Growing businesses ultimately reach a point where spreadsheets are no longer adequate. That’s where enterprise resource planning software comes in: ERP systems gather and organize critical business data, allowing firms to operate lean, efficient operations even as they grow.
Many business professionals have known about ERP, however, they may not fully comprehend what enterprise resource planning solutions can achieve for their organizations. This blog will fully explain what ERP is, how it works, what it can do for your organization, and how to select the best system.
Table of Contents
What is ERP?
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a process used by organizations to manage and integrate the parts such as planning, purchasing, inventory, sales, marketing, finance, human resources, and more. ERP systems assist them in implementing resource planning by unifying all of the operations required to manage their businesses into a single system.
What is an ERP system and how does it work?
ERP system is a type of software used by businesses to handle day-to-day company activities such as accounting, procurement, project management, risk management and compliance, and supply chain operations. A comprehensive enterprise resource planning package also contains enterprise performance management software, which aids in the planning, budgeting, forecasting, and reporting of an organization’s financial outcomes.
An ERP system works by reducing the number of resources required to manage a firm properly while yet maintaining profitability and growth. The ERP system differs from a single application in that it allows your company’s other enterprise modules to share a single database.
The system gathers information from many aspects of the company. It centralizes the data so that employees who require it may access it. It breaks down the silos that plague many firms and ensures that appropriate information is available to those who want it.
Almost every ERP system is nearly completely automated. It conducts the data input in the backend for you and exchanges the information with other units that require it.
For example, when a shipping order is placed for the final item in stock, the inventory management modules must record this information and notify the appropriate departments so that the inventory may be replaced. The sales staff will also be notified so that it does not make promises it cannot keep.
Outstanding benefits of an ERP
Cost savings
Businesses can reduce mistakes and the need to hire new employees at the same rate as the company grows thanks to repetitive operations. Cross-company insight makes it simpler to identify inefficiencies that drive up costs and lead to improved resource deployment across the board. And, with cloud ERP, businesses may immediately discover added value from the software that exceeds what they are spending.
Streamline workflow
Employees with enterprise resource planning system access may manage the status of projects and tasks. This visibility may be very important to managers and leaders, and it is significantly faster and easier than finding the correct papers and asking colleagues for updates.
Reporting and analytics
Leading systems provide powerful reporting and analytics features that enable users to measure KPIs and present any metrics or comparisons. Because an ERP is all-encompassing, it may assist a firm in understanding how a change or problem with a process in one department impacts the rest of the organization.
Data security
ERP vendors recognize that your system contains essential, sensitive data and take the necessary precautions to keep it safe. As the number and scale of cyberattacks rise, this vigilance is more critical than ever. Cloud ERP software employs cutting-edge security mechanisms to ensure that your business is not the victim of a harmful attack.
Reduce risk
Financial controls may be strengthened and fraud reduced through granular access control and established approval protocols. Furthermore, more precise data prevents errors that might result in missed sales or fines. Finally, being able to observe the state of the whole operation allows staff to immediately deal with dangers caused by business disruptions.
Enhance Collaboration
Employees perform best when they cooperate. Enterprise resource planning solutions make it simple to transfer information among teams, such as purchase orders, contracts, and customer-support records. It breaks through departmental barriers by providing employees with real-time data on relevant business operations.
Scalability
The perfect ERP system will be scalable and adaptable enough to meet your company’s demands and expansion in the future. Cloud systems, in particular, adapt to minor and substantial operational changes as the amount of data captured by the business grow and the demand for access grows.
Flexibility
While ERP software assists firms in adhering to standard practices, it also allows for the support of unique procedures and objectives. Administrators may use the system to develop company-specific processes and automated reporting for various departments and executives. An enterprise resource planning solution boosts your company’s innovation and creativity.
Manage External relationship
An ERP system may help a company’s connections with its partners and customers. It may give information on suppliers, shipping carriers, and service providers, with the cloud allowing for even better and more easy information interchange. When it comes to consumers, the system can track survey replies, support requests, refunds, and other information so that the business can keep a pulse on client happiness.
3 Types of ERP Systems
On-premise
These systems are installed on your own servers, so you have more control over them. They’re usually more expensive than cloud-based enterprise resource planning systems, but they’re also more customizable and often have better security.
Cloud-based
These systems are hosted on the cloud, so they’re accessible from anywhere. They’re also usually more affordable than on-premises ERP systems. However, they can be less customizable and may have poorer security. Cloud ERP is becoming the most preferred deployment technique for a variety of reasons, including fewer upfront costs, more scalability and agility, simpler integration, and much more.
Hybrid
These systems combine the best of both worlds, with some components being hosted on the cloud and others being installed on-premises. They can be more expensive than both cloud-based and on-premises ERP systems, but they offer the most flexibility.
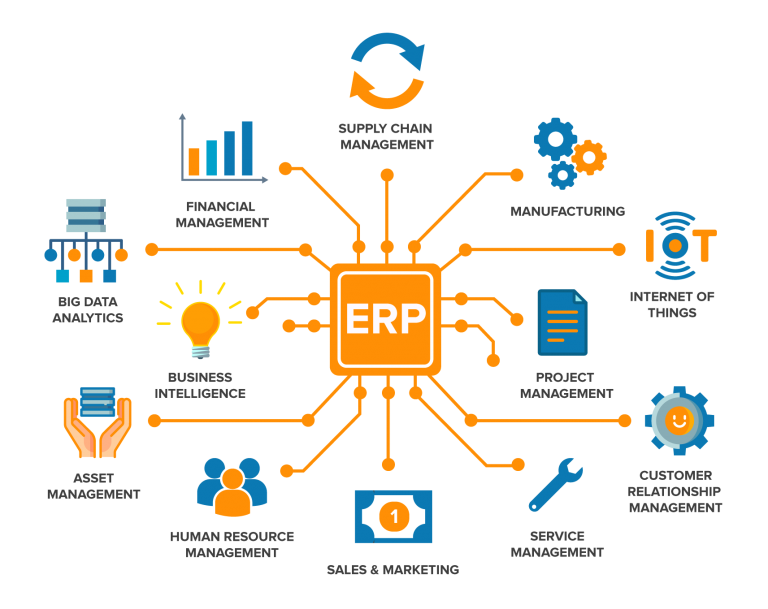
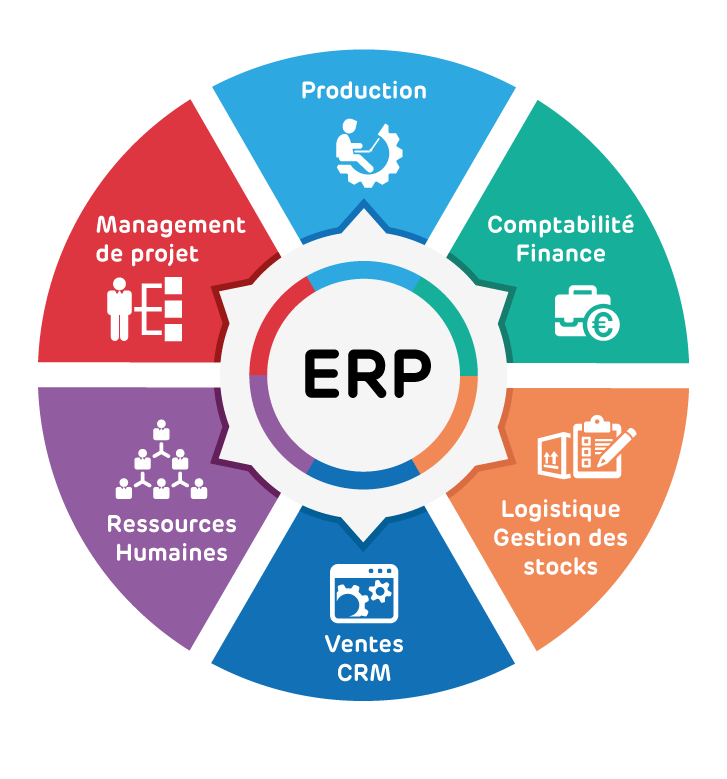
Must-have modules of an ERP system
Enterprise resource planning systems consist of a number of modules that allow for the efficient and effective management of business operations. Some of the most commonly used ERP modules include:
- Financial management: This module covers all aspects of financial management, including budgeting, accounting, and financial reporting.
- Human resources management: This module helps organizations to manage employee records, payroll, and benefits.
- Sales and marketing: This module aids in the management of customer data, sales processes, and marketing campaigns.
- Supply chain management: This module helps organizations to manage their supply chains, from procurement to delivery.
- Manufacturing: This module helps organizations to manage production processes and inventory.
Enterprise resource planning modules can be customized to meet the specific needs of a business. In addition, many ERP vendors offer add-on modules that provide additional functionality. For example, a company may need a financial reporting module that is not included in the standard ERP system. In these cases, the vendor will likely have a partner that can provide the required module.
ERP systems are an important part of business operations, and the modules listed above are some of the most commonly used. When selecting an ERP system, it is important to consider the needs of the organization and ensure that the system has the required modules.
Fundamental features of ERP systems
There are many different enterprise resource planning systems on the market, each with its own unique features and capabilities. However, all ERP systems share some common features that can be beneficial for businesses of all sizes.
Some of the most common features of ERP systems include:
- Centralized database: As mentioned above, one of the key features of ERP systems is their centralized database. This allows businesses to store all of their data in one place, making it easier to access and manage. Additionally, it can help businesses avoid duplication of data and ensure accuracy of information.
- Process automation: ERP systems often include tools that automate business processes, such as order management, invoicing, and shipping. This can help businesses save time and improve efficiency.
- Reporting tools: ERP systems come with a variety of reporting tools that allow businesses to track their performance. This can help businesses make informed decisions about their operations and identify areas for improvement.
ERP examples in different industries
Manufacturing
ERP systems are used to manage production lines and inventory. This allows manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in demand and keep up with shifting market conditions. Enterprise resource planning systems can also help reduce the amount of stock that is held in inventory, leading to lower costs and improved cash flow.
Retail
In the retail industry, ERP systems are used to manage store operations and inventory. This allows retailers to provide better customer service by having the right products in stock and being able to respond quickly to changes in customer demand. Enterprise resource planning systems can also help retailers streamline their back-end operations, leading to improved efficiency and reduced costs.
Banking and financial services
ERP systems can help banks and financial institutions manage their customer accounts, track financial transactions, and monitor compliance with regulatory requirements. Additionally, banks and financial institutions can easily generate reports on customer activity and risk exposure with ERP software.
Healthcare
Enterprise resource planning systems can help hospitals and other healthcare organizations manage their patient records, track inventory levels, and manage supplier and customer relationships. Healthcare organizations can use ERP systems to generate reports on patient activity and performance.
Education
Educational institutions often use ERP software to manage their student records, track financial transactions, and monitor compliance with regulatory requirements. It can provide educational institutions with the ability to generate reports on student activity and performance.
Transport and logistics
Companies can track and control their freight shipping and delivery operations, track inventory levels, and manage supplier and customer relationships. Generating reports on freight shipping and delivery activity is more effective with organizations using ERP systems.
Food and beverage
Besides generating reports and analyzing data, food and beverage companies can manage their production operations, track inventory levels, and manage supplier and customer relationships.
Government and public sector
ERP systems can assist government agencies to control and track their financial resources, tracking inventory levels, and managing supplier and customer relationships.
Choose ERP systems based on business size
Small business
Despite the many benefits that ERP systems offer businesses of all sizes, small businesses often find them to be cost-prohibitive. This is because the smaller the company, the less bargaining power it has when negotiating a price with a software vendor. In addition, small businesses may not have the IT staff on hand to install and maintain an ERP system, further adding to the cost.
Medium-sized businesses
Medium-sized businesses are in a much better position to take advantage of ERP systems. They usually have more negotiating power with software vendors and the IT staff necessary to install and maintain the system. In addition, medium-sized businesses often have more complex operations than small businesses, making an ERP system more beneficial.
Large businesses
Large businesses are the most likely to take full advantage of ERP systems, as they have the resources necessary to implement and maintain them. In addition, large businesses often have complex operations that can benefit greatly from an ERP system.
ERP system implementation
Stages of ERP Implementation
ERP systems are often large and complex, making their implementation a multi-stage process. Here are the four main stages of ERP implementation:
1. Planning
2. Implementation
3. Testing
4. Deployment/ Rollout
Planing
An effective plan properly ensures the success of the project. During this phase, you will develop a clear understanding of your business needs and objectives. You will also need to select the right ERP system for your organization and put together a team of experts to help with the implementation.
Implementation
This stage can be broken down into several sub-stages, including system setup, data migration, and testing. It’s important to take your time and make sure everything is done correctly so that the system works properly and meets your needs.
Testing
This stage is vital to ensure that the ERP system is functioning as expected. This stage typically includes user and system testing, and regression testing to make sure that no previous problems have been created by the new system.
Deployment/ Rollout
After testing to ensure that your ERP system doesn’t have any mistakes, the technical team will go live with your system. During this stage, you will need to provide training for your employees and make any necessary changes to your business processes. You will also need to ensure that the system is functioning properly and meeting your needs.
Cost of ERP system
The cost of ERP system implementation can vary depending on a number of factors. Some of the main factors that can impact the cost of ERP system implementation include:
- Size and complexity of the organization
- Scope of the project
- Functionality required
- Number of users involved
- Geographical location
- Provider chosen
- Duration of the project
The cost of ERP system implementation can also vary depending on whether the organization is implementing the system in-house or outsourcing the project to a third-party provider. In-house implementations are typically more expensive, as the organization will need to purchase and configure the hardware and software and hire and train staff to use the system. Outsourcing the project to a third-party provider can reduce costs, as the provider will typically have experience with ERP system implementations and can offer a more efficient and cost-effective solution.
Takeaways
When considering the use of ERP system implementation, it is important to consider the long-term benefits of the system. ERP systems can improve organizational efficiency, help to optimize business processes and provide a single source of truth for data. The benefits of an ERP system often outweigh the costs of implementation, making it a worthwhile investment for organizations.
If you are considering choosing an appropriate ERP system, just connect to Magenest. As a digital transformation expert having seasoned experience in ERP implementation and corporate with famous partners, namely Odoo and Adobe, Magenest will give you the ultimate solution for your company. Let’s contact our team to have more beneficial information!