In today’s fast-paced and interconnected retail landscape, omnichannel fulfillment has become a pivotal strategy for businesses aiming to meet and exceed customer expectations. As consumers increasingly demand a seamless and cohesive shopping experience across multiple platforms, the ability to deliver products and services efficiently and consistently through various channels has never been more crucial.
Omnichannel fulfillment represents the future of retail, offering a comprehensive and integrated approach to meet the demands of the modern consumer. This comprehensive blog post explores the depth and breadth of omnichannel fulfillment, providing a detailed examination of its definition, scope, and importance in the modern retail environment. We will delve deeper into the various aspects of omnichannel fulfillment, providing insights, case studies, and best practices to help businesses navigate this critical area and achieve long-term success.
Table of Contents
- Omnichannel Fulfillment: Definition and Key Concepts
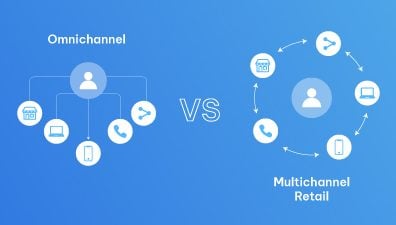
- Omnichannel Fulfillment vs. Omnichannel Retail vs. Omnichannel Distribution
- Core Components of Omnichannel Fulfillment: Detailed Analysis
- Challenges in Implementing Omnichannel Fulfillment
- Best Practices for Successful Omnichannel Fulfillment
- Future Trends in Omnichannel Fulfillment
- Case Studies of Successful Omnichannel Fulfillment
Omnichannel Fulfillment: Definition and Key Concepts
Definition and Scope of Omnichannel Fulfillment
Omnichannel fulfillment refers to the integrated approach businesses use to manage and deliver customer orders across multiple sales channels, including online platforms, physical stores, mobile applications, and more. This strategy aims to provide a seamless and cohesive customer experience, ensuring that shoppers receive consistent service regardless of the channel they choose to interact with. The scope of omnichannel fulfillment is extensive, covering various aspects such as real-time inventory management, advanced order processing systems, efficient logistics, and enhanced customer service.
The definition of omnichannel fulfillment highlights its holistic nature. It goes beyond simply having multiple channels to ensuring these channels are interconnected and work in harmony. This means that an order placed online can be fulfilled by a physical store, or a return initiated through a mobile app can be processed in-store. The key is integration and synchronization, which allows for a unified view of inventory, orders, and customer interactions.
Omnichannel fulfillment encompasses the idea of breaking down silos within a business. Traditionally, online and offline channels might have operated independently, leading to inefficiencies and inconsistencies in customer experience. With omnichannel fulfillment, all channels are part of a single, cohesive system. This integration requires advanced technology and robust processes to ensure that information flows seamlessly between channels, enabling businesses to respond quickly to customer needs and market changes.
Importance in the Modern Retail Landscape
The importance of omnichannel fulfillment in the modern retail landscape cannot be overstated. Consumer behavior has dramatically shifted in recent years, with shoppers expecting a seamless experience across all touchpoints. The rise of eCommerce, mobile shopping, and social media has created a more complex retail environment where customers interact with brands through multiple channels. As a result, businesses must adapt their fulfillment strategies to meet these new expectations.
Omnichannel fulfillment services are crucial for maintaining competitive advantage. In today’s market, customers value convenience, speed, and reliability. They want the flexibility to order products online and pick them up in-store, or to return items purchased online to a physical location. Businesses that can provide these options are more likely to attract and retain customers. For example, omni-channel fulfillment strategies like buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS) or ship-from-store can significantly enhance the shopping experience by offering more convenience and reducing delivery times.
Moreover, omnichannel fulfillment examples demonstrate how businesses can optimize their operations to reduce costs and increase efficiency. By having a unified view of inventory across all channels, companies can better manage stock levels, avoid overstocking or stockouts, and make more informed decisions about replenishment. This not only improves operational efficiency but also leads to better customer satisfaction as products are more likely to be available when and where customers want them.
Components of Omnichannel Fulfillment
Inventory Management
Inventory management is a cornerstone of omnichannel fulfillment. Effective inventory management ensures that products are available across all channels, reducing the risk of stockouts and overstocking. Real-time inventory tracking is essential, allowing businesses to have an up-to-date view of stock levels at all times. This visibility enables better decision-making and ensures that inventory is allocated efficiently to meet customer demand.

One of the key strategies in inventory management is the use of advanced systems like Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Order Management Systems (OMS). These systems integrate with each other and with other business processes to provide a comprehensive view of inventory. For instance, a WMS can help optimize the storage and retrieval of products in a warehouse, while an OMS can manage orders from multiple channels, ensuring that inventory is updated in real-time.
Order Processing
Order processing in an omnichannel fulfillment strategy involves managing orders from multiple channels and ensuring they are processed quickly and accurately. This requires a robust OMS that can handle orders from online stores, mobile apps, and physical stores. The OMS should be able to route orders to the appropriate fulfillment center or store, based on factors like inventory availability, location, and delivery speed.
Automation plays a significant role in order processing. Automated systems can quickly process orders, generate picking lists, and update inventory levels. This reduces the risk of errors and speeds up the fulfillment process, ensuring that customers receive their orders promptly. Additionally, automation can help manage complex order scenarios, such as split shipments or backorders, providing a seamless experience for the customer.
Delivery
Delivery is a critical component of omnichannel fulfillment, directly impacting customer satisfaction. Businesses need to offer multiple delivery options to meet different customer needs, such as standard shipping, express delivery, and same-day delivery. The goal is to provide flexibility and convenience, allowing customers to choose the option that best suits their needs.

Efficient logistics and transportation management are essential for successful delivery. Transportation Management Systems (TMS) can help optimize delivery routes, reduce transportation costs, and ensure timely deliveries. These systems use data analytics to plan the most efficient routes, taking into account factors like traffic, weather, and delivery windows.
Moreover, partnerships with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) can enhance delivery capabilities. 3PLs offer expertise in logistics and can provide additional resources and infrastructure to support omnichannel fulfillment. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses looking to expand their delivery options or enter new markets.
Returns Management
Returns management is another crucial aspect of omnichannel fulfillment. A seamless returns process is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty. Customers should be able to return products through any channel, whether they purchased online or in-store. This requires a unified returns policy and system that can handle returns efficiently, ensuring that the process is quick and hassle-free for the customer. Effective returns management involves several key elements:
- Unified Returns Policy: Establishing a consistent returns policy across all channels helps streamline the returns process and set clear expectations for customers.
- Returns Processing Systems: Utilizing advanced systems to manage returns, including automated return labels, real-time updates on return status, and integration with inventory management systems to update stock levels accordingly.
- Reverse Logistics: Efficiently managing the transportation and processing of returned items to minimize costs and maximize recovery value. This includes refurbishing, repackaging, or redistributing returned products.
- Customer Communication: Keeping customers informed throughout the returns process, from initiating the return to receiving their refund or replacement, helps build trust and satisfaction.
Omnichannel Fulfillment vs. Omnichannel Retail vs. Omnichannel Distribution
While these concepts are interconnected, each plays a distinct role in the overall strategy of delivering products and services efficiently and effectively. This section delves into the definitions, core principles, and customer experience focus of each concept, with a particular emphasis on omnichannel fulfillment.
Omnichannel Fulfillment
Omnichannel fulfillment is a comprehensive strategy that integrates various sales channels and coordinates backend logistics to ensure a seamless and efficient customer experience. It encompasses both customer-facing and backend processes, ensuring that orders are processed and delivered accurately and timely across all channels.
Key Features:
- Unified Customer Experience: Ensuring consistency in branding, messaging, and service levels across online stores, physical retail locations, mobile apps, and more.
- Integrated Technology Systems: Utilizing advanced technologies such as CRM, OMS, WMS, and TMS to integrate sales channels and streamline operations.
- Real-Time Data and Analytics: Leveraging real-time data for inventory management, demand forecasting, and decision-making.
- Flexible Fulfillment Options: Offering a range of fulfillment options such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), same-day delivery, and ship-from-store.
- Scalable Operations: Ensuring fulfillment processes can scale with demand fluctuations and seasonal trends.
- Collaboration with Partners: Partnering with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) to extend reach and enhance capabilities.
Omnichannel Retail
Omnichannel retail focuses primarily on the customer-facing aspects of the shopping experience across multiple channels. It aims to provide a cohesive and integrated experience for customers, ensuring that they can interact with the brand seamlessly, whether online, in-store, or via mobile.
Key Features:
- Unified Shopping Experience: Providing consistency in product offerings, pricing, and promotions across all channels.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Leveraging customer data to personalize interactions and enhance the shopping experience.
- Seamless Channel Integration: Allowing customers to transition between channels effortlessly, such as starting a purchase on a mobile app and completing it in-store.
- Flexible Fulfillment: Offering various fulfillment options to meet customer preferences, enhancing convenience and satisfaction.
- Real-Time Engagement: Engaging with customers through live chat, social media, and in-store assistance to address queries and provide support.
Omnichannel Distribution
Omnichannel distribution focuses on the backend logistics and supply chain activities required to deliver products to customers across multiple channels. It ensures that products are available where and when they are needed, optimizing the movement of goods from suppliers to customers.
Key Features:
- Integrated Logistics Network: Creating a cohesive network of warehouses, distribution centers, and transportation modes to fulfill orders efficiently.
- Real-Time Data and Analytics: Using data analytics for inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics optimization.
- Flexible Supply Chain: Developing a supply chain that can adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands.
- Scalability: Ensuring the distribution network can scale with demand fluctuations and seasonal trends.
- Collaboration with Partners: Partnering with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) to enhance distribution capabilities and extend reach.
Key Differences
- Scope and Focus:
- Omnichannel Fulfillment: Integrates both customer-facing and backend logistics processes to ensure seamless order processing and delivery across all channels.
- Omnichannel Retail: Focuses primarily on the customer experience, ensuring a unified and consistent interaction with the brand across various channels.
- Omnichannel Distribution: Concentrates on the logistics and supply chain activities necessary to deliver products to customers efficiently.
- Technology Integration:
- Omnichannel Fulfillment: Relies heavily on integrated technology systems (CRM, OMS, WMS, TMS) to coordinate sales channels and streamline operations.
- Omnichannel Retail: Uses technology to enhance the customer experience through personalization and seamless channel transitions.
- Omnichannel Distribution: Utilizes logistics and supply chain technologies to optimize the movement of goods and manage inventory effectively.
- Customer Experience:
- Omnichannel Fulfillment: Ensures a seamless and efficient order fulfillment process, enhancing customer satisfaction through timely and accurate deliveries.
- Omnichannel Retail: Prioritizes a cohesive and personalized shopping experience across all customer touchpoints.
- Omnichannel Distribution: Focuses on maintaining inventory availability and ensuring timely deliveries to support the overall customer experience.
- Operational Goals:
- Omnichannel Fulfillment: Aims to create a unified operation that integrates all aspects of retail and distribution to meet customer demands efficiently.
- Omnichannel Retail: Seeks to provide a consistent and engaging customer experience across multiple sales channels.
- Omnichannel Distribution: Strives to optimize logistics and supply chain operations to ensure products are delivered where and when they are needed.
While omnichannel fulfillment, omnichannel retail, and omnichannel distribution are interconnected concepts, each serves distinct roles in enhancing the overall customer experience and operational efficiency. Omnichannel fulfillment integrates customer-facing and backend logistics processes to ensure seamless order processing and delivery. Omnichannel retail focuses on creating a unified and engaging shopping experience across multiple channels. Omnichannel distribution concentrates on the logistics and supply chain activities necessary to deliver products efficiently. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses looking to implement effective omnichannel strategies and stay competitive in the modern retail landscape.
Core Components of Omnichannel Fulfillment: Detailed Analysis
The success of omnichannel fulfillment hinges on several critical components that work together to provide a seamless and efficient customer experience. Among these, effective inventory management stands out as a key pillar, encompassing real-time inventory tracking and optimization across various sales channels. By mastering these elements, businesses can ensure they meet customer demands promptly while maintaining operational efficiency.
Inventory Management
The key aspects of inventory management in an omnichannel context include real-time inventory tracking and inventory optimization across channels.
Real-Time Inventory Tracking
Real-time inventory tracking is essential for maintaining accurate stock levels and ensuring that products are available when and where customers need them. This component of omnichannel fulfillment involves continuously monitoring inventory across all sales channels—online stores, physical retail locations, and mobile platforms—to provide a unified view of stock levels.

What is omnichannel fulfillment without real-time inventory tracking? It would be a fragmented and inefficient system where discrepancies between available and actual stock could lead to customer dissatisfaction, lost sales, and increased operational costs. Real-time tracking helps mitigate these issues by:
- Providing Accurate Stock Data: Ensuring that inventory data is up-to-date across all channels prevents situations where customers order products that are out of stock, thereby enhancing the shopping experience.
- Reducing Stockouts and Overstocks: By maintaining a real-time view of inventory, businesses can avoid stockouts, which lead to lost sales, and overstocks, which tie up capital and increase holding costs.
- Enabling Quick Decision-Making: Real-time data allows businesses to make informed decisions regarding reordering and stock transfers, ensuring that inventory levels are optimized.
Omnichannel fulfillment services often leverage advanced technologies such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags, IoT (Internet of Things) sensors, and integrated software solutions to facilitate real-time inventory tracking. These technologies help in gathering accurate data and automating updates across all platforms.
One of the omnichannel fulfillment examples of successful real-time inventory tracking is Walmart’s implementation of RFID technology in their supply chain. This technology provides Walmart with precise and immediate updates on inventory levels, allowing them to maintain optimal stock levels and improve customer satisfaction through better availability of products.
Inventory Optimization Across Channels
Inventory optimization is another critical component of omnichannel fulfillment. It involves strategically managing inventory across multiple channels to ensure that the right products are available at the right locations, thereby meeting customer demands efficiently.
Omni-channel fulfillment requires a sophisticated approach to inventory optimization, considering factors such as demand forecasting, lead times, and customer preferences. Here are some key strategies for inventory optimization:
- Centralized Inventory Management: A unified inventory management system that consolidates data from all sales channels can provide a comprehensive view of stock levels, enabling more effective inventory allocation and reducing the risk of stock imbalances.
- Dynamic Stock Allocation: Utilizing predictive analytics and AI to forecast demand allows businesses to dynamically allocate inventory to different channels based on predicted sales. This ensures that high-demand products are readily available where they are most needed.
- Safety Stock Management: Maintaining appropriate levels of safety stock across channels to buffer against unexpected spikes in demand or supply chain disruptions. This ensures continuity in order fulfillment without excessive overstocking.
- Cross-Channel Fulfillment: Enabling flexibility in order fulfillment by allowing inventory from one channel (e.g., physical stores) to fulfill orders from another channel (e.g., online store). This reduces the pressure on individual warehouses and leverages the entire network for efficient fulfillment.
Omnichannel order fulfillment is greatly enhanced by effective inventory optimization. For instance, Zara, the fast-fashion retailer, employs a highly efficient inventory optimization strategy that allows it to respond quickly to changing fashion trends. By using real-time data and predictive analytics, Zara can ensure that its inventory is aligned with current consumer demands, reducing markdowns and stockouts.
The omnichannel fulfillment meaning is deeply tied to the ability to manage and optimize inventory across all channels effectively. Without this capability, the promise of a seamless customer experience cannot be fulfilled. Therefore, businesses investing in omnichannel fulfillment strategy must prioritize real-time inventory tracking and optimization to achieve operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Order Processing
Key aspects of order processing in an omnichannel context include streamlining order fulfillment and leveraging automation in order processing.
Streamlining Order Fulfillment
Streamlining order fulfillment is essential for meeting the demands of modern consumers who expect quick and reliable service. In the context of omni-channel fulfillment, this involves coordinating orders from multiple sales channels—online stores, physical retail locations, mobile apps, and more—to ensure a seamless and efficient process.

Omnichannel fulfillment definition involves the integration of various channels to provide a cohesive customer experience. Streamlining order fulfillment in this context includes several strategies:
- Centralized Order Management: Utilizing a unified order management system (OMS) that consolidates orders from all channels into a single platform. This allows for real-time visibility into order status, inventory levels, and fulfillment progress, enabling efficient handling of orders.
- Efficient Order Routing: Implementing intelligent order routing to determine the best fulfillment location based on factors such as proximity to the customer, inventory levels, and delivery speed. This reduces shipping times and costs, improving overall efficiency.
- Flexible Fulfillment Options: Offering customers a range of fulfillment options, such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), same-day delivery, and ship-from-store services. Providing multiple fulfillment options caters to diverse customer preferences and enhances their shopping experience.
- Optimized Picking and Packing: Streamlining the picking and packing process in warehouses and stores by using advanced technologies such as barcode scanning, automated sorting systems, and efficient packing algorithms. This minimizes errors and speeds up the fulfillment process.
Omnichannel fulfillment examples of streamlined order fulfillment include major retailers like Amazon and Walmart, which have developed sophisticated systems to ensure quick and accurate order processing. For instance, Amazon’s use of robotics in its warehouses allows for efficient picking and packing of orders, reducing fulfillment times and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Automation in Order Processing
Automation plays a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of order processing within the omnichannel fulfillment framework. By automating various aspects of order processing, businesses can reduce manual errors, accelerate fulfillment, and optimize resource allocation.
What is omnichannel fulfillment without automation? It would be an inefficient and error-prone process that struggles to keep up with the demands of modern retail. Automation in order processing includes several key components:
- Automated Order Entry: Using electronic data interchange (EDI) and other automated systems to capture and process orders from various channels instantly. This eliminates the need for manual entry, reducing the risk of errors and speeding up the order initiation process.
- Automated Inventory Updates: Ensuring real-time updates of inventory levels as orders are processed. Automated systems can immediately adjust stock levels, preventing overselling and ensuring accurate availability information across all channels.
- Automated Picking Systems: Implementing automated picking solutions such as robotic picking systems, conveyor belts, and automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS). These technologies enhance the speed and accuracy of the picking process, reducing fulfillment times.
- Automated Packaging and Labeling: Using automated packing machines and labeling systems to prepare orders for shipment. Automated systems can select appropriate packaging materials, pack items securely, and print shipping labels accurately, reducing manual labor and errors.
- Automated Order Tracking and Notifications: Providing customers with real-time updates on their order status through automated notifications. These updates can include order confirmation, shipping status, and delivery tracking, enhancing transparency and customer satisfaction.
The omnichannel fulfillment meaning is closely tied to the effective use of automation in order processing. Automation not only streamlines operations but also enables businesses to scale their fulfillment capabilities, handle peak demand periods, and maintain high levels of accuracy and efficiency.
Omnichannel fulfillment services that leverage automation can significantly enhance the customer experience. For example, the use of automated order tracking systems allows customers to receive timely updates on their orders, providing reassurance and reducing the likelihood of inquiries or complaints.
Omnichannel fulfillment strategy must prioritize the integration of automation technologies to achieve optimal results. By investing in automated systems, businesses can ensure that their order processing is efficient, scalable, and capable of meeting the demands of modern consumers.
Shipping and Delivery
Key aspects of shipping and delivery in an omnichannel context include multi-channel delivery strategies and same-day and/or next-day delivery options.
Multi-Channel Delivery Strategies
Multi-channel delivery strategies are essential for ensuring that customers receive their orders through their preferred delivery channels. In an omni-channel fulfillment system, businesses must coordinate deliveries across various channels, including online stores, physical retail locations, and mobile platforms. The goal is to provide a seamless and efficient delivery experience, regardless of the sales channel.

Omnichannel fulfillment definition includes the ability to manage and deliver orders from multiple sources in a cohesive manner. Implementing effective multi-channel delivery strategies involves several key elements:
- Integrated Delivery Networks: Establishing a network of warehouses, distribution centers, and retail stores that work together to fulfill orders. By leveraging physical store locations as mini-distribution centers, businesses can reduce delivery times and costs.
- Flexible Shipping Options: Offering customers a range of shipping options, such as standard delivery, expedited shipping, and store pickup. Providing these options caters to different customer preferences and enhances the overall shopping experience.
- Cross-Channel Coordination: Ensuring that delivery processes are synchronized across all channels. This includes real-time updates on order status, inventory availability, and delivery tracking. A centralized order management system (OMS) can facilitate this coordination by providing a unified view of all orders and deliveries.
- Last-Mile Delivery Solutions: Partnering with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) and using advanced last-mile delivery solutions to optimize the final leg of the delivery process. This ensures that orders reach customers quickly and efficiently, even in densely populated urban areas.
Omnichannel fulfillment examples of successful multi-channel delivery strategies include companies like Walmart and Target. Walmart’s Ship from Store program utilizes its extensive network of retail locations to fulfill online orders, reducing delivery times and leveraging existing inventory. Target’s same-day delivery service, facilitated through its partnership with Shipt, provides customers with fast and flexible delivery options.
Same-Day and/or Next-Day Delivery Options
Same-day and/or next-day delivery options are becoming increasingly important in the competitive retail landscape. Modern consumers expect fast delivery times, and businesses that can meet these expectations gain a significant advantage. In the context of omnichannel fulfillment, offering same-day and/or next-day delivery requires advanced logistics and efficient processes.
What is omnichannel fulfillment without fast delivery options? It would be incomplete, as quick delivery is a key component of providing a superior customer experience. Implementing same-day and/or next-day delivery involves several strategies:
- Optimized Inventory Placement: Strategically placing inventory in locations that are closest to the customer base. This reduces the distance that products need to travel, enabling faster delivery. Businesses can use data analytics to identify high-demand areas and ensure that popular items are stocked nearby.
- Efficient Order Processing: Streamlining the order processing workflow to minimize delays. This includes automated order entry, real-time inventory updates, and efficient picking and packing processes. Automation technologies, such as robotics and AI-driven systems, can significantly speed up these processes.
- Dynamic Routing: Using advanced transportation management systems (TMS) to optimize delivery routes in real-time. Dynamic routing algorithms can consider factors such as traffic conditions, delivery windows, and vehicle capacity to ensure that deliveries are made as quickly and efficiently as possible.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborating with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) that specialize in same-day and/or next-day delivery. These partners often have established networks and expertise in fast delivery, allowing businesses to offer these services without significant internal investment.
Omnichannel fulfillment services that include same-day and/or next-day delivery are exemplified by companies like Amazon and Zara. Amazon’s Prime service offers same-day and/or next-day delivery on a wide range of products, setting a high standard for fast delivery. Zara, known for its fast fashion model, uses a combination of local distribution centers and efficient logistics to offer quick delivery options, ensuring that customers receive the latest fashion trends promptly.
The omnichannel fulfillment meaning is closely tied to the ability to provide flexible and fast delivery options. Same-day and/or next-day delivery not only meet customer expectations but also enhance competitiveness and drive sales. Businesses that can effectively implement these delivery options within their omnichannel fulfillment strategy gain a significant edge in the market.
Returns Management
Key aspects of returns management in an omnichannel context include efficient returns processing and understanding the impact on customer satisfaction.
Efficient Returns Processing
Efficient returns processing is crucial for maintaining a smooth and responsive omnichannel fulfillment operation. In an omni-channel fulfillment system, returns can originate from multiple sales channels, including online stores, physical retail locations, and mobile platforms. To handle these returns effectively, businesses need a well-coordinated approach that minimizes delays and reduces costs.
Omnichannel fulfillment definition includes the capability to manage returns seamlessly across all channels. Implementing efficient returns processing involves several strategies:
- Centralized Returns Management System: Utilizing a centralized system to track and manage returns from all channels. This system should provide real-time updates on return status, inventory levels, and customer interactions. An integrated order management system (OMS) can facilitate this coordination, ensuring a unified view of all returns.
- Automated Returns Authorization: Implementing an automated returns authorization process that allows customers to initiate returns online or in-store quickly. Automated systems can validate returns based on purchase history, product condition, and return policies, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Streamlined Logistics: Coordinating the logistics of returns to ensure that returned items are quickly processed and restocked. This involves using advanced transportation management systems (TMS) to optimize return shipping routes and reduce transit times. Efficient logistics can minimize the impact of returns on inventory levels and sales.
- Flexible Return Options: Offering customers multiple return options, such as returning items in-store, via mail, or through designated drop-off points. Providing flexible return options enhances customer convenience and satisfaction.
- Inspection and Restocking: Implementing efficient inspection and restocking processes to handle returned items. Automated inspection systems can assess the condition of returned products, while integrated warehouse management systems (WMS) can ensure that items are restocked or routed for refurbishment quickly.
Omnichannel fulfillment examples of efficient returns processing include retailers like Nordstrom and Zappos. Nordstrom offers a seamless returns process that allows customers to return items in-store or by mail, with instant credit refunds for qualifying returns. Zappos, known for its customer-centric approach, provides free return shipping and a 365-day return policy, ensuring a hassle-free returns experience for customers.
Impact on Customer Satisfaction
The impact of returns management on customer satisfaction is significant. Efficient and customer-friendly returns processes can enhance customer loyalty and drive repeat business, while cumbersome or restrictive returns policies can deter future purchases and harm the brand’s reputation.
What is omnichannel fulfillment without considering the customer experience in returns management? It would be incomplete, as returns are a critical touchpoint in the customer journey. Understanding the impact on customer satisfaction involves several considerations:
- Ease of Returns: Providing a simple and straightforward returns process is essential for customer satisfaction. Clear return policies, easy-to-follow instructions, and minimal steps for initiating returns can significantly improve the customer experience.
- Quick Refunds: Ensuring that customers receive refunds promptly after returning items enhances trust and satisfaction. Automated refund processing systems can expedite this process, reducing waiting times and improving customer perceptions.
- Transparency and Communication: Keeping customers informed about the status of their returns through automated notifications and real-time updates builds transparency and trust. Clear communication about return policies, timelines, and refund processes is crucial for managing customer expectations.
- Personalized Service: Offering personalized assistance for returns, such as live chat support or dedicated customer service representatives, can help resolve issues quickly and enhance the overall returns experience. Personalized service demonstrates a commitment to customer satisfaction and can turn potentially negative experiences into positive ones.
- Impact on Brand Loyalty: A well-managed returns process can strengthen brand loyalty by showing customers that the business values their satisfaction. Positive returns experiences can lead to higher customer retention rates and increased word-of-mouth referrals.
Omnichannel fulfillment services that prioritize customer satisfaction in returns management are exemplified by companies like Amazon and Costco. Amazon’s hassle-free returns policy allows customers to return items easily through various channels, with quick refunds and transparent communication. Costco, known for its customer-centric approach, offers a generous return policy with no time limits on most products, ensuring that customers feel confident in their purchases.
The omnichannel fulfillment is closely tied to the ability to provide efficient and customer-friendly returns management. By prioritizing ease of returns, quick refunds, transparency, and personalized service, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and build long-term loyalty.
Technology Enablers in Omnichannel Fulfillment
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are essential for optimizing warehouse operations, ensuring that inventory is managed efficiently, and orders are fulfilled accurately.
Features and Benefits:
- Inventory Control: Real-time tracking of inventory levels across multiple locations, reducing the risk of stockouts and overstock situations.
- Order Picking Optimization: Advanced algorithms for picking, packing, and shipping orders efficiently. This includes support for various picking methods such as wave picking, batch picking, and zone picking.
- Labor Management: Tracking and optimizing labor productivity by assigning tasks and monitoring performance. This ensures that warehouse operations run smoothly and efficiently.
- Automation Integration: Integration with automated systems such as conveyor belts, robotic pickers, and automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS) to enhance operational efficiency.
Integration with Other Systems:
- Order Management Systems (OMS): Seamless integration with OMS to ensure that orders are processed and fulfilled accurately. This includes real-time updates on order status and inventory levels.
- Transportation Management Systems (TMS): Coordinating with TMS to optimize shipping routes and reduce delivery times. This integration ensures that orders are delivered efficiently and cost-effectively.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Linking with CRM systems to provide accurate order status updates to customers and enhance overall customer service. Omnichannel fulfillment examples of successful WMS implementation include Amazon and Walmart. Amazon’s sophisticated WMS integrates with its robotic systems to streamline warehouse operations, ensuring quick and accurate order fulfillment. Walmart uses WMS to manage inventory across its vast network of stores and distribution centers, optimizing stock levels and reducing delivery times.
Order Management Systems (OMS)
Order Management Systems (OMS) are crucial for coordinating orders from multiple sales channels and ensuring that they are processed accurately and efficiently.
Key Functionalities:
- Centralized Order Processing: Consolidating orders from online stores, physical retail locations, and mobile platforms into a single system. This provides a unified view of all orders and facilitates efficient processing.
- Inventory Management: Real-time tracking of inventory levels and automatic updates based on order status. This ensures that stock levels are accurate and up-to-date across all channels.
- Order Routing: Intelligent order routing to determine the best fulfillment location based on factors such as proximity to the customer, inventory levels, and delivery speed. This reduces shipping times and costs.
- Returns Management: Streamlining the returns process by providing real-time updates on return status, inventory levels, and customer interactions. This enhances the overall returns experience and improves operational efficiency.
- Importance: The importance of OMS in omnichannel fulfillment cannot be overstated. It ensures that orders are processed quickly and accurately, reducing the risk of errors and delays. By providing real-time visibility into order status and inventory levels, OMS enables businesses to make informed decisions and optimize their fulfillment processes.
Omnichannel fulfillment services that utilize OMS include companies like Nordstrom and Target. Nordstrom’s OMS integrates with its inventory and customer management systems to provide a seamless shopping experience, allowing customers to check product availability, place orders, and manage returns easily. Target’s OMS coordinates orders from its online store and physical locations, ensuring efficient processing and delivery.
Transportation Management Systems (TMS)
Transportation Management Systems (TMS) are vital for optimizing delivery routes and reducing shipping costs, ensuring that orders are delivered efficiently and cost-effectively.
Optimizing Delivery Routes and Costs:
- Route Optimization: Advanced algorithms to determine the most efficient delivery routes, considering factors such as traffic conditions, delivery windows, and vehicle capacity. This reduces transit times and fuel costs.
- Carrier Management: Managing relationships with carriers and negotiating shipping rates to ensure cost-effective delivery. This includes real-time tracking of shipments and performance monitoring.
- Freight Auditing: Ensuring that shipping costs are accurately billed and identifying opportunities for cost savings. This includes auditing carrier invoices and resolving discrepancies.
- How TMS Affect Omnichannel Fulfillment: TMS plays a critical role in omnichannel fulfillment by ensuring that orders are delivered quickly and efficiently. By optimizing delivery routes and managing carrier relationships, TMS reduces shipping costs and enhances customer satisfaction. Additionally, TMS provides real-time visibility into shipment status, allowing businesses to keep customers informed and manage expectations. Omnichannel fulfillment examples of effective TMS implementation include companies like UPS and FedEx. UPS uses advanced TMS to optimize its delivery network, ensuring that packages are delivered quickly and cost-effectively. FedEx’s TMS integrates with its logistics systems to provide real-time tracking and efficient route planning, enhancing the overall delivery experience.
CRM
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are essential for enhancing customer communication and service, ensuring that customers have a positive experience throughout the fulfillment process.

Enhancing Customer Communication and Service:
- Order Status Updates: Providing real-time updates on order status, including order confirmation, shipping status, and delivery tracking. This keeps customers informed and reduces inquiries.
- Personalized Service: Using customer data to provide personalized recommendations, offers, and support. This enhances the overall shopping experience and builds customer loyalty.
- Customer Feedback: Collecting and analyzing customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and address issues promptly. This helps businesses improve their fulfillment processes and enhance customer satisfaction.
- Integration with Fulfillment Processes: Integrating CRM systems with fulfillment processes ensures that customer data is accurately reflected in order processing and delivery. This includes linking CRM with OMS, WMS, and TMS to provide a seamless flow of information and enhance overall efficiency. Omnichannel fulfillment services that leverage CRM systems include companies like Sephora and Apple. Sephora’s CRM integrates with its OMS and WMS to provide personalized service and real-time updates on order status. Apple’s CRM links with its logistics systems to ensure that customers receive timely updates and support throughout the fulfillment process.
Challenges in Implementing Omnichannel Fulfillment
Complexity of Integration
Integrating Multiple Channels and Systems
The complexity of integrating multiple channels and systems in an omni-channel fulfillment strategy involves several critical aspects:
System Compatibility:
- Different sales channels and backend systems often use varied technologies and platforms. Ensuring compatibility and smooth communication between these systems is essential for a cohesive omnichannel fulfillment operation.
- Businesses must invest in middleware solutions or integration platforms that can connect disparate systems, allowing them to work together seamlessly. These platforms act as a bridge, facilitating data exchange and process synchronization across all channels.
Unified Customer Experience:
- Creating a unified customer experience requires consistent branding, messaging, and service levels across all channels. This means integrating customer data, order history, and preferences into a single view accessible from any channel.
- Advanced Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems play a crucial role in this integration. By consolidating customer data from various touchpoints, businesses can provide personalized and consistent experiences across all interactions.
Real-Time Data Synchronization:
- Omnichannel fulfillment relies heavily on real-time data synchronization to ensure accurate inventory levels, order status updates, and delivery tracking. Any delay or discrepancy in data synchronization can lead to stockouts, overselling, and customer dissatisfaction.
- Implementing real-time data synchronization requires robust Order Management Systems (OMS) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) that can update data instantaneously across all channels.
Scalable Infrastructure:
- As businesses grow and add more sales channels, the complexity of integration increases. A scalable infrastructure that can accommodate additional channels and handle increased data volumes is crucial for long-term success.
- Cloud-based solutions offer scalability and flexibility, allowing businesses to expand their omnichannel fulfillment capabilities without significant infrastructure investments.
Vendor and Partner Coordination:
- Integrating with third-party vendors and logistics partners adds another layer of complexity. Coordinating with multiple partners to ensure timely and accurate fulfillment requires seamless data exchange and process alignment.
- Utilizing Transportation Management Systems (TMS) can help optimize delivery routes and coordinate with logistics partners, ensuring efficient and cost-effective fulfillment.
Omnichannel fulfillment examples of successful integration include companies like Zara and Best Buy. Zara’s integrated systems enable real-time inventory updates and efficient order processing across its online and physical stores. Best Buy’s use of advanced OMS and WMS ensures that customers receive consistent service and accurate information, regardless of the channel they use.
Overcoming Data Silos
Overcoming data silos is another critical challenge in implementing omnichannel fulfillment. Data silos occur when information is isolated within different departments or systems, leading to inefficiencies and a fragmented customer experience.

Omnichannel fulfillment involves the seamless flow of information across all channels and systems. Overcoming data silos requires addressing several key issues:
Centralized Data Management:
- Implementing a centralized data management strategy is essential for breaking down data silos. This involves consolidating data from various sources into a single repository that is accessible to all relevant departments and systems.
- Data warehousing solutions and enterprise data platforms can help centralize data and provide a unified view of information across the organization.
Data Integration Tools:
- Utilizing data integration tools and technologies can facilitate the seamless flow of information between systems. These tools enable businesses to extract, transform, and load (ETL) data from disparate sources into a unified format.
- Middleware solutions and API integrations play a crucial role in connecting different systems and ensuring data consistency.
Standardized Data Formats:
- Establishing standardized data formats and protocols ensures that data can be easily exchanged and understood across different systems. This includes defining common data structures, naming conventions, and communication protocols.
- Adopting industry standards, such as Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and XML, can streamline data integration and improve interoperability.
Data Governance:
- Implementing robust data governance practices is essential for maintaining data quality and consistency. This includes defining data ownership, establishing data stewardship roles, and implementing data validation and cleansing processes.
- Regular audits and monitoring of data quality help identify and address discrepancies, ensuring accurate and reliable information.
Cross-Functional Collaboration:
- Encouraging cross-functional collaboration and communication is vital for overcoming data silos. This involves fostering a culture of data sharing and transparency across departments.
- Implementing collaborative tools and platforms, such as intranets and shared databases, can facilitate information exchange and improve coordination.
Omnichannel fulfillment services that effectively overcome data silos include companies like Amazon and Target. Amazon’s centralized data management strategy ensures that customer data, inventory information, and order status are consistently updated across all channels. Target’s use of data integration tools and standardized protocols enables seamless information flow and a unified customer experience.
Omnichannel fulfillment strategy should prioritize the integration of multiple channels and systems while overcoming data silos to ensure a cohesive and efficient operation. By addressing these challenges, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve long-term success in the competitive retail landscape.
Cost Considerations
Initial Investment and Ongoing Operational Costs
Initial Investment:
- Technology Infrastructure: Establishing an effective omnichannel fulfillment system necessitates investing in advanced technology infrastructure, including Order Management Systems (OMS), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, and Transportation Management Systems (TMS). These systems are crucial for integrating various sales channels and ensuring real-time data synchronization. The cost of purchasing and implementing these systems can be significant, often running into millions of dollars for large enterprises. Small and medium-sized businesses may also face considerable expenses, although scaled-down versions of these systems are available to suit their needs.
- System Integration: Integrating multiple channels and systems is a complex process that requires substantial technical expertise and resources. Businesses must invest in middleware solutions, APIs, and custom integrations to ensure seamless communication between different platforms. The cost of system integration can vary widely depending on the complexity and number of systems involved. This process may also require ongoing support and maintenance to address any issues that arise.
- Physical Infrastructure: Developing a robust physical infrastructure is essential for omnichannel fulfillment. This includes setting up distribution centers, enhancing warehouse capabilities, and optimizing retail locations to serve as mini-distribution hubs. The cost of building or upgrading physical infrastructure can be substantial, encompassing real estate, construction, and equipment expenses.
- Training and Development: Training staff to manage and operate new systems and processes is critical for successful omnichannel fulfillment. This involves investing in comprehensive training programs to ensure employees are proficient in using advanced technologies and can adapt to new workflows. Training costs can include hiring specialized trainers, developing training materials, and compensating employees for their time spent in training.
Ongoing Operational Costs:
- Maintenance and Support: Maintaining and supporting the technology infrastructure is an ongoing expense. This includes software updates, hardware maintenance, and technical support to ensure systems run smoothly and efficiently. Businesses must budget for annual maintenance contracts, IT support staff, and potential system upgrades to keep their technology infrastructure current.
- Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management is crucial for omnichannel fulfillment. Businesses must invest in inventory optimization tools and practices to maintain optimal stock levels across all channels. Ongoing costs include inventory carrying costs, warehousing expenses, and investment in technologies like RFID tags and real-time tracking systems.
- Logistics and Transportation: Coordinating logistics and transportation across multiple channels involves significant operational costs. This includes expenses related to shipping, warehousing, and last-mile delivery. Partnering with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) can help manage these costs, but businesses must also invest in transportation management systems to optimize delivery routes and reduce expenses.
- Customer Service: Providing high-quality customer service is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction in an omnichannel environment. This involves staffing customer service teams, investing in CRM systems, and ensuring support is available across all channels. Ongoing costs include salaries for customer service representatives, subscription fees for CRM platforms, and training programs to keep staff updated on best practices.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Conducting a cost-benefit analysis is crucial for evaluating the financial viability of implementing omnichannel fulfillment. This involves comparing the initial investment and ongoing operational costs with the potential benefits to determine the overall value proposition.

Benefits of Omnichannel Fulfillment:
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Omnichannel fulfillment provides a seamless and integrated shopping experience, allowing customers to shop through their preferred channels and receive consistent service. This enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to increased sales and repeat business. Improved customer experience can also result in positive word-of-mouth referrals and higher customer retention rates.
- Increased Sales and Revenue: By offering multiple sales channels and flexible fulfillment options, businesses can capture a broader customer base and increase sales. The convenience of options like BOPIS and same-day delivery can drive higher conversion rates and average order values. Real-time inventory management and demand forecasting enable businesses to optimize stock levels, reducing stockouts and capturing more sales opportunities.
- Operational Efficiency: Advanced technology systems like OMS, WMS, CRM, and TMS streamline operations, reducing manual processes and minimizing errors. This leads to improved efficiency, lower operational costs, and faster order processing times. Efficient logistics and inventory management reduce carrying costs and optimize warehouse space utilization, contributing to cost savings.
- Competitive Advantage: Implementing a robust omnichannel fulfillment strategy provides a competitive edge in the market. Businesses that can offer a seamless and integrated shopping experience are better positioned to attract and retain customers compared to those with less sophisticated fulfillment systems. Staying ahead of competitors in terms of technology adoption and customer service can lead to long-term market leadership and profitability.
Cost-Benefit Analysis Example:
Consider a mid-sized retail business planning to implement omnichannel fulfillment. The initial investment includes technology infrastructure ($2 million), system integration ($500,000), physical infrastructure enhancements ($1 million), and training ($200,000). The total initial investment is $3.7 million.
Ongoing operational costs include maintenance and support ($300,000 per year), inventory management ($500,000 per year), logistics and transportation ($700,000 per year), and customer service ($400,000 per year). The total annual operational cost is $1.9 million.
Over five years, the total investment and operational costs amount to $3.7 million (initial) + $9.5 million (ongoing) = $13.2 million.
Potential benefits over five years include increased sales and revenue ($20 million), operational efficiency savings ($3 million), and enhanced customer loyalty and retention ($5 million). The total benefits amount to $28 million.
Comparing the total costs ($13.2 million) with the total benefits ($28 million) shows a net gain of $14.8 million, demonstrating a positive return on investment and validating the financial viability of the omnichannel fulfillment strategy.
In conclusion, implementing omnichannel fulfillment involves significant initial investment and ongoing operational costs. However, the potential benefits in terms of enhanced customer experience, increased sales, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage can outweigh these costs, leading to long-term profitability and success. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis helps businesses make informed decisions and develop a viable omnichannel fulfillment strategy that meets their goals and objectives.
Scalability Issues
Scaling Fulfillment Operations for Growing Businesses
Scaling fulfillment operations to meet the needs of a growing business is a complex endeavor that requires careful planning and robust infrastructure. Businesses must ensure that their omnichannel fulfillment systems can handle increased volumes without compromising efficiency or customer satisfaction.
As businesses grow, they will certainly face scalability issue; including but not limited to:
- Infrastructure Expansion: As businesses grow, they need to expand their physical infrastructure, including warehouses, distribution centers, and retail locations. This expansion requires significant investment in real estate, construction, and equipment. An efficient omnichannel fulfillment strategy necessitates strategically located facilities to minimize shipping times and costs. This can involve opening new warehouses closer to high-demand areas or repurposing existing retail spaces for fulfillment purposes.
- Technology Upgrades: Growing businesses must invest in advanced technology to support increased order volumes and complex logistics. This includes upgrading Order Management Systems (OMS), Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), and Transportation Management Systems (TMS). Scalable technology solutions, such as cloud-based platforms, provide the flexibility to expand capacity as needed without significant upfront costs. These systems can handle large volumes of data and transactions, ensuring seamless operation during growth spurts.
- Process Optimization: Scaling fulfillment operations requires continuous process optimization to maintain efficiency and reduce bottlenecks. Businesses must regularly review and refine their workflows, including order processing, picking, packing, and shipping. Implementing automation technologies, such as robotic picking systems and automated sorting machines, can enhance productivity and accuracy, allowing businesses to scale their operations effectively.
- Talent Acquisition and Training: Expanding fulfillment operations necessitates hiring additional staff and ensuring they are adequately trained. This includes warehouse workers, logistics coordinators, and customer service representatives. Investing in comprehensive training programs ensures that new hires are proficient in using advanced technologies and following optimized processes. Ongoing training and development help maintain high performance as the business scales.
- Vendor and Partner Coordination: As businesses scale, they often need to collaborate with additional vendors and logistics partners to meet increased demand. This requires effective coordination and communication to ensure timely and accurate fulfillment. Establishing strong relationships with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) can enhance scalability by leveraging their expertise and infrastructure. These partnerships allow businesses to expand their reach and capacity without significant internal investment.
Managing Peak Periods and Seasonal Demand
Managing peak periods and seasonal demand is a critical aspect of omnichannel fulfillment. Businesses must be prepared to handle sudden spikes in order volumes during holidays, sales events, and other peak times without compromising service quality. In order to correctly manage the fluctuation of the market, here are some of the actions businesses should take:
- Accurate Demand Forecasting: Effective demand forecasting is essential for anticipating peak periods and ensuring adequate inventory levels. Businesses must leverage historical sales data, market trends, and predictive analytics to forecast demand accurately. Advanced analytics tools can provide insights into customer behavior and purchasing patterns, allowing businesses to prepare for anticipated spikes in demand.
- Flexible Staffing: Managing peak periods requires a flexible workforce that can scale up or down as needed. Businesses must have strategies in place to hire temporary staff or reallocate existing employees to meet increased demand. Cross-training employees to perform multiple roles can enhance flexibility and ensure that critical tasks are covered during peak times. Partnering with staffing agencies can also provide access to a pool of temporary workers.
- Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management is crucial for meeting peak demand without stockouts or overstocks. Businesses must optimize their inventory levels, ensuring that high-demand products are readily available. Implementing just-in-time inventory practices and utilizing real-time inventory tracking systems can help maintain optimal stock levels. Collaborating with suppliers to ensure timely replenishment is also essential.
- Logistics and Transportation: Coordinating logistics and transportation during peak periods is challenging, requiring robust systems to manage increased order volumes and shipping demands. Businesses must optimize their delivery routes and ensure timely fulfillment. Utilizing advanced TMS and partnering with reliable logistics providers can enhance delivery efficiency. Implementing multiple fulfillment options, such as BOPIS and same-day delivery, can also help manage peak demand effectively.
- Customer Communication: Clear and proactive communication with customers is vital during peak periods to manage expectations and reduce potential dissatisfaction. Businesses must provide real-time updates on order status, shipping delays, and delivery timelines. Leveraging CRM systems to automate customer communication and provide personalized updates can enhance the overall customer experience during busy periods.
Omnichannel fulfillment in the context of scalability involves the ability to expand and contract operations efficiently to meet growing business needs and fluctuating demand. By addressing scalability issues and implementing robust strategies, businesses can ensure a seamless and efficient fulfillment process that enhances customer satisfaction and supports long-term growth.
Best Practices for Successful Omnichannel Fulfillment
Data-Driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision-making is essential for optimizing omnichannel fulfillment. By leveraging data analytics, businesses can gain valuable insights into inventory and order management, enabling them to make informed decisions that enhance efficiency and reduce costs. Additionally, predictive analytics plays a crucial role in demand forecasting, allowing businesses to anticipate customer needs and adjust their operations accordingly.
Leveraging Data Analytics for Inventory and Order Management
Effective inventory and order management are foundational elements of a successful omnichannel fulfillment strategy. Leveraging data analytics enables businesses to monitor inventory levels, streamline order processing, and ensure that products are available when and where customers need them.

Some key aspects of data analytics in Inventory and Order Management include:
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: Real-time inventory tracking is crucial for maintaining accurate stock levels across all channels. Advanced inventory management systems can provide up-to-date information on product availability, helping businesses avoid stockouts and overstock situations. Real-time data allows businesses to respond quickly to changes in demand, ensuring that popular items are always in stock. This capability is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and maximizing sales.
- Optimizing Stock Levels: Data analytics can help businesses optimize their stock levels by analyzing sales patterns, seasonal trends, and market conditions. By understanding which products are in high demand and which are not, businesses can adjust their inventory levels to meet customer needs efficiently. This optimization reduces holding costs and minimizes the risk of obsolete inventory, contributing to overall cost savings and improved profitability.
- Order Processing Efficiency: Leveraging data analytics in order processing can streamline workflows and reduce the time it takes to fulfill orders. Advanced order management systems (OMS) can automate various aspects of order processing, such as order entry, verification, and routing. Automation reduces manual errors and speeds up the fulfillment process, ensuring that orders are processed accurately and delivered on time. This efficiency is critical for maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Inventory Visibility Across Channels: Data analytics provides visibility into inventory levels across all sales channels, including online stores, physical retail locations, and distribution centers. This visibility enables businesses to allocate inventory strategically and fulfill orders from the most appropriate locations. By integrating data from multiple channels, businesses can offer flexible fulfillment options, such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), and ship-from-store. These options enhance the customer experience and drive sales.
Predictive Analytics in Demand Forecasting
Predictive analytics is a powerful tool for demand forecasting in omnichannel fulfillment. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, businesses can anticipate future demand and adjust their operations to meet customer needs proactively. Key aspects of predictive analytics in demand forecasting include:
- Understanding Customer Behavior: Predictive analytics helps businesses understand customer behavior by analyzing past purchasing patterns, browsing history, and demographic information. This understanding allows businesses to anticipate which products customers are likely to buy and when. By leveraging this information, businesses can tailor their marketing and sales strategies to target specific customer segments, enhancing the overall shopping experience and driving sales.
- Anticipating Seasonal Trends: Seasonal trends have a significant impact on demand, and predictive analytics can help businesses anticipate these fluctuations. By analyzing historical sales data, businesses can identify patterns and prepare for peak periods and seasonal demand. This anticipation enables businesses to stock up on high-demand products in advance, ensuring that they can meet customer needs during busy times. It also helps businesses avoid overstocking items that are less popular during certain seasons.
- Optimizing Supply Chain Operations: Predictive analytics can optimize supply chain operations by forecasting demand and aligning production and distribution activities accordingly. By understanding future demand, businesses can adjust their supply chain strategies to ensure timely and cost-effective fulfillment. This optimization reduces lead times and minimizes the risk of supply chain disruptions, contributing to a more efficient and resilient fulfillment operation.
- Enhancing Inventory Management: Predictive analytics enhances inventory management by providing insights into future demand for specific products. By understanding which items are likely to be in high demand, businesses can adjust their inventory levels to ensure availability. This proactive approach reduces the risk of stockouts and overstock situations, contributing to improved customer satisfaction and reduced inventory holding costs.
- Improving Customer Satisfaction: By anticipating customer needs and ensuring that products are available when and where they are needed, predictive analytics enhances customer satisfaction. This proactive approach to demand forecasting helps businesses meet customer expectations and build long-term loyalty. Providing a seamless and efficient shopping experience across all channels is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Omnichannel fulfillment in the context of data-driven decision-making involves utilizing data analytics and predictive analytics to optimize inventory and order management and anticipate customer demand. By leveraging these advanced technologies, businesses can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and provide a superior customer experience.
Customer-Centric Strategies
Enhancing Customer Experience Through Efficient Fulfillment
Efficient fulfillment is at the heart of a positive customer experience. Ensuring that orders are processed quickly, accurately, and delivered on time is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and trust. Efficient omnichannel fulfillment requires seamless integration across all channels, advanced technology, and well-coordinated logistics.

Key elements of efficient fulfillment include:
- Seamless Integration Across Channels: A unified approach to fulfillment ensures that customers have a consistent experience regardless of the channel they use. This involves integrating online stores, physical retail locations, mobile apps, and social media platforms into a cohesive system. Implementing advanced Order Management Systems (OMS) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) allows businesses to track orders and inventory in real-time, ensuring that products are available and delivered promptly.
- Advanced Technology: Leveraging technology is essential for efficient omnichannel fulfillment. This includes using automation to streamline order processing, picking, packing, and shipping. Technologies such as robotic pickers, automated sorting systems, and real-time tracking tools can significantly enhance the speed and accuracy of fulfillment operations.
- Well-Coordinated Logistics: Efficient logistics are critical for meeting delivery promises. Businesses must optimize their transportation management to ensure timely and cost-effective deliveries. Utilizing Transportation Management Systems (TMS) helps in planning optimal delivery routes, managing carrier relationships, and tracking shipments in real-time.
- Inventory Optimization: Maintaining optimal inventory levels is crucial for avoiding stockouts and overstock situations. By analyzing sales data and market trends, businesses can forecast demand and adjust their inventory accordingly. Real-time inventory tracking across all channels ensures that stock levels are accurate and up-to-date, enabling quick response to changes in demand.
- Flexible Fulfillment Options: Offering a variety of fulfillment options, such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), same-day delivery, and ship-from-store, enhances convenience for customers. Flexibility in fulfillment options allows customers to choose the method that best suits their needs, improving their overall shopping experience.
Personalization in Delivery Options
Personalization in delivery options is a powerful strategy for enhancing customer satisfaction in omnichannel fulfillment. By offering tailored delivery choices, businesses can cater to individual preferences and create a more engaging shopping experience. Key aspects of personalization in delivery options can be:
- Multiple Delivery Choices: Providing customers with various delivery options, such as standard shipping, expedited shipping, same-day delivery, and scheduled delivery, allows them to choose based on their urgency and convenience. Options like buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS) and curbside pickup offer additional flexibility, catering to customers who prefer to collect their orders at a convenient time and location.
- Personalized Delivery Windows: Allowing customers to select specific delivery windows ensures that their orders arrive at a time that suits their schedule. This reduces the likelihood of missed deliveries and enhances customer satisfaction. Real-time tracking and notifications keep customers informed about their order status and estimated delivery time, providing transparency and peace of mind.
- Customized Packaging and Presentation: Personalized packaging, such as gift wrapping or including personalized notes, can enhance the unboxing experience and make customers feel valued. Businesses can offer customization options at checkout, allowing customers to choose packaging styles or add personal touches to their orders.
- Subscription Services: Subscription services offer convenience and predictability for customers who regularly purchase specific products. By providing recurring delivery options, businesses can build long-term relationships and ensure consistent sales. Personalized subscription plans based on customer preferences and purchase history can further enhance satisfaction and loyalty.
- Loyalty Program Integration: Integrating delivery personalization with loyalty programs can reward customers with exclusive delivery options, such as free expedited shipping or early access to new products. Personalized offers and incentives based on customer behavior and loyalty status can drive engagement and repeat purchases.
Omnichannel fulfillment in the context of personalization involves tailoring delivery options to meet individual customer preferences, thereby enhancing satisfaction and loyalty. By offering flexible and personalized delivery choices, businesses can differentiate themselves in the competitive market and build stronger relationships with their customers.
Agility and Flexibility
Adapting to Changing Market Conditions
Adapting to changing market conditions is essential for maintaining a resilient and responsive omnichannel fulfillment operation. Market dynamics can shift rapidly due to various factors, including economic fluctuations, consumer behavior changes, technological advancements, and competitive pressures.

To stay ahead, businesses must be agile and ready to adjust their strategies and operations. Key strategies for adapting to changing market conditions:
- Real-Time Market Analysis: Leveraging data analytics to monitor market trends and consumer behavior in real-time is critical for staying informed about changes. Advanced analytics tools can provide insights into sales patterns, customer preferences, and emerging market trends. By analyzing this data, businesses can make informed decisions and quickly adjust their marketing, inventory, and fulfillment strategies to align with current market conditions.
- Flexible Supply Chain Management: A flexible supply chain allows businesses to respond quickly to changes in demand and supply. This involves diversifying suppliers, maintaining buffer stock, and utilizing multiple distribution channels to ensure a steady flow of goods. Implementing agile supply chain practices, such as just-in-time inventory management and dynamic sourcing, helps businesses minimize disruptions and maintain operational efficiency.
- Scalable Infrastructure: Investing in scalable infrastructure is essential for adapting to market fluctuations. Cloud-based systems, such as Order Management Systems (OMS) and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), provide the flexibility to scale operations up or down based on demand. Scalable infrastructure allows businesses to handle peak periods and seasonal demand without compromising on service quality. It also enables quick expansion into new markets or regions.
- Proactive Risk Management: Identifying potential risks and developing contingency plans is crucial for mitigating the impact of market changes. This includes assessing risks related to supply chain disruptions, economic downturns, and competitive threats. Businesses can implement risk management strategies, such as diversifying suppliers, establishing alternative distribution routes, and investing in inventory insurance, to enhance resilience.
- Continuous Improvement: Adopting a culture of continuous improvement ensures that businesses remain agile and responsive. Regularly reviewing and optimizing processes, technologies, and strategies helps identify areas for enhancement and keeps operations aligned with market demands. Encouraging innovation and fostering a learning-oriented environment empowers employees to contribute to process improvements and adapt to changes effectively.
Implementing Flexible Fulfillment Models
Implementing flexible fulfillment models is essential for providing a seamless and efficient omnichannel fulfillment experience. Flexible fulfillment models allow businesses to offer various delivery options, cater to different customer preferences, and optimize operations based on demand.
- Multiple Fulfillment Channels: Offering multiple fulfillment channels, such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), ship-from-store, and same-day delivery, provides customers with the flexibility to choose their preferred delivery method. By leveraging physical stores as fulfillment centers, businesses can reduce shipping times and costs while enhancing customer convenience.
- Dynamic Order Routing: Implementing dynamic order routing ensures that orders are fulfilled from the most efficient location. Advanced Order Management Systems (OMS) can automatically route orders based on factors such as inventory levels, proximity to the customer, and shipping costs. Dynamic order routing optimizes fulfillment operations, reduces delivery times, and minimizes transportation costs.
- On-Demand Fulfillment: On-demand fulfillment models, such as dropshipping and third-party logistics (3PL) partnerships, allow businesses to fulfill orders without holding large amounts of inventory. This model is particularly useful for handling peak periods and seasonal demand. Dropshipping enables businesses to source products directly from suppliers when orders are placed, reducing inventory holding costs and risk. 3PL partnerships provide additional fulfillment capacity and expertise, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Real-Time Inventory Visibility: Maintaining real-time inventory visibility across all channels is essential for flexible fulfillment. Advanced inventory management systems provide accurate and up-to-date information on stock levels, enabling businesses to fulfill orders from the most appropriate location. Real-time inventory visibility ensures that customers receive accurate information about product availability and delivery timelines, enhancing the overall shopping experience.
- Customer-Centric Fulfillment Options: Offering personalized and customer-centric fulfillment options enhances the shopping experience and builds loyalty. This includes providing flexible delivery windows, scheduled deliveries, and subscription services. Personalized fulfillment options cater to individual customer preferences, improving satisfaction and encouraging repeat purchases.
Omnichannel fulfillment in the context of agility and flexibility involves the ability to adapt to changing market conditions and implement flexible fulfillment models that meet customer needs and optimize operations. By prioritizing agility and flexibility, businesses can enhance resilience, drive customer satisfaction, and achieve long-term success in the competitive retail landscape.
Future Trends in Omnichannel Fulfillment
The Rise of AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning (ML) are transforming omnichannel fulfillment by enhancing operational efficiency, improving decision-making, and delivering personalized customer experiences.
These technologies are becoming integral to the fulfillment process, offering numerous benefits and driving innovation.
- Demand Forecasting: AI and ML algorithms analyze vast amounts of historical sales data, market trends, and external factors to predict future demand accurately. This enables businesses to optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize overstock situations. Predictive analytics helps businesses anticipate peak periods and seasonal demand, allowing them to prepare accordingly and maintain high levels of service.
- Inventory Management: AI-driven inventory management systems provide real-time visibility into stock levels across all channels. These systems can automatically reorder products when inventory levels fall below a certain threshold, ensuring that popular items are always in stock. Machine learning models can identify patterns and anomalies in inventory data, helping businesses detect issues such as theft, spoilage, or mismanagement early on.
- Order Processing and Fulfillment: AI-powered order management systems (OMS) optimize order routing by considering factors such as inventory availability, proximity to the customer, and shipping costs. This ensures that orders are fulfilled from the most efficient location, reducing delivery times and costs. Automation in picking, packing, and shipping processes enhances accuracy and speed. Robotics and AI-driven automation can handle repetitive tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more complex activities.
- Personalization and Customer Experience: AI and ML enable businesses to deliver personalized experiences by analyzing customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history. Personalized product recommendations, tailored marketing campaigns, and customized delivery options enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI provide instant customer support, addressing queries and resolving issues efficiently.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI and ML optimize supply chain operations by analyzing data from various sources, such as suppliers, logistics providers, and market conditions. These insights help businesses make informed decisions, reduce lead times, and improve overall supply chain efficiency. Predictive maintenance powered by AI can monitor equipment and infrastructure, predicting potential failures and scheduling maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime and disruptions.
Increased Focus on Customer Experience
Customer experience is becoming a focal point in omnichannel fulfillment as businesses strive to meet the evolving expectations of consumers. Providing a seamless, personalized, and convenient shopping experience across all channels is crucial for building customer loyalty and driving sales.
- Seamless Integration Across Channels: Ensuring a consistent and integrated experience across online stores, physical retail locations, mobile apps, and social media platforms is essential. Customers should be able to transition smoothly between channels, with access to the same product information, promotions, and services. Implementing unified commerce platforms that integrate various channels and systems helps businesses provide a cohesive customer experience.
- Personalized Shopping Experiences: Leveraging customer data to deliver personalized experiences enhances satisfaction and engagement. Personalized product recommendations, tailored promotions, and customized delivery options cater to individual preferences and needs. Advanced Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems enable businesses to track customer interactions, preferences, and purchase history, allowing for more targeted and relevant communications.
- Flexible Fulfillment Options: Offering a variety of fulfillment options, such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), curbside pickup, same-day delivery, and scheduled delivery, provides customers with flexibility and convenience. Allowing customers to choose their preferred delivery method and providing accurate delivery estimates enhances the overall shopping experience.
- Real-Time Communication: Keeping customers informed about their order status, shipping updates, and delivery timelines through real-time notifications builds trust and reduces uncertainty. Utilizing multiple communication channels, such as email, SMS, mobile apps, and social media, ensures that customers receive timely and relevant updates.
- Proactive Customer Support: Providing proactive and responsive customer support is crucial for addressing issues and maintaining satisfaction. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can offer instant support, while dedicated customer service teams can handle more complex inquiries. Offering self-service options, such as FAQ sections and online help centers, empowers customers to find answers to their questions quickly.
The Growing Importance of Data Privacy and Security
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with data privacy regulations is essential for protecting customer information and maintaining trust. Businesses must adhere to various laws and standards, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and other regional regulations.
- Understanding Regulatory Requirements: Businesses must stay informed about relevant data privacy regulations and understand their obligations. This includes knowing what data can be collected, how it should be processed, and the rights of individuals regarding their data. Regularly reviewing and updating privacy policies and practices ensures ongoing compliance with changing regulations.
- Implementing Data Protection Measures: Implementing robust data protection measures, such as encryption, access controls, and secure data storage, helps safeguard customer information from unauthorized access and breaches. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments identify potential risks and areas for improvement.
- Obtaining Consent and Transparency: Clearly communicating data collection practices and obtaining explicit consent from customers is essential for compliance. Businesses should provide transparent information about what data is collected, how it is used, and who it is shared with. Offering customers the ability to manage their data preferences and opt out of data collection builds trust and aligns with regulatory requirements.
- Data Minimization and Retention: Adopting data minimization principles ensures that only the necessary data is collected and retained for as long as needed. Regularly reviewing and deleting outdated or irrelevant data reduces the risk of breaches and compliance issues. Implementing retention policies that specify how long data should be kept and the procedures for securely disposing of it helps maintain compliance.
- Training and Awareness: Providing regular training for employees on data privacy and security best practices ensures that everyone understands their responsibilities and the importance of protecting customer data. Creating a culture of data privacy and security within the organization promotes compliance and reduces the risk of human error.
Building Customer Trust
Building and maintaining customer trust is crucial for long-term success in omnichannel fulfillment. Customers are more likely to share their data and engage with businesses they trust, making data privacy and security a competitive advantage.
- Transparent Communication: Being transparent about data collection practices and how customer information is used helps build trust. Clearly explaining the benefits of data collection and how it enhances the customer experience fosters confidence. Providing easy access to privacy policies and updates ensures that customers are informed and can make educated decisions about their data.
- Demonstrating Accountability: Demonstrating accountability by taking responsibility for data protection and promptly addressing any breaches or issues reassures customers that their information is in safe hands. Establishing clear procedures for handling data breaches and communicating with affected customers transparently helps mitigate the impact and maintain trust.
- Empowering Customers: Empowering customers with control over their data, such as allowing them to manage their preferences, access their information, and request deletions, builds trust and aligns with regulatory requirements. Offering privacy-enhancing features, such as anonymous browsing or data anonymization options, provides additional reassurance to customers concerned about their privacy.
- Consistent Data Protection Practices: Consistently applying data protection practices across all channels and touchpoints ensures that customer information is safeguarded at every stage of the omnichannel fulfillment process. Regularly reviewing and updating security measures to address new threats and vulnerabilities demonstrates a commitment to ongoing data protection.
- Customer-Centric Privacy Policies: Developing customer-centric privacy policies that prioritize the protection of personal information and clearly articulate the business’s commitment to privacy helps build trust. Involving customers in the development of privacy policies, such as seeking feedback and addressing their concerns, ensures that policies are aligned with customer expectations.
Omnichannel fulfillment in the context of data privacy and security involves ensuring compliance with regulations and building customer trust through transparent and accountable practices. By prioritizing data protection, businesses can enhance customer confidence, foster loyalty, and achieve long-term success in the competitive retail landscape.

The future of omnichannel fulfillment is shaped by emerging trends such as the rise of AI and machine learning, an increased focus on customer experience, and the growing importance of data privacy and security. By embracing these trends and implementing best practices, businesses can develop a robust omnichannel fulfillment strategy that meets customer expectations, drives growth, and ensures long-term success. These trends and strategies are essential for creating a seamless and efficient fulfillment experience that enhances customer satisfaction and competitive advantage.
Case Studies of Successful Omnichannel Fulfillment
Nordstrom
Nordstrom, a leading fashion retailer, has successfully implemented omnichannel fulfillment strategies that have significantly enhanced its operational efficiency and customer experience.
This case study provides an overview of Nordstrom’s omnichannel fulfillment strategies, key success factors, and the outcomes achieved through their implementation.
Overview of Nordstrom’s Omnichannel Fulfillment Strategies
Nordstrom has long been recognized for its customer-centric approach and innovative retail strategies. The company’s commitment to delivering a seamless and integrated shopping experience across all channels has driven the development and execution of its omnichannel fulfillment strategies. Key components of Nordstrom’s omnichannel fulfillment approach include:
- Unified Commerce Platform: Nordstrom’s unified commerce platform integrates its online and physical retail operations, ensuring that customers receive a consistent experience regardless of the channel they use. This platform connects various systems, including inventory management, order processing, and customer relationship management, providing real-time visibility into all aspects of the business. The unified platform allows Nordstrom to offer features such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), reserve online, try in-store, and ship-from-store, enhancing flexibility and convenience for customers.
- Advanced Inventory Management: Nordstrom employs advanced inventory management systems to track stock levels in real-time across all channels. This ensures accurate inventory data and enables efficient order fulfillment from the nearest location, whether it be a warehouse or a retail store. The system optimizes inventory allocation, reducing the likelihood of stockouts and overstock situations. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, Nordstrom can meet customer demand promptly and efficiently.
- Dynamic Order Routing: The company’s dynamic order routing system determines the best fulfillment location based on factors such as inventory availability, proximity to the customer, and shipping costs. This system ensures that orders are processed and delivered as quickly and cost-effectively as possible. Dynamic order routing enhances operational efficiency and improves the customer experience by minimizing delivery times and costs.
- Personalized Customer Experience: Nordstrom leverages customer data to deliver personalized shopping experiences. By analyzing purchase history, browsing behavior, and preferences, the company can offer tailored product recommendations, promotions, and services. Personalized experiences extend to fulfillment options, allowing customers to choose the delivery method that best suits their needs, such as same-day delivery or scheduled delivery.
- Integrated Customer Service: Nordstrom’s integrated customer service strategy ensures that customers receive consistent support across all channels. Whether shopping online or in-store, customers can access assistance and resolve issues through multiple touchpoints, including live chat, phone, and in-person interactions. The company’s commitment to exceptional customer service is reinforced by trained staff who are equipped to handle omnichannel interactions effectively.
Key Success Factors and Outcomes
Nordstrom’s success in omnichannel fulfillment can be attributed to several key factors that have driven positive outcomes for the business and its customers.
Key Success Factors:
- Technology Integration: The seamless integration of advanced technologies across Nordstrom’s operations has been instrumental in achieving efficient omnichannel fulfillment. The unified commerce platform, dynamic order routing, and real-time inventory management systems work together to optimize processes and enhance the customer experience. Continuous investment in technology ensures that Nordstrom stays at the forefront of innovation, adapting to evolving market trends and customer expectations.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Nordstrom’s unwavering focus on customer satisfaction drives its omnichannel fulfillment strategies. By prioritizing the needs and preferences of customers, the company delivers a seamless and personalized shopping experience that fosters loyalty and repeat business. Personalized services, flexible fulfillment options, and consistent customer support contribute to Nordstrom’s reputation for exceptional customer service.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficient operations are a cornerstone of Nordstrom’s omnichannel fulfillment strategy. Advanced inventory management, dynamic order routing, and optimized logistics ensure that orders are processed and delivered quickly and accurately. Operational efficiency not only enhances the customer experience but also reduces costs and improves profitability.
- Employee Training and Engagement: Nordstrom invests in training and developing its employees to ensure they are equipped to handle omnichannel interactions and provide exceptional service. Engaged and knowledgeable staff play a critical role in delivering a seamless and satisfying customer experience. Continuous training programs and a supportive work environment contribute to high employee morale and retention, further enhancing the company’s overall performance.
Outcomes:
- Increased Sales and Revenue: Nordstrom’s omnichannel fulfillment strategies have driven significant growth in sales and revenue. The seamless integration of online and physical retail channels has expanded the company’s reach and attracted a broader customer base. Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty, resulting from personalized experiences and efficient fulfillment, have contributed to increased repeat business and higher average order values.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: The focus on delivering a seamless and personalized shopping experience has led to high levels of customer satisfaction. Customers appreciate the flexibility of choosing their preferred fulfillment options and the convenience of accessing consistent support across all channels. Positive customer experiences have strengthened Nordstrom’s brand reputation and contributed to high customer retention rates.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings: The integration of advanced technologies and optimized processes has improved operational efficiency, reducing costs associated with inventory management, order processing, and logistics. Efficient fulfillment operations have enabled Nordstrom to meet customer demand promptly and cost-effectively, enhancing profitability and competitive advantage.
- Innovation and Adaptability: Nordstrom’s commitment to innovation and adaptability has positioned the company as a leader in omnichannel fulfillment. The ability to quickly implement new technologies and strategies allows Nordstrom to stay ahead of market trends and respond to changing customer expectations. Continuous improvement and a forward-thinking approach ensure that Nordstrom remains competitive in the dynamic retail landscape.
The omnichannel fulfillment examples from Nordstrom illustrate the successful implementation of advanced technologies and customer-centric strategies that drive positive outcomes. The company’s unified commerce platform, dynamic order routing, and personalized customer experiences set a benchmark for excellence in omnichannel fulfillment.
Nordstrom’s success highlights the importance of seamless integration, efficient operations, and a customer-centric approach. By prioritizing these factors, businesses can achieve similar success in omnichannel fulfillment, driving growth, customer satisfaction, and long-term profitability. Nordstrom’s case study demonstrates the significant impact of effective omnichannel fulfillment strategies on business performance and customer satisfaction. The company’s commitment to technology integration, operational efficiency, and personalized customer experiences has driven positive outcomes, setting a standard for excellence in the retail industry. By learning from Nordstrom’s success, businesses can develop and implement robust omnichannel fulfillment strategies that enhance their competitive advantage and ensure long-term success.
Decathlon
Decathlon, a global sports retailer, has successfully implemented omnichannel fulfillment strategies that have significantly enhanced its operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.

This case study provides an overview of Decathlon’s omnichannel fulfillment strategies, key success factors, and the outcomes achieved through their implementation.
Overview of Decathlon’s Omnichannel Fulfillment Strategies
Decathlon’s commitment to providing a seamless and integrated shopping experience across all channels has driven the development and execution of its omnichannel fulfillment strategies. Key components of Decathlon’s approach to omnichannel fulfillment include:
- Unified Commerce Platform: Decathlon has developed a unified commerce platform that integrates its online and offline operations. This platform connects various systems, including inventory management, order processing, and customer relationship management (CRM), providing real-time visibility into all aspects of the business. This integration allows Decathlon to offer features such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), reserve online, try in-store, and ship-from-store, enhancing flexibility and convenience for customers.
- Advanced Inventory Management: Decathlon employs advanced inventory management systems to track stock levels in real-time across all channels. This ensures accurate inventory data and enables efficient order fulfillment from the nearest location, whether it be a warehouse or a retail store. The system optimizes inventory allocation, reducing the likelihood of stockouts and overstock situations. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, Decathlon can meet customer demand promptly and efficiently.
- Dynamic Order Routing: Decathlon’s dynamic order routing system determines the best fulfillment location based on factors such as inventory availability, proximity to the customer, and shipping costs. This system ensures that orders are processed and delivered as quickly and cost-effectively as possible. Dynamic order routing enhances operational efficiency and improves the customer experience by minimizing delivery times and costs.
- Personalized Customer Experience: Decathlon leverages customer data to deliver personalized shopping experiences. By analyzing purchase history, browsing behavior, and preferences, the company can offer tailored product recommendations, promotions, and services. Personalized experiences extend to fulfillment options, allowing customers to choose the delivery method that best suits their needs, such as same-day delivery or scheduled delivery.
- Sustainable Fulfillment Practices: Decathlon is committed to sustainability and has integrated eco-friendly practices into its omnichannel fulfillment strategy. This includes using recyclable packaging, optimizing delivery routes to reduce carbon emissions, and promoting in-store pickups to minimize transportation impact. By aligning its fulfillment operations with its sustainability goals, Decathlon not only enhances its brand image but also meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices.
- Omnichannel Customer Service: Decathlon’s integrated customer service strategy ensures that customers receive consistent support across all channels. Whether shopping online or in-store, customers can access assistance and resolve issues through multiple touchpoints, including live chat, phone, and in-person interactions. The company’s commitment to exceptional customer service is reinforced by trained staff who are equipped to handle omnichannel interactions effectively.
Key Success Factors and Outcomes
Decathlon’s success in omnichannel fulfillment can be attributed to several key factors that have driven positive outcomes for the business and its customers.
Key Success Factors:
- Technology Integration: The seamless integration of advanced technologies across Decathlon’s operations has been instrumental in achieving efficient omnichannel fulfillment. The unified commerce platform, dynamic order routing, and real-time inventory management systems work together to optimize processes and enhance the customer experience. Continuous investment in technology ensures that Decathlon stays at the forefront of innovation, adapting to evolving market trends and customer expectations.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Decathlon’s unwavering focus on customer satisfaction drives its omnichannel fulfillment strategies. By prioritizing the needs and preferences of customers, the company delivers a seamless and personalized shopping experience that fosters loyalty and repeat business. Personalized services, flexible fulfillment options, and consistent customer support contribute to Decathlon’s reputation for exceptional customer service.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficient operations are a cornerstone of Decathlon’s omnichannel fulfillment strategy. Advanced inventory management, dynamic order routing, and optimized logistics ensure that orders are processed and delivered quickly and accurately. Operational efficiency not only enhances the customer experience but also reduces costs and improves profitability.
- Sustainability Commitment: Decathlon’s commitment to sustainability is a key factor in its success. By integrating eco-friendly practices into its fulfillment operations, the company meets the growing consumer demand for sustainable products and practices while reducing its environmental impact. This commitment enhances Decathlon’s brand image and aligns with its corporate values, attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
- Employee Training and Engagement: Decathlon invests in training and developing its employees to ensure they are equipped to handle omnichannel interactions and provide exceptional service. Engaged and knowledgeable staff play a critical role in delivering a seamless and satisfying customer experience. Continuous training programs and a supportive work environment contribute to high employee morale and retention, further enhancing the company’s overall performance.
Outcomes:
- Increased Sales and Revenue: Decathlon’s omnichannel fulfillment strategies have driven significant growth in sales and revenue. The seamless integration of online and physical retail channels has expanded the company’s reach and attracted a broader customer base. Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty, resulting from personalized experiences and efficient fulfillment, have contributed to increased repeat business and higher average order values.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: The focus on delivering a seamless and personalized shopping experience has led to high levels of customer satisfaction. Customers appreciate the flexibility of choosing their preferred fulfillment options and the convenience of accessing consistent support across all channels. Positive customer experiences have strengthened Decathlon’s brand reputation and contributed to high customer retention rates.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings: The integration of advanced technologies and optimized processes has improved operational efficiency, reducing costs associated with inventory management, order processing, and logistics. Efficient fulfillment operations have enabled Decathlon to meet customer demand promptly and cost-effectively, enhancing profitability and competitive advantage.
- Sustainability Achievements: Decathlon’s commitment to sustainability has yielded significant achievements in reducing its environmental impact. The use of recyclable packaging, optimized delivery routes, and promotion of in-store pickups have contributed to lower carbon emissions and waste. These efforts resonate with environmentally conscious consumers, enhancing Decathlon’s brand loyalty and attracting a new customer demographic focused on sustainability.
- Innovation and Adaptability: Decathlon’s commitment to innovation and adaptability has positioned the company as a leader in omnichannel fulfillment. The ability to quickly implement new technologies and strategies allows Decathlon to stay ahead of market trends and respond to changing customer expectations. Continuous improvement and a forward-thinking approach ensure that Decathlon remains competitive in the dynamic retail landscape.
Decathlon is one of the excellent omnichannel fulfillment examples that illustrate the successful implementation of advanced technologies and customer-centric strategies that drive positive outcomes. The company’s unified commerce platform, dynamic order routing, and personalized customer experiences set a benchmark for excellence in omnichannel fulfillment.
Decathlon’s success highlights the importance of seamless integration, efficient operations, and a customer-centric approach. By prioritizing these factors, businesses can achieve similar success in omnichannel fulfillment, driving growth, customer satisfaction, and long-term profitability. Decathlon’s case study demonstrates the significant impact of effective omnichannel fulfillment strategies on business performance and customer satisfaction. The company’s commitment to technology integration, operational efficiency, sustainability, and personalized customer experiences has driven positive outcomes, setting a standard for excellence in the retail industry. By learning from Decathlon’s success, businesses can develop and implement robust omnichannel fulfillment strategies that enhance their competitive advantage and ensure long-term success.
John Lewis & Partners
John Lewis & Partners, a renowned British department store chain, has successfully implemented omnichannel fulfillment strategies that have significantly enhanced its operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
This case study provides an overview of John Lewis & Partners’ omnichannel fulfillment strategies, key success factors, and the outcomes achieved through their implementation.
Overview of John Lewis & Partners Omnichannel Fulfillment Strategies
John Lewis & Partners has long been recognized for its commitment to quality and customer service. The company has embraced omnichannel fulfillment to meet the evolving demands of its customers and to remain competitive in the retail industry. Key components of John Lewis & Partners’ approach to omnichannel fulfillment include:
- Unified Commerce Platform: John Lewis & Partners has developed a unified commerce platform that integrates its online and offline operations. This platform connects various systems, including inventory management, order processing, and customer relationship management (CRM), providing real-time visibility into all aspects of the business. This integration allows the company to offer features such as buy online, pick up in-store (BOPIS), reserve online, try in-store, and ship-from-store, enhancing flexibility and convenience for customers.
- Advanced Inventory Management: The company employs advanced inventory management systems to track stock levels in real-time across all channels. This ensures accurate inventory data and enables efficient order fulfillment from the nearest location, whether it be a warehouse or a retail store. The system optimizes inventory allocation, reducing the likelihood of stockouts and overstock situations. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, John Lewis & Partners can meet customer demand promptly and efficiently.
- Dynamic Order Routing: John Lewis & Partners’ dynamic order routing system determines the best fulfillment location based on factors such as inventory availability, proximity to the customer, and shipping costs. This system ensures that orders are processed and delivered as quickly and cost-effectively as possible. Dynamic order routing enhances operational efficiency and improves the customer experience by minimizing delivery times and costs.
- Personalized Customer Experience: John Lewis & Partners leverages customer data to deliver personalized shopping experiences. By analyzing purchase history, browsing behavior, and preferences, the company can offer tailored product recommendations, promotions, and services. Personalized experiences extend to fulfillment options, allowing customers to choose the delivery method that best suits their needs, such as same-day delivery or scheduled delivery.
- Integrated Customer Service: The company’s integrated customer service strategy ensures that customers receive consistent support across all channels. Whether shopping online or in-store, customers can access assistance and resolve issues through multiple touchpoints, including live chat, phone, and in-person interactions. The company’s commitment to exceptional customer service is reinforced by trained staff who are equipped to handle omnichannel interactions effectively.
- Sustainability Initiatives: John Lewis & Partners integrates sustainability into its omnichannel fulfillment strategies. The company focuses on reducing its carbon footprint through eco-friendly packaging, optimizing delivery routes, and promoting in-store pickups. By aligning its fulfillment operations with its sustainability goals, John Lewis & Partners meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices and enhances its brand image.
Key Success Factors and Outcomes
John Lewis & Partners’ success in omnichannel fulfillment can be attributed to several key factors that have driven positive outcomes for the business and its customers.
Key Success Factors:
- Technology Integration: The seamless integration of advanced technologies across John Lewis & Partners’ operations has been instrumental in achieving efficient omnichannel fulfillment. The unified commerce platform, dynamic order routing, and real-time inventory management systems work together to optimize processes and enhance the customer experience. Continuous investment in technology ensures that John Lewis & Partners stays at the forefront of innovation, adapting to evolving market trends and customer expectations.
- Customer-Centric Approach: John Lewis & Partners’ unwavering focus on customer satisfaction drives its omnichannel fulfillment strategies. By prioritizing the needs and preferences of customers, the company delivers a seamless and personalized shopping experience that fosters loyalty and repeat business. Personalized services, flexible fulfillment options, and consistent customer support contribute to John Lewis & Partners’ reputation for exceptional customer service.
- Operational Efficiency: Efficient operations are a cornerstone of John Lewis & Partners’ omnichannel fulfillment strategy. Advanced inventory management, dynamic order routing, and optimized logistics ensure that orders are processed and delivered quickly and accurately. Operational efficiency not only enhances the customer experience but also reduces costs and improves profitability.
- Sustainability Commitment: John Lewis & Partners’ commitment to sustainability is a key factor in its success. By integrating eco-friendly practices into its fulfillment operations, the company meets the growing consumer demand for sustainable products and practices while reducing its environmental impact. This commitment enhances John Lewis & Partners’ brand image and aligns with its corporate values, attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
- Employee Training and Engagement: John Lewis & Partners invests in training and developing its employees to ensure they are equipped to handle omnichannel interactions and provide exceptional service. Engaged and knowledgeable staff play a critical role in delivering a seamless and satisfying customer experience. Continuous training programs and a supportive work environment contribute to high employee morale and retention, further enhancing the company’s overall performance.
Outcomes:
- Increased Sales and Revenue: John Lewis & Partners’ omnichannel fulfillment strategies have driven significant growth in sales and revenue. The seamless integration of online and physical retail channels has expanded the company’s reach and attracted a broader customer base. Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty, resulting from personalized experiences and efficient fulfillment, have contributed to increased repeat business and higher average order values.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: The focus on delivering a seamless and personalized shopping experience has led to high levels of customer satisfaction. Customers appreciate the flexibility of choosing their preferred fulfillment options and the convenience of accessing consistent support across all channels. Positive customer experiences have strengthened John Lewis & Partners’ brand reputation and contributed to high customer retention rates.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings: The integration of advanced technologies and optimized processes has improved operational efficiency, reducing costs associated with inventory management, order processing, and logistics. Efficient fulfillment operations have enabled John Lewis & Partners to meet customer demand promptly and cost-effectively, enhancing profitability and competitive advantage.
- Sustainability Achievements: John Lewis & Partners’ commitment to sustainability has yielded significant achievements in reducing its environmental impact. The use of recyclable packaging, optimized delivery routes, and promotion of in-store pickups have contributed to lower carbon emissions and waste. These efforts resonate with environmentally conscious consumers, enhancing John Lewis & Partners’ brand loyalty and attracting a new customer demographic focused on sustainability.
- Innovation and Adaptability: John Lewis & Partners’ commitment to innovation and adaptability has positioned the company as a leader in omnichannel fulfillment. The ability to quickly implement new technologies and strategies allows the company to stay ahead of market trends and respond to changing customer expectations. Continuous improvement and a forward-thinking approach ensure that John Lewis & Partners remains competitive in the dynamic retail landscape.
Omnichannel fulfillment examples from John Lewis & Partners illustrate the successful implementation of advanced technologies and customer-centric strategies that drive positive outcomes. The company’s unified commerce platform, dynamic order routing, and personalized customer experiences set a benchmark for excellence in omnichannel fulfillment.
John Lewis & Partners’ success highlights the importance of seamless integration, efficient operations, and a customer-centric approach. By prioritizing these factors, businesses can achieve similar success in omnichannel fulfillment, driving growth, customer satisfaction, and long-term profitability. John Lewis & Partners’ case study demonstrates the significant impact of effective omnichannel fulfillment strategies on business performance and customer satisfaction. The company’s commitment to technology integration, operational efficiency, sustainability, and personalized customer experiences has driven positive outcomes, setting a standard for excellence in the retail industry. By learning from John Lewis & Partners’ success, businesses can develop and implement robust omnichannel fulfillment strategies that enhance their competitive advantage and ensure long-term success.
Conclusion
Adapting to an omnichannel approach is crucial for businesses aiming to thrive in the current market. It enables companies to offer a unified shopping experience, ensuring consistency and convenience across all touchpoints. By leveraging advanced technologies and data analytics, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, optimize inventory management, and streamline order processing, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
The retail landscape is constantly changing, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer preferences, and competitive pressures. To remain relevant and successful, businesses must continually evolve and optimize their omnichannel fulfillment strategies. This involves staying abreast of emerging trends, investing in innovative technologies, and adopting a culture of continuous improvement. By doing so, businesses can not only meet but exceed customer expectations, ensuring long-term success and growth.
Finally, omnichannel fulfillment is a vital component of modern retail strategy, offering numerous benefits for both businesses and customers. By understanding the key elements and challenges of omnichannel fulfillment, implementing best practices, and learning from successful case studies, businesses can develop robust strategies that enhance their competitive advantage and drive sustained success in the dynamic retail landscape.