other channels such as websites or physical stores. Each platform offers unique features and caters to different demographics, allowing businesses to tailor their messaging and campaigns to specific audiences.
- Email: Email marketing is a powerful tool in multichannel strategies, used primarily for nurturing leads, promoting products or services, and maintaining customer relationships. Email campaigns can be personalized based on customer data, making them highly effective in driving conversions and retaining customers. Regular newsletters, promotional offers, and personalized recommendations are common email marketing tactics within a multichannel framework.
- Websites: A company’s website serves as the central hub for multichannel marketing efforts. It is often the primary destination where social media posts, email campaigns, and paid ads direct traffic. Websites provide a space for detailed product information, customer reviews, and eCommerce functionality. An optimized website is essential for ensuring a seamless customer experience across all channels.
- Physical Stores: For businesses with a brick-and-mortar presence, physical stores are a key component of multichannel marketing. They offer a tangible touchpoint where customers can experience products firsthand, interact with staff, and complete purchases. Physical stores often complement online efforts by providing in-store promotions, events, and exclusive offers that encourage foot traffic and drive sales.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile apps are increasingly important in multichannel marketing, offering a personalized and convenient way for customers to interact with a brand. Apps can provide tailored experiences, push notifications, loyalty programs, and mobile-specific promotions. They also facilitate seamless transactions and customer support, enhancing the overall customer journey.
- Paid Advertising: Paid advertising, including pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns, social media ads, and display ads, helps drive traffic across various channels. These ads are often targeted based on customer behavior and demographics, ensuring that the right message reaches the right audience at the right time.
Strategies for Incorporating These Channels
While multichannel marketing involves the use of various independent channels, integrating these channels strategically can enhance the overall effectiveness of the marketing efforts. Here are some key strategies for integrating channels in a multichannel marketing approach:
- Consistent Branding: One of the most important aspects of multichannel marketing is maintaining consistent branding across all channels. This includes using the same logos, color schemes, messaging, and tone of voice. Consistency helps reinforce the brand’s identity and ensures that customers recognize the brand no matter which channel they are interacting with.
- Cross-Promotions: Cross-promotion involves using one channel to promote another, creating a synergy that enhances overall campaign effectiveness. For example, social media posts can drive followers to sign up for an email newsletter, while emails can encourage subscribers to follow the brand on social media. Similarly, in-store promotions can direct customers to the brand’s website or mobile app for additional offers.
- Customer Data Integration: Integrating customer data across all channels is crucial for creating personalized and relevant marketing efforts. Data from social media interactions, website visits, email engagement, and in-store purchases can be combined to form a comprehensive view of each customer. This integrated data allows businesses to tailor their marketing messages and offers based on customer behavior and preferences, improving engagement and conversion rates.
- Unified Customer Experience: While multichannel marketing may involve independent channels, the goal should be to create a unified customer experience. This means ensuring that no matter where a customer interacts with the brand—whether online or offline—the experience is seamless and cohesive. For example, a customer should be able to browse products online, receive a personalized email based on their browsing history, and redeem an in-store discount seamlessly.
- Coordinated Campaigns: Coordinating campaigns across multiple channels can amplify the impact of marketing efforts. For example, a product launch could be simultaneously promoted through social media ads, email blasts, in-store displays, and website banners. Each channel would play a role in driving awareness and sales, but the message and timing would be coordinated to maximize effectiveness.
- Analytics and Performance Tracking: To effectively integrate channels in multichannel marketing, it’s essential to track performance across all touchpoints. Analytics tools can provide insights into how each channel is performing and how customers are moving through the marketing funnel. By analyzing this data, businesses can adjust their strategies, allocate resources more effectively, and optimize their multichannel efforts.
Multichannel marketing involves a diverse range of channels, each contributing to the overall strategy in unique ways. Understanding and leveraging the components of multichannel marketing is essential for businesses looking to thrive in today’s competitive market.
Benefits of Multichannel Marketing
Multichannel marketing offers several significant benefits, making it an attractive strategy for businesses looking to expand their reach and engage with a broader audience. Two of the most notable advantages are its ability to provide a wider reach and audience engagement, as well as its inherent flexibility and adaptability.
Wider Reach and Audience Engagement
One of the primary benefits of multichannel marketing is its capacity to extend a brand’s reach across diverse platforms, thereby engaging a wider audience. In the debate of omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, multichannel marketing stands out for its ability to tap into different customer segments by leveraging various channels. For example, social media channels like Instagram or TikTok might attract younger audiences, while email newsletters or LinkedIn are more effective for reaching professionals and older demographics. By being present on multiple platforms, businesses can ensure they are visible to different audience groups, increasing the chances of engagement and conversion.
This wide-reaching approach is particularly effective in today’s fragmented media landscape, where consumers interact with brands across numerous touchpoints. With multichannel marketing, businesses can meet customers wherever they are—whether they’re browsing social media, checking their email, or visiting a physical store. This ensures that the brand remains top-of-mind across the customer’s journey, leading to higher engagement rates and a stronger brand presence.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Another key benefit of multichannel marketing is its flexibility and adaptability, allowing businesses to tailor their strategies to the unique strengths of each channel. Unlike omnichannel marketing, where the focus is on creating a seamless and integrated customer experience, multichannel marketing allows each channel to operate independently, catering to its specific audience and goals. This flexibility enables businesses to experiment with different messages, formats, and tactics on each platform, optimizing their efforts based on the unique characteristics of each channel.

For example, a business might use Instagram for visual storytelling and brand awareness, while focusing on detailed product descriptions and reviews on its website. Similarly, email campaigns can be used to deliver personalized offers and drive direct conversions, while physical stores might focus on providing an immersive brand experience. This adaptability allows businesses to respond quickly to changes in consumer behavior, market trends, and emerging technologies, ensuring that their marketing efforts remain relevant and effective.
Moreover, the flexibility of multichannel marketing makes it easier for businesses to scale their efforts up or down depending on their resources and objectives. For smaller businesses, starting with a few key channels and expanding over time is a viable strategy. Larger enterprises can leverage a more extensive multichannel approach, optimizing each channel for maximum impact. This scalability is one of the reasons why multichannel marketing remains a popular choice for businesses of all sizes.
The benefits of multichannel marketing—wider reach and audience engagement, along with flexibility and adaptability—make it a powerful strategy for businesses looking to connect with diverse customer segments. While it may not offer the same level of integration as omnichannel marketing, multichannel marketing’s ability to tailor efforts across various platforms ensures that businesses can effectively engage with their audience in a dynamic and ever-changing market.
Challenges and Limitations
When comparing omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, these challenges highlight some of the complexities that come with managing multiple, often independent, channels.
Potential for Fragmented Customer Experience
One of the most significant challenges of multichannel marketing is the potential for a fragmented customer experience. Since each channel in a multichannel strategy often operates independently, customers may encounter different messaging, offers, and branding depending on the platform they are using. For example, a customer might receive a promotion via email that differs from what they see on social media or in a physical store. This lack of consistency can lead to confusion and diminish the overall customer experience, as customers may feel disconnected from the brand if their interactions across different channels don’t align.
Unlike omnichannel marketing, which aims to create a seamless and integrated experience, multichannel marketing’s independent approach can make it difficult to ensure that every touchpoint contributes to a cohesive customer journey. As a result, businesses must work harder to align their strategies across channels, ensuring that the customer experience remains consistent and satisfying, even when channels operate separately.
Difficulties in Consistent Messaging
Maintaining consistent messaging across all channels is another significant challenge in multichannel marketing. Because each channel is often managed by different teams or departments, the messaging and tone used in one channel may not be reflected in another. This inconsistency can lead to mixed messages, where the brand’s identity and values are not clearly communicated, potentially weakening the brand’s position in the market.
For example, a company might emphasize sustainability and ethical practices on its website but fail to reinforce these messages in its social media campaigns or in-store promotions. This inconsistency can dilute the brand’s message, making it less memorable and impactful. In the omnichannel vs multichannel marketing debate, omnichannel marketing generally has the upper hand in maintaining consistent messaging due to its integrated nature. However, businesses employing a multichannel strategy must invest in strong coordination and communication across teams to ensure that all channels reflect the same core messages and values.
Measurement and Analytics Challenges
Measuring the effectiveness of multichannel marketing efforts is often more complex than in an omnichannel approach due to the independent nature of each channel. In multichannel marketing, data is typically siloed, meaning that the information gathered from one channel may not be easily integrated with data from another. This can make it difficult to gain a holistic view of the customer journey and to accurately measure the impact of each channel on overall performance.

For instance, tracking a customer’s path from seeing an ad on social media to making a purchase in-store can be challenging if the data from these channels is not connected. This lack of integration can lead to gaps in understanding customer behavior, making it harder to optimize marketing strategies and allocate resources effectively. Furthermore, without a comprehensive view of the customer journey, businesses may struggle to identify which channels are driving the most value, potentially leading to suboptimal decision-making.
In contrast, omnichannel marketing’s integrated approach typically allows for more seamless data collection and analysis, providing businesses with clearer insights into customer behavior across all touchpoints. To overcome the measurement and analytics challenges inherent in multichannel marketing, businesses must invest in advanced analytics tools and processes that enable them to track and analyze customer interactions across all channels, even when those channels operate independently.
In summary, while multichannel marketing offers flexibility and the ability to reach a wide audience, it also presents challenges such as the potential for a fragmented customer experience, difficulties in maintaining consistent messaging, and measurement and analytics hurdles. Understanding these challenges is crucial for businesses looking to maximize the effectiveness of their multichannel marketing strategies and ensure a positive customer experience across all platforms.
Understanding Omnichannel Marketing
Unlike multichannel marketing, where each channel operates independently, omnichannel marketing focuses on creating a unified journey for the customer across all touchpoints.
Definition
Omnichannel marketing is a comprehensive strategy designed to create a unified and seamless customer experience across all channels, whether they are online or offline. Unlike multichannel marketing, where each channel may operate independently, omnichannel marketing focuses on integrating all channels so that customer interactions across different touchpoints are interconnected and consistent. This approach ensures that customers receive a cohesive experience as they transition from one channel to another, whether they are shopping online, engaging through social media, or visiting a physical store.

In omnichannel marketing, the customer is at the center of the strategy. The goal is to provide a consistent and personalized experience at every stage of the customer journey. For example, a customer might browse products on a brand’s website, add items to their cart, and later receive a reminder email about the abandoned cart. If they visit the physical store, sales associates could have access to this information, allowing them to offer personalized recommendations based on the customer’s online activity. This level of integration ensures that every interaction feels connected and relevant, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Components of Omnichannel Marketing
The effectiveness of omnichannel marketing lies in its ability to seamlessly integrate various channels, ensuring a consistent and personalized customer experience across all touchpoints.
Integrated Approach Across Channels
At the core of omnichannel marketing is its integrated approach, which ensures that all channels—whether online or offline—are interconnected and work together to create a cohesive customer experience. Unlike multichannel marketing, where channels may operate independently, omnichannel marketing strives to break down silos, allowing customer data, messaging, and brand interactions to flow seamlessly between platforms. This integration ensures that no matter where or how a customer interacts with the brand, their experience is consistent and personalized, reinforcing the brand’s identity and enhancing customer satisfaction.
For example, a customer who begins their journey by browsing a product on a brand’s mobile app might later receive a personalized follow-up email or see an advertisement for that product on social media. If they visit a physical store, the sales staff could have access to their online browsing history, enabling them to offer personalized recommendations or complete a transaction started online. This level of integration across channels not only improves the customer experience but also helps businesses create more effective marketing strategies by leveraging data and insights gathered from multiple touchpoints.
Emphasis on Seamless Customer Experience
Omnichannel marketing places a strong emphasis on delivering a seamless customer experience across all channels. The goal is to ensure that every interaction a customer has with the brand feels like part of a continuous and connected journey, rather than a series of isolated events. This focus on seamlessness is what sets omnichannel marketing apart from multichannel marketing, where the customer experience can often feel disjointed due to the lack of integration between channels.
A seamless customer experience means that customers can move effortlessly between different channels without encountering inconsistencies or disruptions. For example, if a customer adds an item to their cart on a desktop computer, they should be able to view and purchase that item from their mobile device without having to start the process over. Additionally, the messaging, offers, and branding should be consistent across all channels, reinforcing the customer’s perception of the brand and building trust.

This emphasis on a seamless experience is particularly important in today’s market, where customers expect brands to be accessible and responsive across a variety of platforms. Businesses that can deliver a consistent and unified experience across all touchpoints are more likely to foster customer loyalty and drive repeat business.
Role of Technology in Omnichannel Strategies
Technology plays a crucial role in enabling and enhancing omnichannel marketing strategies. The ability to integrate data across various channels, personalize customer interactions, and maintain consistent messaging would not be possible without advanced technological tools and platforms. In omnichannel marketing, technology serves as the backbone that connects all the different channels, ensuring that they work together harmoniously to deliver a unified customer experience.
Key technologies that support omnichannel marketing include customer relationship management (CRM) systems, data analytics platforms, and marketing automation tools. CRM systems allow businesses to collect and manage customer data from multiple sources, providing a comprehensive view of each customer’s interactions with the brand. This data can then be used to personalize marketing efforts and ensure that customers receive relevant messages and offers based on their behavior and preferences.
Data analytics platforms play a vital role in tracking and analyzing customer behavior across channels, enabling businesses to understand how customers move through their journey and where they might encounter friction. By leveraging these insights, businesses can optimize their omnichannel strategies, removing obstacles and enhancing the customer experience at every touchpoint.

Marketing automation tools are also essential in omnichannel strategies, allowing businesses to execute coordinated campaigns across multiple channels simultaneously. These tools can automate tasks such as sending personalized emails, launching social media ads, or triggering follow-up actions based on customer behavior, ensuring that the right message reaches the right customer at the right time.
The components of omnichannel marketing—integrated channels, seamless customer experience, and the critical role of technology—are what make this approach so effective in today’s competitive landscape. By focusing on these elements, businesses can create a more cohesive and engaging customer journey, ultimately driving greater satisfaction, loyalty, and business success.
Benefits of Omnichannel Marketing
The benefits of omnichannel marketing are profound, offering businesses a competitive edge by focusing on creating a seamless and integrated customer experience across all touchpoints. This approach not only enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring consistency and personalization but also significantly improves customer retention and loyalty.
Enhanced Customer Experience and Satisfaction
One of the most significant benefits of omnichannel marketing is its ability to enhance the overall customer experience, leading to higher levels of satisfaction. In the omnichannel vs multichannel marketing debate, omnichannel marketing stands out because it prioritizes a seamless and integrated experience across all touchpoints. Customers today expect consistent and personalized interactions with brands, regardless of the channel they choose. Omnichannel marketing addresses this expectation by ensuring that all channels work together to provide a unified experience.
For example, a customer might start their journey by browsing products on a brand’s website, adding items to their cart on a mobile app, and finally making the purchase in a physical store. Throughout this process, the customer’s information and preferences are shared across channels, allowing for a smooth transition from one platform to another. This seamless integration not only makes the shopping experience more convenient but also builds trust in the brand, as customers feel that their needs are understood and catered to at every step.

Moreover, omnichannel marketing enables personalized interactions that further enhance customer satisfaction. By collecting and analyzing data from various channels, businesses can tailor their messaging and offers to meet the specific needs and preferences of individual customers. This level of personalization is difficult to achieve with multichannel marketing, where channels often operate independently. As a result, customers are more likely to feel valued and appreciated, leading to increased satisfaction and a stronger emotional connection with the brand.
Improved Customer Retention and Loyalty
Another critical benefit of omnichannel marketing is its ability to improve customer retention and loyalty. In the context of omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, omnichannel strategies are particularly effective in fostering long-term relationships with customers. By delivering a consistent and personalized experience across all touchpoints, omnichannel marketing helps build trust and loyalty, encouraging customers to return to the brand repeatedly.

Customer retention is significantly influenced by the quality of the customer experience. When customers have a positive and seamless experience with a brand, they are more likely to stay loyal and continue doing business with that brand. Omnichannel marketing’s focus on integrating all channels ensures that customers receive the same high level of service and attention, whether they are interacting with the brand online, in-store, or through mobile apps. This consistency reassures customers that they can expect the same positive experience every time they engage with the brand, which is a key factor in building loyalty.
Additionally, omnichannel marketing allows businesses to implement effective loyalty programs that are accessible across all channels. For example, customers can earn and redeem loyalty points both online and in-store, ensuring that their rewards are always within reach, regardless of how they choose to shop. This convenience further strengthens the customer’s relationship with the brand, as they are incentivized to continue shopping with the brand to maximize their rewards.
Challenges and Limitations
While omnichannel marketing offers significant benefits, it also presents several challenges and limitations that businesses must consider. These challenges can complicate the implementation of an omnichannel strategy, requiring careful planning and substantial investment.
Complexity in Implementation
One of the primary challenges of omnichannel marketing is its complexity. Unlike multichannel marketing, where channels often operate independently, omnichannel marketing requires seamless integration across all touchpoints. This means that every aspect of the customer journey must be interconnected, from online interactions to in-store experiences. Implementing such a strategy involves coordinating various departments, technologies, and processes, which can be overwhelming, especially for large organizations with multiple channels and customer touchpoints.

This complexity can lead to challenges in aligning teams and resources, ensuring that everyone is working towards the same goals. For example, marketing, sales, customer service, and IT departments must collaborate closely to ensure that data is shared and that customer interactions are consistent across all channels. Additionally, the complexity of omnichannel marketing requires businesses to continuously monitor and optimize their strategies to adapt to changing customer behaviors and preferences.
High Initial Investment in Technology and Integration
Another significant limitation of omnichannel marketing is the high initial investment required for technology and integration. To successfully implement an omnichannel strategy, businesses need to invest in advanced technologies that can support seamless data integration and communication across channels. This includes CRM systems, data analytics platforms, marketing automation tools, and more. These technologies are essential for collecting, analyzing, and utilizing customer data to create personalized and consistent experiences across all touchpoints.
The cost of these technologies, combined with the resources needed for their implementation and maintenance, can be substantial, especially for smaller businesses with limited budgets. Moreover, the integration of these technologies across various channels can be a complex and time-consuming process, requiring expertise in data management, system integration, and user experience design. Businesses must weigh the potential benefits of omnichannel marketing against the significant investment required to achieve a fully integrated system.
Data Management and Analytics Issues
Data management and analytics are critical components of any successful omnichannel marketing strategy, but they also present significant challenges. Omnichannel marketing relies heavily on the ability to collect and analyze data from various sources to create a unified view of the customer. However, managing this data effectively can be difficult, particularly when it comes from different channels and systems that may not be easily integrated.
Data silos, where information is stored separately in different systems or departments, can hinder the ability to gain a comprehensive understanding of the customer journey. Additionally, the volume and complexity of data generated by an omnichannel strategy can be overwhelming, making it difficult to extract actionable insights. Businesses must invest in sophisticated data analytics tools and develop robust data governance practices to ensure that data is accurate, accessible, and useful for driving marketing decisions.

Furthermore, ensuring data privacy and security is a significant concern in omnichannel marketing. As businesses collect more customer data across multiple channels, they must comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, which require stringent data protection measures. Failure to manage data effectively can lead to security breaches, legal penalties, and damage to the brand’s reputation.
While omnichannel marketing offers the potential for enhanced customer experiences and increased loyalty, it also comes with challenges and limitations. The complexity of implementation, high initial investment in technology, and data management issues are significant hurdles that businesses must overcome to fully realize the benefits of an omnichannel approach. Understanding and addressing these challenges is essential for any business looking to succeed in the competitive landscape of omnichannel vs multichannel marketing.
Key Differences Between Omnichannel vs Multichannel Marketing
While both approaches aim to engage customers across various platforms, they differ significantly in execution and impact. These differences affect how brands connect with their audience, manage customer data, and create overall experiences that resonate with consumers.
Customer Experience
Customer experience is at the heart of the distinction between omnichannel and multichannel marketing. Omnichannel marketing prioritizes a seamless, integrated experience across all touchpoints, ensuring consistency and personalization throughout the customer journey. In contrast, multichannel marketing often results in fragmented interactions, where each channel operates independently, potentially leading to inconsistencies in customer engagement and satisfaction. Understanding these contrasts is essential for optimizing customer journeys and fostering long-term loyalty.
How Each Approach Impacts the Customer Journey
The customer experience is where the fundamental differences between omnichannel vs multichannel marketing become most evident. Both strategies aim to engage customers across various channels, but they do so in fundamentally different ways that have significant implications for the customer journey.
In a multichannel marketing strategy, each channel functions independently. While customers can interact with the brand through multiple platforms—such as social media, email, physical stores, and websites—these interactions are often siloed, meaning that they do not necessarily inform or connect with one another. As a result, the customer journey can be fragmented, with different experiences and messages encountered depending on the channel used. For example, a customer might see a promotional offer on social media that is not reflected in the store or on the website, leading to confusion and a disjointed experience.
Omnichannel marketing, on the other hand, is designed to create a seamless and integrated customer journey across all touchpoints. In this approach, every channel is interconnected, and customer data flows freely between them. This allows for a more personalized and consistent experience, where customers can move effortlessly from one channel to another without encountering discrepancies or disruptions. For instance, a customer might start their journey by researching products on a mobile app, continue by receiving personalized recommendations via email, and complete their purchase in a physical store—each interaction informed by the previous ones and contributing to a cohesive overall experience.
Illustrating Customer Experience in Both Strategies
To illustrate the differences in customer experience between omnichannel and multichannel marketing, consider the following scenarios:
- Multichannel Experience: A customer begins their interaction by browsing a brand’s website and adding items to their cart. Later, they visit the brand’s physical store, but the items in their online cart are not reflected in their in-store experience. The customer receives a generic promotion via email that does not consider their previous online behavior. As a result, the customer experiences disjointed interactions with the brand, leading to frustration and a potentially lost sale.
- Omnichannel Experience: A customer browses a brand’s website and adds items to their cart. They then visit the brand’s physical store, where the sales associate is aware of the items in the customer’s online cart and offers to help complete the purchase. Later, the customer receives an email with a personalized discount on those same items, encouraging them to finalize the purchase. The entire experience is seamless, with each interaction building on the previous one, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and a successful sale.
In summary, the key difference in customer experience between omnichannel and multichannel marketing lies in the level of integration. Omnichannel marketing provides a cohesive, personalized journey that enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty, while multichannel marketing often results in fragmented experiences that can weaken the overall customer relationship. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their customer engagement strategies and build stronger, more lasting relationships with their audience.
Channel Integration
Channel integration is a defining element in the distinction between omnichannel and multichannel marketing. In omnichannel marketing, all channels are interconnected, providing a seamless and unified customer experience across every touchpoint. This contrasts with multichannel marketing, where each channel operates independently, often leading to a more fragmented customer journey.
Level of Integration in Omnichannel vs. Multichannel
One of the most significant differences between omnichannel and multichannel marketing lies in the level of integration across channels. In a multichannel marketing strategy, each channel typically operates independently. This means that while a brand may be present on multiple platforms—such as social media, email, websites, and physical stores—these channels are not necessarily connected or synchronized. As a result, the customer’s experience on one channel may not inform or enhance their experience on another. For instance, a customer might receive different offers or encounter inconsistent messaging depending on the channel they are using, leading to a fragmented customer journey.

In contrast, omnichannel marketing is defined by its deep level of integration across all channels. Here, every channel is interconnected, allowing for a seamless flow of information and a consistent customer experience regardless of the platform. In an omnichannel approach, customer data is shared across all touchpoints, ensuring that interactions on one channel are reflected on others. For example, a customer might add an item to their cart on a mobile app and later receive a personalized email with a discount for that item. If they visit the store, the staff can access this information and assist in completing the purchase, creating a cohesive and unified experience.
This integration in omnichannel marketing not only enhances the customer experience but also provides businesses with a more comprehensive understanding of their customers’ behavior, enabling more effective and personalized marketing efforts.
When Does a Marketing Strategy Become Omnichannel?
A marketing strategy becomes omnichannel when it moves beyond simply being present on multiple platforms to create a fully integrated and cohesive customer experience across all channels. The transition from multichannel to omnichannel involves several key steps:
- Unified Customer Data: The foundation of omnichannel marketing is the ability to collect and integrate customer data from all channels. This includes tracking customer interactions, preferences, and behaviors across platforms and using this data to inform marketing strategies. When a business can access and utilize a unified view of the customer, it can begin to deliver more personalized and consistent experiences.
- Seamless Customer Experience: A marketing strategy becomes omnichannel when the customer’s journey is seamless across all touchpoints. This means that customers can start an interaction on one channel and continue it on another without encountering disruptions or inconsistencies. For instance, a customer might research a product online, receive a personalized recommendation via email, and then visit a physical store where the sales staff are aware of their online activity and can offer relevant assistance.
- Consistent Messaging and Branding: In an omnichannel strategy, messaging, and branding are consistent across all channels. This consistency helps reinforce the brand’s identity and ensures that customers receive the same information and experience regardless of the platform they use. Whether through social media, email, or in-store interactions, the brand’s voice, values, and offers remain aligned.
- Cross-Channel Coordination: Omnichannel marketing requires close coordination between all departments and teams involved in customer interactions, including marketing, sales, customer service, and IT. This coordination ensures that all channels work together to create a unified customer experience. For example, if a customer interacts with a brand on social media, their preferences and feedback should be communicated to the customer service team to improve future interactions.
- Advanced Technology and Automation: The use of advanced technologies, such as CRM systems, marketing automation tools, and data analytics platforms, is essential for implementing an omnichannel strategy. These tools enable businesses to manage and analyze customer data, automate personalized marketing efforts, and ensure that all channels are integrated and aligned.
A marketing strategy becomes omnichannel when it successfully integrates all channels to provide a seamless, personalized, and consistent customer experience. This level of integration not only enhances customer satisfaction but also allows businesses to build stronger relationships with their customers and achieve better marketing outcomes. Understanding the differences in channel integration between omnichannel and multichannel marketing is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their marketing strategies and stay competitive in today’s dynamic marketplace.
Data and Analytics
In the comparison of omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, the collection, management, and utilization of data stand out as critical differentiators. Both strategies rely on data to drive marketing decisions, but the approach to data management and the role of analytics differ significantly.
How Data is Collected, Managed, and Utilized
In multichannel marketing, data is typically collected and managed independently within each channel. For example, data from social media interactions may be stored separately from data collected via email campaigns or in-store purchases. This siloed approach can lead to fragmented insights, as there is limited communication and data sharing between channels. Each channel generates its own data, which is then analyzed in isolation, often resulting in a lack of a unified customer view.
On the other hand, omnichannel marketing emphasizes the integration of data across all touchpoints. In an omnichannel strategy, customer data is collected from every interaction—whether online or offline—and is aggregated into a single, unified customer profile. This approach allows businesses to have a comprehensive understanding of each customer’s journey, preferences, and behaviors. By integrating data across channels, businesses can ensure that customer interactions on one platform inform and enhance experiences on another. For example, a customer’s browsing history on a website can influence the content they see in a subsequent email or the recommendations they receive in-store.

The integration of data in omnichannel marketing not only improves the accuracy and relevance of customer interactions but also enables real-time decision-making. Marketers can leverage this comprehensive data to deliver personalized experiences, tailor offers, and predict customer needs, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
The Role of Analytics in Optimizing Marketing Strategies
Analytics play a crucial role in both omnichannel and multichannel marketing, but the depth and effectiveness of these analytics differ due to the varying levels of data integration.
In multichannel marketing, analytics are often channel-specific. Marketers analyze data within individual channels to measure performance, understand customer behavior, and optimize campaigns. While this approach can provide valuable insights into how each channel is performing, it can also lead to a disjointed understanding of the overall customer journey. For example, analytics might show that a social media campaign is driving traffic to a website, but without integrated data, it’s challenging to track whether that traffic converts into sales or continues the journey through other channels.

Omnichannel marketing, with its integrated data approach, allows for more comprehensive and advanced analytics. By consolidating data from all channels, businesses can gain a holistic view of the customer journey and identify patterns and trends that might be missed in a multichannel approach. This 360-degree view enables marketers to analyze the effectiveness of cross-channel interactions, measure the impact of specific touchpoints on the overall customer experience, and optimize marketing strategies accordingly.
Advanced analytics in omnichannel marketing also facilitate predictive modeling and personalized recommendations. By analyzing past behaviors and interactions across multiple channels, businesses can anticipate customer needs and proactively offer solutions or products that align with their preferences. This level of personalization is difficult to achieve in a multichannel environment, where data is not as seamlessly integrated.
Moreover, omnichannel analytics provide valuable insights into customer lifetime value (CLV), enabling businesses to identify their most valuable customers and tailor strategies to retain and engage them over time. This data-driven approach to CRM is a key advantage of omnichannel marketing, as it allows businesses to build deeper, more meaningful connections with their customers.
The differences in data collection, management, and utilization between omnichannel and multichannel marketing are significant. While both approaches rely on data and analytics to drive decisions, omnichannel marketing’s integrated data strategy allows for more comprehensive insights, personalized customer experiences, and optimized marketing strategies. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses looking to enhance their marketing efforts and deliver more effective, customer-centric campaigns.
Technology and Tools
The success of any marketing strategy, whether omnichannel or multichannel, heavily depends on the technology and tools used to manage customer interactions and data. While both approaches require specific technological frameworks, the depth of integration and the sophistication of tools vary significantly between them. Omnichannel marketing demands a more advanced, interconnected technological ecosystem that ensures a seamless and personalized customer experience across all touchpoints. In contrast, multichannel marketing often relies on separate tools for each channel, resulting in less integration and more fragmented customer experiences. Understanding these technological distinctions is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their marketing efforts.
Technological Requirements for Omnichannel and Multichannel Marketing
In the discussion of omnichannel vs multichannel marketing; technology plays a pivotal role in differentiating the two approaches. Both strategies require specific technological frameworks to manage customer interactions, but the depth and complexity of these requirements vary significantly.
For multichannel marketing, the technological requirements are relatively straightforward. Each channel operates independently, so the technology needed is often limited to tools that manage individual channels effectively. For instance, businesses might use separate platforms for email marketing, social media management, CRM, and point-of-sale (POS) systems. These tools are often designed to function well within their respective channels but lack the integration necessary to share data and insights across multiple platforms.

Omnichannel marketing, on the other hand, demands a more sophisticated technological infrastructure. The goal of omnichannel marketing is to create a seamless and unified customer experience across all channels, which requires deep integration of various technologies. Businesses must invest in systems that can collect and synchronize data across multiple touchpoints, enabling a consistent and personalized experience regardless of the channel. This includes integrating CRM systems with marketing automation tools, data analytics platforms, and eCommerce solutions. Additionally, real-time data processing capabilities are crucial for ensuring that customer interactions are relevant and up-to-date across all channels.
Overview of Tools and Platforms Used in Each Approach
In multichannel marketing, the tools used are typically designed to manage specific channels without much interaction between them. Some of the common tools and platforms include:
- Email Marketing Platforms: Tools like Mailchimp or Constant Contact are used to design, send, and track email campaigns. These platforms focus solely on email communication, with analytics limited to metrics like open rates, click-through rates, and conversions.
- Social Media Management Tools: Platforms such as Hootsuite or Buffer help businesses schedule and manage posts across various social media channels. They provide analytics on social media engagement but do not necessarily integrate with other marketing efforts.
- Standalone CRM Systems: Basic CRM systems like Salesforce Essentials or HubSpot CRM manage customer relationships within specific sales or service channels but may not fully integrate with marketing automation or analytics tools.
- POS Systems: For brick-and-mortar stores, POS systems like Square or Clover manage in-store transactions. These systems often operate independently of online sales platforms, creating potential disconnects between online and offline customer experiences.
Omnichannel marketing, in contrast, relies on a suite of integrated tools that work together to create a seamless customer journey. These include:
- Integrated CRM Systems: Advanced CRM systems like Salesforce or Microsoft Dynamics 365 offer robust integration capabilities, allowing customer data to be shared and utilized across multiple channels. These platforms can connect with eCommerce systems, marketing automation tools, and customer service platforms to ensure a consistent experience.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: Tools like Marketo or HubSpot integrate with CRM systems to automate and personalize marketing efforts across channels. These platforms can trigger actions based on customer behavior, ensuring that messages are relevant and timely.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Tools like Google Analytics 360 or Adobe Analytics provide comprehensive insights into customer behavior across all touchpoints. In an omnichannel strategy, these platforms help businesses understand the complete customer journey, from initial contact to final purchase, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- eCommerce Integration: For businesses with both online and offline presences, integrating eCommerce platforms like Shopify or Magento with in-store POS systems is crucial. This integration ensures that inventory, pricing, and customer data are consistent across all sales channels, providing a unified shopping experience.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs like Segment or Tealium are essential in omnichannel marketing for aggregating and managing customer data from multiple sources. These platforms create a single, unified customer profile that can be used to personalize interactions across all channels.
Generally, while both omnichannel and multichannel marketing require technological support, the level of complexity and integration is much higher in omnichannel marketing. The tools used in omnichannel strategies are designed to work together, ensuring that customer interactions are consistent and personalized across all touchpoints. Understanding the technological requirements and tools associated with each approach is crucial for businesses looking to implement effective and customer-centric marketing strategies.
Cost and Resource Allocation
When implementing a marketing strategy, understanding the cost and resource allocation differences between omnichannel and multichannel marketing is crucial. Each approach demands distinct levels of investment and management, impacting the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the marketing efforts. Omnichannel marketing, with its focus on integration and seamless customer experiences, often requires a higher initial investment and more complex resource management. In contrast, multichannel marketing tends to have lower upfront costs but may lead to inefficiencies and higher long-term expenses due to its fragmented nature. This section explores these dynamics in detail.
Cost Implications of Implementing Each Strategy
When comparing omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, one of the key differences lies in the cost implications associated with each approach. Implementing a multichannel marketing strategy is generally less expensive upfront because it involves managing each channel independently. Businesses can choose to focus on a few key channels, investing in specific tools and resources tailored to those platforms. For example, a business might allocate budget toward social media marketing, email campaigns, and a basic website, each managed separately with its own tools and team. This allows for flexibility in spending, as businesses can scale their efforts up or down based on the performance of each channel.
However, the lack of integration in multichannel marketing can lead to inefficiencies and higher long-term costs. Since each channel operates independently, businesses may need to invest in separate technologies, duplicate resources, and maintain multiple teams to manage these channels. Over time, these costs can add up, especially if there is a need to synchronize messaging or customer data across channels to improve the customer experience.

On the other hand, omnichannel marketing typically requires a higher initial investment due to the complexity of integrating multiple channels into a cohesive system. This includes the cost of advanced technologies such as integrated CRM systems, data analytics platforms, and marketing automation tools that can synchronize customer interactions across all touchpoints. Additionally, businesses need to invest in training staff to use these systems effectively and ensure that all departments are aligned in their efforts to deliver a seamless customer experience.
Despite the higher upfront costs, omnichannel marketing can lead to more efficient use of resources and better long-term ROI. By integrating channels and centralizing data, businesses can reduce redundancies, streamline processes, and enhance the overall customer experience, which can drive higher customer loyalty and revenue growth.
Resource Management and Allocation
Resource management in multichannel marketing tends to be more segmented, with each channel requiring its own set of resources, including technology, staff, and budget. This segmentation allows businesses to tailor their resources to the specific needs of each channel, but it can also lead to challenges in coordination and consistency. For example, a company might allocate resources to a dedicated social media team, a separate email marketing team, and another team for in-store promotions. While this approach allows for specialization, it can also result in silos, where teams work independently with little cross-channel collaboration.
In contrast, omnichannel marketing requires a more unified approach to resource management. Because the goal is to create a seamless experience across all channels, businesses need to allocate resources in a way that promotes integration and coordination. This often involves creating cross-functional teams that can work together to manage customer interactions holistically. For example, a single team might be responsible for managing both online and offline customer experiences, ensuring that the messaging and branding are consistent across all touchpoints.

Additionally, omnichannel marketing necessitates investment in technologies that can centralize and synchronize data across channels, allowing for more efficient resource use. By having a unified view of customer data, businesses can better allocate their marketing budgets, target high-value customers, and optimize their campaigns across all platforms. This integrated approach not only improves resource efficiency but also enhances the ability to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer behaviors.
In summary, the cost and resource allocation strategies in omnichannel vs multichannel marketing differ significantly. While multichannel marketing allows for more flexibility and lower initial costs, it can lead to inefficiencies and higher long-term expenses due to the lack of integration. Omnichannel marketing, although more resource-intensive upfront, offers greater efficiency and better ROI in the long run by providing a seamless, integrated customer experience that drives loyalty and growth. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses looking to choose the right marketing strategy and optimize their resource allocation.
Strategic Implementation
Implementing an effective marketing strategy requires careful planning and execution, particularly when deciding between omnichannel and multichannel approaches. This section focuses on how to develop and manage a multichannel marketing strategy, outlining the key steps, best practices, and tools necessary to ensure your efforts are coordinated and impactful across various platforms.
Implementing Multichannel Marketing
Successfully implementing a multichannel marketing strategy requires thoughtful planning and coordination across various platforms. Unlike an omnichannel approach, which integrates all channels for a seamless customer experience, multichannel marketing focuses on optimizing each channel individually to reach and engage specific audience segments.
Steps for Developing a Multichannel Marketing Strategy
Developing a multichannel marketing strategy involves several key steps that ensure your brand reaches its audience effectively across various platforms. The first step is to identify your target audience by understanding their preferences, behaviors, and preferred channels of communication. Next, you need to define clear objectives for each channel, such as increasing brand awareness, generating leads, or driving sales. These objectives will guide your overall strategy and ensure that each channel contributes to your broader business goals.
After setting objectives, the next step is to select the appropriate channels that align with your target audience’s preferences. For example, if your audience is highly active on social media, you might prioritize platforms like Instagram or Facebook. If your audience prefers more direct communication, email marketing might be a primary focus. Once channels are selected, develop tailored content for each platform to ensure that your messaging resonates with your audience while maintaining brand consistency.
Finally, it’s crucial to monitor and analyze the performance of each channel. Use analytics tools to track metrics such as engagement rates, conversion rates, and ROI. This data will help you refine your strategy over time, optimizing your efforts for better results.
Best Practices for Channel Selection and Integration
When implementing a multichannel marketing strategy, selecting the right channels and integrating them effectively is essential for success. One of the best practices for channel selection is to focus on quality over quantity. It’s better to excel on a few channels that are most relevant to your audience than to spread your resources thin across many platforms.

Another best practice is to maintain consistent messaging across all channels. Even though each channel may have its unique style and audience, your brand’s voice and messaging should remain cohesive. This helps reinforce your brand identity and ensures that your audience receives a unified experience, regardless of the platform.
In terms of integration, it’s important to use cross-channel promotion to enhance engagement. For example, you can promote your social media channels through email newsletters or encourage in-store customers to follow your brand online. Cross-channel promotion helps drive traffic between platforms and maximizes the reach of your content.
Tools and Platforms for Managing Multichannel Marketing
Managing a multichannel marketing strategy requires the right tools and platforms to streamline operations and ensure efficiency. Social media management tools like Hootsuite or Buffer allow you to schedule posts, track engagement, and analyze performance across multiple social platforms from a single dashboard.
For email marketing, platforms like Mailchimp or Constant Contact enable you to create, send, and analyze email campaigns, helping you manage subscriber lists and automate communications.
CRM systems like HubSpot or Salesforce are invaluable for managing customer interactions across various channels. These tools allow you to track customer data, segment your audience, and personalize marketing efforts based on individual preferences and behaviors.
Additionally, analytics platforms such as Google Analytics or Adobe Analytics provide insights into how your audience interacts with your brand across different channels. These tools help you understand the customer journey, measure the effectiveness of your campaigns, and make data-driven decisions to optimize your multichannel strategy.
All in all, implementing a successful multichannel marketing strategy involves careful planning, thoughtful channel selection, and the use of robust tools and platforms to manage and analyze your efforts. By following best practices and leveraging the right technologies, you can create a cohesive and effective multichannel marketing strategy that drives results and enhances customer engagement.
Implementing Omnichannel Marketing
Implementing an omnichannel marketing strategy is a comprehensive process that requires meticulous planning, coordination, and the right technological infrastructure. Unlike multichannel marketing, which focuses on individual channel optimization, omnichannel marketing aims to create a seamless and integrated customer experience across all touchpoints. This section will provide a detailed guide on the steps involved in developing an omnichannel marketing strategy, best practices for ensuring a consistent and personalized customer experience, and the tools and platforms essential for managing an effective omnichannel approach.
Steps for Developing an Omnichannel Marketing Strategy
- Understand Your Customer Journey: The first step in developing an omnichannel marketing strategy is to gain a deep understanding of your customer’s journey. This involves mapping out all the touchpoints where customers interact with your brand—whether online or offline—and understanding how these interactions influence their decision-making process. By identifying the key moments of engagement, you can begin to see how different channels intersect and how you can create a more cohesive experience across them.
- Integrate Data Across Channels: A successful omnichannel strategy relies on the integration of customer data from all touchpoints. This means collecting data from every interaction—whether through a website, mobile app, social media, email, or in-store—and consolidating it into a unified customer profile. By integrating data across channels, you can gain a comprehensive view of each customer’s preferences, behaviors, and needs. This data forms the foundation for delivering personalized experiences and ensuring that every interaction feels relevant and consistent.
- Personalize the Customer Experience: With a unified view of your customer’s data, the next step is to personalize the customer experience across all channels. Personalization in omnichannel marketing goes beyond simply addressing the customer by name; it involves tailoring the content, offers, and interactions to meet the specific needs and preferences of each customer. For example, if a customer frequently purchases certain products online, they might receive personalized recommendations or promotions the next time they visit a physical store. The goal is to make each customer feel valued and understood, regardless of the channel they choose to engage with.
- Ensure Consistent Messaging Across Channels: Consistency is key in omnichannel marketing. To create a seamless experience, it’s crucial that your brand’s messaging, tone, and values are consistent across all channels. Whether a customer interacts with your brand through social media, email, or in-store, they should receive the same information and experience the same brand identity. This consistency helps build trust and reinforces the customer’s perception of your brand as reliable and cohesive.
- Coordinate Cross-Channel Campaigns: Omnichannel marketing involves running coordinated campaigns across multiple channels simultaneously. This means that your marketing efforts on one channel should complement and enhance those on another. For example, a promotion launched on social media should be reflected in email newsletters, on your website, and in-store signage. By coordinating campaigns across channels, you can amplify your reach and ensure that customers receive a unified message, regardless of how they interact with your brand.
- Invest in the Right Technology: Implementing an omnichannel marketing strategy requires a robust technological infrastructure. This includes investing in advanced CRM systems, marketing automation tools, data analytics platforms, and (CDPs). These technologies are essential for integrating data, personalizing interactions, and managing campaigns across multiple channels. The right technology enables you to execute your omnichannel strategy efficiently and effectively, ensuring that all channels work together to create a seamless customer experience.
Best Practices for Creating a Seamless Customer Experience
- Prioritize Customer-Centricity: At the heart of omnichannel marketing is a customer-centric approach. This means putting the customer’s needs and preferences at the forefront of your strategy. To create a seamless experience, focus on understanding what your customers want and how they prefer to interact with your brand. Use customer feedback, surveys, and data analytics to continuously refine your approach and ensure that every touchpoint aligns with customer expectations.
- Leverage Real-Time Data: Real-time data is crucial for delivering a seamless omnichannel experience. By leveraging data as it is generated, you can provide timely and relevant interactions that resonate with customers in the moment. For example, if a customer abandons their cart online, you can trigger a real-time email reminder or personalized offer to encourage them to complete their purchase. Real-time data allows you to be responsive and proactive, enhancing the overall customer experience.
- Foster Cross-Department Collaboration: Implementing an omnichannel strategy requires collaboration across multiple departments, including marketing, sales, customer service, and IT. To create a seamless experience, it’s important that all teams are aligned and working towards the same goals. Regular communication and collaboration ensure that everyone is on the same page and that customer data is shared and utilized effectively across all touchpoints.
- Optimize for Mobile: With the increasing use of mobile devices, optimizing your omnichannel strategy for mobile is essential. Ensure that your website, emails, and digital content are mobile-friendly and that customers can easily interact with your brand on their smartphones or tablets. Mobile optimization is key to providing a seamless experience, especially as customers frequently switch between devices during their journey.
- Measure and Adjust Continuously: Creating a seamless omnichannel experience is an ongoing process that requires continuous measurement and adjustment. Use data analytics to track the performance of your channels and campaigns, and be prepared to make changes as needed. Regularly assess how well your channels are integrated and how effectively they are delivering a consistent and personalized experience. By continuously refining your approach, you can ensure that your omnichannel strategy remains effective and aligned with customer expectations.
Tools and Platforms for Managing Omnichannel Marketing
- CRM Systems: Advanced CRM systems like Salesforce, Microsoft Dynamics 365, or HubSpot are critical for managing customer data across multiple channels. These platforms allow you to store and analyze customer interactions, providing a unified view that is essential for personalization and consistent messaging.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: Tools like Marketo, HubSpot, or Pardot enable you to automate and coordinate marketing efforts across channels. These platforms allow you to trigger personalized campaigns based on customer behavior and preferences, ensuring that your marketing efforts are timely and relevant.
- CDPs: The ones like Segment, Tealium, or Adobe Experience Platform aggregate customer data from various sources to create a unified customer profile. These platforms are essential for omnichannel marketing, as they allow you to track customer behavior across all touchpoints and deliver a consistent experience.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Platforms such as Google Analytics 360, Adobe Analytics, or Tableau provide insights into customer interactions and campaign performance. These tools help you understand the customer journey, measure the effectiveness of your omnichannel strategy, and make data-driven decisions to optimize your efforts.
- eCommerce and POS Integration: For businesses with both online and offline presences, integrating eCommerce platforms like Shopify or Magento with point-of-sale (POS) systems like Square or Lightspeed is crucial. This integration ensures that inventory, pricing, and customer data are consistent across all sales channels, providing a seamless shopping experience.
- Customer Experience Management (CEM) Tools: CEM platforms like Qualtrics or Medallia help businesses measure and manage customer experiences across all touchpoints. These tools collect feedback in real-time, allowing businesses to respond quickly to customer needs and improve the overall experience.
Implementing an omnichannel marketing strategy requires a comprehensive approach that integrates data, and personalized customer interactions, and ensures consistent messaging across all channels. By following the steps outlined above, adhering to best practices, and leveraging the right tools and platforms, businesses can create a seamless and effective omnichannel experience that drives customer satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term success.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Implementing an effective marketing strategy, whether omnichannel or multichannel, involves navigating various challenges that can undermine your efforts if not properly addressed. Understanding these common pitfalls is essential for businesses aiming to successfully execute their marketing strategies and maximize their impact across all channels.
Potential Issues in Implementation
- Lack of Integration: One of the most common pitfalls in both omnichannel and multichannel marketing is the failure to achieve proper integration across channels. In multichannel marketing, this often manifests as disjointed customer experiences where channels operate in silos, leading to inconsistent messaging and fragmented customer journeys. In omnichannel marketing, inadequate integration can prevent the seamless flow of data and customer information between channels, reducing the effectiveness of personalization and coordination efforts.
- Inconsistent Customer Experience: Inconsistent customer experiences are a major challenge, particularly in multichannel marketing, where different channels may offer varying levels of service, branding, and communication. This inconsistency can confuse customers and weaken brand loyalty. For example, a customer might receive excellent service online but have a poor experience in-store, leading to dissatisfaction and lost sales.
- Overcomplication of Technology: Both omnichannel and multichannel marketing rely on various tools and platforms to manage customer interactions, data, and campaigns. However, businesses can fall into the trap of overcomplicating their technological stack, using too many tools that do not integrate well with each other. This can lead to inefficiencies, data silos, and increased operational costs, making it difficult to execute a cohesive marketing strategy.
- Insufficient Data Management: Effective data management is crucial for the success of both omnichannel and multichannel marketing. Poor data quality, fragmented data sources, and inadequate data governance can result in inaccurate customer insights and ineffective marketing efforts. In an omnichannel strategy, where data integration is key, insufficient data management can severely undermine the ability to deliver personalized and consistent experiences across channels.
- Resource Allocation Issues: Misallocation of resources is another common pitfall. In multichannel marketing, businesses may spread their resources too thin by trying to maintain a presence on too many channels without prioritizing those that deliver the best ROI. In omnichannel marketing, the challenge lies in allocating sufficient resources to ensure seamless integration and a unified customer experience across all channels.
Tips for Overcoming Common Challenges
- Focus on Integration: To avoid the pitfalls of poor integration, businesses should invest in technologies that facilitate seamless data sharing and communication across channels. For multichannel marketing, this means finding ways to synchronize messaging and customer interactions, even if channels are managed independently. In omnichannel marketing, it’s crucial to implement integrated CRM systems, data platforms, and automation tools that enable a holistic view of the customer and support a consistent experience across all touchpoints.
- Maintain Consistency Across Channels: To prevent inconsistencies in customer experience, businesses should establish clear brand guidelines and communication standards that apply to all channels. Regular training for staff across different departments—such as online support, in-store sales, and customer service—can help ensure that customers receive the same level of service and care, regardless of the channel they use. Additionally, using centralized content management systems can help maintain consistent messaging and branding.
- Simplify Your Technology Stack: Avoid overcomplicating your technology stack by selecting tools and platforms that offer strong integration capabilities and can cover multiple functions. Prioritize technologies that can scale with your business and provide robust support for both multichannel and omnichannel strategies. Regularly review your technology stack to eliminate redundant tools and ensure that your systems work harmoniously together.
- Implement Strong Data Management Practices: To overcome challenges related to data management, businesses should establish strong data governance practices. This includes standardizing data collection methods, regularly cleaning and updating data, and ensuring that data is accessible and actionable across all departments. In an omnichannel strategy, investing in a CDP can help centralize customer data and provide a unified view that supports personalization and analytics.
- Prioritize Resource Allocation: Effective resource allocation requires businesses to focus on channels that deliver the highest ROI and align with their overall marketing goals. In multichannel marketing, this might mean scaling back on underperforming channels to concentrate resources on those that generate the most engagement and conversions. In omnichannel marketing, ensuring that sufficient resources are dedicated to technology integration, data management, and customer experience initiatives is key to achieving a seamless and effective strategy.
Case Studies: Multichannel vs. Omnichannel
Subway
Subway, a globally recognized fast-food chain, embarked on a comprehensive multichannel marketing campaign known as Two Ways to Subway in the U.K. and Ireland. The campaign aimed to promote both its online and in-store offerings, focusing on convenience and accessibility. By leveraging a variety of platforms, Subway sought to reach a wide audience and enhance its brand visibility across multiple touchpoints. The campaign’s core message revolved around the flexibility of enjoying Subway meals either through online ordering or by visiting physical stores.
Channels Utilized
Subway’s multichannel marketing approach involves a blend of both traditional and digital channels. The campaign included:
- Television and Radio: These traditional media channels were used to create broad awareness and reinforce Subway’s brand presence in the everyday lives of consumers.
- Video on Demand (VOD) and Online Video Advertising: To target a more digitally engaged audience, Subway utilized online video platforms. These ads were strategically placed on streaming services and other online video outlets to capture the attention of viewers who might prefer digital content over traditional TV.
- Social Media: Social media channels, including Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter, were integral to engaging with a younger, more digitally savvy audience. Subway used these platforms to share promotional content, engage with customers, and encourage user-generated content.
- Outdoor Advertising: Billboards and other outdoor advertising formats were employed to maintain brand visibility and remind potential customers of Subway’s offerings while they were on the go.
- Influencer Marketing: Subway collaborated with influencers to extend the campaign’s reach, particularly among younger demographics. Influencers helped to create buzz around the campaign by sharing their personal experiences with Subway’s offerings.
Campaign Impact
The multichannel marketing campaign was highly successful in achieving its goals. Subway effectively reached 96% of its target demographic—18 to 44-year-olds in the U.K. and Ireland—through the various channels utilized. This broad reach was instrumental in boosting brand awareness and driving traffic to both online and physical stores. The integration of traditional and digital media allowed Subway to maintain a strong presence in the daily lives of consumers, whether they were at home watching TV, browsing online, or out and about in their communities.
Moreover, the campaign demonstrated the effectiveness of a well-coordinated multichannel strategy, highlighting how different channels can complement each other to create a cohesive brand message. By engaging customers through multiple touchpoints, Subway was able to reinforce its brand identity and promote its offerings in a way that resonated with a diverse audience. This approach not only increased immediate sales but also strengthened customer loyalty by providing a consistent and convenient experience across all platforms.

Subway’s Two Ways to Subway campaign serves as an excellent example of how a well-executed multichannel marketing strategy can enhance brand visibility, engage a broad audience, and drive both online and in-store traffic. The campaign’s success underscores the importance of utilizing a variety of channels to meet customers where they are, whether they prefer traditional media, digital platforms, or a combination of both.
Sephora
Sephora has long been a leader in adopting omnichannel marketing strategies, seamlessly blending online and offline experiences to offer a personalized and cohesive customer journey. One of their standout initiatives is its integrated Beauty Insider program, which ties together Sephora’s website, mobile app, and physical stores. This program was designed to enhance customer engagement by offering personalized recommendations, loyalty rewards, and exclusive content, all accessible through any channel the customer chooses to engage with.
Sephora’s approach to omnichannel marketing emphasizes the creation of a unified experience, where every customer interaction, whether online or in-store, is informed by previous engagements. This strategy is grounded in the belief that customers should be able to transition effortlessly between channels, with each touchpoint enhancing their overall experience with the brand.
Channels Utilized
Sephora’s omnichannel strategy employs a variety of interconnected channels, each contributing to a seamless customer experience:
- Mobile App: The Sephora mobile app is a central hub in the omnichannel strategy, offering features such as virtual try-on, product recommendations, and access to the Beauty Insider program. The app allows customers to scan products in-store to view reviews and tutorials, bridging the gap between physical and digital shopping.
- Website: Sephora’s website is another key component, providing a rich online shopping experience with personalized product recommendations, beauty tutorials, and the ability to book in-store services. The website is fully integrated with the mobile app and in-store systems, ensuring that customer data and preferences are consistent across platforms.
- Physical Stores: Sephora’s physical stores are equipped with digital tools that enhance the shopping experience. Customers can use in-store tablets to access their Beauty Insider accounts, view personalized recommendations, and even check out products using mobile payment options. The stores also offer services like makeup consultations, which are coordinated with the customer’s online profile.
- Social Media: Sephora actively engages customers through social media platforms like Instagram, YouTube, and Facebook, where they share beauty tips, tutorials, and product launches. Social media is integrated with other channels, allowing customers to shop directly from posts or link to their online accounts.
- Email Marketing: Personalized email campaigns are sent based on customer preferences and behaviors, offering tailored promotions, product recommendations, and reminders about Beauty Insider rewards. These emails are synchronized with the customer’s activity on the mobile app and website, ensuring that the messaging is relevant and timely.
Campaign Impact
Sephora’s omnichannel marketing strategy has had a profound impact on the brand’s customer engagement, loyalty, and sales. By integrating data across all channels, Sephora can provide a highly personalized experience that keeps customers coming back. The seamless transition between online and offline interactions has not only improved customer satisfaction but also increased the average purchase value and frequency of purchases.

The Beauty Insider program, which is a cornerstone of Sephora’s omnichannel approach, has significantly boosted customer loyalty. Members of the program enjoy personalized rewards and exclusive content, which are accessible across all channels. This level of personalization has led to higher customer retention rates and increased spending among loyal customers.
Furthermore, Sephora’s use of technology to enhance the in-store experience—such as virtual try-on tools and mobile payment options—has helped bridge the gap between digital and physical shopping. This has attracted tech-savvy consumers who value convenience and innovation, further strengthening Sephora’s position as a leader in the beauty industry.
All in all, Sephora’s successful omnichannel marketing strategy highlights the power of integrating digital and physical touchpoints to create a seamless, personalized customer experience. By leveraging technology and data, Sephora has been able to build a loyal customer base, increase sales, and maintain its reputation as a forward-thinking brand in the competitive beauty market. This case study illustrates the effectiveness of omnichannel marketing in driving business success and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Comparative Analysis
In comparing Subway’s multichannel strategy with Sephora’s omnichannel approach, it becomes clear that each strategy offers distinct advantages depending on the marketing objectives. While Subway’s multichannel marketing effectively broadened reach and increased brand visibility, Sephora’s omnichannel marketing excelled in creating a seamless, personalized customer experience that deepened loyalty. This analysis highlights the importance of aligning marketing strategies with specific business goals, whether the focus is on widespread reach or fostering long-term customer engagement.
Comparing the Outcomes of Multichannel and Omnichannel Strategies
The case studies of Subway and Sephora offer a clear contrast between multichannel and omnichannel marketing strategies, highlighting their respective strengths and outcomes.
Subway’s Two Ways to Subway campaign exemplifies a successful multichannel marketing approach. The strategy effectively reached a wide audience by utilizing various channels—such as television, radio, online video, social media, and outdoor advertising—each operating independently. This approach allowed Subway to tailor its messaging for specific channels, maximizing reach and brand visibility. However, the multichannel nature of the campaign meant that each channel functioned somewhat in isolation, with limited integration across touchpoints. While this approach was effective for broadening reach and increasing brand awareness, it lacked the seamless customer experience that characterizes omnichannel marketing.
On the other hand, Sephora’s omnichannel strategy illustrates the power of a fully integrated approach. By connecting all customer touchpoints—online, mobile, and in-store—Sephora created a unified and personalized customer experience. The integration of data across channels allowed Sephora to provide consistent messaging and personalized recommendations, enhancing customer engagement and loyalty. The seamless transition between channels ensured that customers could interact with the brand in a way that felt natural and cohesive, whether they were shopping online, using the mobile app, or visiting a physical store.
Key Takeaways from Each Case Study
- Audience Reach vs. Customer Experience:
- Subway’s multichannel strategy was highly effective in maximizing audience reach through the use of multiple independent channels. This approach is ideal for campaigns focused on brand awareness and broad reach.
- Sephora’s omnichannel strategy, however, excelled in creating a seamless and personalized customer experience. By integrating channels and data, Sephora was able to foster deeper customer engagement and loyalty, which are critical for long-term business success.
- Channel Integration:
- Subway’s multichannel approach demonstrated that while independent channels can effectively reach diverse audiences, the lack of integration can result in a fragmented customer journey.
- Sephora’s omnichannel approach highlighted the benefits of channel integration, where every customer interaction across various touchpoints contributes to a consistent and cohesive experience.
- Technology and Personalization:
- Subway’s campaign utilized traditional and digital channels effectively, but the personalization was limited to the capabilities of each individual channel.
- Sephora’s strategy, in contrast, leveraged advanced technology to integrate data across channels, enabling personalized interactions that significantly enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Impact on Brand Loyalty:
- Subway’s multichannel campaign was successful in driving immediate sales and brand awareness but did not necessarily enhance long-term customer loyalty due to the lack of a unified experience.
- Sephora’s omnichannel strategy strengthened customer loyalty by offering a consistent and personalized experience, ensuring that customers felt valued and understood across all interactions.
The comparative analysis of Subway’s multichannel strategy and Sephora’s omnichannel approach underscores the distinct advantages and challenges of each. While multichannel marketing is effective for broad reach and diverse audience engagement, omnichannel marketing excels in creating a unified, personalized experience that fosters customer loyalty and long-term success. Businesses must carefully consider their goals and resources when deciding between these two strategies, as each offers unique benefits depending on the desired outcomes.
Practical Tips and Recommendations
Selecting the right marketing strategy is a crucial decision for any business, as it directly impacts customer engagement, brand loyalty, and overall success. In the debate of omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, each approach offers unique benefits and challenges. This section provides practical tips to help businesses make informed choices, considering factors such as customer expectations, resource availability, and industry-specific needs. By understanding these considerations, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies to align with their goals and optimize their efforts for maximum impact.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Selecting between omnichannel and multichannel marketing is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business’s success. Each strategy offers distinct advantages, and the choice depends on various factors such as your business goals, target audience, industry dynamics, and available resources. Understanding these factors and how they align with the capabilities of each approach is crucial for making an informed decision.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Between Omnichannel and Multichannel
Customer Expectations:
- Omnichannel: If your customers expect a seamless, consistent experience across all touchpoints, an omnichannel strategy is ideal. This approach ensures that whether they interact with your brand online, in-store, or via mobile, their experience is cohesive and personalized. Omnichannel marketing is particularly beneficial for businesses where customer loyalty and long-term relationships are critical, such as in retail, banking, and hospitality.
- Multichannel: If your primary goal is to maximize reach and engage with different segments of your audience on their preferred platforms, a multichannel strategy may be more suitable. This approach is effective for businesses that aim to broaden their brand awareness and capture a wide audience, such as in media, entertainment, and consumer goods.
Resource Availability:
- Omnichannel: Implementing an omnichannel strategy requires significant investment in technology, data integration, and cross-channel coordination. If your business has the resources to invest in advanced CRM systems, marketing automation tools, and analytics platforms, and the capacity to manage these systems effectively, omnichannel marketing can provide a strong ROI by enhancing customer experiences and fostering loyalty.
- Multichannel: If your business has limited resources, a multichannel strategy may be more practical. It allows you to focus on individual channels and optimize them independently, without the need for extensive integration. This approach is less resource-intensive and can be scaled according to your budget and capabilities.
Business Objectives:
- Omnichannel: If your primary objective is to increase customer retention, build long-term relationships, and create a unified brand experience, omnichannel marketing is the right choice. It is particularly effective for businesses that rely on repeat customers and need to ensure that every interaction reinforces brand loyalty.
- Multichannel: If your objective is to drive immediate sales, generate leads, and expand your brand’s reach, multichannel marketing may be more appropriate. This strategy allows you to deploy targeted campaigns on specific channels to quickly reach a large audience and achieve short-term marketing goals.
Technology Infrastructure:
- Omnichannel: A robust technology infrastructure is essential for executing an omnichannel strategy. If your business is equipped with integrated CRM systems, CDPs, and advanced analytics tools, you can effectively implement and manage an omnichannel approach. This infrastructure allows you to collect, analyze, and utilize data across all channels to deliver personalized experiences.
- Multichannel: For businesses with more basic technology capabilities, a multichannel strategy can be a better fit. It allows you to leverage existing tools and platforms to manage individual channels effectively, without the need for complex integration. This approach is often easier to implement and manage, especially for small to mid-sized businesses.
Industry-Specific Recommendations
Retail:
- Omnichannel: Retail businesses, especially those with both online and physical presences, benefit significantly from omnichannel marketing. By integrating online and offline channels, retailers can provide a seamless shopping experience, encouraging customers to interact with the brand across multiple touchpoints. This approach enhances customer loyalty and drives higher sales through personalized recommendations and consistent messaging.
- Multichannel: Smaller retail businesses or those focused on niche markets might find a multichannel approach more manageable. This allows them to effectively reach different customer segments on their preferred platforms, such as social media or email marketing, without the need for extensive integration.
Healthcare:
- Omnichannel: For healthcare providers, an omnichannel strategy is crucial for ensuring that patients receive consistent information and care across various channels. This can include integrating patient portals, mobile apps, and in-person consultations to create a unified experience. Omnichannel marketing in healthcare can improve patient satisfaction and engagement by providing personalized care and communication.
- Multichannel: Healthcare organizations with limited digital capabilities or those focused on specific services might opt for a multichannel strategy. This allows them to target patients effectively through specific channels like email newsletters, social media campaigns, or direct mail, depending on the audience’s preferences.
Financial Services:
- Omnichannel: Financial institutions benefit from an omnichannel approach by providing customers with a seamless experience across online banking, mobile apps, ATMs, and branch visits. This integration ensures that customers can manage their finances consistently and conveniently, regardless of the channel they use. An omnichannel strategy in financial services enhances customer trust and loyalty, which are vital in this industry.
- Multichannel: Smaller financial firms or those with a specific focus, such as investment services or insurance, may find a multichannel approach more practical. This allows them to engage clients through targeted campaigns on platforms like email, social media, and web-based services, without the need for full integration.
Hospitality:
- Omnichannel: In the hospitality industry, an omnichannel strategy is essential for creating a seamless guest experience across booking platforms, mobile apps, in-hotel services, and customer support. By integrating these touchpoints, hospitality businesses can enhance guest satisfaction and encourage repeat visits through personalized services and consistent communication.
- Multichannel: Smaller hotels or niche hospitality businesses may choose a multichannel approach to effectively market their services on specific platforms, such as travel websites, social media, or email campaigns. This allows them to reach potential guests without the need for extensive technological integration.
Choosing between omnichannel and multichannel marketing requires a careful assessment of your business’s goals, resources, and industry context. While omnichannel marketing offers the advantage of creating a seamless and personalized customer experience, it requires significant investment and technological infrastructure. Multichannel marketing, on the other hand, provides flexibility and is less resource-intensive, making it suitable for businesses with specific marketing objectives or limited resources. By considering these factors and industry-specific recommendations, businesses can select the strategy that best aligns with their needs and delivers the desired outcomes.
Tips for Optimizing Marketing Channels
Optimizing marketing channels is essential for enhancing customer experience and improving the overall effectiveness of your marketing strategy. Whether you are employing an omnichannel or multichannel marketing approach, certain best practices can help you maximize the impact of your efforts.
Enhancing Customer Experience Across Channels
- Consistency is Key: Ensure that your brand’s messaging, tone, and visual identity are consistent across all channels. In an omnichannel marketing strategy, this consistency is crucial for creating a seamless experience as customers move between different touchpoints. In multichannel marketing, even though channels operate independently, maintaining consistent messaging helps reinforce your brand identity and avoid confusing your audience.
- Personalization: Leverage data to personalize the customer experience across channels. In omnichannel marketing, integrated data from all touchpoints allows you to offer personalized recommendations and content based on a comprehensive view of the customer’s interactions. Even in a multichannel approach, using channel-specific data to tailor content and offers can significantly enhance the customer experience.
- Responsive Design: Ensure that your digital platforms—websites, emails, mobile apps—are optimized for different devices. This is especially important in an omnichannel strategy, where customers may switch between devices during their journey. A responsive design ensures that no matter how customers engage with your brand, they receive a consistent and user-friendly experience.
- Streamlined Customer Support: Offer consistent and accessible customer support across all channels. Whether a customer reaches out via social media, email, or phone, they should receive the same level of service. In omnichannel marketing, integrating customer service tools across channels allows for a unified support experience, where previous interactions are readily available to the support team, reducing friction and improving satisfaction.
Leveraging Data and Analytics for Better Decision-Making
- Centralize Data Collection: In omnichannel marketing, centralizing data collection from all channels into a single platform is crucial. This unified data source allows you to gain a holistic view of your customers, enabling more informed and accurate decision-making. In multichannel marketing, while channels may operate independently, ensuring that data is easily accessible and comparable across platforms is key to making strategic decisions.
- Use Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics can help you anticipate customer behavior and tailor your marketing efforts accordingly. In an omnichannel approach, predictive analytics can enhance personalization by analyzing past interactions across all channels to forecast future needs. In multichannel marketing, predictive analytics can help identify which channels are likely to yield the best results, allowing you to allocate resources more effectively.
- Regularly Monitor and Analyze Performance: Continuously track the performance of each channel using key metrics such as engagement, conversion rates, and ROI. In omnichannel marketing, this analysis should focus on how well channels are integrated and how effectively they contribute to a seamless customer experience. In multichannel marketing, performance analysis helps you understand which channels are performing best independently and where adjustments might be needed.
- A/B Testing: Conduct A/B testing across different channels to determine which strategies resonate most with your audience. In an omnichannel context, A/B testing can help optimize cross-channel strategies, such as how offers presented on one channel influence behavior on another. In multichannel marketing, A/B testing within each channel can help refine individual campaigns and improve overall effectiveness.

Optimizing your marketing channels—whether within an omnichannel or multichannel framework—requires a focus on enhancing the customer experience and leveraging data and analytics for informed decision-making. By implementing these tips, businesses can improve the effectiveness of their marketing strategies, driving greater engagement, satisfaction, and overall success.
Resource Management and Budgeting
Efficiently managing resources and budgeting are crucial elements in successfully implementing either an omnichannel or multichannel marketing strategy. Both approaches require careful planning to ensure that the allocation of resources aligns with your marketing objectives, and that your budget is spent effectively to maximize return on investment (ROI).
Efficient Allocation of Resources for Marketing Strategies
- Prioritize High-Impact Channels: In both omnichannel and multichannel marketing, it’s essential to prioritize the channels that offer the highest ROI. Begin by identifying the channels where your target audience is most active and engaged. In an omnichannel approach, focus on integrating these high-impact channels first to ensure a seamless experience. For multichannel marketing, concentrate your resources on optimizing these channels independently for maximum effectiveness.
- Leverage Cross-Functional Teams: Resource management in omnichannel marketing often requires collaboration across various departments, such as marketing, sales, and IT. Creating cross-functional teams ensures that efforts are coordinated, and that resources are used efficiently across all channels. In multichannel marketing, while teams may be more siloed, it’s still important to foster communication and collaboration to avoid duplicated efforts and ensure that each channel is aligned with overall business goals.
- Automate Where Possible: Automation can be a powerful tool for managing resources efficiently in both omnichannel and multichannel strategies. Use marketing automation tools to handle repetitive tasks, such as email campaigns, social media posting, and customer segmentation. This frees up your team to focus on more strategic activities and ensures consistency across all touchpoints. In an omnichannel strategy, automation can also help in synchronizing customer data across channels, enabling real-time personalization.
- Monitor and Reallocate Resources as Needed: Regularly assess the performance of each channel and be prepared to reallocate resources based on what’s working best. In omnichannel marketing, this might involve shifting resources toward channels that are most effectively driving seamless customer experiences. In multichannel marketing, it could mean doubling down on the channels that generate the most engagement or conversions. Agile resource management ensures that your strategy remains responsive to changes in customer behavior and market conditions.
Cost-Effective Solutions for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
- Start Small and Scale Gradually: For small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), implementing a full-scale omnichannel strategy might be resource-intensive. Instead, consider starting with a few key channels that are most critical to your business, and focus on integrating these effectively. As your business grows and resources expand, you can gradually incorporate additional channels into your omnichannel strategy.
- Utilize Freemium Tools: There are numerous free or low-cost tools available that can help SMBs manage their marketing efforts without breaking the bank. For multichannel marketing, tools like Mailchimp for email marketing, Buffer for social media management, and Google Analytics for performance tracking offer robust features at little to no cost. For omnichannel marketing, look for affordable CRM platforms that offer basic integration capabilities, such as HubSpot or Zoho CRM.
- Focus on Core Channels: SMBs should focus on a few core channels that are most likely to reach their target audience effectively. In a multichannel strategy, this might mean prioritizing social media and email marketing, which tend to offer high engagement at a low cost. For an omnichannel approach, ensure that these core channels are well-integrated and that customer data flows seamlessly between them to create a unified experience.
- Outsource Where Necessary: If resource constraints make it challenging to manage all aspects of your marketing strategy in-house, consider outsourcing certain functions. Freelancers or agencies can provide specialized expertise in areas like content creation, SEO, or data analysis, helping you achieve your marketing goals without the need for a large internal team.
- Measure ROI Continuously: Cost-effectiveness in marketing is all about maximizing ROI. Continuously measure the performance of your marketing channels, and be ready to adjust your strategy as needed. Whether you’re pursuing an omnichannel or multichannel approach, focus on the channels that deliver the best returns, and consider phasing out or scaling back on those that are underperforming.

Efficient resource management and smart budgeting are key to the success of both omnichannel and multichannel marketing strategies. By prioritizing high-impact channels, leveraging automation, and making use of cost-effective tools and services, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts and achieve their goals within their budget constraints. Whether you’re a small business starting with a multichannel strategy or an established brand looking to implement an omnichannel approach, these tips can help you allocate resources effectively and maximize the impact of your marketing activities.
Conclusion
In the debate of omnichannel vs multichannel marketing, it is clear that each approach offers unique advantages depending on a business’s goals, resources, and target audience. While both strategies aim to engage customers across multiple touchpoints, they differ in execution. Multichannel marketing focuses on maximizing reach by optimizing individual channels independently, whereas omnichannel marketing integrates these channels to create a seamless and personalized customer experience.
Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses seeking to tailor their marketing strategies effectively. Multichannel marketing provides a strong foundation by establishing a presence across various platforms, allowing businesses to reach a broad audience. However, as consumer expectations evolve, omnichannel marketing emerges as the next level of sophistication, offering deeper engagement through consistency and integration across all customer interactions.
Leveraging both strategies, where appropriate, can provide businesses with a competitive edge. By starting with a multichannel approach and gradually integrating channels to transition into omnichannel marketing, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction, build loyalty, and drive long-term success.
In final thoughts, the choice between omnichannel and multichannel marketing should align with your business objectives and customer needs. While multichannel marketing is a strong strategy for reaching diverse audiences, omnichannel marketing offers the opportunity to elevate customer experience and deepen relationships through a cohesive and integrated approach. As the marketing landscape continues to evolve, embracing the principles of both strategies will enable businesses to stay competitive and thrive in an increasingly connected world.