Omnichannel ERP refers to an ERP solution that integrates all sales channels—both online and offline—into a cohesive platform, ensuring that inventory, customer data, and order management are synchronized across every touchpoint. For eCommerce businesses, this means offering a seamless shopping experience, where customers can browse online, purchase in-store, and return products via multiple channels without any disruption.
An omnichannel ERP system enables businesses to manage this complexity effectively, improving both operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. This system ensures that stock levels are accurate across all platforms, orders are processed swiftly, and customer interactions remain consistent, no matter where or how they engage with the brand.
In this blog post, we take a deep look into the world of omnichannel ERP, exploring how it works, its critical role in the success of eCommerce businesses, and why adopting it is essential for long-term growth in a hyper-competitive market.
Table of Contents
Understanding Omnichannel ERP
Omnichannel ERP, at its core, refers to an enterprise resource planning system designed to unify and streamline business operations across multiple sales channels, including online, in-store, mobile, and even marketplaces like Amazon or eBay. Unlike traditional ERP systems, which often operate in silos and manage only specific aspects of a business (such as finance, inventory, or HR), omnichannel ERP integrates all sales, inventory, and customer management data into a single system that operates in real-time. This synchronization allows businesses to deliver a seamless and consistent experience to their customers, no matter how or where they choose to engage with the brand.
One of the key components of omnichannel ERP is real-time data synchronization. This means that any action taken in one channel, such as a customer purchasing an item online, is immediately reflected across all other channels—be it inventory levels in physical stores or order management systems. This eliminates the risk of errors, such as overselling products, and ensures customers have access to accurate information about stock availability.

Another crucial component of omnichannel ERP is integrated order management. This feature allows businesses to efficiently manage orders coming from different sources, whether they originate from a website, a mobile app, or a brick-and-mortar store. The system processes these orders centrally, ensuring that fulfillment, shipping, and customer communication are consistent, regardless of where the transaction took place. This level of integration enhances the overall efficiency of operations and improves the customer experience by reducing delays and errors in order processing.
Furthermore, omnichannel ERP includes CRM integration, which is vital for delivering personalized experiences. With CRM tools built into the omnichannel ERP system, businesses can track customer preferences, purchase histories, and interactions across all platforms. This wealth of information enables businesses to offer personalized promotions, recommend relevant products, and build stronger relationships with their customers, ultimately driving loyalty and increasing sales.
Key Features of Omnichannel ERP
Integrated Data Management
Unified Customer Profiles and Data Across Channels
One of the most powerful features of omnichannel ERP is its ability to create and maintain unified customer profiles. In a traditional setup, customer data is often siloed across different systems, such as point-of-sale (POS) terminals, eCommerce platforms, and CRM tools. This fragmented approach can lead to inconsistencies in customer interactions, missed opportunities for personalized service, and an incomplete understanding of customer behavior.
With omnichannel ERP, customer data from every touchpoint is centralized into one platform, allowing businesses to build comprehensive, unified customer profiles. These profiles include a wealth of information, such as purchase history, preferences, interaction history, and even feedback or service issues. By maintaining this data in a single system, businesses can ensure that every interaction with the customer is informed and consistent, regardless of the channel.
For example, if a customer makes a purchase online and later visits a physical store, the sales associate can access the customer’s entire purchase history and offer personalized recommendations. Likewise, if a customer calls customer service with an issue, the representative has immediate access to all previous interactions, making it easier to resolve the problem quickly and efficiently. This unified view not only improves the customer experience but also enhances the business’s ability to drive sales and build brand loyalty through targeted marketing and personalized offers.
In addition to improving customer interactions, unified customer profiles in an omnichannel ERP system enable more precise marketing strategies. With all customer data consolidated in one place, businesses can analyze purchasing patterns, preferences, and trends to create more personalized marketing campaigns. These insights allow businesses to segment customers effectively and deliver tailored offers, increasing the likelihood of conversions and boosting customer retention.
Real-time Inventory and Supply Chain Management
Another critical aspect of integrated data management in omnichannel ERP is real-time inventory and supply chain management. In a world where customers expect immediate access to products and fast delivery, businesses need to have complete visibility into their inventory levels at all times. Traditional ERP systems often struggle to provide up-to-the-minute insights across multiple locations, leading to stock discrepancies, delayed orders, and dissatisfied customers.
Omnichannel ERP solves this problem by offering real-time tracking of inventory across all channels and locations. Whether it’s a warehouse, a retail store, or an online platform, omnichannel ERP ensures that inventory data is constantly updated. This means that when a customer purchases a product online, the system immediately reflects that sale across all other channels, preventing overselling and stockouts. It also allows businesses to offer services like buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS) or ship from store, providing customers with more flexibility and convenience in how they receive their products.

Real-time inventory management also plays a vital role in optimizing the supply chain. With omnichannel ERP, businesses can track the movement of goods from suppliers to warehouses and retail locations in real-time. This level of visibility allows businesses to identify potential delays or bottlenecks in the supply chain and take proactive measures to address them. For example, if a particular item is selling out faster than anticipated, the system can trigger automatic reordering from suppliers to prevent stockouts. Additionally, businesses can optimize their distribution by analyzing inventory levels across locations and redistributing stock to where it’s needed most.
Furthermore, real-time data in omnichannel ERP enhances demand forecasting. By analyzing sales patterns and inventory movement across channels, businesses can make more accurate predictions about future demand and adjust their stock levels accordingly. This reduces the risk of overstocking or understocking, ultimately saving costs and improving overall efficiency. It also enables businesses to manage seasonal spikes in demand more effectively, ensuring they have enough stock on hand without tying up excess capital in inventory.
The integration of inventory and supply chain management into an omnichannel ERP system also helps businesses meet customer expectations for faster and more reliable shipping. Customers today expect near-instant gratification, and delays in order fulfillment can lead to lost sales and damaged brand reputation. With omnichannel ERP, businesses can streamline their fulfillment processes by automating key tasks, such as order routing and shipment tracking. This ensures that orders are processed quickly and accurately, whether they are being shipped from a warehouse or a retail location.
Order Management
Centralized Order Processing from Multiple Channels
With omnichannel ERP, orders from all channels—whether online or offline—are automatically routed into a centralized system where they can be processed, tracked, and fulfilled. This unified approach eliminates the need for separate workflows for each channel, streamlining the entire order management process. For example, a customer may place an order online for in-store pickup, while another customer orders the same product via a mobile app for home delivery. An omnichannel ERP system can process both orders simultaneously and ensure they are fulfilled according to the customers’ preferences without the need for manual intervention or complex, channel-specific processes.

Centralized order processing also brings significant benefits in terms of efficiency and accuracy. Because all orders flow into a single system, businesses can reduce the risk of duplicate orders, miscommunications, or data entry errors that can occur when using separate systems for different channels. Additionally, the system can automatically update stock levels across all locations, ensuring that inventory is correctly reflected and preventing overselling or stockouts. This integration is particularly important for businesses that offer features like buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS) or ship from store, where accurate, real-time visibility into inventory and order statuses is crucial.
Moreover, centralized order processing in omnichannel ERP systems enhances the ability to manage complex order fulfillment options, such as split shipments, backorders, and multiple delivery methods. For instance, a business may need to fulfill a single customer’s order from multiple locations—one product from a warehouse and another from a nearby retail store. An omnichannel ERP system can seamlessly coordinate these activities, ensuring that the customer receives their complete order in the most efficient and timely manner possible.
Tracking Orders Across Online and Offline Touchpoints
One of the most significant advantages of an omnichannel ERP system is its ability to track orders across both online and offline touchpoints in real time. In a multi-channel retail environment, customers expect full transparency when it comes to their orders, including up-to-date information on order statuses, shipping timelines, and delivery confirmations. Traditional ERP systems often fall short in this regard, as they are typically siloed, meaning that orders from different channels are tracked separately, making it difficult to provide customers with consistent and timely updates.
Omnichannel ERP addresses this problem by integrating order tracking into a single, unified system. From the moment an order is placed—whether online, in-store, or via a mobile app—businesses can track its progress through every stage of fulfillment, from picking and packing to shipping and delivery. This level of transparency allows businesses to provide customers with real-time updates, enhancing the overall customer experience and reducing the likelihood of inquiries about order status.
For example, a customer who orders a product online can log into their account and see exactly where their order is in the fulfillment process, whether it’s being packed, shipped, or out for delivery. Similarly, a customer who purchases an item in-store can track their order if they choose to have it shipped to their home. This real-time tracking capability not only improves customer satisfaction but also helps reduce the workload on customer service teams, as customers are less likely to contact support for updates when they have access to detailed order tracking information.
Another key aspect of omnichannel ERP’s order tracking feature is its ability to consolidate information from multiple shipping carriers. Many businesses use different shipping providers for different channels or geographic regions, which can make it difficult to track orders accurately across all platforms. Omnichannel ERP systems integrate with a wide range of shipping and logistics partners, allowing businesses to manage and track shipments regardless of the carrier being used. This means that customers receive consistent tracking information, no matter how their order is being shipped.
Additionally, omnichannel ERP systems can provide businesses with valuable insights into their order fulfillment performance. By analyzing data on order processing times, shipping durations, and delivery success rates, businesses can identify areas for improvement in their fulfillment processes. For example, a business might discover that orders placed through one channel are consistently slower to fulfill than others, or that certain shipping methods result in more delayed deliveries. With this information, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize their fulfillment operations and ensure that customers receive their orders as quickly and reliably as possible.
Inventory Management
Traditional ERP systems often struggle to provide the level of integration and real-time data necessary to manage inventory effectively in a multi-channel environment. This is where omnichannel ERP systems excel. By offering businesses real-time visibility into their stock levels and automating critical processes like replenishment and demand forecasting, omnichannel ERP transforms inventory management from a reactive to a proactive function. This section will explore how omnichannel ERP enables real-time stock visibility and helps businesses optimize their inventory with automation.
Real-Time Stock Visibility Across All Channels
One of the most powerful features of an omnichannel ERP system is its ability to provide real-time stock visibility across all sales channels. Whether a business operates brick-and-mortar stores, eCommerce websites, mobile apps, or third-party marketplaces, omnichannel ERP ensures that inventory levels are accurately reflected across every platform in real-time. This seamless synchronization is vital in ensuring that customers receive accurate information about product availability, preventing situations like overselling or stockouts.
In a traditional setup, businesses often manage inventory separately for each sales channel, which can lead to discrepancies in stock levels. For instance, a product may be listed as available online, but in reality, it’s sold out in the warehouse, leading to customer frustration and lost sales. With omnichannel ERP, businesses can consolidate all inventory data into a single platform, ensuring that stock levels are updated instantly whenever a sale is made, no matter the channel. This level of visibility not only reduces the risk of stock discrepancies but also empowers businesses to offer more flexible fulfillment options, such as “buy online, pick up in-store” (BOPIS) or “ship from store.”

Real-time inventory visibility is also essential for maintaining customer trust. When customers browse products online, they expect the information to be accurate. A customer who places an order only to find out later that the item is out of stock may lose confidence in the brand and choose to shop elsewhere. By leveraging omnichannel ERP, businesses can provide customers with real-time updates on product availability, offering them the assurance that what they see is what they get.
Additionally, real-time stock visibility enables businesses to manage their inventory more effectively across multiple locations. For example, if a product is selling well in one region but underperforming in another, omnichannel ERP can help businesses redistribute stock to meet local demand, reducing the need for markdowns and optimizing profitability. The ability to view and manage inventory across all locations in real-time also helps businesses reduce carrying costs by avoiding overstocking while still ensuring that popular items are always available where they are needed most.
Automating Replenishment and Forecasting Demand
Another critical feature of omnichannel ERP in inventory management is its ability to automate replenishment and forecast demand. In a fast-paced retail environment, manually managing stock levels and reordering products can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Businesses that rely on manual processes often struggle to keep up with fluctuating demand, leading to stockouts or excess inventory. Omnichannel ERP addresses this challenge by automating key aspects of inventory management, ensuring that stock levels are optimized at all times.
One of the most valuable automation tools offered by omnichannel ERP is automated replenishment. This feature allows businesses to set predetermined stock thresholds, at which point the system will automatically trigger a reorder from suppliers. For example, if a popular product’s stock falls below a certain level, the system can automatically generate a purchase order and send it to the supplier, ensuring that the product is restocked before it runs out. This eliminates the need for constant manual monitoring of stock levels and significantly reduces the risk of stockouts.
Automating replenishment also helps businesses reduce excess inventory, which can tie up capital and increase storage costs. By setting appropriate reorder points and using real-time sales data, omnichannel ERP ensures that businesses only order what they need, when they need it. This level of precision is particularly important for businesses with multiple sales channels, as it allows them to manage stock efficiently across all locations while minimizing waste.
In addition to automating replenishment, omnichannel ERP systems are equipped with powerful demand forecasting tools. These tools analyze historical sales data, seasonal trends, and external factors—such as market conditions or upcoming promotions—to predict future demand for products. By forecasting demand accurately, businesses can plan their inventory purchases more effectively, ensuring that they have enough stock on hand to meet customer needs without overcommitting resources.
Demand forecasting is especially valuable in industries where consumer behavior can be unpredictable. For instance, during holiday seasons or promotional events, demand for certain products may spike unexpectedly. With the help of omnichannel ERP’s forecasting capabilities, businesses can anticipate these fluctuations and adjust their inventory levels accordingly, ensuring they can meet increased demand without running out of stock. This proactive approach not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring that popular products are always available when needed.
Moreover, omnichannel ERP systems allow businesses to refine their demand forecasting over time. As the system collects more data from sales across different channels, it becomes better at identifying patterns and predicting future demand. This continuous improvement in forecasting accuracy enables businesses to make smarter inventory decisions, reducing the risk of both stockouts and excess inventory.
CRM Integration
Personalized Customer Interactions Based on Integrated Data
One of the most significant advantages of CRM integration in omnichannel ERP is the ability to deliver personalized customer interactions based on integrated data. In today’s competitive market, customers are no longer satisfied with generic marketing messages and one-size-fits-all approaches. They expect businesses to recognize their unique needs and offer tailored experiences that reflect their preferences, purchasing behavior, and interaction history.
With omnichannel ERP, businesses can use integrated CRM data to create a 360-degree view of each customer. This view includes not only transactional information, such as past purchases, but also insights into how customers engage with the brand across various channels. For example, a customer might browse products online, abandon their cart, then visit a physical store to make a purchase. With the integrated CRM functionality of an omnichannel ERP system, businesses can track these interactions and use the data to personalize follow-up communications, such as sending a reminder about the abandoned cart or offering a personalized discount for in-store purchases.

This ability to deliver personalized customer interactions extends beyond just marketing efforts. Customer service representatives, for instance, can use CRM data from the omnichannel ERP system to provide more relevant and timely support. If a customer calls in with an issue, the representative can quickly access the customer’s entire interaction history—whether online or in-store—and offer a solution that takes the customer’s previous experiences into account. This level of personalization not only resolves issues more effectively but also makes the customer feel valued and understood, ultimately driving stronger brand loyalty.
Personalization through omnichannel ERP is not limited to individual interactions. Businesses can also use CRM data to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer segments. By analyzing customer behavior and preferences, businesses can segment their audience into different groups based on factors such as shopping frequency, product preferences, or location. These insights enable businesses to create highly relevant and personalized marketing campaigns that are more likely to result in engagement and conversions.
Loyalty Programs and Cross-Channel Promotions
Loyalty programs are a powerful tool for building long-term relationships with customers, and when integrated into an omnichannel ERP system, they become even more effective. A well-executed loyalty program rewards customers for their continued engagement and purchases, encouraging repeat business and fostering brand loyalty. With omnichannel ERP and CRM integration, businesses can take loyalty programs to the next level by offering personalized rewards and promotions that are tailored to each customer’s preferences and shopping behavior.
For example, an omnichannel ERP system can track a customer’s purchase history across all channels—whether online, in-store, or through a mobile app—and offer rewards that are relevant to the products they buy most often. If a customer frequently purchases a specific brand or product category, the system can automatically offer discounts or reward points on those items. This type of personalization makes loyalty programs more appealing to customers, as they feel that the rewards are specifically designed for them.

Additionally, omnichannel ERP enables businesses to implement cross-channel promotions that drive engagement across multiple platforms. A common challenge for businesses is encouraging customers to interact with them on more than one channel. Omnichannel ERP can help bridge this gap by offering promotions that incentivize customers to move between different channels. For instance, a business might offer a special discount to customers who browse products online and then make a purchase in-store, or they could offer bonus loyalty points for customers who sign up for the company’s mobile app.
Cross-channel promotions not only increase customer engagement but also provide businesses with valuable data about customer preferences and behavior. By encouraging customers to interact with the brand on multiple platforms, businesses can gain insights into which channels are most effective for driving sales and engagement. This data can then be used to refine marketing strategies and optimize future promotions, ensuring that each campaign delivers maximum results.
Another advantage of using omnichannel ERP for loyalty programs and promotions is the ability to track and manage customer rewards in real time. In traditional loyalty programs, managing points, rewards, and promotions across multiple channels can be a logistical nightmare, often leading to confusion for both customers and employees. With omnichannel ERP, loyalty points and rewards are automatically updated across all platforms, ensuring that customers have a consistent and accurate view of their account, no matter where they interact with the brand. This streamlined approach not only improves the customer experience but also reduces the administrative burden on businesses.
Accounting and Finance Automation
One of the primary benefits of using an omnichannel ERP system is the automation of accounting and finance processes. Unlike traditional ERP systems, which often require manual input and reconciliation across multiple systems, omnichannel ERP provides a unified platform that consolidates all financial data from every sales channel. This integration not only streamlines financial management but also ensures that businesses have access to real-time, accurate data that can be used to make informed decisions. The automation of financial tasks—ranging from reporting to tax compliance—allows businesses to optimize their workflows, reduce the risk of human error, and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Real-time Financial Reporting Across Multiple Channels
A key feature of omnichannel ERP systems is real-time financial reporting. In a multi-channel business environment, financial data is constantly being generated, whether through online sales, in-store purchases, or mobile transactions. Traditional accounting methods often struggle to keep up with the volume and speed of these transactions, leading to delayed reporting and discrepancies in financial data. However, with omnichannel ERP, businesses can automatically collect, consolidate, and analyze financial information in real time, providing a clear and accurate picture of their financial health at any given moment.
Real-time financial reporting is especially important for businesses that operate across multiple channels, as it enables them to track sales, expenses, and profits from each platform simultaneously. For example, a business might run a flash sale on its eCommerce platform while also offering in-store promotions and discounts. With omnichannel ERP, the financial data from these activities is captured instantly, allowing the business to monitor the financial impact of each channel in real time. This level of visibility enables businesses to identify trends, measure the success of marketing campaigns, and make data-driven decisions to optimize their performance.

In addition to providing a real-time view of financial performance, omnichannel ERP systems allow businesses to generate detailed reports that can be customized to meet specific needs. For instance, a business can create reports that break down revenue by channel, product category, or geographic region, providing insights into which areas are performing well and where improvements are needed. These reports can be generated automatically, reducing the need for manual data entry and analysis, and ensuring that financial information is always up-to-date.
Furthermore, real-time financial reporting helps businesses stay agile in a constantly changing market. Whether responding to shifts in customer demand or adjusting pricing strategies, having access to real-time data enables businesses to make proactive decisions that can improve profitability and reduce financial risks. This is particularly important in industries like retail and eCommerce, where trends and consumer behavior can change rapidly, and businesses need to be able to adapt quickly to maintain their competitive edge.
Handling Transactions and Taxes for eCommerce, In-store, and Mobile
Another significant advantage of omnichannel ERP is its ability to handle transactions and taxes seamlessly across all channels. In a multi-channel business environment, each platform—whether it’s an online store, a physical retail location, or a mobile app—generates its own set of transactions, which must be accurately processed and recorded. Traditional systems often require businesses to manually reconcile these transactions from each channel, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. Omnichannel ERP automates this process by integrating all transaction data into a single system, ensuring that sales, payments, and refunds are processed consistently across all channels.
For eCommerce businesses, omnichannel ERP simplifies the management of online transactions by automating key tasks such as payment processing, invoicing, and refunds. The system can automatically capture payment information from online sales and update financial records in real time, ensuring that the business’s financial data is always accurate and up to date. Similarly, for in-store transactions, omnichannel ERP integrates with point-of-sale (POS) systems to capture sales data and process payments instantly, reducing the need for manual entry and reconciliation.

Mobile transactions, which are becoming increasingly common as more customers use smartphones to make purchases, are also seamlessly integrated into omnichannel ERP systems. Whether a customer uses a mobile app to buy a product or makes a contactless payment in-store, the system automatically records the transaction and updates the financial records accordingly. This ensures that all transactions, regardless of the channel, are processed efficiently and accurately.
Tax management is another area where omnichannel ERP provides significant benefits. Managing taxes in a multi-channel business environment can be complex, particularly when dealing with different tax rates and regulations for online and offline sales. For example, sales tax may vary depending on the location of the customer or the type of product being sold. With omnichannel ERP, businesses can automate tax calculations for every transaction, ensuring that the correct tax is applied based on the location and applicable regulations. This automation not only reduces the risk of errors but also simplifies tax reporting, making it easier for businesses to stay compliant with local, national, and international tax laws.
Additionally, omnichannel ERP systems can handle multiple currencies and tax jurisdictions, making them ideal for businesses that operate globally or sell to customers in different regions. Whether processing an online order from an international customer or handling in-store transactions across multiple locations, omnichannel ERP ensures that all taxes are calculated and applied correctly, regardless of the channel or geographic region.
Omnichannel ERP also simplifies the process of generating financial reports for tax purposes. Businesses can automatically generate reports that break down sales tax, VAT, or other applicable taxes by channel, location, or product category, making it easier to file tax returns and stay compliant with regulations. This level of automation reduces the administrative burden on businesses and helps ensure that tax filings are accurate and submitted on time.
Top 10 Omnichannel ERP Solutions in the Market
SAP S/4HANA
SAP S/4HANA is one of the leading ERP solutions on the market, known for its advanced capabilities, flexibility, and ability to support large-scale enterprises. Launched by SAP in 2015 as the successor to its traditional ERP system, SAP ERP Central Component (ECC), SAP S/4HANA is built on SAP’s proprietary in-memory database technology, HANA. The in-memory architecture allows the system to process vast amounts of data in real time, making it ideal for businesses that require high-speed data analysis and decision-making.
SAP S/4HANA is specifically designed to handle the complexities of modern businesses, including omnichannel operations. It supports companies in managing various processes across different departments—such as finance, procurement, sales, manufacturing, and logistics—under one integrated platform. The solution’s flexibility allows businesses to customize it to their specific needs, making it suitable for both industry-specific and multi-channel enterprises. SAP S/4HANA is available as both an on-premise and cloud-based solution, giving companies the option to choose the deployment model that best suits their infrastructure and scalability requirements.
Key Features
SAP S/4HANA offers a wide range of features that make it a powerful solution for businesses looking to adopt an omnichannel approach. Some of its most important features include:
- Real-time Data Processing: SAP S/4HANA leverages its in-memory HANA database to process data in real time. This allows businesses to track their inventory, financials, and customer interactions across all channels simultaneously, enabling faster decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
- Integrated Supply Chain Management: The solution offers robust supply chain management tools that help businesses manage their logistics, warehousing, and fulfillment operations. This is particularly important for omnichannel businesses that need to ensure consistent stock levels and timely deliveries across multiple locations.
- CRM Integration: SAP S/4HANA integrates CRM functionality directly into the ERP system, enabling businesses to manage customer data, personalize interactions, and track customer journeys across both online and offline channels. This is key for businesses that want to offer personalized services while maintaining a unified customer view.
- Omnichannel Order Management: The system allows businesses to manage orders from multiple channels, including eCommerce platforms, in-store transactions, and mobile sales. It ensures that orders are processed efficiently and that customers can access real-time updates on their orders, regardless of the sales channel.
- Financial and Accounting Automation: SAP S/4HANA includes powerful financial management features that automate accounting tasks, generate real-time financial reports, and manage transactions across multiple currencies and tax jurisdictions. This makes it ideal for businesses that operate in multiple regions or serve customers globally.
- Industry-Specific Solutions: SAP S/4HANA offers tailored solutions for various industries, including retail, manufacturing, automotive, healthcare, and more. This allows businesses to implement industry-specific best practices while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to their unique operations.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Scalability: SAP S/4HANA is designed to support enterprises of all sizes, making it highly scalable for businesses that expect to grow or expand into new markets.
- Real-Time Data: The ability to process and analyze data in real time enables faster decision-making and operational adjustments, which is essential for businesses operating in competitive environments.
- Advanced Omnichannel Capabilities: The integration of sales, inventory, customer management, and financial operations into one system makes SAP S/4HANA a powerful tool for businesses with complex omnichannel operations.
- Customization and Flexibility: SAP S/4HANA offers extensive customization options, allowing businesses to tailor the system to their specific needs, including industry-specific configurations and custom workflows.
- Global Compliance: SAP S/4HANA supports multiple languages, currencies, and tax systems, making it a great choice for businesses with a global presence that need to comply with various regulations.
Cons:
- Complexity and Implementation Time: Due to its wide range of features and customization options, SAP S/4HANA can be complex to implement. The implementation process may take months, or even longer for large enterprises, and requires skilled consultants for setup.
- Cost: SAP S/4HANA is one of the more expensive ERP solutions on the market. While the system offers a high level of functionality, the cost of implementation, licensing, and ongoing maintenance can be a significant investment, particularly for smaller businesses.
- Steep Learning Curve: The system’s vast array of features can be overwhelming for new users, requiring extensive training and onboarding for employees to fully utilize the system’s capabilities.
Pricing
The pricing structure for SAP S/4HANA depends on the deployment model and the specific needs of the business. SAP offers both on-premise and cloud-based solutions, with the latter typically being more cost-effective for smaller businesses due to lower upfront infrastructure costs. The on-premise version usually requires a higher initial investment for hardware and implementation services, while the cloud-based version operates on a subscription-based model, with pricing based on the number of users and the modules required.
SAP S/4HANA is generally considered one of the more expensive ERP options on the market. Licensing costs start at around $1,000 to $2,000/user/year for the cloud-based version, with additional costs for implementation, customization, and support services. On-premise implementations can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the size of the organization and the complexity of the deployment.
Suitable For
SAP S/4HANA is best suited for medium to large enterprises that require a robust, scalable ERP solution with advanced omnichannel capabilities. It is particularly beneficial for businesses that operate across multiple regions or industries, as the system’s flexibility and industry-specific solutions allow for extensive customization. Retailers, manufacturers, and global enterprises with complex supply chains will benefit from the system’s real-time data processing, omnichannel order management, and financial automation features.
However, due to its cost and complexity, SAP S/4HANA may not be the best option for small businesses or startups with limited budgets or simpler operational needs.
Oracle NetSuite
Oracle NetSuite, originally founded in 1998 as NetLedger, was one of the first cloud-based ERP systems designed to help businesses manage their core functions from a single platform. In 2016, the company was acquired by Oracle Corporation, which expanded NetSuite’s capabilities and market reach, positioning it as one of the leading ERP solutions for growing businesses and enterprises alike. Oracle NetSuite is particularly well-suited for businesses that operate across multiple channels, as it provides integrated tools for managing financials, inventory, customer relationships, and eCommerce.
Oracle NetSuite is a fully cloud-based solution, which means that businesses can access the system from anywhere, at any time. This flexibility is particularly valuable for companies with distributed teams or those managing operations across different geographic regions. NetSuite’s omnichannel capabilities allow businesses to manage their sales channels holistically, ensuring that all departments—from finance to sales to customer service—are working from the same set of data.
One of the standout features of Oracle NetSuite is its modular design, allowing businesses to scale the system according to their specific needs. Companies can start with basic ERP functionality and then add modules for eCommerce, supply chain management, or CRM as their operations expand. This flexibility makes NetSuite a popular choice for businesses in a wide range of industries, from retail and wholesale distribution to manufacturing and professional services.
Key Features
Oracle NetSuite is packed with a wide array of features that make it an ideal choice for businesses looking for a comprehensive omnichannel ERP system. Some of its key features include:
- Unified Cloud-Based Platform: Oracle NetSuite offers a fully integrated cloud-based platform that allows businesses to manage all aspects of their operations from one place. This includes financial management, inventory control, order processing, CRM, and eCommerce, ensuring that data from all channels is consolidated and easily accessible.
- Omnichannel Order Management: One of NetSuite’s core strengths is its ability to manage orders across multiple sales channels. Whether a business is processing online orders, in-store purchases, or transactions from mobile apps, NetSuite ensures that all orders are tracked, processed, and fulfilled from a centralized system. This reduces the risk of errors and improves overall efficiency.
- Real-Time Inventory Management: With NetSuite, businesses gain real-time visibility into their inventory levels across all locations and channels. The system automatically updates stock levels as orders are placed and fulfilled, ensuring that businesses can avoid stockouts and overselling. This feature is particularly valuable for businesses with complex supply chains or multiple warehouses.
- Financial Management and Reporting: NetSuite’s powerful financial management tools automate accounting tasks such as invoicing, payment processing, and financial reporting. Businesses can generate real-time financial reports that provide a clear view of their financial health, including revenue, expenses, and profitability by channel or location. This real-time reporting helps businesses make informed decisions and stay agile in a rapidly changing market.
- CRM and Customer Engagement: NetSuite’s integrated CRM module allows businesses to manage customer relationships effectively. The system provides a 360-degree view of each customer, including their purchase history, preferences, and interactions with the brand. This enables businesses to deliver personalized marketing campaigns and improve customer service across all channels.
- eCommerce Integration: For businesses that operate online stores, NetSuite offers a powerful eCommerce integration that synchronizes inventory, orders, and customer data between the ERP system and the online storefront. This ensures that eCommerce operations are fully integrated with the rest of the business, streamlining processes and improving the customer experience.
- Global Business Management: NetSuite supports multiple currencies, languages, and tax regulations, making it ideal for businesses that operate internationally. The system simplifies global operations by providing tools for managing transactions across different regions and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Comprehensive Feature Set: Oracle NetSuite provides an extensive range of features that cover every aspect of a business’s operations, from financials and inventory to customer management and eCommerce. This makes it an all-in-one solution for omnichannel businesses.
- Scalable and Modular: NetSuite’s modular design allows businesses to start small and add functionality as needed, making it highly scalable. Whether a business is a small start-up or a large enterprise, NetSuite can be tailored to meet its needs.
- Cloud-Based and Accessible: Being fully cloud-based, Oracle NetSuite can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, which is particularly beneficial for businesses with remote teams or multiple locations. This also eliminates the need for on-premise infrastructure and reduces IT overhead.
- Real-Time Data and Reporting: NetSuite provides real-time insights into inventory levels, financial performance, and customer behavior, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions quickly. This level of visibility is crucial for businesses that need to respond to market changes and customer demands in real time.
- Omnichannel Capabilities: NetSuite excels in its ability to manage orders, inventory, and customer data across multiple sales channels, ensuring that businesses can provide a seamless experience to their customers, no matter where they shop.
Cons:
- Cost: Oracle NetSuite is a premium ERP solution, and its pricing may be prohibitive for smaller businesses or those with limited budgets. The cost includes not only licensing fees but also implementation and ongoing support, which can add up for larger, more complex deployments.
- Complexity: While NetSuite’s comprehensive feature set is one of its strengths, it can also be overwhelming for new users or businesses with limited ERP experience. The system may require significant customization and training to fully leverage its capabilities.
- Customization and Implementation Time: Due to its flexibility, NetSuite can take time to implement, especially for businesses with complex needs or those requiring extensive customization. The implementation process can take several months, depending on the size of the business and the number of modules being deployed.
Pricing
Oracle NetSuite’s pricing is based on a subscription model, with the cost determined by several factors, including the number of users, the specific modules required, and the level of customization needed. On average, licensing fees for NetSuite start at around $1,000/user/year, though this can increase depending on the scope of the deployment.
In addition to licensing fees, businesses should factor in the cost of implementation, which typically includes consulting services, customization, and data migration. These costs can range from $25,000 to $100,000 or more, depending on the complexity of the implementation. For businesses that require ongoing support, NetSuite also offers various support packages that can add to the overall cost.
Despite the high cost, many businesses find that NetSuite’s robust feature set and scalability make it a worthwhile investment, particularly for those looking to manage complex operations across multiple sales channels.
Suitable For
Oracle NetSuite is suitable for a wide range of businesses, from mid-sized companies to large enterprises. It is particularly well-suited for businesses that operate in industries with complex omnichannel operations, such as retail, wholesale distribution, and manufacturing. Businesses that manage multiple sales channels, including eCommerce, in-store, and mobile, will benefit from NetSuite’s integrated order management and inventory tracking capabilities.
Additionally, NetSuite is a great fit for companies that operate internationally, thanks to its multi-currency, multi-language, and multi-tax jurisdiction support. For businesses looking for a scalable, flexible ERP solution that can grow with their needs, Oracle NetSuite is one of the most comprehensive options available, making it a top choice for businesses of all sizes that require advanced omnichannel ERP capabilities.
Odoo ERP
Odoo ERP is an open-source ERP system that was originally launched in 2005 as TinyERP. Over the years, the platform has evolved significantly and rebranded as Odoo, becoming one of the most popular ERP solutions globally. What sets Odoo ERP apart from other solutions is its open-source nature, which allows businesses to customize the platform according to their specific needs. Odoo offers a highly modular system, with more than 30 core applications and over 16,000 third-party apps, making it suitable for businesses across a wide range of industries, including retail, manufacturing, and services.
Odoo is unique in that it offers two main versions: Odoo Community (the free, open-source version) and Odoo Enterprise (a paid version with additional features and professional support). Both versions offer a comprehensive suite of tools designed to help businesses manage their operations more efficiently, but the Enterprise version provides enhanced functionalities, such as advanced reporting, scalability, and integrations that make it particularly well-suited for larger organizations or those with more complex needs.
Odoo ERP’s flexibility and affordability make it an attractive option for businesses that require omnichannel capabilities but may not have the budget for more expensive systems like SAP S/4HANA or Oracle NetSuite. It’s especially well-regarded for its ability to manage both eCommerce and in-store sales seamlessly, providing businesses with a unified view of their operations across all channels.
Key Features
Odoo ERP is rich in features that make it an ideal choice for businesses looking to implement a cost-effective omnichannel ERP solution. Here are some of the key features that stand out:
- Modular Design: Odoo ERP offers a highly modular system, meaning businesses can choose and integrate only the apps they need. The platform includes modules for sales, inventory, accounting, CRM, eCommerce, and more. This allows businesses to tailor their ERP system to their unique requirements and scale it as they grow.
- Omnichannel Sales Management: One of Odoo ERP’s strongest features is its ability to manage omnichannel sales from a unified platform. Whether a business is processing online orders through its eCommerce store, handling in-store transactions, or accepting orders via mobile, Odoo consolidates all sales data into one system. This ensures that inventory, order fulfillment, and customer data are consistent and up to date across all channels.
- Inventory and Supply Chain Management: Odoo provides robust tools for managing inventory across multiple locations and sales channels. Businesses can track stock levels in real time, automatically update inventory after each sale, and even automate reordering when stock levels fall below a certain threshold. This real-time visibility is crucial for businesses that operate across multiple channels and want to avoid stockouts or overstocking.
- eCommerce Integration: For businesses that operate online stores, Odoo ERP includes a fully integrated eCommerce module. This allows businesses to build and manage their online storefronts directly within the ERP system. The eCommerce module syncs with other apps, such as inventory, CRM, and accounting, ensuring that online sales are fully integrated with other business processes.
- CRM and Customer Data Management: Odoo ERP includes a comprehensive CRM module that enables businesses to manage their customer relationships across all channels. The CRM provides a 360-degree view of customer interactions, including purchase history, inquiries, and communication records. This helps businesses offer personalized customer experiences, whether the interaction occurs online, in-store, or via a support channel.
- Accounting and Finance Automation: Odoo includes powerful accounting tools that automate invoicing, payment processing, and financial reporting. This makes it easy for businesses to manage their finances in real time, while also ensuring compliance with tax regulations across multiple jurisdictions. The financial tools are fully integrated with other modules, such as sales and inventory, providing a unified view of business performance.
- Third-Party Integrations and Customization: As an open-source platform, Odoo allows businesses to customize the system extensively. With access to over 16,000 third-party apps, businesses can integrate Odoo with other software they are already using, such as shipping providers, payment gateways, and marketing tools. This makes Odoo one of the most flexible ERP solutions available, capable of being tailored to meet the unique needs of each business.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Flexibility and Customization: One of Odoo ERP’s greatest strengths is its flexibility. Businesses can customize the platform by adding only the modules they need and can develop additional functionality through third-party apps or custom development. This allows businesses to tailor the system to their specific processes and requirements.
- Cost-Effective: Odoo’s open-source model makes it a cost-effective solution, especially for small and mid-sized businesses that may not have the budget for expensive ERP systems. The Community version is free, and the Enterprise version offers affordable pricing compared to other top-tier ERP systems.
- User-Friendly Interface: Odoo ERP offers a modern, intuitive interface that is easy for users to navigate, reducing the learning curve for employees and making it easier to implement across the organization.
- Strong eCommerce Integration: For businesses with a significant online presence, Odoo’s built-in eCommerce module provides seamless integration with other parts of the business, such as inventory, CRM, and finance. This integration makes it easier to manage both online and offline sales from a single platform.
- Scalability: Odoo is designed to grow with a business. As companies expand their operations, they can add new modules and functionality to meet their evolving needs, ensuring that the ERP system can scale alongside their growth.
Cons:
- Limited Features in Community Version: While the free Community version of Odoo is attractive to many businesses, it lacks some of the advanced features and support that come with the Enterprise version. Larger businesses or those with more complex needs may find that they require the paid version for access to essential tools like advanced reporting and scalability options.
- Customization and Maintenance Costs: Although Odoo’s open-source nature provides flexibility, businesses that require extensive customization may incur additional costs for development and maintenance. This can lead to higher long-term costs for companies that need to continuously adapt or add new features to their ERP system.
- Implementation Time: Depending on the complexity of the business and the level of customization required, Odoo can take time to implement. Businesses with large-scale operations or highly specialized needs may face longer implementation times and require professional consulting services to ensure a smooth rollout.
Pricing
Odoo offers a pricing structure that is highly competitive compared to other ERP solutions on the market. The open-source Community version is free to use, making it an attractive option for small businesses or those looking to test the platform before committing to a paid plan. For businesses that need more advanced features and professional support, the Enterprise version is available on a subscription basis.
The pricing for Odoo Enterprise starts at around $24/user/month, which includes access to core modules like sales, CRM, inventory, and accounting. Additional fees may apply for specific modules or third-party integrations, but overall, Odoo remains a cost-effective solution for businesses of all sizes.
Given its affordability and flexibility, Odoo is often viewed as an excellent value for businesses that need a powerful ERP system without the high upfront costs typically associated with enterprise-grade software.
Suitable For
Odoo ERP is suitable for a wide range of businesses, from small startups to large enterprises. Its modular design and customization options make it an excellent choice for companies that want to tailor their ERP system to their specific needs without incurring the high costs associated with more rigid platforms.
Small and mid-sized businesses, particularly those in retail, eCommerce, and manufacturing, will find Odoo’s omnichannel capabilities particularly valuable. Its ability to manage sales, inventory, and customer relationships across multiple channels provides businesses with the tools they need to offer a seamless customer experience while optimizing their internal processes. For larger organizations or those with more complex needs, Odoo’s Enterprise version offers the scalability and advanced features necessary to support growth and expansion.
Microsoft Dynamics 365
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is an integrated suite of ERP and CRM applications. Launched in 2016, Dynamics 365 represents Microsoft’s vision of combining ERP and CRM capabilities with advanced analytics and AI in one platform. It builds on the foundation of Microsoft’s earlier ERP products, including Dynamics AX, Dynamics GP, and Dynamics NAV, while adding cloud-based services and deep integration with the Microsoft ecosystem.
As a cloud-first solution, Microsoft Dynamics 365 is designed to help businesses manage operations across various departments, such as finance, sales, supply chain, customer service, and more. Its cloud-based architecture makes it highly scalable, allowing businesses to add new features and users as they grow. Furthermore, the platform’s flexibility allows it to cater to a wide range of industries, including retail, manufacturing, distribution, and professional services.
One of the major strengths of Microsoft Dynamics 365 is its ability to support omnichannel operations, enabling businesses to manage their customer interactions, sales, and inventory across multiple touchpoints. Whether through eCommerce, brick-and-mortar stores, or mobile apps, Dynamics 365 provides real-time data and insights that help businesses deliver a seamless customer experience.
Key Features
Microsoft Dynamics 365 offers a rich set of features designed to support omnichannel businesses in managing their operations effectively. Some of the key features include:
- Unified Operations Across All Channels: Microsoft Dynamics 365 integrates sales, customer service, and supply chain operations into one platform. This allows businesses to manage customer interactions, orders, and inventory seamlessly across online and offline channels, ensuring that all departments are aligned and working from the same data.
- Real-Time Data and Analytics: The platform provides real-time visibility into inventory, customer orders, and financial performance, helping businesses make informed decisions quickly. This real-time data is especially critical for omnichannel operations, where businesses need to track inventory levels, manage orders, and monitor customer interactions across various platforms.
- Comprehensive CRM Functionality: Microsoft Dynamics 365 includes robust CRM tools that allow businesses to manage their customer relationships across all channels. The CRM module provides a 360-degree view of each customer, tracking their interactions, purchase history, and preferences. This enables businesses to personalize customer experiences and deliver targeted marketing campaigns.
- Advanced AI and Machine Learning: Dynamics 365 leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to provide advanced analytics and predictive insights. This allows businesses to forecast demand, identify trends, and automate routine tasks, helping them stay ahead of market changes and customer expectations.
- Integrated eCommerce and Retail Solutions: For retail and eCommerce businesses, Dynamics 365 offers integrated tools to manage online storefronts, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and in-store operations. This ensures that inventory levels, orders, and customer data are synced across all sales channels, providing a unified view of the business.
- Supply Chain and Inventory Management: Dynamics 365 includes powerful supply chain management tools that help businesses optimize their logistics and inventory operations. The platform allows businesses to track inventory levels in real-time, automate reordering, and manage complex fulfillment operations, such as dropshipping or multi-location warehousing.
- Integration with Microsoft Products: As part of the Microsoft ecosystem, Dynamics 365 integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products, such as Office 365, Azure, Power BI, and Teams. This deep integration enables businesses to streamline workflows, collaborate more effectively, and access advanced analytics through Power BI.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Comprehensive Feature Set: Microsoft Dynamics 365 provides a full suite of ERP and CRM capabilities, making it a complete solution for managing all aspects of a business, from finance and operations to sales and customer service.
- Scalability: As a cloud-based platform, Dynamics 365 can scale with a business’s growth. Businesses can start with the modules they need and add new functionality as they expand, making it a flexible solution for both small businesses and large enterprises.
- Omnichannel Support: Dynamics 365 excels in supporting omnichannel businesses by integrating operations across multiple sales channels. Whether selling online, in-store, or through mobile, businesses can manage inventory, customer relationships, and orders in real-time from a single platform.
- Advanced AI and Predictive Analytics: The inclusion of AI-driven insights and machine learning capabilities sets Dynamics 365 apart, helping businesses optimize their operations and make data-driven decisions.
- Integration with Microsoft Ecosystem: The platform’s seamless integration with other Microsoft products is a significant advantage, particularly for businesses already using Office 365, Power BI, or Azure. This integration allows for better collaboration, streamlined workflows, and access to advanced analytics tools.
Cons:
- Complexity: Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a highly comprehensive platform, which can make it challenging to implement and configure, particularly for smaller businesses or those with limited IT resources. Customization and setup may require expert assistance, leading to longer implementation times.
- Cost: While Dynamics 365 offers a scalable pricing model, the costs can add up, especially for businesses that require advanced modules or customizations. Licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing support can make it a significant investment, particularly for larger enterprises.
- Learning Curve: Given the vast array of features, new users may face a steep learning curve. Training and user onboarding are often required to fully leverage the system’s capabilities, which can take time and resources.
Pricing
Microsoft Dynamics 365 offers flexible pricing options depending on the specific modules and features a business needs. Pricing is generally based on a subscription model, with costs determined by the number of users and the functionalities selected. There are two primary categories of pricing: ERP functionality (known as Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations) and CRM functionality (known as Dynamics 365 Sales, Customer Service, or Marketing).
For example, Dynamics 365 Finance starts at around $180/user/month, while Dynamics 365 Sales is available for $65 per user per month. Additional modules, such as Supply Chain Management, Customer Service, or Marketing, may come with their own subscription costs, and prices can vary based on the level of customization and the number of users.
Implementation costs should also be considered, as businesses may need to engage consultants or IT experts to help configure and deploy the system. Customization, integration with third-party applications, and ongoing support can add to the overall cost. Despite the investment, many businesses find that the scalability and extensive feature set of Dynamics 365 provide excellent value for money, especially for companies looking to grow.
Suitable For
Microsoft Dynamics 365 is suitable for a wide range of businesses, from small and mid-sized companies to large enterprises. It is particularly well-suited for organizations with complex omnichannel operations that require real-time visibility and management across multiple departments and channels. Industries such as retail, manufacturing, distribution, and professional services can benefit from the platform’s robust ERP and CRM capabilities.
The platform’s scalability and modularity make it an ideal choice for businesses that plan to grow or expand into new markets. Additionally, businesses already using Microsoft’s other products, such as Office 365 or Azure, will find Dynamics 365 to be a natural extension of their existing systems, as the integration allows for streamlined processes and improved collaboration across departments.
Large enterprises with complex supply chains, global operations, or multi-location fulfillment needs will particularly appreciate Dynamics 365’s powerful supply chain and inventory management features. However, smaller businesses may also benefit from the platform’s flexibility, especially if they require an ERP solution that can scale with their growth over time.
Epicor ERP
Epicor ERP is a comprehensive enterprise resource planning solution that has been developed over several decades to cater to the unique needs of various industries. Originally founded in 1972, Epicor Software Corporation has become a leader in the ERP market by offering solutions that are tailored to specific industry sectors, such as manufacturing, distribution, retail, and services. Unlike generic ERP systems, Epicor focuses on delivering industry-specific functionalities that address the challenges faced by businesses in those sectors.
Epicor ERP is a fully integrated solution that supports businesses in managing their end-to-end processes, from supply chain management and production to finance, human resources, and CRM. It is designed to handle the complexities of multi-location, multi-channel operations, making it particularly well-suited for businesses with an omnichannel strategy. Whether it’s managing inventory across eCommerce platforms and physical stores or automating production workflows in manufacturing, Epicor ERP provides real-time data and insights that help businesses optimize their operations and deliver seamless customer experiences.
Epicor ERP can be deployed both on-premise and in the cloud, giving businesses the flexibility to choose the deployment model that best fits their infrastructure and scalability needs. Its modular approach also allows businesses to start with the core features they need and add additional modules as their operations expand.
Key Features
Epicor ERP offers a wide range of features that are specifically designed to support businesses with complex, multi-channel operations. Below are some of the key features that make Epicor ERP an ideal choice for omnichannel businesses:
- Omnichannel Inventory and Order Management: Epicor ERP provides businesses with real-time visibility into their inventory across all channels, ensuring that stock levels are accurately reflected no matter where the sale occurs. This feature is crucial for businesses that operate in both digital and physical spaces, as it helps prevent stockouts, overstocking, and inaccurate order fulfillment. The system also integrates order management across all channels, allowing businesses to process orders from eCommerce, in-store, or mobile platforms in a single system.
- Industry-Specific Functionality: One of Epicor ERP’s standout features is its industry-specific functionality. For example, manufacturers benefit from advanced tools for production scheduling, materials management, and quality control, while retailers can take advantage of point-of-sale (POS) integration, merchandising tools, and customer engagement features. This industry focus ensures that businesses have access to the tools and workflows they need to address their specific operational challenges.
- Supply Chain Management: Epicor ERP includes powerful supply chain management features that allow businesses to optimize their procurement, warehousing, and distribution processes. The system provides real-time insights into supplier performance, order tracking, and shipment scheduling, helping businesses streamline their supply chain and ensure timely delivery of products across all channels.
- CRM: Epicor ERP integrates CRM functionality, providing businesses with a unified view of their customers across all sales channels. This enables businesses to manage customer interactions, track purchase history, and deliver personalized experiences, whether customers are shopping online, in-store, or through mobile apps. CRM integration is essential for businesses looking to enhance customer loyalty and drive repeat sales in an omnichannel environment.
- Financial Management and Reporting: Epicor ERP offers robust financial management tools that automate key accounting processes, such as invoicing, payments, and financial reporting. The system allows businesses to generate real-time financial reports that provide insights into profitability by channel, product line, or geographic location, helping businesses make data-driven decisions.
- Cloud and On-Premise Deployment Options: Epicor ERP provides businesses with the flexibility to choose between cloud-based or on-premise deployment, depending on their needs. Cloud deployment is ideal for businesses looking for scalability, lower upfront costs, and remote access, while on-premise deployment offers greater control over data and infrastructure.
- Advanced Analytics and Business Intelligence: Epicor ERP comes with built-in analytics and business intelligence (BI) tools that allow businesses to analyze their operational performance in real time. These tools provide insights into sales trends, customer behavior, production efficiency, and financial health, empowering businesses to optimize their operations and make informed decisions.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Industry-Specific Solutions: Epicor ERP is highly tailored to the specific needs of industries like manufacturing, distribution, and retail. This ensures that businesses have access to features and workflows that are designed to solve their unique challenges.
- Comprehensive Omnichannel Support: Epicor ERP excels in its ability to integrate operations across multiple sales channels. Businesses can manage inventory, orders, and customer relationships in real time, regardless of whether the transaction occurs online, in-store, or through mobile channels.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The platform’s modular design and flexible deployment options make it scalable for businesses of all sizes. As a business grows or expands into new markets, Epicor ERP can be adapted to meet its evolving needs.
- Real-Time Data and Analytics: Epicor ERP provides real-time insights into business operations, allowing businesses to monitor inventory, orders, and financial performance in real time. This enables faster decision-making and improved responsiveness to market changes.
- Strong Supply Chain Management: Epicor ERP’s supply chain management tools are particularly beneficial for businesses with complex logistics needs. The system’s ability to track supplier performance, manage procurement, and optimize distribution processes helps businesses streamline their operations and reduce costs.
Cons:
- Complex Implementation: Epicor ERP’s robust feature set and industry-specific functionality can make implementation complex, particularly for larger businesses with extensive customization needs. The implementation process may take several months, and businesses may need to engage consultants to ensure a successful rollout.
- High Cost for Customization: While Epicor ERP offers flexibility and customization, businesses that require extensive customization may face higher costs. Customizing the system to meet specific operational needs can add to the overall implementation and maintenance costs.
- Steep Learning Curve: The system’s vast array of features can be overwhelming for new users, particularly those without prior ERP experience. Training and onboarding may be required to fully utilize the platform’s capabilities, which can increase the time to fully adopt the system.
Pricing
Epicor ERP does not have a one-size-fits-all pricing model, as costs depend on several factors, including the size of the business, the number of users, and the specific modules required. Epicor offers both subscription-based pricing for its cloud version and licensing fees for its on-premise deployment. For cloud-based deployments, pricing typically starts at around $175/user/month, but this can vary based on the modules selected and the level of customization required.
On-premise deployment usually involves a higher upfront cost, as businesses must invest in the necessary hardware and infrastructure. In addition to licensing fees, businesses should consider the costs associated with implementation, customization, training, and ongoing maintenance.
While Epicor ERP is generally considered more affordable than high-end solutions like SAP S/4HANA, the overall cost can still be significant for businesses that require extensive customization or additional modules. However, many businesses find that the system’s scalability, industry-specific functionality, and omnichannel capabilities provide excellent value for money.
Suitable For
Epicor ERP is best suited for medium to large enterprises that operate in industries with complex operational needs, such as manufacturing, distribution, and retail. Its industry-specific solutions make it particularly well-suited for businesses that require advanced tools for production scheduling, supply chain management, and inventory control. Retailers and eCommerce businesses with omnichannel strategies will benefit from the system’s ability to integrate operations across all sales channels, ensuring real-time visibility into inventory and orders.
Epicor ERP is also a strong choice for businesses that are looking for flexibility in deployment. The platform’s ability to be deployed either in the cloud or on-premise makes it ideal for businesses with varying IT infrastructure requirements. Additionally, businesses that anticipate growth or expansion into new markets will appreciate the system’s scalability and modular design.
However, smaller businesses or startups with limited resources may find the system’s complexity and customization costs to be a barrier. For these businesses, a simpler or less expensive ERP solution may be more appropriate until they reach a scale where they can fully leverage the capabilities of Epicor ERP.
Acumatica Cloud ERP
Acumatica Cloud ERP is a cloud-based enterprise resource planning solution designed to provide businesses with a flexible, scalable platform that supports all core business functions. Founded in 2008, Acumatica was built from the ground up as a cloud-first ERP system, meaning that businesses can access the platform from anywhere with an internet connection. Unlike many legacy ERP systems that transitioned to the cloud, Acumatica was natively developed for the cloud, giving it a unique advantage in terms of flexibility and scalability.
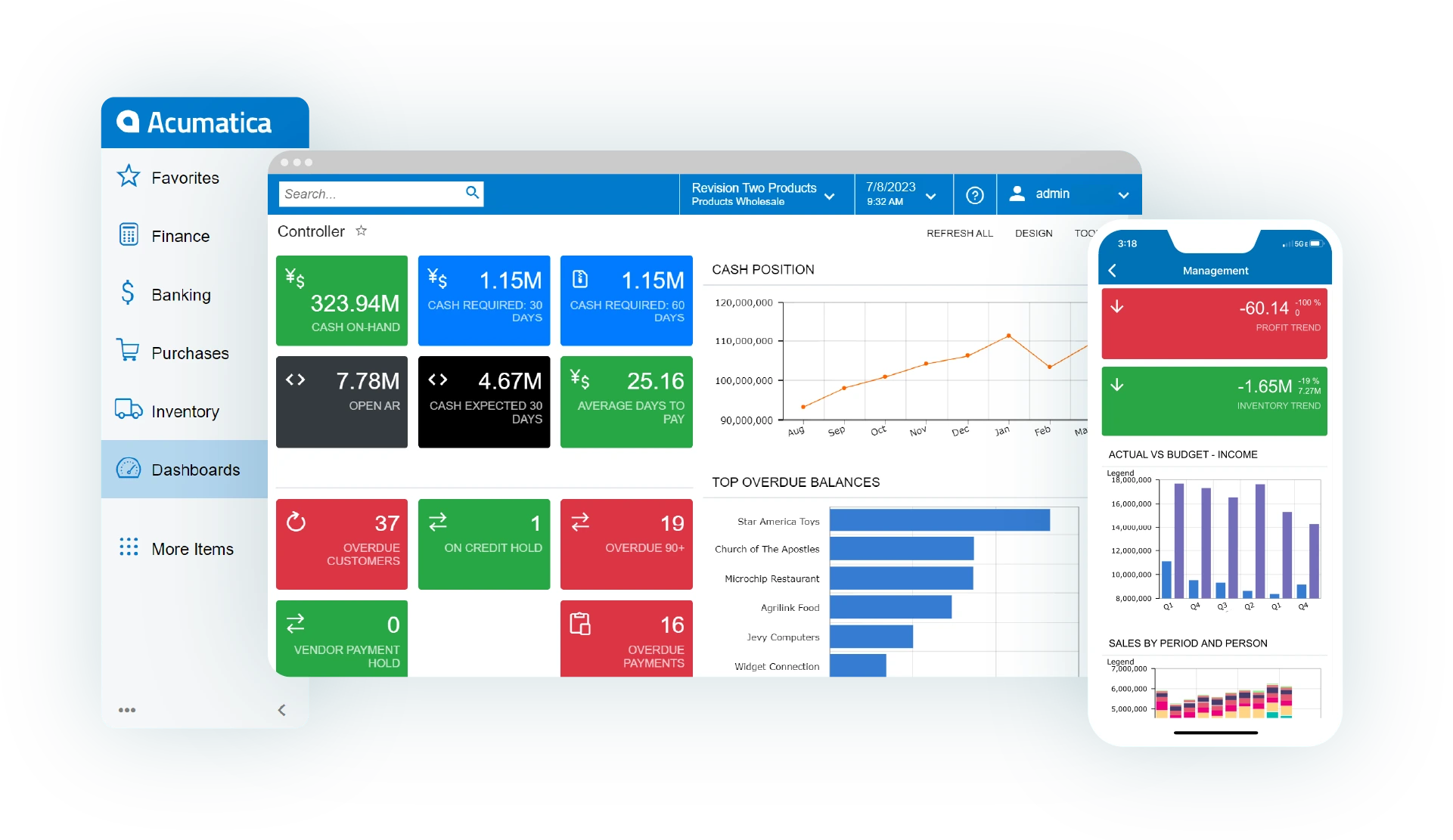
Acumatica’s cloud-native architecture allows businesses to manage their operations in real-time, with all data centralized in the cloud for easy access. The platform is designed to support businesses across a wide range of industries, including retail, manufacturing, construction, distribution, and professional services. Acumatica’s modular structure means that businesses can choose the specific features they need and add additional functionality as their operations grow.
One of the standout features of Acumatica Cloud ERP is its focus on providing a true omnichannel experience. The platform integrates seamlessly with eCommerce platforms, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and mobile apps, allowing businesses to manage their entire operation from a single platform. Whether handling online orders, managing inventory across multiple locations, or processing in-store transactions, Acumatica provides real-time visibility and control over the entire business.
Key Features
Acumatica Cloud ERP offers a broad range of features that cater to businesses looking to manage their omnichannel operations more efficiently. Below are some of the key features that make Acumatica a leading choice for omnichannel ERP:
- Cloud-Native Architecture: Acumatica was built for the cloud, making it one of the most flexible and scalable ERP solutions on the market. Businesses can access the system from any device with an internet connection, allowing for remote work and easy access to real-time data. The cloud architecture also means that businesses do not need to invest in expensive on-premise infrastructure.
- Omnichannel Sales and Order Management: Acumatica provides businesses with tools to manage sales and orders across all channels, including eCommerce, retail, and mobile platforms. Orders from online stores, in-store purchases, and mobile transactions are automatically synced in the system, ensuring that inventory levels, customer data, and financials are updated in real-time. This unified approach ensures that businesses can offer a seamless experience to customers, no matter how they interact with the brand.
- Real-Time Inventory Management: One of the core strengths of Acumatica is its ability to track inventory in real time across multiple locations and channels. The system provides full visibility into stock levels, helping businesses avoid stockouts and overstocking. Inventory can be tracked at multiple warehouses, retail locations, or distribution centers, and the system can automatically trigger reorders when stock levels fall below predefined thresholds.
- Advanced Financial Management: Acumatica includes robust financial management tools that automate key accounting tasks, such as invoicing, payment processing, and financial reporting. The system provides real-time insights into cash flow, revenue, expenses, and profitability, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions. Acumatica also supports multiple currencies, tax jurisdictions, and legal entities, making it ideal for businesses with international operations.
- CRM Integration: Acumatica ERP includes a fully integrated CRM module that helps businesses manage their customer relationships across all touchpoints. The CRM module consolidates customer data, including purchase history, interactions, and preferences, allowing businesses to deliver personalized experiences and improve customer satisfaction. The integration of CRM with the ERP system ensures that all customer interactions—whether online or offline—are tracked and managed within the same platform.
- eCommerce and Mobile Integration: Acumatica integrates seamlessly with popular eCommerce platforms, such as Shopify and Magento, as well as mobile apps, providing businesses with a fully integrated omnichannel solution. This integration ensures that inventory, orders, and customer data are synchronized across all channels, enabling businesses to manage their entire operation from a single platform.
- Flexibility and Customization: Acumatica is highly flexible and can be customized to meet the specific needs of a business. The system allows businesses to add or remove modules as needed, making it easy to scale as operations grow. Additionally, the platform’s open API enables businesses to integrate Acumatica with third-party applications or develop custom solutions to meet unique business requirements.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Cloud-Native Flexibility: As a cloud-native platform, Acumatica offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing businesses to access the system from anywhere. This cloud-first approach also reduces the need for costly IT infrastructure and simplifies maintenance and updates.
- Real-Time Data: Acumatica provides real-time visibility into inventory, financials, and customer interactions, ensuring that businesses can make informed decisions quickly. This is especially important for omnichannel businesses that need to manage operations across multiple platforms in real time.
- Scalability: Acumatica’s modular design allows businesses to scale their ERP system as they grow. Businesses can start with the core modules they need and add additional functionality over time, making it a great choice for growing companies.
- Comprehensive Omnichannel Support: Acumatica’s ability to manage sales, inventory, and customer data across multiple channels—whether online, in-store, or mobile—makes it an ideal solution for businesses with complex omnichannel operations.
- Customization and Integration: Acumatica offers a high level of customization and integration, allowing businesses to tailor the platform to their specific needs. The system’s open API enables easy integration with third-party applications and custom development.
Cons:
- Complex Implementation: While Acumatica is highly customizable and flexible, this also means that implementation can be complex, particularly for businesses with extensive customization needs. Companies may need to invest time and resources into configuring the system and ensuring it aligns with their workflows.
- Upfront Costs for Customization: While Acumatica’s modular design allows businesses to start small, businesses that require extensive customization or third-party integrations may face higher upfront costs. Customizing the platform to meet unique needs can add to the implementation cost.
- Learning Curve: The platform’s comprehensive feature set and customization options can be overwhelming for new users, especially those without prior ERP experience. Businesses may need to invest in training and onboarding to ensure employees can fully leverage the system’s capabilities.
Pricing
Acumatica offers a unique pricing model that is based on resource consumption rather than the traditional per-user pricing structure used by many ERP vendors. This means that businesses are charged based on the computing resources they consume—such as the number of transactions and the complexity of the workflows—rather than the number of users accessing the system. This pricing model is particularly beneficial for growing businesses, as it allows them to scale the platform without worrying about escalating per-user costs.
While Acumatica does not publicly disclose exact pricing, the cost typically depends on the size and complexity of the business’s operations, the number of modules required, and the level of customization. Businesses should expect to pay for the core ERP modules, as well as any additional functionality or custom development that may be needed. Implementation and training costs should also be factored into the total cost of ownership.
For many businesses, Acumatica’s pricing model provides excellent value, as it allows for flexibility and scalability without the need to pay per user. However, businesses with high transaction volumes or complex workflows may face higher costs depending on their specific resource usage.
Suitable For
Acumatica Cloud ERP is suitable for a wide range of businesses, from small to mid-sized enterprises to larger organizations that require a flexible, cloud-based ERP solution. Its scalability makes it an excellent choice for businesses that anticipate growth or expansion into new markets. Acumatica’s comprehensive omnichannel capabilities—such as its real-time inventory management, eCommerce integration, and CRM tools—make it particularly well-suited for retailers, distributors, and manufacturers that operate across multiple sales channels.
Additionally, businesses that require a high level of customization or that operate in industries with unique workflows will benefit from Acumatica’s flexible architecture and open API. Companies that want to integrate their ERP system with third-party applications, or that need to build custom functionality, will find Acumatica to be a powerful and adaptable platform.
However, businesses looking for a simpler, out-of-the-box ERP solution with minimal customization may find that Acumatica’s flexibility comes with a steeper learning curve and potentially higher implementation costs.
SYSPRO ERP
SYSPRO ERP was founded in 1978, making it one of the longest-standing players in the ERP market. Initially focused on manufacturing and distribution industries, SYSPRO has continued to evolve, adapting its ERP platform to meet the growing demands of today’s multi-channel, digital economy. The system is designed to help businesses gain end-to-end control over their operations by integrating functions such as inventory management, production planning, financials, customer relationships, and more into one unified platform.
What sets SYSPRO ERP apart from many other solutions is its deep specialization in the manufacturing and distribution sectors. While it has grown to support businesses in other industries, it is particularly well-known for helping manufacturers and distributors manage the complex supply chains, production processes, and inventory management challenges that are inherent in these sectors. SYSPRO ERP offers both cloud-based and on-premise deployment options, giving businesses the flexibility to choose the infrastructure that best suits their needs.
SYSPRO ERP is also well-suited for businesses that operate across multiple sales channels, offering powerful omnichannel capabilities to manage inventory, orders, and customer data in real-time. With features like automated order processing, real-time stock visibility, and integration across eCommerce, in-store, and mobile platforms, SYSPRO provides the tools businesses need to ensure a consistent customer experience across all channels.
Key Features
SYSPRO ERP includes a range of features that are specifically designed to support businesses with complex, multi-channel operations. Below are some of the key features that make SYSPRO ERP a standout choice for omnichannel businesses:
- Omnichannel Inventory Management: SYSPRO ERP provides real-time visibility into inventory levels across all sales channels and locations, enabling businesses to effectively manage stock across eCommerce platforms, physical stores, and mobile sales. This feature helps businesses avoid stockouts, overstocking, and discrepancies in inventory, ensuring that customers can access accurate stock information regardless of how they interact with the brand.
- Advanced Supply Chain Management: SYSPRO’s powerful supply chain management tools allow businesses to optimize their logistics and warehousing operations. The system enables businesses to track orders, manage procurement, and ensure timely deliveries across all sales channels, improving overall efficiency and reducing operational costs.
- CRM: SYSPRO ERP integrates CRM functionality, giving businesses a 360-degree view of their customers across all touchpoints. The CRM module allows businesses to track customer interactions, manage customer support, and deliver personalized experiences based on purchase history and preferences. This level of integration ensures that businesses can build stronger relationships with their customers, leading to increased loyalty and repeat sales.
- Automated Order Processing: SYSPRO ERP automates order processing across all channels, ensuring that orders from eCommerce platforms, in-store purchases, and mobile sales are captured and fulfilled in real-time. This eliminates the need for manual order entry and helps businesses reduce errors in order fulfillment, improving both operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Financial Management and Reporting: SYSPRO ERP includes comprehensive financial management tools that automate key accounting tasks, such as invoicing, payment processing, and financial reporting. Businesses can generate real-time reports on profitability, revenue, and expenses, broken down by channel, product line, or region, enabling more informed decision-making.
- Production Management: For businesses in the manufacturing sector, SYSPRO ERP offers advanced production management tools that help optimize production scheduling, materials planning, and quality control. The system provides real-time insights into production workflows, helping businesses improve efficiency and reduce lead times.
- eCommerce and Mobile Integration: SYSPRO ERP integrates with leading eCommerce platforms and mobile applications, enabling businesses to manage their omnichannel operations seamlessly. The system synchronizes inventory, orders, and customer data across all channels, ensuring that businesses have a unified view of their operations and can provide a consistent customer experience.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Industry Specialization: SYSPRO ERP is highly specialized for the manufacturing and distribution sectors, making it a perfect fit for businesses that need deep functionality in areas like production scheduling, supply chain management, and inventory control.
- Comprehensive Omnichannel Capabilities: SYSPRO’s ability to manage inventory, orders, and customer data across multiple sales channels in real-time makes it a powerful solution for businesses with complex omnichannel operations. This ensures that businesses can deliver a consistent customer experience across eCommerce, retail, and mobile platforms.
- Scalability: SYSPRO ERP is scalable, making it suitable for both mid-sized businesses and larger enterprises. The system’s modular structure allows businesses to add new features and expand their operations as they grow.
- Cloud and On-Premise Flexibility: SYSPRO offers both cloud-based and on-premise deployment options, providing businesses with the flexibility to choose the infrastructure that best suits their needs. This makes it suitable for businesses with varying IT requirements and resources.
- Strong Supply Chain and Production Management: For manufacturers and distributors, SYSPRO ERP’s advanced supply chain and production management tools are a significant advantage. These features enable businesses to optimize their procurement processes, improve production workflows, and reduce lead times.
Cons:
- Complex Implementation: Due to the system’s robust feature set and industry-specific functionality, implementing SYSPRO ERP can be complex and time-consuming. Businesses may need to invest in consultants or additional resources to ensure a smooth implementation process.
- Customization Costs: While SYSPRO ERP offers extensive customization options, businesses that require significant customization to meet their unique workflows or industry-specific needs may face higher implementation and maintenance costs.
- Steep Learning Curve: Given the breadth of features available in SYSPRO ERP, new users may face a steep learning curve. Businesses may need to invest in training and support to ensure that employees can fully utilize the system’s capabilities.
Pricing
SYSPRO ERP pricing is tailored to each business’s specific needs, and costs can vary significantly depending on factors such as the size of the organization, the number of users, and the modules required. SYSPRO offers both cloud-based and on-premise pricing models, with subscription fees for the cloud version and licensing costs for the on-premise version.
While SYSPRO does not publicly disclose specific pricing, businesses should expect to pay for the core ERP modules, as well as any additional industry-specific features or customizations. Implementation costs, including consulting, training, and data migration, should also be factored into the overall cost of ownership.
Despite the potentially high upfront costs, many businesses find that SYSPRO ERP provides excellent value for money, particularly for those in the manufacturing and distribution sectors. The system’s deep functionality, scalability, and omnichannel capabilities make it a worthwhile investment for businesses looking to optimize their operations.
Suitable For
SYSPRO ERP is best suited for mid-sized to large businesses in the manufacturing and distribution sectors. Its industry-specific functionality makes it particularly well-suited for companies that require advanced tools for production management, inventory control, and supply chain optimization. Manufacturers with complex production workflows and distributors with multi-location warehousing operations will benefit from SYSPRO’s ability to provide real-time visibility and control over their operations.
Retailers and eCommerce businesses that operate across multiple sales channels will also find SYSPRO’s omnichannel capabilities valuable, as the system ensures seamless integration of inventory, orders, and customer data across all touchpoints. The platform’s ability to manage both online and offline operations makes it ideal for businesses with omnichannel strategies.
While SYSPRO ERP is a powerful solution for businesses with complex needs, smaller businesses or those with simpler operational requirements may find the system’s complexity and customization costs to be a barrier. For these businesses, a more streamlined ERP solution may be more appropriate.
Sage X3
Sage X3 is an advanced ERP solution developed by Sage Group, one of the world’s leading providers of business management software. Originally launched in the 1990s, Sage X3 has evolved into a comprehensive ERP platform that supports mid-sized to large enterprises. While Sage offers several ERP solutions, Sage X3 is the most powerful and flexible, catering to industries such as manufacturing, distribution, food and beverage, and professional services.
Sage X3 distinguishes itself with its ability to manage complex multi-channel operations, making it a top contender in the omnichannel ERP space. It helps businesses streamline their processes by offering a unified system that integrates all key functions—such as inventory, sales, procurement, finance, and customer relationship management—into a single platform. Whether a business operates across eCommerce, in-store retail, or mobile, Sage X3 provides real-time data and insights, ensuring that all aspects of the business are aligned and optimized.
Available as both a cloud-based and on-premise solution, Sage X3 provides the flexibility needed to meet the varying infrastructure requirements of businesses. Its modular design allows companies to customize the system based on their specific needs, enabling them to scale their operations efficiently.
Key Features
Sage X3 is packed with features that make it an ideal solution for businesses seeking a robust omnichannel ERP system. The following are some of its key features:
- Multi-Channel Inventory Management: Sage X3 provides businesses with real-time visibility into their inventory across all sales channels, including eCommerce platforms, retail stores, and mobile apps. The system tracks inventory levels at multiple warehouses and locations, ensuring that stock is managed efficiently and accurately across the entire supply chain. This helps prevent stockouts, overstocking, and delays in order fulfillment, which are critical for omnichannel operations.
- Integrated Financial Management: Sage X3 includes advanced financial management tools that automate accounting tasks, such as invoicing, payments, and financial reporting. Businesses can generate real-time financial reports, allowing them to track profitability, expenses, and cash flow by channel, location, or product line. Sage X3 supports multiple currencies, tax regulations, and legal entities, making it an ideal choice for businesses with international operations.
- Advanced Supply Chain Management: One of the standout features of Sage X3 is its ability to optimize supply chain processes. The system provides real-time insights into procurement, logistics, and supplier performance, enabling businesses to streamline their operations and reduce lead times. By automating key supply chain tasks—such as reordering stock and managing shipments—Sage X3 helps businesses ensure timely deliveries across all sales channels.
- CRM: Sage X3 integrates CRM functionality to help businesses manage their customer relationships across all touchpoints. The CRM module tracks customer interactions, purchase history, and preferences, enabling businesses to deliver personalized experiences and improve customer engagement. The system’s unified view of customer data helps businesses build loyalty and drive repeat sales.
- Production Management: For manufacturers, Sage X3 offers comprehensive production management features that support planning, scheduling, and quality control. The system provides real-time insights into production workflows, allowing businesses to optimize their manufacturing processes and ensure that products are delivered on time and meet quality standards.
- eCommerce and Mobile Integration: Sage X3 integrates seamlessly with eCommerce platforms and mobile applications, enabling businesses to manage their omnichannel operations efficiently. This integration ensures that inventory, orders, and customer data are synchronized across all channels, providing a unified view of the business and ensuring a consistent customer experience.
- Business Intelligence and Analytics: Sage X3 includes built-in business intelligence (BI) tools that help businesses analyze their operations in real time. The system generates detailed reports and dashboards that provide insights into sales performance, customer behavior, and operational efficiency. These analytics help businesses make data-driven decisions and identify opportunities for improvement.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Comprehensive Omnichannel Capabilities: Sage X3 excels in managing complex omnichannel operations, offering real-time visibility into inventory, orders, and customer data across all sales channels. This ensures that businesses can deliver a seamless experience to customers, whether they shop online, in-store, or via mobile.
- Strong Financial and Supply Chain Management: Sage X3’s financial management and supply chain optimization tools are particularly beneficial for businesses with complex logistics and international operations. The system’s ability to handle multiple currencies, tax regulations, and procurement processes makes it ideal for global businesses.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Sage X3’s modular design allows businesses to customize the system based on their specific needs and scale their operations as they grow. This makes it suitable for both mid-sized companies and large enterprises.
- Cloud and On-Premise Deployment: Sage X3 offers both cloud-based and on-premise deployment options, giving businesses the flexibility to choose the infrastructure that best fits their IT requirements.
- Advanced Analytics and Reporting: The system’s business intelligence tools provide businesses with detailed insights into their operations, allowing them to track performance and make data-driven decisions. This helps businesses identify inefficiencies, optimize workflows, and improve overall profitability.
Cons:
- Complexity and Implementation: Due to its robust feature set, Sage X3 can be complex to implement, especially for businesses with unique workflows or extensive customization needs. The implementation process may take several months and require expert consultants to ensure a smooth rollout.
- High Customization Costs: While Sage X3 offers extensive customization options, businesses that require significant customization may face higher implementation and ongoing maintenance costs. Tailoring the system to meet specific operational needs can add to the overall cost of ownership.
- Learning Curve: Given the system’s comprehensive features, new users may face a steep learning curve. Businesses may need to invest in training and support to ensure that employees can fully utilize the system’s capabilities.
Pricing
Sage X3 pricing is not publicly disclosed, as costs are tailored to the specific needs of each business. The total cost of ownership depends on factors such as the number of users, the modules selected, and the level of customization required. Sage X3 offers both subscription-based pricing for its cloud deployment and licensing fees for on-premise deployment.
In addition to licensing and subscription fees, businesses should consider the cost of implementation, customization, and training. Given the complexity of the system, many businesses engage third-party consultants or Sage partners to help with the implementation process, which can increase the overall cost. However, businesses often find that the system’s scalability and advanced functionality provide a strong return on investment, particularly for companies with complex omnichannel or international operations.
Suitable For
Sage X3 is best suited for mid-sized to large enterprises, particularly those in industries such as manufacturing, distribution, and food and beverage. Its industry-specific functionality makes it ideal for businesses with complex production workflows, supply chain operations, and international logistics. Manufacturers and distributors that require deep visibility into their operations, along with real-time data and advanced production management tools, will find Sage X3 especially valuable.
Retailers and eCommerce businesses with omnichannel operations will also benefit from Sage X3’s ability to manage inventory, orders, and customer relationships across multiple sales channels. The system’s integration with eCommerce platforms and mobile apps ensures that businesses can provide a consistent and seamless customer experience across all touchpoints.
While Sage X3 is a powerful solution for businesses with complex needs, smaller businesses or those with simpler operations may find the system’s complexity and customization costs to be a barrier. For these businesses, a more lightweight or out-of-the-box ERP solution may be more appropriate.
Infor CloudSuite
Infor CloudSuite is a comprehensive ERP platform developed by Infor, a global leader in business software solutions. Infor has a long history in the ERP market and has leveraged its experience to create industry-specific solutions that meet the unique needs of various sectors. Infor CloudSuite was introduced to provide cloud-based ERP functionality with a focus on flexibility, scalability, and deep industry specialization.
Unlike traditional on-premise ERP systems, Infor CloudSuite is entirely cloud-based, meaning that businesses can access the platform from anywhere and benefit from continuous updates and improvements. The system is built on Infor’s highly advanced technology stack, known as Infor OS (Operating Service), which provides powerful analytics, AI-driven insights, and automation tools. Infor CloudSuite is designed to support omnichannel operations by integrating key business functions such as inventory management, financials, sales, CRM, and supply chain management in one unified platform.
What makes Infor CloudSuite particularly appealing to businesses with omnichannel needs is its ability to deliver real-time visibility and control over every aspect of operations, regardless of the sales channel. Whether customers are shopping online, in physical stores, or via mobile, Infor CloudSuite ensures that inventory, orders, and customer data are updated in real time, allowing businesses to provide a seamless and consistent customer experience.
Key Features
Infor CloudSuite offers a wide range of features that make it a powerful omnichannel ERP solution. Below are some of the key features that differentiate Infor CloudSuite:
- Omnichannel Inventory Management: Infor CloudSuite provides businesses with real-time visibility into their inventory levels across all channels, ensuring that stock is managed efficiently and consistently. This feature is particularly valuable for businesses that operate in both eCommerce and brick-and-mortar environments, as it ensures that inventory is always up-to-date, helping avoid stockouts and overstocking.
- Advanced Supply Chain Management: One of Infor CloudSuite’s standout features is its advanced supply chain management functionality. The platform provides businesses with tools to optimize procurement, logistics, and warehousing, allowing for real-time tracking of shipments, automated reordering, and better supplier performance management. This feature helps businesses ensure timely deliveries and reduce lead times.
- Financial and Accounting Automation: Infor CloudSuite includes a robust financial management module that automates key accounting tasks such as invoicing, payments, and financial reporting. The system’s real-time financial insights allow businesses to track revenue, expenses, and profitability across multiple sales channels, regions, or product lines, making it easier to maintain a clear understanding of the company’s financial health.
- CRM: Infor CloudSuite integrates CRM functionality to help businesses manage their customer relationships more effectively. The CRM module tracks customer interactions, purchases, and preferences, allowing businesses to offer personalized services and improve customer engagement. This unified view of customer data ensures that all interactions are consistent, whether customers engage online, in-store, or through mobile.
- Industry-Specific Capabilities: One of Infor CloudSuite’s key strengths is its focus on providing industry-specific solutions. The platform includes tailored modules for industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and distribution, ensuring that businesses have access to the tools and workflows they need to address their unique challenges. For example, manufacturers benefit from features like production planning and materials management, while retailers can take advantage of merchandising, POS integration, and customer engagement tools.
- eCommerce and Mobile Integration: Infor CloudSuite integrates with leading eCommerce platforms and mobile applications, enabling businesses to manage their entire omnichannel operation from one system. Whether processing orders from online stores, mobile apps, or physical locations, Infor CloudSuite ensures that all transactions and inventory updates are synced in real time.
- Artificial Intelligence and Analytics: Infor CloudSuite leverages AI and machine learning to provide businesses with predictive analytics and data-driven insights. The platform’s analytics tools generate reports and dashboards that offer real-time insights into sales performance, customer behavior, inventory trends, and more, helping businesses make informed decisions.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Comprehensive Omnichannel Functionality: Infor CloudSuite is designed to support businesses with omnichannel strategies by integrating inventory, order management, and customer data across multiple sales channels. This allows businesses to deliver a seamless experience to their customers, regardless of the platform.
- Industry-Specific Solutions: Infor CloudSuite offers industry-specific modules that provide businesses with the tools they need to manage their operations effectively. This level of specialization ensures that businesses have access to features that are tailored to their industry, whether it’s manufacturing, retail, healthcare, or distribution.
- Cloud-Based Flexibility: As a cloud-native ERP system, Infor CloudSuite offers flexibility and scalability, allowing businesses to access the platform from anywhere and scale as their operations grow. The system’s cloud-based architecture also ensures continuous updates, reducing the need for costly on-premise maintenance.
- Advanced Analytics and AI: Infor CloudSuite’s use of AI and machine learning provides businesses with predictive analytics and actionable insights, helping them optimize their operations and make data-driven decisions. This is especially valuable for businesses that need to forecast demand, manage inventory, and improve customer engagement.
- Seamless Integration: Infor CloudSuite integrates seamlessly with other systems, including eCommerce platforms, POS systems, and third-party applications. This ensures that businesses can manage their entire omnichannel operation from a single platform, reducing the risk of data silos and improving efficiency.
Cons:
- Complexity and Implementation Time: Due to its robust feature set and industry-specific functionality, implementing Infor CloudSuite can be complex and time-consuming. Businesses may need to engage consultants to ensure a successful implementation, which can add to the overall cost and time to deploy.
- Customization Costs: While Infor CloudSuite offers a high degree of flexibility and customization, businesses that require significant customization to meet their unique needs may face higher implementation and maintenance costs.
- Learning Curve: The platform’s advanced features and customization options may be overwhelming for new users, particularly those without previous ERP experience. Training and onboarding may be required to ensure employees can fully utilize the system’s capabilities.
Pricing
Infor CloudSuite operates on a subscription-based pricing model, with costs varying based on the size of the business, the number of users, and the specific modules required. As with many enterprise ERP solutions, pricing is tailored to the individual needs of the business, and Infor does not publicly disclose exact pricing figures.
In general, businesses should expect to pay a monthly or annual subscription fee for the cloud-based solution, with additional costs for specific industry modules, customization, and third-party integrations. For businesses with complex requirements or those needing extensive customization, the cost of implementation and training may also add to the overall total cost of ownership.
Despite the potential for high costs, many businesses find that the system’s scalability, industry-specific features, and advanced functionality offer significant value, especially for companies with complex omnichannel or global operations.
Suitable For
Infor CloudSuite is best suited for mid-sized to large enterprises that operate in industries such as manufacturing, retail, healthcare, and distribution. Its industry-specific capabilities make it particularly well-suited for businesses that require tailored ERP solutions to manage complex operations across multiple sales channels. Manufacturers with complex production workflows and distributors managing multi-location warehouses will benefit from Infor CloudSuite’s advanced supply chain management and inventory optimization features.
Retailers and eCommerce businesses that need to integrate online and offline operations into a single platform will also find Infor CloudSuite’s omnichannel capabilities valuable. The system’s ability to manage inventory, orders, and customer data in real-time ensures that businesses can provide a consistent customer experience across all touchpoints.
However, small businesses or those with simpler operational needs may find the system’s complexity and customization costs to be prohibitive. For these businesses, a simpler or more cost-effective ERP solution may be more appropriate.
Priority ERP
Priority ERP is a comprehensive, cloud-based enterprise resource planning system designed to help small, medium, and large enterprises manage their business operations efficiently. Founded in 1986, Priority Software has developed a flexible and easy-to-use ERP solution that covers a wide range of business needs, including finance, inventory, CRM, supply chain management, and manufacturing. Over the years, Priority ERP has become a strong contender in the omnichannel ERP market, particularly for businesses looking for a solution that provides agility, cost-effectiveness, and a wide range of modules to meet diverse business requirements.
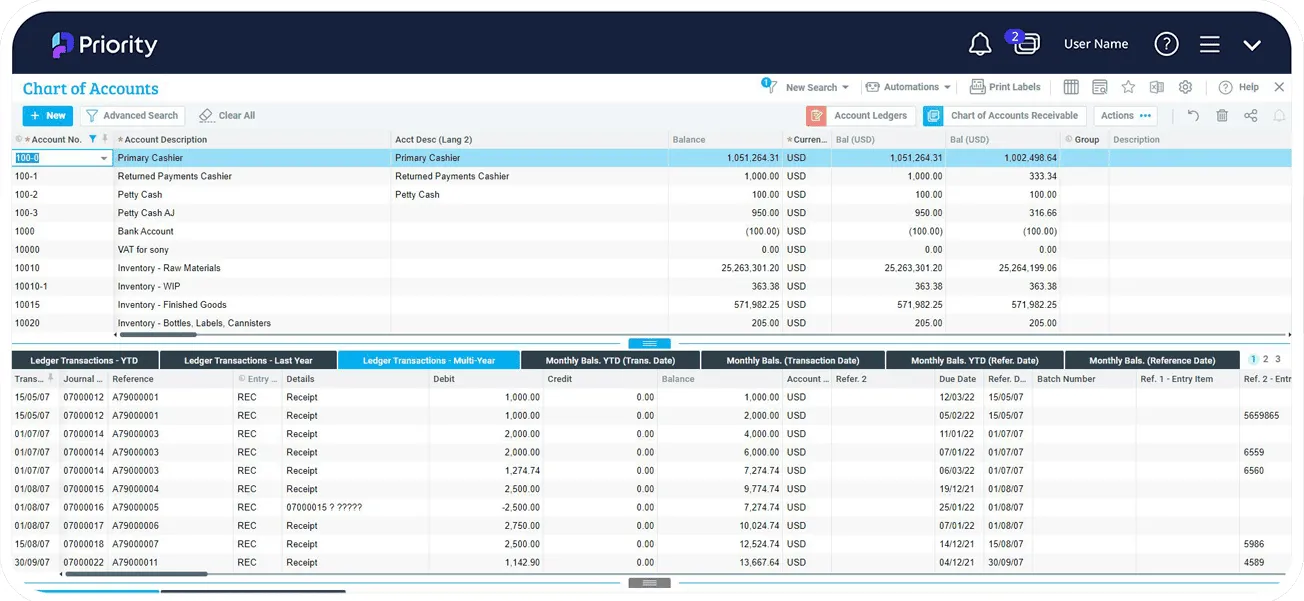
What sets Priority ERP apart from other systems is its commitment to simplicity without sacrificing functionality. The platform is designed to be user-friendly, making it accessible even for businesses without large IT departments. However, it still offers the robust capabilities needed for managing complex omnichannel operations. Whether businesses are operating in eCommerce, retail, manufacturing, or services, Priority ERP provides real-time insights and tools to help businesses stay agile in an increasingly competitive market.
The system can be deployed both in the cloud and on-premise, offering businesses the flexibility to choose the model that best suits their operational needs. This flexibility, combined with its wide array of industry-specific modules, makes Priority ERP a popular choice for businesses looking to streamline their processes and improve customer experiences.
Key Features
Priority ERP comes equipped with a comprehensive range of features that help businesses manage their operations across multiple sales channels. Below are some of the key features that make Priority ERP a top choice for omnichannel businesses:
- Omnichannel Inventory Management: One of the standout features of Priority ERP is its ability to manage inventory across multiple locations and channels in real time. The system provides full visibility into stock levels, helping businesses avoid stockouts, overstocking, and inventory discrepancies. Whether products are being sold through online stores, physical locations, or mobile platforms, inventory data is synchronized in real-time, ensuring businesses always have an accurate view of their stock.
- Order Management and Fulfillment: Priority ERP’s order management system enables businesses to manage orders from various channels, including eCommerce platforms, retail stores, and mobile apps. The system automates order processing, from the moment a customer places an order to the fulfillment and delivery stages. This ensures that businesses can process orders efficiently and deliver a consistent customer experience across all touchpoints.
- Financial Management: Priority ERP includes advanced financial management tools that help businesses automate accounting tasks such as invoicing, billing, payment processing, and financial reporting. The system provides real-time financial insights, allowing businesses to monitor cash flow, profitability, and expenses by channel or location. These tools help businesses maintain financial control, even as they expand their operations across multiple channels.
- CRM: Priority ERP integrates a comprehensive CRM module that helps businesses manage their customer relationships more effectively. The CRM module tracks customer interactions, purchase history, and preferences, enabling businesses to offer personalized experiences and targeted marketing. This feature is especially valuable for omnichannel businesses, as it ensures that all customer data is consolidated and accessible from a single platform, improving engagement and satisfaction.
- Supply Chain Management: For businesses with complex supply chains, Priority ERP provides powerful tools to manage procurement, warehousing, and logistics operations. The system helps businesses optimize their supply chain by automating key tasks such as reordering, inventory transfers, and shipment tracking. This ensures that products are delivered on time, reducing lead times and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Mobile and eCommerce Integration: Priority ERP integrates seamlessly with eCommerce platforms and mobile applications, allowing businesses to manage their omnichannel operations from a unified system. The integration ensures that all customer data, inventory, and order information is synchronized across online and offline channels, providing a consistent and efficient customer experience.
- Business Intelligence and Reporting: Priority ERP includes robust business intelligence (BI) and reporting tools that provide real-time insights into business performance. The system allows businesses to generate customized reports and dashboards, offering data-driven insights into sales trends, customer behavior, and operational efficiency. These insights enable businesses to make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- User-Friendly Interface: One of the major strengths of Priority ERP is its user-friendly interface. The platform is designed to be intuitive and easy to use, making it accessible for businesses that do not have extensive technical expertise. This reduces the learning curve and makes it easier for employees to adopt the system quickly.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Priority ERP is highly flexible, allowing businesses to customize the system to meet their specific needs. Its modular design means that businesses can start with the features they need and add more functionality as their operations grow. This scalability makes it an ideal solution for both small businesses and larger enterprises.
- Comprehensive Omnichannel Capabilities: Priority ERP excels in providing businesses with the tools needed to manage their operations across multiple sales channels. Its real-time inventory management, order processing, and CRM integration ensure that businesses can provide a seamless customer experience across online, in-store, and mobile platforms.
- Cloud and On-Premise Deployment: The system’s flexibility extends to deployment options, with businesses able to choose between cloud-based or on-premise deployments. This flexibility ensures that businesses can select the model that best fits their operational requirements and infrastructure.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to other ERP solutions with similar functionality, Priority ERP is considered cost-effective, particularly for small to mid-sized businesses. The system provides robust features without the high price tag associated with many enterprise-level ERP solutions.
Cons:
- Limited Advanced Features for Large Enterprises: While Priority ERP is a strong solution for small to medium-sized businesses, large enterprises with highly complex operations may find that the system lacks some of the advanced features offered by more specialized ERP solutions. For example, businesses with extremely complex supply chain requirements or multinational operations may need more advanced customization and support.
- Customization Costs: Although Priority ERP is flexible and customizable, businesses that require significant customization to meet their specific needs may face additional costs. Customization can extend the implementation time and add to the overall cost of ownership.
- Complex Implementation for Larger Businesses: For businesses with more complex operational needs, the implementation process for Priority ERP can be time-consuming, particularly if significant customization or integration with other systems is required. Businesses should plan for a longer implementation timeline if they require extensive features.
Pricing
Priority ERP offers a flexible pricing model that is tailored to the needs of each business. While the exact pricing details are not publicly disclosed, the system operates on a subscription-based model for cloud deployments and a licensing fee for on-premise installations. Pricing is influenced by several factors, including the number of users, the modules selected, and the level of customization required.
For small to mid-sized businesses, Priority ERP is often considered a cost-effective solution due to its modular design, allowing companies to start with core features and add more functionality as their business grows. However, businesses that require extensive customization or additional third-party integrations may face higher implementation costs.
Priority Software typically works with businesses to provide customized pricing based on their specific needs, and businesses should factor in the costs of implementation, training, and ongoing support when calculating the total cost of ownership.
Suitable For
Priority ERP is best suited for small to mid-sized businesses across a wide range of industries, including retail, eCommerce, manufacturing, and distribution. Its flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness make it an attractive option for businesses that need an ERP solution to manage their omnichannel operations without the complexity or high costs associated with larger enterprise-level systems.
Retailers and eCommerce businesses that need to manage inventory across multiple locations and sales channels will benefit from Priority ERP’s real-time inventory management and order processing capabilities. Additionally, manufacturers and distributors with complex supply chains will find the system’s supply chain management tools useful for optimizing procurement, logistics, and inventory transfers.
While Priority ERP is an excellent solution for small to medium-sized businesses, large enterprises with highly specialized or complex operations may find that they need a more robust system with advanced features tailored to their needs.
Benefits of Omnichannel ERP for Businesses
Enhanced Customer Experience
Unified Customer Experience Across All Touchpoints
One of the core benefits of omnichannel ERP is its ability to provide a unified customer experience across all touchpoints. Modern customers often switch between channels during their shopping journey, browsing products online before purchasing in-store or vice versa. In such an environment, businesses need to ensure that each customer interaction is part of a coherent, seamless experience. This is where omnichannel ERP excels, offering real-time visibility and integration across all sales and customer engagement channels.
With omnichannel ERP, businesses can track customer interactions in real time, regardless of the platform. Whether a customer is browsing on an eCommerce website, placing an order through a mobile app, or making a purchase at a physical retail location, all interactions are recorded and synchronized in the ERP system. This level of visibility allows businesses to maintain a consistent customer profile, ensuring that no matter where the customer interacts with the brand, their preferences, purchase history, and current orders are readily available.

For example, a customer might add items to their shopping cart on an eCommerce site but then decide to complete the purchase at a physical store. With an omnichannel ERP system, the in-store sales team can access the customer’s online cart, ensuring that the transaction can continue seamlessly. This ability to bridge online and offline experiences creates a unified, frictionless journey for the customer, which is critical in today’s competitive retail environment.
Additionally, omnichannel ERP systems allow customer service teams to offer better support by having all customer information centralized. If a customer reaches out with an inquiry or complaint, the representative can quickly access their full transaction history, no matter which channel was used, allowing for faster issue resolution and improved customer satisfaction.
Personalized Offers and Seamless Transition Between Channels
In addition to unifying the customer experience, omnichannel ERP systems enable businesses to offer personalized offers and facilitate seamless transitions between channels. Personalization is a key differentiator in today’s market, where customers expect brands to know and understand their preferences, shopping habits, and purchase history. Omnichannel ERP systems make this level of personalization possible by collecting and integrating data from all customer touchpoints into one centralized system.
Using the real-time data gathered by an omnichannel ERP system, businesses can segment their customers based on various criteria, such as purchasing behavior, location, or product preferences. This allows businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns and personalized offers that resonate with individual customers. For example, a customer who frequently purchases a specific product category online may receive personalized discounts or recommendations for related products when they visit a brick-and-mortar store. Similarly, businesses can send personalized offers via email or mobile app notifications based on recent browsing behavior or abandoned carts.
Omnichannel ERP also allows businesses to provide cross-channel promotions that encourage customers to engage with the brand across multiple platforms. For instance, a retailer might offer a discount to customers who browse products online and then complete their purchase in-store. This kind of promotion not only drives foot traffic to physical stores but also enhances the overall customer experience by making it more dynamic and engaging.

Furthermore, the seamless transition between channels is one of the key hallmarks of an omnichannel ERP system. As customers move from one channel to another, whether browsing online and purchasing in-store or starting an inquiry on social media and completing it via customer service, omnichannel ERP ensures that no information is lost along the way. This is particularly important when managing order fulfillment, returns, and customer support interactions. If a customer makes an online purchase and later chooses to return or exchange the item in-store, the ERP system can immediately access the original transaction data, streamlining the process for both the customer and the business.
The ability to offer consistent, personalized experiences across all channels helps businesses build stronger relationships with their customers. Consumers feel valued when they receive relevant offers and encounter fewer obstacles when switching between online and offline channels. This not only improves customer loyalty but also increases the likelihood of repeat purchases, as customers are more likely to engage with a brand that offers convenience and personalization.
Streamlined Operations
Reduced Manual Processes and Better Resource Allocation
One of the key advantages of implementing an omnichannel ERP system is the ability to reduce manual processes across the business, which directly contributes to greater efficiency and more effective resource allocation. In many companies, managing separate sales channels—such as eCommerce platforms, brick-and-mortar stores, and mobile applications—without an integrated ERP system can result in disconnected processes. This often leads to time-consuming manual tasks, such as updating inventory levels, processing orders, and managing customer information separately for each channel. These redundant processes not only slow down operations but also increase the likelihood of errors, which can negatively impact both operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
An omnichannel ERP system automates these processes by integrating all channels into a single, cohesive platform. Instead of manually entering sales data or updating inventory records for each channel, the ERP system automatically synchronizes data across all touchpoints. This automation reduces the need for manual intervention, saving time and minimizing the risk of errors. For example, when a customer makes a purchase online, the system automatically updates inventory levels in real time across all warehouses and stores, ensuring that stock availability is accurate. Similarly, financial transactions, customer data, and order fulfillment are all synchronized without the need for manual data entry.

By reducing the reliance on manual processes, omnichannel ERP systems also allow businesses to allocate their resources more effectively. Employees who were previously tasked with time-consuming data entry or order processing can now focus on higher-value activities, such as customer engagement, product development, or strategic decision-making. For example, a retail business may repurpose employees who were once dedicated to reconciling inventory discrepancies across multiple sales channels into roles focused on improving customer service or driving marketing initiatives. This shift in resource allocation can lead to increased productivity and better overall performance.
Furthermore, the automation of back-office functions such as accounting, procurement, and order management helps reduce operational bottlenecks, leading to faster processing times and smoother workflows. As a result, businesses can operate more efficiently, with fewer delays and interruptions to daily operations.
Real-Time Decision-Making and Improved Agility
Another significant benefit of omnichannel ERP systems is the ability to enable real-time decision-making by providing businesses with access to up-to-date data across all their operations. In today’s fast-paced business environment, the ability to make timely and informed decisions is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. However, without an integrated ERP system, businesses often face delays in accessing critical information, such as sales performance, inventory levels, or customer trends, leading to slower decision-making and missed opportunities.
With an omnichannel ERP system, data from all sales channels and business processes is consolidated in real time, allowing managers and decision-makers to have a clear and comprehensive view of the entire business. For example, if a company experiences a sudden spike in demand for a particular product on its eCommerce platform, the ERP system can provide real-time insights into inventory levels, supplier lead times, and sales performance, enabling the business to make quick adjustments, such as replenishing stock or rerouting shipments. This level of real-time visibility is particularly important for businesses with multiple sales channels, where inventory and order management can become complex.

Moreover, real-time data allows businesses to respond to market changes with greater agility. Whether it’s adapting to seasonal demand, launching a new product, or managing supply chain disruptions, having immediate access to accurate data enables businesses to make proactive decisions that help them stay ahead of the competition. For instance, a retailer may notice that a specific product category is underperforming in-store but selling well online. With real-time data from an omnichannel ERP, the retailer can quickly adjust pricing strategies, marketing efforts, or inventory allocation to address the disparity and optimize sales performance across channels.
Omnichannel ERP systems also enhance business agility by providing the tools needed to quickly scale operations. As businesses grow and add new sales channels, geographic locations, or product lines, an omnichannel ERP system allows them to scale seamlessly without disrupting existing operations. The flexibility of the system ensures that new data flows, business units, or sales channels can be integrated into the existing platform with minimal downtime or manual intervention.
Furthermore, the ability to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and generate real-time reports allows businesses to continuously monitor their performance and make data-driven decisions. For example, a business can use the ERP system to generate sales reports by channel, region, or product line, allowing managers to identify trends, measure the success of marketing campaigns, and optimize operations accordingly.
In addition, real-time data analytics helps businesses mitigate risks and respond to challenges more effectively. For instance, in the event of supply chain disruptions or unexpected spikes in demand, businesses can use the ERP system to adjust procurement schedules, reallocate inventory, or reroute shipments in real time, ensuring minimal disruption to operations. This level of agility is critical for businesses operating in dynamic and competitive industries, where the ability to adapt quickly can be a key differentiator.
Inventory Optimization
Minimized Stockouts and Overstock Issues
One of the primary benefits of omnichannel ERP is its ability to minimize stockouts and overstock issues, a common challenge for businesses managing inventory across multiple channels. Stockouts—when a product is out of stock and unavailable for purchase—can lead to lost sales, dissatisfied customers, and potential damage to a brand’s reputation. On the other hand, overstock—when too much inventory is held in storage—can result in excess holding costs, cash flow constraints, and wasted resources. Balancing the right amount of inventory is especially difficult for businesses that operate across various platforms, such as eCommerce, brick-and-mortar stores, and mobile channels.

An omnichannel ERP system helps solve these challenges by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels across all sales channels and warehouse locations. Businesses can instantly view available stock for each product, no matter where the inventory is held or how it is being sold. This enables companies to adjust inventory levels dynamically based on actual demand rather than relying on outdated or siloed data. For example, if a product is selling rapidly online but moving slowly in physical stores, the ERP system can provide insights to reallocate stock to where it’s needed most, preventing stockouts in high-demand areas while avoiding overstock in others.
Moreover, omnichannel ERP systems integrate sales and inventory data, enabling businesses to predict demand more accurately through the use of data analytics and forecasting tools. By analyzing historical sales data and current trends, the system can forecast future demand and adjust inventory accordingly. This level of predictive insight helps businesses proactively manage their stock levels, reducing the likelihood of stockouts during peak sales periods or promotional events and ensuring that they have enough inventory to meet customer demand without overstocking.
Additionally, the automation features within omnichannel ERP systems help streamline the process of reordering stock. Instead of relying on manual checks or delayed reports, the system can be configured to automatically trigger purchase orders when inventory levels fall below predefined thresholds. This reduces the risk of human error and ensures that stock is replenished before it runs out, keeping operations running smoothly.
Improved Warehouse Management and Reduced Lead Times
Another key benefit of omnichannel ERP systems is improved warehouse management and reduced lead times, both of which are critical to maintaining an efficient supply chain and ensuring timely order fulfillment. In a multi-channel environment, where inventory is often distributed across various warehouses and fulfillment centers, managing stock efficiently can be challenging. Disconnected systems, manual processes, and siloed data can lead to inefficiencies, such as misplaced inventory, delays in fulfillment, or the inability to fulfill customer orders from the nearest warehouse.
Omnichannel ERP systems address these challenges by integrating all warehouse operations into a unified platform. With real-time data on inventory levels, location, and movement, businesses can optimize their warehouse operations to ensure that stock is always stored in the right locations and ready for fulfillment. This includes better control over stock allocation, faster picking and packing processes, and improved inventory accuracy.
One of the ways omnichannel ERP systems improve warehouse management is by providing advanced tracking capabilities. Businesses can track products through the entire supply chain, from the moment they are received at the warehouse to the moment they are shipped to the customer. This real-time tracking allows for greater transparency and control over stock movement, reducing the likelihood of errors or delays. For example, if a product is available in multiple warehouses, the ERP system can automatically direct fulfillment from the nearest location to the customer, ensuring faster delivery times while minimizing shipping costs.
Omnichannel ERP systems also enable businesses to optimize warehouse layouts and workflows, improving efficiency within the warehouse itself. By analyzing data on order volume, product movement, and fulfillment times, the system can suggest optimal warehouse layouts, helping staff to pick and pack orders more quickly and accurately. This leads to shorter lead times and faster order fulfillment, which is crucial in meeting customer expectations for timely deliveries, particularly in the eCommerce space.
Another way omnichannel ERP systems help reduce lead times is through better coordination with suppliers. The system’s real-time data enables businesses to monitor supplier performance and lead times more effectively, ensuring that stock is replenished before it runs out. By automating the procurement process and integrating supplier data into the ERP system, businesses can reduce the delays associated with manual reordering and ensure that suppliers are meeting their delivery commitments. This not only improves the efficiency of the supply chain but also ensures that customers receive their orders on time.
For businesses with complex distribution networks, omnichannel ERP systems also support multi-location inventory management. This means that businesses can fulfill orders from multiple warehouses or distribution centers, allowing for greater flexibility and responsiveness in order fulfillment. If one warehouse is low on stock, the ERP system can automatically reroute orders to another location that has the available inventory, reducing the risk of delays or stockouts and ensuring that customers receive their orders without interruption.
Data-Driven Insights
Analytics on Customer Behavior and Sales Trends
A key advantage of using omnichannel ERP systems is the ability to generate analytics on customer behavior and sales trends. In a business environment where customer interactions span across multiple channels—such as eCommerce platforms, physical stores, and mobile apps—it can be challenging to get a unified view of customer behavior. Without integration across channels, businesses risk missing critical insights into how customers engage with the brand, which products are most popular, and where improvements in the customer journey can be made.
Omnichannel ERP systems address this challenge by consolidating data from all sales channels into a single platform. This unified view enables businesses to track and analyze customer behavior across touchpoints, including browsing history, purchase patterns, average order values, and interaction preferences. For instance, if a customer frequently browses products online but prefers to make purchases in-store, the ERP system captures this data, allowing businesses to understand how their customers navigate between channels. This level of insight is invaluable for creating personalized marketing campaigns, improving customer engagement, and boosting retention.
In addition to individual customer insights, omnichannel ERP systems provide businesses with the ability to track sales trends across different product categories, regions, and time periods. By analyzing this data, businesses can identify patterns in consumer demand, such as seasonal spikes or emerging product trends. For example, an ERP system may reveal that certain product categories sell better in specific regions during certain times of the year, allowing businesses to optimize inventory allocation and marketing efforts accordingly.
Furthermore, omnichannel ERP analytics can reveal which channels are driving the most sales and how customers move between these channels. This helps businesses prioritize investments in the most effective platforms while identifying underperforming areas that need attention. By understanding which channels are most successful in driving sales, businesses can allocate resources more efficiently and ensure that their omnichannel strategy is aligned with customer preferences.
Moreover, these analytics extend beyond sales data to include insights into customer service interactions, returns, and post-purchase behavior. This holistic view of customer behavior helps businesses refine their overall customer experience strategy, addressing pain points and capitalizing on opportunities for upselling or cross-selling based on detailed customer data.
Better Forecasting and Strategic Decision-Making
In addition to offering insights into customer behavior and sales trends, omnichannel ERP systems empower businesses with the tools needed for better forecasting and strategic decision-making. Accurate forecasting is essential for managing inventory, optimizing supply chains, and ensuring that businesses are prepared to meet customer demand without overstocking or running out of products. Traditional forecasting methods often rely on historical data that is siloed across different departments or channels, leading to inaccurate predictions and inefficient resource allocation.
With an omnichannel ERP system, all sales, inventory, and customer data is integrated into a single platform, providing businesses with a comprehensive view of their operations. This real-time data allows for more accurate demand forecasting by taking into account the latest sales trends, customer behavior patterns, and external factors such as market conditions or seasonal variations. For example, a retailer can use the ERP system’s forecasting tools to predict demand for specific products during a holiday season, based on previous sales data and current customer engagement metrics. The system can also factor in promotions, price changes, or marketing campaigns to adjust the forecast dynamically, ensuring that businesses are well-prepared for fluctuations in demand.

Beyond inventory management, omnichannel ERP systems enhance strategic decision-making by providing businesses with data-driven insights that inform critical business choices. These systems allow businesses to generate detailed reports and dashboards that highlight key performance indicators (KPIs) across all aspects of the business, from sales and customer satisfaction to supply chain efficiency and financial performance. By tracking these KPIs in real time, managers and decision-makers can make informed decisions on where to allocate resources, how to improve operational efficiency, and which areas of the business need strategic adjustments.
For example, if sales data indicates that certain products are consistently underperforming in one channel but performing well in another, the business can adjust its marketing strategies, pricing, or product placement accordingly. Similarly, if the ERP system reveals that certain regions are experiencing higher-than-expected demand, businesses can prioritize shipments or adjust inventory distribution to capitalize on the opportunity.
Omnichannel ERP systems also enable scenario planning and what-if analysis, allowing businesses to model different strategic outcomes based on various factors. This capability is especially valuable in dynamic industries where market conditions can change rapidly. For instance, a business might use the ERP system to simulate the impact of a price change on sales volume or to evaluate the potential effects of opening a new store location. By testing different scenarios in advance, businesses can make more informed decisions and minimize the risks associated with major operational or strategic changes.
Additionally, the integration of AI and ML into many omnichannel ERP systems enhances the accuracy and depth of forecasting and decision-making. These advanced technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict future outcomes, and provide recommendations for optimizing business processes. For example, AI-driven analytics can help businesses predict customer demand more accurately by analyzing a combination of historical sales data, current market trends, and customer engagement patterns. This leads to smarter decision-making and more agile responses to changes in the market or customer preferences.
Improved Collaboration Between Departments
Centralized Data Leads to Better Communication Across Departments
A key benefit of implementing an omnichannel ERP system is the ability to centralize data, which in turn leads to better communication across departments. In traditional business environments, departments often operate using separate systems and databases. Marketing may use one platform for CRM, while sales and finance might rely on entirely different systems for order processing and financial tracking. This fragmented approach creates silos where data is not shared effectively, leading to breakdowns in communication and limiting the ability to collaborate effectively.
Omnichannel ERP addresses these issues by consolidating all business functions into one integrated system. This means that data from sales, marketing, finance, and operations is stored and accessible in a single platform, making it easier for teams to access the information they need in real time. For example, the marketing team can access up-to-date sales data to understand how their campaigns are performing and adjust their strategies accordingly. Similarly, the finance department can see real-time inventory and sales information to make more informed financial decisions.
This centralized data not only makes internal communications more transparent but also improves cross-departmental workflows. For example, when a sales team closes a deal, the information is instantly available to the finance and operations teams, who can then begin processing the order and managing inventory without the need for additional communication. This seamless exchange of information reduces delays, minimizes errors, and ensures that all departments are working from the same data, leading to better collaboration and faster decision-making.
Moreover, omnichannel ERP systems provide tools like shared dashboards and real-time reporting, which allow different departments to visualize performance data and collaborate on action plans. If a campaign run by the marketing department results in an unexpected spike in demand, the operations team can immediately see the impact on inventory and adjust procurement or production schedules accordingly. This real-time coordination ensures that departments can work in harmony, improving overall efficiency and responsiveness to market changes.
Break Down Silos Between Marketing, Sales, Finance, and Operations
One of the major challenges faced by businesses, particularly those with multiple sales channels, is the creation of departmental silos. When marketing, sales, finance, and operations teams operate in isolation, it leads to inefficiencies and lost opportunities for growth. Each department may be focused solely on its own goals and KPIs, resulting in a lack of alignment and coordination. Omnichannel ERP systems play a pivotal role in breaking down these silos by integrating all functions into a unified system.
For example, in a business without an omnichannel ERP system, the sales team might close deals without being aware of potential inventory shortages, leading to delayed order fulfillment. Meanwhile, the marketing team could be running campaigns to promote products that are no longer in stock, creating confusion and dissatisfaction for customers. The finance department might struggle to track revenue accurately because they don’t have access to real-time sales data from the front-end systems. This disconnect not only creates inefficiencies but can also lead to lost revenue, increased costs, and strained customer relationships.
An omnichannel ERP system bridges these gaps by ensuring that all departments have access to the same data in real time. For example, when the sales department processes a new order, the ERP system immediately updates inventory levels, and this information becomes visible to the marketing team, which can then adjust campaigns accordingly. Meanwhile, the finance team receives real-time data on sales, enabling them to track revenue, manage cash flow, and make informed financial decisions. Operations teams can see the same sales data and adjust production schedules or shipping logistics as needed. This integrated approach ensures that all departments are aligned and working towards common business goals.
Breaking down silos between marketing, sales, finance, and operations also leads to more cohesive strategy execution. For example, during product launches, marketing and sales teams need to collaborate closely to ensure that the right messages are communicated to the right audiences. With an omnichannel ERP, the marketing team can access customer data to tailor campaigns, while the sales team can track campaign performance in real time, helping them adjust their sales pitches accordingly. Both teams can then provide feedback to the operations department, which can manage stock levels and shipping processes based on the success of the campaign.
Similarly, collaboration between finance and operations is crucial for managing costs and optimizing profitability. The finance team needs accurate and up-to-date data from operations to ensure that budgeting, forecasting, and financial planning are aligned with actual performance. An omnichannel ERP system allows for continuous communication between these departments, enabling them to work together to streamline processes, reduce waste, and identify cost-saving opportunities.
Additionally, omnichannel ERP systems encourage more cross-functional collaboration by providing all departments with access to shared tools and data. Teams are no longer forced to work in isolation, relying on outdated or incomplete information to make decisions. Instead, they can collaborate in real time, share insights, and coordinate efforts to improve overall business performance. This increased collaboration leads to greater innovation, faster problem-solving, and more efficient operations.
Challenges in Adopting Omnichannel ERP
High Initial Setup Costs
Significant Capital Investment Required
The process of adopting an omnichannel ERP system begins with a significant capital investment. This is one of the most challenging aspects for businesses considering the shift to omnichannel ERP, particularly for those that are still relying on legacy systems or operating with disjointed platforms for different departments. Moving to an integrated ERP solution that supports omnichannel operations requires both financial resources and careful planning.
One of the main areas where this capital investment is directed is software licensing. Omnichannel ERP systems typically come with complex licensing models that are determined by factors such as the number of users, modules required, and the scale of the business operations. Depending on the ERP provider, licensing fees can vary widely, with enterprise-grade solutions such as SAP S/4HANA, Oracle NetSuite, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 often carrying higher upfront licensing costs. These fees cover the software’s core functionalities, but businesses may also need to purchase additional modules or third-party integrations to support specific needs like advanced analytics, eCommerce integration, or specialized inventory management features.

In addition to software costs, businesses must also invest in hardware infrastructure to support the omnichannel ERP system. For companies opting for on-premise solutions, this may involve purchasing new servers, storage solutions, and network equipment to ensure that the ERP system runs efficiently and securely. Even for businesses opting for cloud-based ERP systems, there may be hardware upgrades required to ensure that end-users can access the system without performance issues, especially if the company’s current infrastructure is outdated. These hardware investments can be considerable and often require businesses to reallocate capital from other areas to cover the costs.
Beyond software and hardware, implementation services are another significant cost factor. Implementing an omnichannel ERP system is a highly technical and complex process that involves configuring the system to align with the specific operational needs of the business. This process typically requires the expertise of external consultants or ERP implementation partners who can guide the business through everything from initial system setup to data migration, system testing, and user training. These consulting and implementation fees can represent a substantial portion of the overall investment, particularly if extensive customization is required to tailor the ERP system to fit the company’s existing workflows and operational processes.
Customization needs can further drive up the initial setup costs. While many ERP systems offer out-of-the-box functionality, most businesses—especially those with complex omnichannel operations—require some level of customization to ensure that the ERP system integrates seamlessly with existing platforms and processes. Whether it’s configuring specific modules to support multi-location inventory management, custom order fulfillment workflows, or integrating the ERP system with eCommerce platforms and point-of-sale systems, customization can be time-consuming and costly. These customizations also often require the ongoing support of external consultants or in-house IT teams, adding to the initial financial burden.
Ongoing Costs Related to System Upgrades, Maintenance, and Support
While the initial capital investment in omnichannel ERP systems is significant, businesses must also consider the ongoing costs that come with maintaining and supporting the system over time. These costs are essential for ensuring that the system continues to operate effectively, remains secure, and can scale with the business as it grows or evolves.
One of the primary ongoing costs is related to system upgrades. As technology advances and business needs change, ERP providers regularly release updates and new versions of their software. These upgrades are essential for improving system performance, adding new features, and addressing security vulnerabilities. However, depending on the ERP provider, businesses may need to pay additional fees for access to these upgrades, especially if they are using an on-premise solution where upgrades are not automatically included in the initial licensing agreement. Moreover, upgrading an ERP system can be a complex process that requires planning, testing, and additional consulting services, all of which contribute to ongoing costs.
For cloud-based omnichannel ERP solutions, while upgrades are typically included as part of the subscription model, businesses may still need to invest in additional integration work to ensure that new features or updates do not disrupt existing workflows or third-party systems. This is particularly true for businesses that rely on custom integrations or have highly complex omnichannel setups, where even minor changes can have significant downstream impacts on other parts of the business.
In addition to upgrades, system maintenance is another ongoing expense. ERP systems, particularly those that support large-scale omnichannel operations, require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. This may include server maintenance (for on-premise solutions), database management, performance tuning, and security updates to protect the system from potential cyber threats. For businesses without in-house IT teams capable of managing this, the cost of outsourcing maintenance to third-party service providers can add up over time.
Another critical ongoing cost is related to technical support. Businesses implementing omnichannel ERP systems need to have access to dedicated support services in case of system issues, outages, or unexpected errors. ERP providers typically offer varying levels of support, ranging from basic helpdesk services to more comprehensive 24/7 support packages. For businesses operating in a fast-paced, multi-channel environment, having reliable and responsive technical support is essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring that operations continue to run smoothly. However, these support packages can represent a recurring cost, and businesses must factor them into their long-term budget.
Training is also an ongoing consideration. As businesses evolve and bring on new employees, additional training sessions may be required to ensure that staff can use the ERP system effectively. This is especially true in businesses where the ERP system plays a critical role in day-to-day operations across multiple departments, such as marketing, sales, finance, and logistics. Without proper training, businesses risk underutilizing the system’s features, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities for optimization.
Lastly, as businesses grow, they may need to scale their ERP systems, which can involve additional licensing costs, upgrades to cloud storage, or even more advanced modules to support new operations or product lines. While these costs are associated with the growth of the business, they still add to the overall financial commitment required to maintain an omnichannel ERP system.
Complex System Integration
Difficulty in Integrating Omnichannel ERP with Existing Legacy Systems
One of the most daunting challenges in the adoption of omnichannel ERP systems is the difficulty of integrating the new ERP system with existing legacy systems and third-party applications. Many businesses, especially those that have been in operation for several years, rely on outdated or fragmented legacy systems to manage various aspects of their operations, such as finance, inventory, or customer management. These systems were often built without the need to communicate with one another or adapt to new technologies, making the process of integrating them with a modern omnichannel ERP particularly challenging.
Legacy systems are typically rigid and lack the flexibility needed to seamlessly integrate with contemporary ERP platforms. For instance, a company might have separate software for managing its online store, point-of-sale (POS) systems for physical retail, and another system for managing warehouse operations. While an omnichannel ERP is designed to unify all these functions, the older software may not be built to communicate with a centralized platform. This lack of compatibility can create significant roadblocks during the integration process, requiring businesses to invest additional time and resources into developing custom interfaces or middleware to bridge the gap between systems.

Another major concern is the integration of third-party applications that many businesses rely on for day-to-day operations. These applications might include eCommerce platforms like Shopify or Magento, CRM software like Salesforce, and specialized tools for marketing automation, supply chain management, or financial analytics. The success of an omnichannel ERP system often depends on its ability to integrate seamlessly with these external applications to create a truly unified business environment. However, ensuring that all third-party tools can interact with the new ERP system without disruptions or compatibility issues is a complex task.
The process of integrating omnichannel ERP with third-party applications often requires the use of application programming interfaces (APIs) or custom-built connectors to enable smooth data flow between systems. While modern ERP systems typically offer robust API support, not all third-party applications or legacy systems may have the necessary integration capabilities. This can result in additional costs for developing custom solutions and ongoing maintenance to ensure that the different systems continue to communicate effectively as they are updated or modified over time.
Moreover, the integration of different software systems requires close collaboration between the ERP implementation team, the IT department, and third-party software providers. Without this coordinated effort, businesses risk encountering compatibility issues, data inconsistencies, or system failures that can disrupt daily operations. These complexities can significantly lengthen the timeline for ERP implementation, increasing the overall costs and delaying the benefits that the ERP system is expected to deliver.
Potential Disruptions During the Data Migration Process
In addition to the difficulties posed by integrating an omnichannel ERP system with legacy systems and third-party applications, businesses often face significant challenges during the data migration process. Data migration involves transferring existing data—such as customer records, inventory levels, financial transactions, and operational workflows—from the old system into the new ERP platform. While this might seem like a straightforward task, it is one of the most complex and risky aspects of ERP implementation.
Legacy systems, which have often been in place for many years, tend to store data in formats that are not easily compatible with modern ERP platforms. Moreover, data in these systems is often fragmented, incomplete, or inaccurate, making it difficult to transfer seamlessly into the new system. The process of cleaning, standardizing, and migrating this data into the omnichannel ERP can be labor-intensive and prone to errors. Data migration failures, such as missing or corrupted data, can severely impact business operations and lead to costly delays.
For businesses that operate across multiple channels, the risks associated with data migration are even greater. Omnichannel ERP systems rely on real-time data from various sources to manage inventory, track customer orders, and ensure a consistent customer experience across touchpoints. Any disruption to the accuracy or availability of data during migration can have ripple effects throughout the entire business, from inventory inaccuracies leading to stockouts or overstock situations to customer dissatisfaction due to order fulfillment issues.
In addition to the data migration challenges, the system transition itself poses significant risks to daily operations. During the transition from legacy systems to the new omnichannel ERP, businesses often experience periods of downtime or operational disruptions as data is transferred, systems are tested, and employees are trained on the new platform. Even the smallest errors in system configuration or data transfer can lead to widespread operational delays, such as incorrect inventory counts, delayed shipments, or financial reporting errors. In industries where timing is critical, such as retail, manufacturing, or eCommerce, these disruptions can result in lost revenue and damage to customer relationships.
Moreover, businesses that rely heavily on manual processes or custom workflows in their legacy systems may find it difficult to replicate these workflows in the new ERP system. While omnichannel ERP platforms are designed to standardize and automate processes, this often requires businesses to re-engineer their existing workflows to fit the new system’s structure. This process can be time-consuming and require significant internal resources, as employees must adapt to new ways of working while maintaining operational continuity.
One of the strategies businesses can adopt to mitigate these risks is to phase the ERP implementation by rolling out the new system in stages, rather than all at once. For example, a company may begin by implementing the ERP system in one department, such as finance or inventory management, before expanding it to other areas of the business. This phased approach allows businesses to test the system, identify potential issues, and make adjustments without disrupting all areas of the company at once. However, even with a phased rollout, businesses must carefully plan for potential disruptions and ensure that contingency plans are in place to maintain daily operations during the transition.
Finally, training employees on the new system is a crucial step in minimizing disruptions during the transition. Many businesses underestimate the time and resources needed to ensure that all staff members are comfortable using the new ERP system. Proper training is essential for reducing the learning curve, avoiding user errors, and ensuring that the business can continue to operate efficiently as it transitions to the new platform.
Customization Needs
Tailoring Omnichannel ERP to Fit Unique Operational Processes
No two businesses operate in the same way, and this is especially true for companies that manage operations across multiple sales channels. Each business has its own set of processes, workflows, and unique operational requirements that have been developed over time to meet the demands of its specific market or customer base. For an omnichannel ERP system to be truly effective, it must not only integrate all aspects of the business—such as sales, inventory, finance, and customer management—but also adapt to the business’s existing workflows. This often requires significant customization.
One of the main reasons businesses need to customize their omnichannel ERP is to ensure that it aligns with industry-specific processes. For example, a retailer may need to customize the system’s inventory management module to handle complex stock allocations across multiple warehouses or integrate the system with specific point-of-sale (POS) solutions for seamless customer transactions. A manufacturer, on the other hand, may require the ERP system to include features that support advanced production planning, supply chain management, and materials tracking to ensure that orders are fulfilled accurately and on time. Similarly, businesses in industries like healthcare, finance, or eCommerce often have regulatory or compliance requirements that must be built into the system.

Moreover, many companies have existing workflows that are essential to their daily operations. While omnichannel ERP systems are designed to standardize and automate many business processes, they may not always fit the way a business already operates. For instance, a company may have developed custom workflows for managing product returns, customer interactions, or inventory replenishment that differ from the out-of-the-box functionality provided by the ERP system. To avoid disrupting these workflows, businesses need to customize the ERP system to maintain continuity in their operations. This often involves developing new features, modifying existing ones, or integrating third-party applications that align with the company’s established processes.
Customization is also frequently needed to ensure that the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) of the ERP system are intuitive and efficient for employees. Businesses may need to tailor the system’s interface to match the specific roles and responsibilities of different users, ensuring that each department has access to the tools and data they need to perform their tasks effectively. For example, the marketing team may require dashboards that provide insights into campaign performance and customer behavior, while the finance team needs real-time access to financial reporting and accounting tools. Customizing the user interface not only improves efficiency but also reduces the learning curve for employees, helping them adopt the new system more quickly.
Implementation Time and Costs
While customization is often necessary to make an omnichannel ERP system work effectively for a business, it also comes with its own set of challenges. One of the most significant is the increase in implementation time and costs associated with customizing the system. The more tailored the ERP system needs to be, the longer it takes to configure and deploy. This can delay the overall implementation timeline, leading to longer periods of disruption or reduced efficiency during the transition.
Customizing an omnichannel ERP system requires expert consultation from both internal IT teams and external ERP implementation specialists. These experts must work closely with the business to understand its unique requirements, design solutions that fit those needs, and ensure that the customizations are properly implemented without causing operational issues. This can be a time-consuming process, as it involves several stages of development, testing, and refinement to ensure that the customized ERP system functions correctly.

For businesses that require extensive customization, the complexity of the project can increase significantly. For example, integrating the ERP system with third-party applications—such as eCommerce platforms, supply chain management software, or CRM tools—can add to the complexity, requiring additional development work to ensure seamless data flow between systems. These integrations must be carefully managed to prevent data inconsistencies or communication errors that could disrupt operations. This complexity increases the need for development resources, which in turn drives up the cost of implementation.
Moreover, extensive customization often requires custom coding and ongoing support from developers. While many ERP systems offer built-in modules that can be configured to meet different business needs, some businesses require features that are not available in the standard version of the software. In these cases, custom code must be written to add new functionality or modify existing modules. Writing and testing this code requires specialized knowledge and expertise, further increasing the costs of customization.
Beyond the initial implementation, businesses must also consider the long-term maintenance of customized ERP systems. Custom code and integrations often require regular updates to ensure that they continue to function properly as the business grows or as new features are added to the ERP system. For example, if the ERP provider releases an update to the core system, the custom code must be tested and, if necessary, modified to ensure that it remains compatible with the new version. This ongoing maintenance adds to the total cost of ownership and requires businesses to allocate resources for continued support and development.
Customization can also lead to increased risk during the ERP implementation process. The more a system is customized, the greater the potential for issues to arise during deployment. For instance, custom integrations may create conflicts with other modules or result in system slowdowns if they are not properly optimized. Additionally, highly customized ERP systems can be more difficult to troubleshoot and support, particularly if the customizations are not well-documented or if the original developers are no longer available to provide assistance.
Despite these challenges, businesses often find that the benefits of customization outweigh the costs, as a tailored omnichannel ERP system allows them to operate more efficiently and meet the specific needs of their industry. However, to manage the risks associated with customization, businesses must work closely with ERP consultants and implementation specialists to develop a clear strategy for how the system will be customized, tested, and maintained over time.
Staff Training and Adoption
Learning Curve
One of the most significant challenges associated with adopting an omnichannel ERP system is the learning curve that employees experience as they adapt to new technologies and workflows. Omnichannel ERP systems are designed to integrate a wide array of business functions—ranging from inventory management and sales to CRM, finance, and supply chain logistics. While this integration can enhance operational efficiency, it also requires employees to learn how to navigate and use a completely new system that is often much more complex than the individual tools or legacy systems they previously used.
Employees in departments like marketing, sales, operations, finance, and customer service may have become accustomed to using specific platforms and processes that are now being replaced by the omnichannel ERP system. For instance, a sales team that has been using standalone CRM software will now need to interact with a fully integrated ERP system that not only tracks customer data but also manages orders, inventory levels, and financial transactions. This can create confusion and frustration, especially if employees are not provided with sufficient guidance on how to use the new system.
The difficulty in adjusting to new workflows is particularly pronounced when employees are required to switch from manual or semi-automated processes to a fully automated ERP system. For example, in a company that previously relied on spreadsheets and manual data entry to track inventory, employees must now learn to work with automated tools that track stock levels in real time, integrate with supply chain partners, and provide predictive analytics on demand trends. While these features ultimately make the business more efficient, the initial learning curve can be steep, especially for employees who are less tech-savvy or have limited experience with advanced software systems.
Moreover, the breadth and depth of omnichannel ERP systems mean that employees across different departments may need to learn how to use entirely new modules and tools that they were not previously exposed to. For instance, warehouse staff may need to familiarize themselves with real-time stock monitoring and automated order fulfillment processes, while marketing teams may need to integrate their campaigns with sales data to better measure customer engagement and conversion rates. This shift can create initial resistance among employees who feel overwhelmed by the complexity of the new system or who are hesitant to move away from established practices.
Comprehensive Training Programs and Ongoing Support
To overcome the challenges associated with staff training and adoption, businesses must invest in comprehensive training programs and ongoing support to ensure that all employees are comfortable using the new omnichannel ERP system. A well-structured training program is crucial not only for teaching employees how to use the new system but also for helping them understand the benefits of the ERP solution and how it will improve their daily work processes.
One of the first steps in ensuring smooth adoption is conducting a needs assessment to identify the specific training requirements for different departments. Since omnichannel ERP systems impact various functions within a business—such as finance, sales, marketing, and operations—each department will require customized training that is relevant to their specific tasks. For instance, the finance team will need in-depth training on financial reporting, budgeting, and invoicing modules, while the operations team will focus on inventory management, procurement, and supply chain logistics. Customizing the training program for each department ensures that employees receive targeted instruction on the aspects of the ERP system that are most relevant to their roles.

Hands-on training is particularly important for ensuring that employees can confidently use the new system in real-world scenarios. This can be achieved through a combination of in-person workshops, online tutorials, and practical exercises where employees are encouraged to simulate their day-to-day tasks using the new ERP platform. Role-based training sessions, where employees can practice using the specific features they will use most frequently, can help reduce the initial intimidation factor and make the transition smoother.
Another critical aspect of the training process is ensuring that employees understand how the omnichannel ERP system integrates with their current workflows. Since ERP systems are designed to streamline processes across multiple departments, employees need to be aware of how their tasks fit into the broader operational ecosystem. For example, sales teams need to understand how their input of customer orders feeds into the inventory management system and triggers actions in procurement and shipping. By giving employees a clear picture of how the ERP system supports cross-departmental collaboration, businesses can help them see the value of the new system, reducing resistance to change.
Additionally, the role of ongoing support cannot be overstated. While initial training is crucial, it is common for employees to encounter challenges as they begin to use the omnichannel ERP system in real-time operations. Having access to ongoing support—such as help desks, online resources, and in-house ERP specialists—ensures that employees can resolve issues quickly and continue to work efficiently without major disruptions. Many businesses also benefit from implementing peer support networks, where employees who have become proficient in using the system can assist their colleagues in troubleshooting issues and learning advanced features.
For long-term success, businesses should also focus on continuous training and development. As the ERP system evolves with new updates or additional modules, employees will need refresher courses to stay up to date with new features or changes in functionality. Regular training sessions or “lunch and learn” workshops can keep employees engaged with the system and help them leverage advanced capabilities to improve productivity.
Finally, businesses need to ensure that the company culture supports the adoption of new technologies. Leadership must champion the benefits of the omnichannel ERP system and create an environment where employees feel encouraged to ask questions, share feedback, and participate in the learning process. By fostering a culture of learning and continuous improvement, businesses can reduce the resistance to adopting new systems and ensure that the workforce is fully engaged in the successful implementation of the ERP platform.
Data Security and Compliance
As businesses manage increasingly large amounts of sensitive customer and business data across multiple platforms and touchpoints, ensuring that this data remains secure and compliant with global regulations becomes a complex and ongoing challenge. Failure to adequately address these concerns can lead to significant financial and reputational damage, making data security and regulatory compliance essential considerations in any omnichannel ERP implementation.
Ensuring the Protection of Sensitive Business and Customer Data
As businesses adopt omnichannel ERP systems to integrate operations across eCommerce platforms, brick-and-mortar stores, mobile apps, and other customer touchpoints, the protection of sensitive business and customer data becomes a key challenge. Omnichannel ERP systems handle a vast amount of data—ranging from customer profiles, purchase history, and payment information to internal financial records, inventory levels, and supplier contracts. This data flows through multiple channels and systems, creating multiple potential entry points for cyberattacks or data breaches.
The risk of a data breach is heightened in an omnichannel environment because businesses must manage and secure data across disparate systems and platforms. For example, a retailer that sells products through both an online store and physical locations must ensure that customer payment data is secure in both environments. Additionally, if third-party applications such as payment gateways, CRM systems, or supply chain management tools are integrated with the omnichannel ERP system, these external connections can create vulnerabilities if not properly secured. A breach in any one system could compromise the entire network, exposing sensitive customer information and damaging the business’s reputation.

To address these risks, businesses must implement robust cybersecurity measures that are specifically tailored to the omnichannel nature of their operations. This often involves deploying advanced encryption techniques, ensuring secure data transmission across channels, and implementing strong authentication protocols for users accessing the system. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, is critical for protecting sensitive information, such as customer payment details and business financials, from unauthorized access. Additionally, businesses should implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all employees accessing the ERP system to prevent unauthorized access in case of compromised credentials.
One of the complexities of securing omnichannel ERP systems is ensuring that data is protected across multiple locations. For example, a business with multiple warehouses, offices, and retail locations must ensure that all data flowing between these sites is secure. This may involve using virtual private networks (VPNs) to protect data transmitted between different physical locations, as well as setting up firewalls and intrusion detection systems to monitor for potential security threats.
Another key aspect of data security in omnichannel ERP systems is role-based access control (RBAC). Given the vast amount of data stored within an ERP system, not all employees should have access to every part of the system. By setting up role-based access controls, businesses can restrict access to sensitive information based on job responsibilities. For instance, customer service representatives might only have access to customer order histories, while finance teams would have access to financial reports and payment details. This reduces the risk of internal data breaches and ensures that only authorized personnel can access critical information.
Despite these security measures, no system is entirely immune to attacks, and businesses must prepare for the possibility of a breach. As part of an omnichannel ERP implementation, businesses should establish a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in the event of a data breach. This includes identifying the source of the breach, mitigating the impact, notifying affected customers, and taking corrective actions to prevent future incidents. Having a clear and well-documented response plan can minimize the damage caused by a breach and ensure that the business can recover quickly.
Compliance with Global Regulations or Industry-Specific Standard
In addition to data security, businesses adopting omnichannel ERP systems must also navigate the complexities of regulatory compliance. As data is collected and stored across various platforms and geographic locations, businesses are required to comply with a range of global data protection regulations and industry-specific standards. Failure to meet these regulatory requirements can result in significant financial penalties, legal action, and loss of customer trust.
One of the most well-known and stringent data protection regulations is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which applies to businesses operating within the European Union (EU) or processing the personal data of EU citizens. Under GDPR, businesses must ensure that personal data is collected, processed, and stored in a manner that protects individual privacy rights. For businesses using omnichannel ERP systems, this means implementing strict controls over how customer data is handled, ensuring that individuals can access, correct, or delete their data upon request, and reporting any data breaches within 72 hours.
GDPR compliance is particularly challenging in an omnichannel environment because customer data is often collected across multiple touchpoints—such as websites, mobile apps, and in-store transactions—and then consolidated within the ERP system. Businesses must ensure that they have clear consent from customers before collecting their data and that all data is stored securely. They must also implement mechanisms for customers to easily manage their personal data, such as allowing them to opt out of marketing communications or request the deletion of their information. Ensuring compliance across multiple channels and platforms can be both time-consuming and costly, especially for businesses with a global customer base.
Similarly, businesses operating in industries such as healthcare must comply with regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. HIPAA sets strict guidelines for how personal health information (PHI) must be stored, accessed, and shared. For businesses using omnichannel ERP systems to manage healthcare operations, this requires implementing stringent security measures to ensure that PHI is protected from unauthorized access. Additionally, businesses must maintain detailed audit logs to track who has accessed health records and for what purpose, as required by HIPAA. Non-compliance can result in severe fines and legal penalties, making it essential for businesses to prioritize regulatory compliance as part of their ERP implementation.
Beyond GDPR and HIPAA, many industries have their own compliance standards that businesses must adhere to. For example, businesses in the financial services sector may need to comply with regulations such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), which governs the secure handling of credit card information. Compliance with PCI DSS involves implementing specific security measures—such as encryption, secure payment gateways, and regular security audits—to ensure that credit card data is protected during online and in-store transactions.
Navigating these regulatory requirements can be complex and costly, particularly for businesses operating across multiple regions or industries. However, failing to comply with these standards can result in significant legal and financial repercussions. As part of their omnichannel ERP implementation, businesses must work closely with legal and compliance teams to ensure that their data protection practices align with all relevant regulations. This may involve conducting regular compliance audits to identify potential gaps in security or data handling practices and implementing corrective measures to address any issues.
Additionally, ERP vendors often offer compliance support as part of their services, helping businesses configure their systems to meet regulatory requirements. This support can be invaluable in ensuring that the ERP system is properly set up to handle sensitive data in a compliant manner and that any necessary audit trails or documentation are maintained.
Best Practices for Successful Omnichannel ERP Implementation
Define Clear Business Goals
Align ERP Implementation with Your Overall Omnichannel Strategy
One of the most important aspects of a successful omnichannel ERP implementation is ensuring that the system is aligned with the company’s broader omnichannel strategy. The core purpose of omnichannel ERP is to integrate various business processes—such as inventory management, customer service, finance, and sales—across all sales and communication channels. However, the benefits of this integration can only be realized if the ERP system is deployed with clear business goals that complement the company’s long-term strategy.
To begin with, businesses need to assess how their existing omnichannel strategy functions and what improvements are needed. This involves evaluating the current customer experience across different channels (eCommerce, in-store, mobile, social media), identifying bottlenecks in supply chain management or customer service, and understanding how information flows between departments. Once the pain points and areas of improvement are clear, these findings should guide the ERP system’s implementation.

For example, if the business’s omnichannel strategy includes providing a seamless shopping experience where customers can transition smoothly between online and offline stores, the ERP system should be configured to ensure that data from all customer touchpoints is available in real-time across departments. This will enable store associates, customer service representatives, and marketing teams to access the same customer information, providing a consistent and personalized experience. Furthermore, the ERP system should support inventory visibility across all channels, ensuring that a product purchased online can easily be picked up in-store or returned through any channel.
By aligning the ERP implementation with the overarching omnichannel goals, businesses can create a system that enhances efficiency, drives better collaboration between departments, and supports a unified customer journey across all channels. Failing to align these goals may result in a system that addresses only certain operational needs without fully supporting the omnichannel vision, leading to gaps in service and inefficiencies.
Set Measurable KPIs for Success
In addition to aligning the ERP system with broader business objectives, it’s crucial to establish measurable KPIs that can track the system’s effectiveness and overall success. Setting clear KPIs ensures that the ERP implementation is not just a technical upgrade, but a strategic initiative that delivers tangible business benefits. These KPIs should focus on areas such as improved customer experience, reduced operational costs, and increased revenue, as these are often the key drivers of omnichannel ERP investments.
- Improved Customer Experience: The ability to deliver a consistent and seamless customer experience across channels is a key benefit of omnichannel ERP systems. To measure success in this area, businesses can track customer satisfaction metrics such as Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer retention rates, and overall feedback from post-purchase surveys. Additionally, metrics such as reduced customer service response times, fewer complaints related to order fulfillment, and the ability to handle more complex returns or exchanges across different channels can serve as indicators of improved customer service through the ERP system. A well-implemented omnichannel ERP should facilitate faster, more accurate responses to customer inquiries, enhance personalization by providing access to complete customer profiles, and streamline order processing, regardless of the channel in which a customer interacts.
- Reduced Operational Costs: One of the primary reasons businesses implement ERP systems is to streamline operations and reduce costs. For omnichannel ERP, this can involve optimizing inventory management, reducing the costs associated with stockouts or overstocking, and improving supply chain efficiency. By providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, automating reorder processes, and integrating data from multiple warehouses and retail locations, omnichannel ERP systems can significantly reduce operational inefficiencies. KPIs in this area might include tracking the reduction in inventory carrying costs, a decrease in order processing times, and improvements in supply chain lead times. Another important KPI is labor cost savings achieved through automation, as ERP systems can reduce the need for manual data entry and human intervention in routine tasks, freeing up staff to focus on higher-value activities.
- Increased Revenue: Ultimately, a successful omnichannel ERP implementation should contribute to revenue growth by enhancing sales channels and improving overall business performance. Businesses can measure the impact of the ERP system on revenue by tracking metrics such as increased sales from omnichannel customers (those who shop across multiple platforms), higher average order values, and improved conversion rates. Additionally, the ERP system’s ability to support personalized marketing and promotions—based on unified customer data—can lead to increased customer engagement and higher sales. Tracking revenue growth attributed to these omnichannel strategies, along with increases in repeat purchases and cross-channel upselling, will demonstrate the system’s direct contribution to business profitability.
Setting measurable KPIs also allows businesses to conduct ongoing performance reviews, ensuring that the ERP system continues to meet evolving business needs. Regularly assessing the system against these KPIs enables businesses to make adjustments where necessary—whether through system updates, further customization, or changes in internal processes—ensuring that the ERP implementation delivers long-term value.
Choose the Right ERP Vendor
Evaluate Vendors
Scalability is a crucial factor when selecting an ERP vendor, especially for businesses operating in an omnichannel environment where growth can happen quickly as new sales channels are introduced. The chosen omnichannel ERP system must be able to scale in line with the business’s growth, allowing for the integration of additional sales platforms, customer engagement tools, and back-end processes without compromising system performance or functionality.
For example, a retailer that starts with an online store and a few brick-and-mortar locations may eventually expand into mobile apps, third-party marketplaces, or international markets. The ERP system must be capable of handling this expansion, providing the flexibility to add new channels seamlessly. Scalability also refers to the system’s ability to manage increasing transaction volumes, larger customer databases, and more complex supply chain operations as the business grows. A scalable ERP ensures that as business operations become more intricate, the system can still provide real-time insights and maintain efficient workflows without requiring a complete overhaul or replacement.

When evaluating ERP vendors for scalability, businesses should look at the vendor’s track record with other clients in similar industries. For instance, if the ERP provider has successfully implemented scalable systems for large, multi-channel retailers or rapidly growing eCommerce brands, it demonstrates their ability to support businesses as they expand. In addition, businesses should assess the ERP system’s modular architecture—the ability to add or remove functionalities as needed. A modular system allows businesses to start with the essential features they need at the outset and gradually add more advanced modules as they grow, such as advanced analytics, warehouse management, or multi-location inventory tracking.
Another consideration is the cloud versus on-premise deployment model. Cloud-based ERP systems are inherently more scalable, allowing businesses to increase storage, computing power, and functionalities as needed without investing in additional hardware. For businesses expecting rapid growth, cloud-based omnichannel ERP solutions often offer the flexibility and scalability required to keep pace with expanding operations. Moreover, cloud solutions typically offer automatic updates and patches, ensuring the system remains up to date with the latest features and security measures.
Consider Customization Options, Support Services, and the Industry Expertise
While scalability is essential, businesses must also consider the customization options offered by ERP vendors to ensure that the system can be tailored to their specific needs. No two businesses operate in exactly the same way, and the ability to customize the ERP system is crucial for aligning it with existing workflows, industry-specific requirements, and unique operational processes.
For example, a company in the retail sector may need custom integrations with specific eCommerce platforms, payment gateways, or logistics providers, while a manufacturing business may require custom modules for production planning and inventory management. The ERP vendor should provide robust customization capabilities, allowing businesses to configure the system according to their particular needs. This may include custom dashboards, role-based access controls, and integrations with third-party applications that the business relies on for day-to-day operations.
When assessing customization options, businesses should also consider the long-term implications of customizations. While tailoring the system to fit specific workflows is beneficial, excessive customization can lead to challenges when it comes to upgrading the system or applying software patches. As such, it’s important to choose an ERP vendor that offers flexible customization options without compromising the system’s upgradeability or stability over time. Businesses should inquire about the vendor’s approach to customization, whether it involves configuration through built-in tools or custom coding, and what level of ongoing support is available for maintaining these customizations.

In addition to customization, support services provided by the ERP vendor play a vital role in ensuring long-term success. Implementing an omnichannel ERP system is not a one-time event—it requires continuous support, updates, and potential troubleshooting as the system evolves with the business. The vendor’s post-implementation support services are critical for addressing any issues that arise, from system glitches to performance optimization. Vendors that offer comprehensive support packages—including 24/7 technical support, regular system health checks, and proactive performance monitoring—can ensure that the system continues to function smoothly and efficiently.
Training services are also a key component of vendor support. As employees are trained on how to use the omnichannel ERP system, the vendor’s ability to provide role-specific training materials, on-site or remote training sessions, and ongoing education ensures that the workforce is fully equipped to use the system effectively. Businesses should seek out vendors that prioritize customer success and offer robust training and support frameworks that empower employees to adapt to the new system.
Finally, the vendor’s industry expertise is a critical factor in selecting the right ERP provider. Every industry has unique challenges, regulations, and workflows that must be taken into account during ERP implementation. For example, a business in the healthcare industry will have very different requirements than a retailer, especially in terms of compliance with data protection regulations like HIPAA or managing supply chains for medical products. A vendor with deep knowledge of the specific industry can provide invaluable insights, offer tailored solutions, and implement best practices based on their experience with other businesses in the same field.
When evaluating ERP vendors, businesses should inquire about the vendor’s experience with similar companies. Have they successfully implemented omnichannel ERP systems for other businesses in your industry? Do they understand the challenges your business faces, such as complex regulatory environments or industry-specific operational workflows? Vendors with strong industry expertise can help businesses avoid common pitfalls and ensure a smoother, more effective implementation process.
Plan for Integration with Existing Systems
Ensuring Smooth Data Migration
One of the most critical aspects of adopting an omnichannel ERP system is ensuring a smooth data migration from existing systems to the new ERP platform. Many businesses already operate with multiple systems, such as standalone inventory management tools, financial software, CRM systems, and eCommerce platforms, all of which contain vital data that needs to be transferred to the ERP system. This data is essential for ensuring that the new ERP system functions correctly and can support omnichannel operations without disrupting day-to-day activities.
Data migration is often a complex and time-consuming process, as it involves transferring large amounts of data—such as customer records, transaction histories, inventory levels, and financial reports—from legacy systems to the omnichannel ERP. Ensuring that this process is done accurately and efficiently is crucial, as any errors or data loss during migration can lead to operational disruptions, such as incorrect inventory counts, missing customer orders, or delayed financial reporting.

To minimize the risk of disruptions, businesses should thoroughly plan the data migration process well in advance of the ERP system’s go-live date. This involves mapping out all existing data sources, cleaning and standardizing data to ensure consistency, and determining the best approach for transferring the data into the new system. In many cases, businesses may need to engage with ERP implementation consultants or IT professionals who specialize in data migration to ensure that the process goes smoothly.
A key part of this planning involves data validation—verifying the accuracy and completeness of data before, during, and after the migration. By conducting tests and audits throughout the migration process, businesses can ensure that the data transferred to the omnichannel ERP system is correct and that no critical information has been lost or corrupted. For example, validating inventory data across multiple warehouses ensures that stock levels are accurate and reflect real-time availability across all sales channels. Similarly, validating customer data ensures that all records, purchase histories, and preferences are correctly imported into the ERP’s CRM module.
In addition to data validation, businesses should consider using a phased migration approach, where data is migrated in stages rather than all at once. This allows businesses to test smaller batches of data first, ensuring that each part of the system is functioning correctly before proceeding with the full migration. A phased approach helps minimize the risk of operational disruptions and gives businesses the flexibility to address any issues before they escalate.
Throughout the migration process, businesses should also plan for contingency measures to ensure business continuity. This includes having backup copies of all critical data and a detailed rollback plan in case any major issues arise during migration. By anticipating potential challenges and having contingency plans in place, businesses can minimize downtime and ensure a smooth transition to the new system.
Focus on Integrating with Critical Systems
A key benefit of implementing an omnichannel ERP system is its ability to integrate all critical business functions under a single platform, thereby eliminating data silos and improving operational efficiency. However, for this benefit to be realized, the ERP system must be properly integrated with existing critical systems such as CRM, inventory management, and eCommerce platforms.
One of the most common challenges businesses face is the existence of data silos, where information is isolated in separate systems and not easily accessible across departments. For example, a company might use one system for managing online orders, another for tracking in-store sales, and yet another for managing customer interactions. Without proper integration, these systems may not communicate with one another, leading to fragmented data, inconsistent reporting, and operational inefficiencies.
The goal of an omnichannel ERP system is to unify all business data in a centralized platform, ensuring that every department has access to the same information in real time. For this to happen, the ERP system must be integrated with critical systems such as CRM tools, which house customer data and interaction histories, and inventory management systems, which track product availability across warehouses and sales channels.
Integrating the ERP system with a CRM platform is particularly important for providing a seamless customer experience. With a unified CRM-ERP integration, sales and customer service teams can access real-time data about customer orders, preferences, and previous interactions across all channels. This integration enables businesses to provide personalized customer service and marketing, as the ERP system can feed customer insights into ongoing campaigns or tailor product recommendations based on historical purchase behavior. Without this integration, customer data remains siloed, limiting the ability of teams to collaborate effectively and deliver a cohesive experience across touchpoints.
In addition to CRM integration, inventory management plays a critical role in the success of an omnichannel strategy. Ensuring that the ERP system is integrated with real-time inventory management tools allows businesses to accurately track stock levels across multiple locations and sales channels. This integration helps prevent stockouts and overstocking, improves order fulfillment accuracy, and allows for more efficient allocation of inventory across different channels. For example, when a customer places an online order for in-store pickup, the system can automatically check inventory levels in both the warehouse and the nearest store to ensure that the item is available and ready for pickup. Without proper integration, inventory discrepancies can lead to delayed orders, stockouts, or missed sales opportunities.
eCommerce platforms are another critical area for integration. Many businesses operate multiple eCommerce sites, marketplaces, and digital channels, each generating large amounts of sales and customer data. Integrating these platforms with the omnichannel ERP system ensures that all sales data is automatically captured, processed, and reflected in other systems, such as CRM, inventory management, and financial reporting. This allows businesses to gain a holistic view of their sales performance across all digital channels and make informed decisions about marketing strategies, inventory planning, and customer service.
Additionally, businesses should focus on integrating the ERP system with supply chain management tools, especially if they operate in industries with complex logistics and procurement needs. By integrating supply chain data into the ERP system, businesses can optimize procurement, manage supplier relationships more effectively, and reduce lead times for key products. This integration also allows for real-time visibility into order statuses, shipping delays, and supplier performance, ensuring that businesses can respond quickly to disruptions in the supply chain.
To ensure successful integration with these critical systems, businesses should work closely with their ERP vendor and implementation partners to develop a comprehensive integration strategy. This includes mapping out how data flows between systems, setting up APIs or middleware to facilitate communication between platforms, and conducting rigorous testing to ensure that all integrations function correctly.
Invest in Employee Training
Provide Training for Employees Across All Departments
A successful omnichannel ERP implementation relies heavily on employee adoption. Since the ERP system impacts nearly every department in a business—ranging from sales and marketing to operations, finance, and customer service—each team must understand how to use the system to perform their specific tasks efficiently. To facilitate this, businesses should provide comprehensive, hands-on training that equips employees with the skills and knowledge they need to navigate the system with confidence.
Comprehensive training goes beyond basic system tutorials. It involves delivering role-specific instruction that focuses on how the omnichannel ERP system integrates with each department’s daily operations. For example, the sales team needs training on how to access real-time inventory data, manage customer orders, and track sales performance, while the finance team requires a deep understanding of how the ERP system automates financial reporting, manages invoices, and tracks revenue across multiple channels. Providing role-based training ensures that employees can directly apply what they learn to their job functions, which enhances both adoption and productivity.

Hands-on training is particularly important because it allows employees to familiarize themselves with the ERP system in real-world scenarios. Rather than simply watching demonstrations or reading manuals, employees should have the opportunity to practice using the system in a controlled environment. This could involve simulations of common tasks, such as processing customer orders, managing inventory transfers, or generating financial reports. By actively engaging with the system, employees can develop a deeper understanding of its functionality, identify areas where they need further clarification, and build confidence in their ability to use the ERP platform effectively.
Additionally, ERP training should be delivered in phases to ensure that employees are not overwhelmed with too much information at once. The training program should start with basic system navigation and core functionalities, and gradually introduce more advanced features as employees become comfortable with the system. This approach helps to ease the learning curve and allows employees to absorb the material at their own pace. For example, employees might first be trained on how to enter data into the system, and then later learn how to generate reports, access dashboards, and interpret analytics.
It is also critical to ensure that training covers how the omnichannel ERP system supports cross-departmental workflows. One of the main benefits of an ERP system is its ability to unify data and processes across various departments, providing a seamless flow of information between teams. To fully realize this benefit, employees must understand not only how to use the system for their own tasks but also how their work impacts other departments. For example, the operations team needs to know how inventory data entered into the system affects the sales team’s ability to fulfill customer orders. Likewise, the customer service team needs access to the ERP system’s CRM functionality to resolve issues related to orders, returns, or product availability. By fostering a collaborative mindset, businesses can ensure that all employees are aligned with the company’s omnichannel goals and can use the system to improve cross-departmental communication and efficiency.
Offer Ongoing Support and Resources
While initial training is crucial for system adoption, it is equally important to provide ongoing support and resources to ensure that employees continue to develop their proficiency with the omnichannel ERP system. As the ERP system evolves—with new updates, features, or integrations—employees will need continuous learning opportunities to stay up to date and make the most of the system’s capabilities.
A key component of ongoing support is the establishment of a help desk or dedicated IT support team that employees can contact when they encounter issues or have questions about the ERP system. This provides employees with a reliable source of assistance, ensuring that minor issues do not escalate into larger operational disruptions. A help desk can also track common user questions and challenges, allowing businesses to identify areas where additional training may be needed.
In addition to real-time support, businesses should provide online resources such as tutorials, knowledge bases, and FAQs that employees can access on-demand. These resources are especially valuable for new employees who need to learn the system or for existing staff who want to refresh their knowledge on specific features. Online tutorials and interactive guides that walk users through step-by-step processes can help employees troubleshoot common issues and learn how to use advanced features independently. This self-service model encourages continuous learning and reduces the reliance on direct IT support, empowering employees to become more self-sufficient in their use of the ERP system.
Regular refresher training sessions or workshops can also help employees stay proficient with the system over time. As the omnichannel ERP system is updated with new functionalities or as business processes evolve, employees may need additional training to keep their skills current. Hosting periodic workshops or training webinars ensures that employees remain engaged with the system and are aware of any new features that could enhance their productivity. These sessions also provide an opportunity for employees to ask questions, share their experiences, and discuss best practices for using the system effectively.
Moreover, creating a culture of peer-to-peer learning can enhance system adoption and proficiency across departments. Businesses can identify “power users” or ERP champions who have demonstrated a high level of expertise with the system and encourage them to mentor other employees. This peer support network allows employees to learn from one another and gain insights into how different teams are leveraging the ERP system to solve challenges. It also fosters a collaborative environment where employees feel more comfortable seeking help and sharing tips for using the system more efficiently.
Lastly, as businesses grow and add new employees, onboarding new staff to the omnichannel ERP system becomes a continuous process. Having a structured onboarding program that includes ERP training ensures that new hires can quickly get up to speed and contribute to the organization’s goals without lengthy delays. Incorporating ERP training into the onboarding process also sets clear expectations for how employees will interact with the system and reinforces the importance of its role in the company’s overall operations.
Prioritize Customer-Centric Features
Focus on Enhancing the Customer Experience
One of the key benefits of omnichannel ERP systems is their ability to enhance the customer experience by integrating data and processes across various touchpoints, including physical stores, eCommerce platforms, mobile apps, and customer service channels. In an omnichannel environment, customers expect a seamless and consistent experience whether they are shopping online, visiting a store, or interacting with customer service. By prioritizing customer-centric features within the omnichannel ERP system, businesses can meet these expectations and deliver a high level of service that strengthens customer loyalty and drives repeat business.
A critical aspect of improving the customer experience through omnichannel ERP systems is the ability to provide personalized interactions. Modern customers expect brands to understand their preferences, anticipate their needs, and deliver tailored recommendations based on their past interactions. Omnichannel ERP systems make this possible by centralizing customer data from all channels, including purchase histories, browsing behavior, engagement with marketing campaigns, and interactions with customer support. With this integrated data, businesses can create detailed customer profiles that enable them to offer personalized product suggestions, targeted promotions, and customized offers based on individual customer preferences.

For example, if a customer frequently purchases a certain category of products through an eCommerce platform but visits physical stores for other purchases, the ERP system can track this behavior and provide personalized promotions when they visit the store. Similarly, if a customer’s browsing history indicates an interest in a particular product, the ERP system can trigger targeted email campaigns or in-app notifications with recommendations or special offers for that product. This level of personalization not only enhances the shopping experience but also increases the likelihood of conversions and fosters stronger customer relationships.
Beyond personalization, omnichannel ERP systems enable businesses to offer seamless service across all channels, ensuring that customers can transition smoothly between platforms without encountering inconsistencies. For instance, a customer might begin their shopping journey by researching products online, place an order through a mobile app, and then pick up the product at a physical store. With an omnichannel ERP system, businesses can track the customer’s journey across all these touchpoints, ensuring that each interaction is informed by previous ones. Whether a customer contacts customer service to check the status of their order, or visits a store to inquire about product availability, the system provides employees with access to real-time customer data, enabling them to offer a more informed and responsive service.
A well-integrated omnichannel ERP system can also improve the post-purchase experience, allowing customers to return or exchange products through any channel, regardless of where the original purchase was made. This flexibility is increasingly important in modern retail, as customers expect convenience and consistency in how they engage with a brand. By unifying inventory management, order processing, and customer service data, the ERP system makes it easy for businesses to accommodate returns, exchanges, and customer inquiries, improving overall customer satisfaction.
Ensure the ERP System Supports Real-Time Data Tracking
Another critical feature of omnichannel ERP systems is their ability to provide real-time data tracking, which is essential for delivering responsive and efficient customer service. In an omnichannel environment, where customers interact with businesses through multiple platforms, having access to real-time data ensures that businesses can meet customer needs quickly and accurately, regardless of where or when the interaction occurs.
Real-time data tracking is especially important in managing inventory and order fulfillment across multiple channels. For example, when a customer places an online order for in-store pickup, the ERP system must immediately update inventory levels to reflect the sale and reserve the product for that customer. If a product is out of stock in one location but available in another, the system can automatically update inventory availability and offer alternative fulfillment options, such as shipping from another warehouse or store. By providing accurate, up-to-date information on product availability, omnichannel ERP systems help prevent stockouts, reduce order cancellations, and improve overall customer satisfaction.
Additionally, real-time data tracking allows businesses to respond more quickly to customer inquiries. For instance, if a customer contacts customer service to inquire about the status of their order, the ERP system can provide immediate visibility into the order’s progress, from processing to shipping to delivery. This not only improves the customer’s experience but also reduces the time and effort required for customer service representatives to locate and provide the necessary information.
Real-time tracking also plays a crucial role in managing customer relationships and maintaining high levels of satisfaction. With a unified view of customer interactions, sales teams and customer service representatives can access the most up-to-date information on each customer, including recent orders, service requests, and feedback. This enables them to offer more personalized service and address issues promptly. For example, if a customer has recently experienced a delay in receiving their order, the ERP system can flag this issue and trigger a follow-up action, such as offering a discount on a future purchase or expediting the next shipment to ensure a positive customer experience.
In the context of customer support, real-time data tracking ensures that support teams have access to the latest information on every aspect of the customer’s journey. Whether a customer is contacting support about a product they purchased online or seeking help with a product warranty in-store, the ERP system provides a complete view of their history, allowing support teams to offer faster and more accurate solutions. This level of responsiveness not only enhances customer satisfaction but also builds trust in the brand.
Moreover, businesses can leverage real-time data from the omnichannel ERP system to make informed decisions about customer service strategies and improvements. For instance, businesses can analyze patterns in customer inquiries, feedback, and returns to identify potential issues in the supply chain or product offerings. By using this data to address pain points proactively, businesses can improve the overall customer experience and reduce the need for reactive customer service interventions.
Conclusion
The adoption of omnichannel ERP has become essential for businesses seeking to maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly interconnected and customer-driven marketplace. By unifying data and processes across various sales channels—whether in-store, online, or through mobile—omnichannel ERP systems offer unparalleled efficiency and real-time visibility into business operations. These systems streamline workflows, enhance customer satisfaction through personalized interactions, and enable businesses to adapt swiftly to the changing demands of a digital-first world. The ability to centralize data across departments such as sales, inventory, finance, and customer service fosters collaboration, reduces errors, and ultimately drives greater business performance. The importance of omnichannel ERP cannot be overstated, as it allows businesses to meet the evolving expectations of customers who demand consistent, high-quality experiences regardless of where or how they engage with a brand.
Implementing omnichannel ERP is not just a technological upgrade—it is a strategic initiative that can drive competitive advantage in a rapidly evolving marketplace. Businesses that invest in the right omnichannel ERP system and follow best practices, such as aligning the ERP with business goals, providing comprehensive employee training, and ensuring seamless integration with existing systems, will be well-positioned to capitalize on the benefits of a unified business platform. Omnichannel ERP enables businesses to operate more efficiently, respond to customer needs in real-time, and gain actionable insights from data across all departments. This holistic approach not only reduces operational costs but also enhances the customer experience, leading to increased revenue and brand loyalty. As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of omnichannel operations, those that prioritize the adoption of an omnichannel ERP system will be better equipped to adapt, compete, and thrive in the future.