In today’s rapidly evolving marketing landscape, businesses are continually seeking innovative strategies to connect with their audiences and stay ahead of the competition. Among the most discussed and implemented approaches are omnichannel and integrated marketing. As the lines between online and offline interactions blur, the debate of omnichannel vs integrated marketing has become increasingly relevant. Understanding the nuances between these two strategies is crucial for marketers aiming to create seamless customer experiences and achieve long-term success.
This blog post delves into the differences between omnichannel and integrated marketing, exploring their core principles, benefits, challenges, and how they fit into the modern marketing landscape. By the end of this in-depth analysis, you’ll have a clearer understanding of why omnichannel marketing is considered a more evolved form of integrated marketing, and how adopting the right strategy can significantly impact your business’s success.
Table of Contents
Omnichannel vs Integrated Marketing
Core Principles of Integrated Marketing
In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing conversation, it’s important to highlight the core principles that define integrated marketing. These principles have been instrumental in its effectiveness and widespread adoption.
Consistency in Messaging Across Channels
One of the most critical elements of integrated marketing is the emphasis on consistency. Consistency ensures that regardless of where or how a consumer interacts with a brand, they receive the same message, tone, and brand values. This uniformity builds trust and reinforces the brand’s identity, making it easier for consumers to recognize and relate to the brand. In integrated marketing, every piece of content, advertisement, or communication is carefully crafted to align with the overall brand narrative, ensuring that there is no discrepancy between what is communicated on different platforms.

This consistency is vital in building brand loyalty and establishing a strong brand presence. When consumers encounter consistent messaging, they are more likely to remember and trust the brand, leading to increased engagement and conversions. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing discussion, while omnichannel marketing also values consistency, integrated marketing specifically focuses on maintaining a uniform message across all channels, making it a cornerstone of its approach.
Coordination Between Various Marketing Efforts
Integrated marketing goes beyond just consistency in messaging; it also emphasizes the coordination of marketing efforts across different departments and channels. This coordination ensures that all marketing activities, whether online or offline, are aligned with the brand’s overall strategy and objectives. In practice, this means that marketing teams work closely with sales, customer service, and other departments to ensure that campaigns are not only consistent in messaging but also in their goals and execution.
Effective coordination in integrated marketing involves detailed planning and communication among teams to ensure that all campaigns support one another, creating a unified customer experience. For example, a television ad campaign may be complemented by social media promotions, in-store displays, and email newsletters, all of which are designed to reinforce the same core message. This level of coordination enhances the overall impact of the marketing efforts, making them more effective in reaching and engaging the target audience.
In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing context, while omnichannel marketing also requires coordination, integrated marketing is often more focused on ensuring that all marketing efforts are working towards a common goal, rather than adapting to the individual needs of each customer segment.
Integration of Traditional and Digital Marketing Tactics
The integration of traditional and digital marketing tactics is another key principle of integrated marketing. In the past, traditional marketing channels such as print, radio, and television were the primary means of reaching consumers. However, with the advent of digital media, new channels such as websites, social media, and email marketing have become increasingly important. Integrated marketing seeks to combine these traditional and digital tactics into a cohesive strategy that leverages the strengths of each channel.

For example, a brand may use a television commercial to build awareness, followed by digital retargeting ads to engage viewers who have visited the brand’s website. Meanwhile, direct mail campaigns might complement email marketing efforts, ensuring that consumers receive consistent messaging through both physical and digital touchpoints. This integration allows brands to reach a wider audience and engage them in multiple ways, increasing the likelihood of conversion.
The integration of traditional and digital tactics is a shared characteristic between omnichannel vs integrated marketing. However, integrated marketing primarily focuses on ensuring that these tactics are aligned in their messaging and objectives, rather than creating a seamless, personalized experience across all channels, which is the hallmark of omnichannel marketing.
Understanding Omnichannel Marketing
As marketing strategies have evolved, omnichannel marketing has emerged as a more sophisticated and customer-centric approach, building upon the foundations laid by integrated marketing but taking it several steps further.
Definition and Fundamental Concepts
Omnichannel marketing is a holistic approach that aims to provide a seamless and integrated customer experience across all available channels and touchpoints. Unlike traditional multichannel or even integrated marketing strategies, which often treat each channel as a separate entity, omnichannel marketing views the entire customer journey as interconnected and fluid.

At its core, omnichannel marketing is designed to create a consistent, personalized experience for the customer, regardless of how they interact with a brand—whether it’s through a physical store, a website, a mobile app, social media, or customer service. The goal is to ensure that the transition between these different touchpoints is as smooth as possible, providing customers with a unified brand experience that meets their expectations and preferences at every stage of their journey.
The concept of omnichannel marketing is rooted in the understanding that today’s consumers interact with brands through multiple channels, often simultaneously. For example, a customer might browse products on a mobile app, read reviews on social media, and then make a purchase in-store. Omnichannel marketing recognizes these diverse behaviors and aims to create a cohesive experience that ties all these interactions together, making it easier for customers to move from one channel to another without feeling disjointed or confused.
In the debate of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, omnichannel marketing is often seen as the more evolved strategy because it not only focuses on consistency but also prioritizes the customer experience by ensuring that all channels work together harmoniously to serve the customer’s needs.
Key Components of Omnichannel Marketing
The effectiveness of omnichannel marketing lies in its key components, which distinguish it from integrated marketing. These components are designed to ensure that the customer experience is not only consistent but also seamless, personalized, and responsive to real-time interactions.
Seamless Customer Experience Across All Touchpoints
One of the most defining aspects of omnichannel marketing is its focus on providing a seamless customer experience across all touchpoints. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing conversation, this component is where omnichannel marketing truly shines. While integrated marketing ensures that the brand message is consistent across channels, omnichannel marketing takes it further by ensuring that the experience itself is uninterrupted and fluid, regardless of how or where the customer interacts with the brand.
For instance, if a customer starts their shopping journey on a mobile app but decides to complete the purchase in a physical store, omnichannel marketing ensures that their online interactions are recognized and continued in-store. This could mean that the products they added to their online cart are easily accessible when they enter the store, or that any loyalty points or discounts they earned online are automatically applied at checkout. The objective is to eliminate any friction that might disrupt the customer’s journey, providing them with a consistent and enjoyable experience no matter which touchpoint they choose to engage with.
In contrast to integrated marketing, which may still treat each channel as distinct in terms of operations, omnichannel marketing operates under the principle that all channels are interconnected and should work together to enhance the overall customer experience. This seamlessness is critical in retaining customers and fostering brand loyalty in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Data Integration and Customer Journey Mapping
Another critical component of omnichannel marketing is data integration and customer journey mapping. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing debate, this aspect underscores the advanced nature of omnichannel marketing. It involves gathering and integrating data from various channels to create a comprehensive view of the customer’s interactions with the brand.
Data integration in omnichannel marketing is not just about collecting information from different sources; it’s about synthesizing that data to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and pain points. This integrated data approach allows businesses to map out the customer journey in detail, identifying key touchpoints and moments where the customer might need additional support or engagement.
Customer journey mapping is a strategic process that visualizes the end-to-end experience of the customer across all channels. By understanding the path that customers typically take—from initial awareness to purchase and beyond—businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to meet the needs of customers at each stage of the journey. For example, if data shows that customers frequently abandon their carts after viewing shipping costs, the business can adjust its strategy by offering more transparent pricing or free shipping options.
In contrast to integrated marketing, which might focus on coordinating campaigns across channels, omnichannel marketing uses data integration and customer journey mapping to ensure that each interaction is contextually relevant and contributes to a smoother overall experience. This level of personalization and responsiveness is a key factor that differentiates omnichannel marketing from more traditional integrated approaches.
Personalization and Real-Time Engagement
Personalization and real-time engagement are at the heart of omnichannel marketing, setting it apart in the omnichannel vs integrated marketing discussion. Omnichannel marketing leverages data to deliver personalized experiences that are tailored to the individual preferences and behaviors of each customer. This goes beyond simply addressing the customer by name in communications; it involves creating experiences that resonate with the customer’s specific needs and desires.
Real-time engagement is a crucial aspect of this personalization. In the fast-paced digital landscape, customers expect brands to respond to their actions and inquiries instantly. Omnichannel marketing utilizes real-time data to engage customers at the right moment with relevant content, offers, and support. For example, if a customer is browsing a particular product category on a website, omnichannel marketing might trigger a personalized discount offer or a chat window offering assistance, encouraging the customer to complete their purchase.
This level of personalization and immediacy is difficult to achieve with integrated marketing alone, which tends to focus on broad campaigns rather than individual interactions. Omnichannel marketing, by contrast, is designed to adapt to the customer’s behavior in real-time, creating a dynamic and responsive experience that feels tailored to the individual.
Benefits of Omnichannel Marketing Over Integrated Marketing
Holistic Customer View and Enhanced Customer Experience
One of the most significant benefits of omnichannel marketing over integrated marketing is its ability to offer a holistic view of the customer. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing debate, this advantage is often cited as a primary reason for the shift towards omnichannel strategies.
Omnichannel marketing integrates data from all customer interactions across various channels—whether online or offline—to create a unified and comprehensive profile of each customer. This holistic view allows businesses to understand their customers better, including their preferences, behaviors, and pain points. With this detailed insight, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and expectations of each customer, leading to a significantly enhanced customer experience.
For example, if a customer frequently browses certain products online but prefers to make purchases in-store, omnichannel marketing enables businesses to recognize this pattern and provide personalized offers or suggestions that cater to this behavior. This seamless integration of data and customer journey mapping allows for a more responsive and personalized approach, ensuring that customers feel understood and valued at every touchpoint.
In contrast, integrated marketing, while effective in maintaining consistency across channels, often lacks the depth of customer insight that omnichannel marketing provides. Integrated marketing typically focuses on ensuring that the brand message is consistent, but it may not fully capture the intricacies of each customer’s journey. This can result in a more generalized approach to marketing, which, while coherent, may not be as effective in delivering the personalized experiences that today’s consumers expect.
The enhanced customer experience offered by omnichannel marketing leads to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and ultimately, higher conversion rates. By creating a more personalized and seamless journey, businesses can build stronger relationships with their customers, setting themselves apart in a crowded market.
Coherent Brand Message
Another critical benefit of omnichannel marketing in the omnichannel vs integrated marketing comparison is its ability to deliver a coherent brand message across all channels while simultaneously providing personalized experiences. This balance between consistency and personalization is where omnichannel marketing truly excels.
In integrated marketing, the primary focus is on maintaining a consistent brand message across various channels. This consistency is crucial for building brand recognition and ensuring that customers receive the same message, regardless of how they interact with the brand. However, this approach can sometimes lead to a rigid marketing strategy that does not account for the nuances of different channels or the individual preferences of customers.

Omnichannel marketing, on the other hand, combines the consistency of integrated marketing with the flexibility to adapt the brand message to different contexts and customer interactions. It ensures that the core brand message remains coherent, but it also allows for variations in how that message is delivered based on the specific channel or touchpoint. For example, a customer might receive a more detailed product explanation via email, a quick reminder via SMS, and a personalized offer through a mobile app—all reinforcing the same brand message but tailored to the medium and the customer’s current stage in the journey.
This ability to adapt while maintaining a coherent brand message is a significant advantage of omnichannel marketing. It ensures that customers have a consistent understanding of the brand, no matter where or how they engage with it, while also feeling that the communication is relevant and tailored to their needs.
General Comparison
When comparing omnichannel vs integrated marketing, it’s clear that both strategies offer valuable benefits, but omnichannel marketing provides a more advanced and customer-focused approach. Integrated marketing is highly effective in creating a consistent brand presence across multiple channels, ensuring that all marketing efforts are aligned and reinforcing the same message. This approach is particularly beneficial for maintaining brand coherence and driving home key marketing messages.
However, omnichannel marketing takes this a step further by not only maintaining consistency but also enhancing the customer experience through personalization and real-time engagement. While integrated marketing ensures that the brand message is consistent, omnichannel marketing ensures that this message is also relevant, timely, and tailored to the individual customer’s journey.
Moreover, the holistic view of the customer that omnichannel marketing provides allows businesses to make more informed decisions and create marketing strategies that are more likely to resonate with their audience. This leads to a more engaged and loyal customer base, as customers are more likely to respond positively to a brand that understands their needs and preferences.
Detailed Comparison Between Omnichannel vs Integrated Marketing
Strategic Differences Between Omnichannel and Integrated Marketing
When evaluating the strategic differences between omnichannel vs integrated marketing, one of the most critical aspects to consider is their approach to customer-centricity. Both strategies aim to connect with customers and drive engagement, but they differ significantly in how they prioritize and address the customer experience. The key difference lies in the focus each strategy places on the customer journey and overall experience versus campaign consistency and coherence.
Customer-Centric Focus
The concept of being customer-centric is at the heart of modern marketing strategies, but omnichannel and integrated marketing interpret and implement this concept in distinct ways. Understanding these differences is essential for businesses looking to adopt the most effective strategy for their goals.
Omnichannel: Emphasis on the Customer Journey and Experience
In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, omnichannel marketing stands out for its profound emphasis on the customer journey and experience. Omnichannel marketing is inherently customer-centric, meaning that every aspect of the strategy is designed around the needs, preferences, and behaviors of the customer. Rather than viewing marketing efforts through the lens of individual campaigns, omnichannel marketing considers the entire customer journey—from the initial point of contact through to purchase and beyond.

The omnichannel approach prioritizes the seamless integration of all customer touchpoints, ensuring that customers can move fluidly between different channels without encountering any disruption in their experience. Whether a customer interacts with a brand online, in-store, via mobile app, or through customer service, omnichannel marketing ensures that these interactions are connected and consistent, creating a cohesive and personalized experience.
This focus on the customer journey allows omnichannel marketing to deliver a more personalized experience. By leveraging data from multiple channels, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of each customer’s unique journey and tailor their marketing efforts accordingly. For example, if a customer frequently engages with a brand’s mobile app but has not made a purchase, omnichannel marketing might trigger a personalized promotion via email or a targeted ad on social media to encourage conversion. This real-time responsiveness and personalization are hallmarks of the omnichannel approach, making it highly effective in enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Omnichannel marketing’s emphasis on the customer journey reflects a shift in marketing strategy from product-centric to customer-centric. In the past, businesses might have focused more on promoting their products and services across various channels. However, in the omnichannel framework, the customer’s needs and preferences take center stage, driving the marketing strategy and ensuring that the customer experience is as smooth and engaging as possible.
Integrated: Emphasis on Campaign Consistency and Coherence
While omnichannel marketing is deeply rooted in enhancing the customer journey, integrated marketing takes a different approach, focusing primarily on campaign consistency and coherence. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing debate, integrated marketing is often praised for its ability to unify and streamline marketing efforts across various channels, ensuring that the brand message is consistent no matter where it is delivered.
Integrated marketing is built on the principle of delivering a cohesive brand message across all marketing channels. The idea is to create a unified narrative that reinforces the brand’s identity, values, and key messages, regardless of the medium through which it is communicated. This consistency helps build brand recognition and ensures that customers receive the same message whether they encounter the brand on social media, in a television commercial, or through a direct mail campaign.

The emphasis on campaign consistency in integrated marketing is crucial for maintaining a strong and recognizable brand presence. It ensures that all marketing efforts are aligned and work together to support the brand’s overall objectives. For example, a brand might launch a new product with an integrated marketing campaign that includes TV ads, social media posts, email newsletters, and in-store promotions—all of which share the same core message and branding elements. This consistency helps reinforce the brand’s message and makes it more memorable for the customer.
However, while integrated marketing excels at maintaining consistency, it may not always be as responsive to the individual needs and behaviors of customers as omnichannel marketing. Integrated marketing tends to focus more on the delivery of the brand’s message than on the adaptation of that message to fit the specific context or needs of the customer at any given moment. As a result, integrated marketing might not provide the same level of personalized engagement that omnichannel marketing can offer.
Data Utilization and Personalization
The use of data has become a cornerstone of modern marketing strategies, enabling businesses to tailor their efforts to meet the needs of their customers more effectively. However, the way omnichannel and integrated marketing leverage data reveals a fundamental divergence in their approach to personalization and customer engagement.
Omnichannel: Real-Time Data and Personalized Interactions
In the debate of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, omnichannel marketing stands out for its sophisticated use of real-time data and its emphasis on creating personalized interactions. Omnichannel marketing is designed to be highly responsive, utilizing real-time data to engage with customers at the right moment with the right message. This approach allows businesses to deliver highly personalized experiences that are tailored to the individual preferences and behaviors of each customer.
Omnichannel marketing collects data from various touchpoints—such as websites, mobile apps, social media, and in-store interactions—and integrates this information to create a comprehensive view of the customer. This real-time data integration is crucial for understanding the customer’s current needs and context, enabling businesses to deliver relevant content, offers, and recommendations instantaneously.
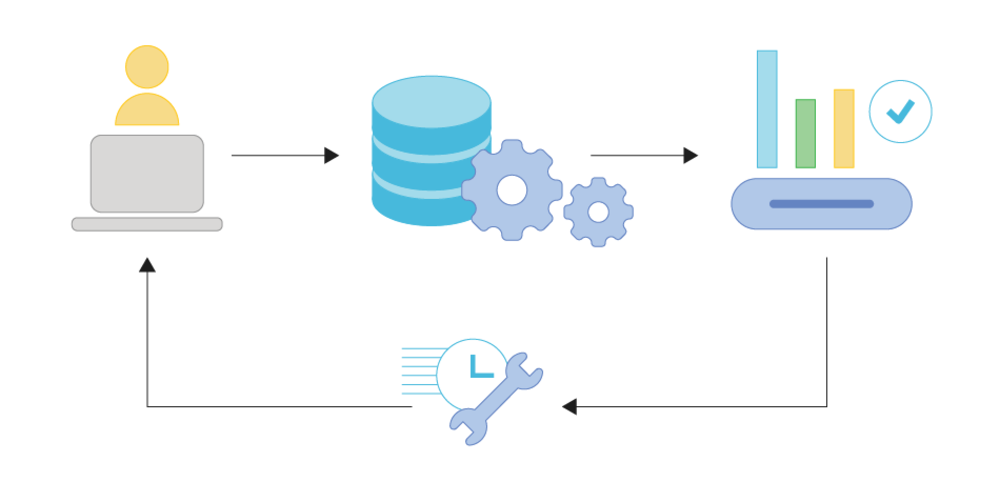
For example, if a customer is browsing a particular category on a retailer’s website, omnichannel marketing can trigger personalized product recommendations or a special discount offer in real-time, either through a pop-up on the website, an email, or a push notification on the customer’s mobile app. Similarly, if a customer leaves items in their online shopping cart, an omnichannel strategy might automatically send a reminder or offer a limited-time discount to encourage them to complete the purchase.
The ability to respond in real-time with personalized interactions is one of the key advantages of omnichannel marketing. It ensures that customers receive timely and relevant communications, enhancing their overall experience and increasing the likelihood of conversion. This dynamic use of data sets omnichannel marketing apart from integrated marketing, making it particularly effective in today’s fast-paced, customer-centric environment.
Integrated: Periodic Data Analysis and Segmented Targeting
While omnichannel marketing excels in real-time data utilization, integrated marketing takes a different approach by focusing on periodic data analysis and segmented targeting. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing comparison, integrated marketing is often characterized by its methodical and structured use of data to inform marketing campaigns.
Integrated marketing typically relies on periodic data collection and analysis, which is then used to inform broader marketing strategies and campaigns. This approach involves gathering data at specific intervals—such as quarterly or annually—and using this information to segment the target audience into different groups based on demographics, behavior, or other criteria. Marketing efforts are then tailored to these segments, with each group receiving messages and offers that are designed to resonate with their specific characteristics.
For example, a company might analyze its customer data to identify key segments, such as young professionals, families, and retirees. Based on this analysis, the company would develop targeted campaigns for each segment, ensuring that the messaging, content, and offers align with the preferences and needs of each group. While this approach allows for some level of personalization, it is typically more broad and less dynamic than the real-time personalization offered by omnichannel marketing.
The segmented targeting approach of integrated marketing is effective in creating consistent and cohesive campaigns that resonate with specific audience groups. However, because the data is analyzed periodically rather than in real-time, integrated marketing may not always be as responsive to immediate changes in customer behavior or market conditions. This can result in a less personalized experience, as the messaging may not be as closely aligned with the customer’s current context or needs.
Channel Coordination and Integration
Channel coordination and integration are at the heart of any successful marketing strategy, ensuring that a brand’s message is consistently delivered and resonates with the target audience. However, the methods by which omnichannel and integrated marketing achieve this coordination and integration differ significantly.
Omnichannel: Seamless Integration Across All Touchpoints
In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, omnichannel marketing is renowned for its ability to create seamless integration across all customer touchpoints. Omnichannel marketing is designed to provide a unified and consistent experience, no matter where or how a customer interacts with the brand. This approach views each touchpoint—whether it’s a physical store, a website, a mobile app, or social media—as part of a single, interconnected ecosystem.

Omnichannel marketing achieves seamless integration by ensuring that all channels are not only aligned in terms of messaging but are also interconnected in a way that allows customers to move effortlessly between them. For example, a customer might start their shopping journey by browsing products on a mobile app, continue by seeking further information on the brand’s website, and finally complete the purchase in a physical store. Throughout this journey, omnichannel marketing ensures that the customer’s experience is consistent and fluid, with no disruptions or inconsistencies in the messaging or experience.
This seamless integration is made possible through the use of advanced technology and data systems that enable real-time communication between channels. By integrating customer data from all touchpoints, omnichannel marketing can provide a personalized experience that adapts to the customer’s journey. For instance, if a customer adds an item to their online shopping cart but does not complete the purchase, the same cart might be available when they visit the brand’s store, or they might receive a personalized email reminder. This level of integration not only enhances the customer experience but also increases the likelihood of conversion and customer loyalty.
The emphasis on seamless integration across all touchpoints is one of the defining features of omnichannel marketing. It ensures that customers receive a consistent and cohesive experience, regardless of how they choose to interact with the brand. This approach is particularly effective in today’s digital age, where customers expect brands to be accessible and responsive across multiple channels.
Integrated: Coordination of Messaging and Campaigns Across Selected Channels
In contrast to omnichannel marketing, integrated marketing focuses on the coordination of messaging and campaigns across selected channels. While omnichannel marketing seeks to integrate all touchpoints into a single, seamless experience, integrated marketing typically involves aligning and coordinating marketing efforts across a few key channels.
Integrated marketing is based on the principle of consistency in messaging. The goal is to ensure that the brand’s message is coherent and unified across all selected channels, creating a strong and recognizable brand presence. This approach involves carefully planning and executing marketing campaigns that are consistent in their messaging, tone, and visuals, regardless of the channel through which they are delivered.

For example, an integrated marketing campaign might include television commercials, social media ads, and email newsletters, all of which convey the same core message and branding elements. The coordination of these efforts ensures that the brand’s message is reinforced across multiple platforms, increasing its impact and memorability. However, unlike omnichannel marketing, integrated marketing does not necessarily seek to create a seamless experience across all touchpoints. Instead, it focuses on ensuring that each campaign is consistent and aligned with the overall brand strategy.
The coordination of messaging and campaigns across selected channels is a key strength of integrated marketing. It allows businesses to maintain control over their brand narrative and ensure that their marketing efforts are focused and cohesive. However, this approach may not provide the same level of flexibility and responsiveness as omnichannel marketing, as it typically involves predefined campaigns rather than real-time adjustments based on customer interactions.
Operational Differences Between Omnichannel and Integrated Marketing
In the ongoing comparison between omnichannel vs integrated marketing, one of the most significant aspects to consider is the operational differences, particularly in the realm of technology and tools. Both strategies rely heavily on technology to execute their marketing efforts, but they do so in different ways, reflecting their distinct approaches to customer engagement and campaign execution. Understanding these differences in technology and tools is crucial for businesses looking to implement the most effective marketing strategy for their needs.
Technology and Tools
The tools and technologies employed in omnichannel vs integrated marketing are designed to support the core objectives of each strategy. While integrated marketing often leverages traditional and digital marketing tools to maintain consistency across channels, omnichannel marketing goes a step further by utilizing advanced Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, artificial intelligence (AI), and automation tools to deliver a seamless and personalized customer experience across all touchpoints.
Omnichannel: Advanced CRM, AI, and Automation Tools
Omnichannel marketing is deeply rooted in the use of advanced technology to create a cohesive and personalized customer experience. The complexity of managing and integrating multiple customer touchpoints requires sophisticated tools that can handle large volumes of data, enable real-time interactions, and provide deep insights into customer behavior. In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, omnichannel marketing’s reliance on advanced CRM, AI, and automation tools is a defining characteristic that sets it apart.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: At the heart of omnichannel marketing is the CRM system, which serves as the central hub for managing customer data across all channels. An advanced CRM system enables businesses to collect, store, and analyze data from various sources—whether it’s from in-store purchases, online interactions, mobile app usage, or social media engagement. This integrated data allows businesses to gain a 360-degree view of each customer, providing insights into their preferences, behaviors, and interactions with the brand. With this comprehensive view, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and expectations of each customer, enhancing the overall customer experience.
- AI: This plays a critical role in omnichannel marketing by enabling real-time personalization and automation. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict customer behavior, and deliver personalized content at the right time and place. For example, AI can be used to recommend products based on a customer’s browsing history, optimize email campaigns by predicting the best time to send messages, or even manage customer service inquiries through chatbots that provide instant, personalized responses. The use of AI in omnichannel marketing allows businesses to engage with customers in a more meaningful and efficient way, driving higher engagement and conversion rates.
- Automation Tools: Automation is another key component of omnichannel marketing, allowing businesses to streamline their marketing processes and deliver consistent experiences across all channels. Automation tools can be used to manage and coordinate marketing campaigns, trigger personalized communications based on customer actions, and ensure that all touchpoints are aligned with the overall brand strategy. For instance, an automation tool might send a follow-up email to a customer who abandoned their shopping cart, offer a discount to encourage completion of the purchase, and then update the CRM system with the customer’s response. By automating these processes, businesses can ensure that every customer interaction is timely, relevant, and consistent with the brand’s messaging.
The use of advanced CRM, AI, and automation tools in omnichannel marketing enables businesses to deliver a highly personalized and seamless customer experience. These tools not only help manage the complexity of multiple channels but also allow for real-time adjustments based on customer behavior, making omnichannel marketing a dynamic and responsive strategy.
Integrated: Traditional and Digital Marketing Tools
In contrast to the advanced technology used in omnichannel marketing, integrated marketing typically relies on a combination of traditional and digital marketing tools. The primary goal of integrated marketing is to ensure consistency in messaging and branding across selected channels, and the tools used reflect this focus. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing comparison, integrated marketing’s reliance on traditional and digital tools highlights its emphasis on campaign coherence and consistency rather than real-time personalization.
- Traditional Marketing Tools: Integrated marketing often incorporates traditional marketing tools such as print advertisements, television commercials, radio spots, and direct mail campaigns. These tools are effective in reaching a broad audience and building brand awareness. Traditional marketing tools are typically used in conjunction with digital efforts to create a comprehensive campaign that spans multiple platforms. For example, a brand might launch a new product with a television commercial that is supported by print ads in magazines and newspapers, along with direct mail brochures sent to targeted customers. The consistency of the message across these traditional channels is key to reinforcing the brand’s identity and ensuring that the campaign is memorable.
- Digital Marketing Tools: In addition to traditional tools, integrated marketing also leverages digital marketing tools such as email marketing platforms, social media management software, and content management systems (CMS). These tools enable businesses to extend their reach online and engage with customers through digital channels. However, unlike the advanced automation and AI tools used in omnichannel marketing, digital tools in integrated marketing are often used to maintain consistency in messaging rather than to deliver real-time personalization. For example, an integrated marketing campaign might involve scheduling a series of social media posts that align with the messaging in a television commercial or sending out an email newsletter that mirrors the content of a print ad. The focus is on ensuring that the message remains consistent across all digital touchpoints.
The reliance on traditional and digital marketing tools in integrated marketing reflects its structured approach to campaign execution. While these tools are effective in maintaining consistency and coherence, they may not offer the same level of flexibility or responsiveness as the advanced technologies used in omnichannel marketing. Integrated marketing campaigns are typically planned and executed over a set period, with adjustments made based on periodic analysis rather than real-time data.
Team Structure and Collaboration
Team structure and collaboration are fundamental to the success of both omnichannel and integrated marketing strategies. However, the focus and organization of these teams differ significantly, reflecting the unique goals and methods of each approach. In this section, we will explore how team structure and collaboration vary between omnichannel and integrated marketing, and how these differences influence the overall marketing strategy.
Omnichannel: Cross-Functional Teams with a Focus on Customer Experience
In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, omnichannel marketing requires a more dynamic and cross-functional team structure. The primary focus of omnichannel marketing is on delivering a seamless and personalized customer experience across all touchpoints. Achieving this goal necessitates a high level of collaboration between different departments and expertise areas within an organization.

- Cross-Functional Teams: Omnichannel marketing typically relies on cross-functional teams that bring together individuals from various departments, such as marketing, sales, customer service, IT, and product development. These teams work closely together to ensure that every aspect of the customer journey is considered and optimized. For example, marketing and IT teams might collaborate to integrate customer data from online and offline channels into a centralized CRM system, while customer service and product development teams might work together to address customer feedback and improve the product experience.
The cross-functional nature of omnichannel teams allows for a more holistic approach to marketing, where all aspects of the customer journey are seamlessly connected. By involving different departments, omnichannel marketing ensures that the customer experience is consistent and that any issues or opportunities can be addressed quickly and efficiently. This approach not only enhances the overall customer experience but also fosters innovation and agility within the organization. - Focus on Customer Experience: In omnichannel marketing, the customer experience is the central focus of all marketing efforts. This customer-centric approach requires teams to continuously monitor and analyze customer behavior across all touchpoints, using data to personalize interactions and improve the overall journey. The collaborative nature of cross-functional teams enables businesses to respond to customer needs in real-time, adjusting strategies and tactics as needed to ensure a seamless experience.
For instance, if customer feedback indicates a gap in the online shopping experience, the marketing, IT, and customer service teams can quickly collaborate to implement changes that address the issue. This level of responsiveness is essential in omnichannel marketing, where the goal is to create a unified and satisfying customer journey.
Integrated: Marketing Teams Focused on Campaign Execution and Coordination
On the other hand, integrated marketing typically involves a more traditional team structure that focuses on campaign execution and coordination. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing comparison, integrated marketing teams are often organized around specific campaigns or channels, with each team responsible for executing and coordinating their efforts to maintain consistency across all platforms.
- Marketing-Focused Teams: Integrated marketing teams are usually composed of marketing professionals who specialize in different areas, such as content creation, social media management, email marketing, and advertising. These teams are often organized by channel or campaign, with each team working on specific aspects of the overall marketing strategy. For example, one team might be responsible for executing a social media campaign, while another team focuses on email marketing efforts.
- The primary responsibility of integrated marketing teams is to ensure that all campaigns are aligned with the brand’s overall messaging and objectives. This involves coordinating efforts across different channels to maintain a consistent and cohesive brand presence. While these teams may collaborate with other departments, the focus is generally on executing marketing campaigns rather than on the broader customer experience.
- Focus on Campaign Execution and Coordination: In integrated marketing, the emphasis is on the effective execution of marketing campaigns and the coordination of messaging across selected channels. This approach requires meticulous planning and coordination to ensure that all marketing efforts are synchronized and reinforce the same core message. For example, a product launch might involve coordinated efforts across television, print, social media, and email, with each channel delivering a consistent message to the target audience.
- While integrated marketing teams excel at maintaining consistency and coherence across campaigns, they may not have the same level of flexibility or responsiveness as cross-functional omnichannel teams. Because integrated marketing is often organized around specific campaigns, it may be less adaptable to real-time changes in customer behavior or market conditions. However, this structured approach is highly effective for maintaining brand consistency and executing well-planned marketing strategies.
Implementation and Execution
The implementation and execution of a marketing strategy are critical components that determine its success. Omnichannel and integrated marketing each have their distinct approaches, shaped by their underlying goals and operational frameworks. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the right strategy for your business.
Omnichannel: Continuous Optimization and Real-Time Adjustments
Omnichannel marketing is inherently dynamic, designed to adapt quickly to changing customer behaviors and market conditions. One of the defining features of omnichannel marketing is its focus on continuous optimization and real-time adjustments, making it a highly responsive and customer-centric approach. In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, this adaptability is a significant advantage, allowing businesses to remain agile and relevant in an increasingly fast-paced digital environment.
- Continuous Optimization: In omnichannel marketing, the process of optimization is ongoing. This means that marketing efforts are continuously monitored, analyzed, and refined to ensure that they are meeting the needs of customers and achieving business goals. The use of advanced data analytics and AI-powered tools enables businesses to track customer interactions across all channels in real-time, providing insights into what is working and what isn’t. For example, if a particular email campaign is not generating the expected engagement, omnichannel marketing allows marketers to quickly adjust the content, timing, or targeting to improve performance.
- This continuous optimization process is integral to the success of omnichannel marketing, as it ensures that marketing efforts are always aligned with current customer expectations and market trends. By making incremental improvements on an ongoing basis, businesses can enhance the customer experience, increase engagement, and drive higher conversion rates.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Another critical aspect of omnichannel marketing is its ability to make real-time adjustments based on customer behavior and external factors. Unlike traditional marketing approaches that rely on pre-planned campaigns, omnichannel marketing is designed to be flexible and responsive. For example, if a customer abandons their shopping cart online, an omnichannel strategy might immediately trigger a follow-up email with a special offer or a reminder to complete the purchase. Similarly, if a sudden trend emerges on social media, the marketing team can quickly create and deploy content that capitalizes on the trend, ensuring that the brand remains relevant and engaged with its audience.
- The capability for real-time adjustments allows omnichannel marketing to maintain a high level of personalization and relevance, which is essential for meeting the demands of today’s consumers. This adaptability also makes it possible for businesses to respond quickly to unexpected challenges or opportunities, minimizing the risk of missed opportunities or ineffective campaigns.
Integrated: Planned Campaigns with Periodic Evaluations
In contrast to the dynamic nature of omnichannel marketing, integrated marketing is characterized by a more structured and methodical approach to implementation and execution. Integrated marketing typically involves planned campaigns that are executed over a set period, with periodic evaluations to assess their effectiveness. This approach emphasizes consistency and coherence across all marketing efforts, ensuring that the brand message is unified and reinforced across all channels.

- Planned Campaigns: The foundation of integrated marketing lies in the careful planning and execution of marketing campaigns. These campaigns are typically designed well in advance, with specific goals, messaging, and tactics outlined for each channel. For example, a company might develop a six-month marketing plan that includes a series of coordinated campaigns across social media, email, print, and television. Each campaign is meticulously planned to ensure that it aligns with the overall brand strategy and objectives.
- The advantage of planned campaigns in integrated marketing is that they allow for thorough preparation and coordination. By planning campaigns in advance, businesses can ensure that all marketing efforts are synchronized and that the brand message is consistently delivered across all channels. This approach is particularly effective for maintaining brand coherence and ensuring that marketing efforts are aligned with long-term business goals.
- Periodic Evaluations: While omnichannel marketing focuses on continuous optimization, integrated marketing relies on periodic evaluations to assess the effectiveness of its campaigns. These evaluations are typically conducted at regular intervals, such as quarterly or annually, and involve analyzing KPIs such as engagement rates, conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI). Based on these evaluations, adjustments may be made to future campaigns to improve performance.
- The periodic evaluation process allows integrated marketing teams to take a step back and review the overall effectiveness of their campaigns. This approach is valuable for identifying trends, understanding what resonates with the target audience, and making informed decisions about future marketing efforts. However, because these evaluations are conducted periodically rather than in real-time, integrated marketing may be less responsive to immediate changes in customer behavior or market conditions.
The planned nature of integrated marketing campaigns, combined with periodic evaluations, ensures that marketing efforts are consistent and aligned with the brand’s overall strategy. While this approach may not offer the same level of flexibility as omnichannel marketing, it is highly effective for maintaining a cohesive brand presence and achieving long-term marketing objectives.
Customer Experience in Omnichannel vs Integrated Marketing
Personalization and Engagement
The concept of personalization has evolved dramatically over the years, from basic segmentation techniques to highly sophisticated, data-driven strategies that allow businesses to interact with customers on a deeply individualized level. In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, the degree and nature of personalization offered by each approach are markedly different, influencing how customers perceive and engage with a brand.
Omnichannel: Tailored experiences based on individual customer data
Omnichannel marketing is fundamentally built on the idea of creating tailored experiences based on individual customer data. This approach leverages advanced technologies, such as AI and machine learning, to gather and analyze vast amounts of data from various touchpoints, including online and offline interactions. By integrating this data into a unified customer profile, omnichannel marketing enables businesses to deliver highly personalized content, offers, and recommendations that resonate with the unique preferences and behaviors of each customer.

For example, consider a customer who frequently browses a specific product category on a brand’s website but has not yet made a purchase. Omnichannel marketing allows the brand to recognize this behavior and respond with personalized content, such as product recommendations or a special discount, delivered through the customer’s preferred channel—be it email, social media, or a mobile app notification. This level of personalization extends beyond simple product recommendations; it encompasses the entire customer journey, ensuring that every interaction is relevant, timely, and aligned with the customer’s needs and desires. As a result, omnichannel marketing creates a seamless and cohesive experience that feels uniquely tailored to the individual, fostering deeper engagement and stronger loyalty.
Integrated: Consistent messaging tailored to broad audience segments
In contrast, integrated marketing approaches personalization from a broader perspective, focusing on delivering consistent messaging that is tailored to broad audience segments rather than to individual customers. While integrated marketing certainly recognizes the value of personalization, it typically employs it through segmentation techniques that group customers based on shared characteristics, such as demographics, purchasing behavior, or geographic location. These segments are then targeted with messaging and offers that are designed to appeal to the common interests and needs of the group as a whole.

For instance, a brand might segment its audience into groups such as young professionals, families, and retirees, and create marketing campaigns that are tailored to the general preferences and lifestyles of each segment. While this approach allows for some degree of personalization, it is inherently less precise than the one-to-one personalization enabled by omnichannel marketing. Integrated marketing’s focus on segmentation means that the messaging is consistent across channels but may not always be as directly relevant to each individual customer. This can result in a more generalized customer experience, which, while coherent and aligned with the brand’s overall strategy, may not engage customers as deeply as the highly personalized experiences offered by omnichannel marketing.
Customer Journey Mapping
Customer journey mapping is a powerful tool that helps businesses visualize and understand the steps customers take as they interact with a brand. It involves identifying the various touchpoints where customers engage with the brand, from initial awareness to post-purchase interactions, and mapping out the pathways customers typically follow. The approach to customer journey mapping differs significantly in omnichannel vs integrated marketing, reflecting each strategy’s unique focus and objectives.
Omnichannel: Detailed mapping of customer interactions across all touchpoints
In omnichannel marketing, customer journey mapping is an intricate and detailed process that aims to capture every possible interaction a customer might have with a brand across all channels and touchpoints. The goal of omnichannel marketing is to create a seamless and cohesive customer experience, regardless of how or where the customer chooses to interact with the brand. To achieve this, omnichannel customer journey mapping involves integrating data from multiple sources—both online and offline—to build a comprehensive view of the customer’s journey.
For example, a customer might begin their journey by seeing an ad on social media, then visit the brand’s website to browse products, sign up for a newsletter, and finally make a purchase in a physical store. In an omnichannel marketing strategy, each of these interactions is carefully mapped and analyzed to ensure that the customer receives a consistent and personalized experience at every step. This detailed mapping allows businesses to identify potential friction points or opportunities for engagement, enabling them to optimize the journey in real-time. The result is a highly customized experience that adapts to the customer’s behavior and preferences, enhancing satisfaction and fostering long-term loyalty.
Omnichannel customer journey mapping is not limited to a linear path; it accounts for the fact that customers may move back and forth between different channels, or even engage with multiple channels simultaneously. For instance, a customer might use a mobile app to check product availability while standing in a physical store or might interact with a customer service chatbot while browsing a website. Omnichannel marketing ensures that all these interactions are interconnected, providing a unified and seamless experience that feels natural and intuitive to the customer.
Integrated: Focus on touchpoints relevant to specific campaigns
In contrast, integrated marketing approaches customer journey mapping with a focus on the touchpoints relevant to specific campaigns. Integrated marketing is centered around the coordination and consistency of messaging across selected channels, typically organized around distinct marketing campaigns. As a result, the customer journey mapping process in integrated marketing tends to be more campaign-specific, concentrating on the interactions that are most pertinent to the campaign’s objectives.
For example, if a brand is running a holiday promotion campaign, integrated marketing would focus on mapping the customer journey as it relates to that specific promotion. The journey might include touchpoints such as email newsletters announcing the promotion, social media ads highlighting special offers, and in-store signage directing customers to discounted products. The mapping process would involve identifying the key moments where customers are likely to engage with the campaign and ensuring that the messaging is consistent and aligned across these touchpoints.
While integrated marketing’s approach to customer journey mapping is effective in creating focused and coherent campaigns, it may not provide the same level of detail or personalization as omnichannel marketing. Because integrated marketing is often tied to specific campaigns, the customer journey mapping process may not fully capture the complexity of the customer’s interactions with the brand as a whole. Instead, it emphasizes the touchpoints that are most relevant to the campaign, ensuring that the messaging is delivered consistently but possibly overlooking other aspects of the customer’s journey that fall outside the scope of the campaign.
Customer Feedback and Adaptation
Customer feedback is an invaluable resource for businesses, providing insights into customer preferences, pain points, and overall satisfaction with the brand. How this feedback is utilized—whether in real-time or post-campaign—can significantly impact the effectiveness of a marketing strategy. In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, the timing and method of feedback integration highlight the distinct philosophies underlying each approach.
Omnichannel: Real-time feedback integration and adaptation
Omnichannel marketing is inherently designed to be responsive and adaptive, with a strong emphasis on real-time feedback integration. This approach recognizes that customer expectations and behaviors can change rapidly, and businesses must be able to adjust their strategies accordingly to maintain a positive customer experience. In an omnichannel marketing framework, customer feedback is continuously collected from various touchpoints—such as social media interactions, customer service inquiries, website behavior, and in-store experiences—and analyzed in real-time.

For example, if a customer expresses dissatisfaction with a particular aspect of their experience, such as difficulty navigating a mobile app or a delay in delivery, omnichannel marketing allows the brand to address the issue immediately. This might involve deploying an update to the app, sending a personalized apology along with a discount offer, or even adjusting logistics to improve delivery times. By integrating feedback in real-time, omnichannel marketing ensures that issues are resolved quickly, minimizing negative impacts on the customer experience and demonstrating the brand’s commitment to customer satisfaction.
This real-time feedback loop is not only reactive but also proactive. Omnichannel marketing uses advanced analytics and AI to predict potential issues before they escalate, allowing businesses to make preemptive adjustments. For instance, if data indicates that a certain product is frequently returned due to sizing issues, the brand can adjust its product descriptions, offer size guides, or even redesign the product to better meet customer expectations. This ability to adapt in real-time enhances the customer experience by ensuring that the brand remains responsive to customer needs and can make swift improvements to its offerings.
Integrated: Post-campaign feedback and future adjustments
On the other hand, integrated marketing typically adopts a more traditional approach to customer feedback, focusing on post-campaign feedback and future adjustments. Integrated marketing strategies are often organized around specific campaigns with clearly defined start and end points. Feedback is usually gathered at the conclusion of these campaigns, allowing the brand to evaluate the overall effectiveness of the marketing efforts and identify areas for improvement.
For example, after running a multi-channel advertising campaign, a brand using an integrated marketing approach might conduct surveys, analyze sales data, and review customer service interactions to assess how well the campaign resonated with the target audience. Based on this post-campaign feedback, the brand can make adjustments to future campaigns, such as refining messaging, adjusting targeting strategies, or improving product offerings. While this approach allows for thoughtful analysis and strategic planning, it may not provide the same level of immediacy as the real-time feedback integration seen in omnichannel marketing.
The post-campaign feedback process in integrated marketing is valuable for long-term planning and optimization. It enables businesses to take a comprehensive view of their marketing efforts, learning from past experiences to improve future campaigns. However, because this feedback is typically collected after the fact, it may not allow for immediate adjustments during the campaign itself. This can be a disadvantage in fast-paced markets where customer preferences and competitive dynamics can shift rapidly.
Summary of Differences Between Omnichannel vs Integrated Marketing
Both strategies offer distinct advantages, but they differ fundamentally in how they approach marketing efforts, operational execution, and customer experience. Omnichannel marketing is renowned for its ability to create a seamless, personalized customer journey across all touchpoints, driven by real-time data and advanced technology.
In contrast, integrated marketing emphasizes consistency and coherence, focusing on well-planned campaigns that deliver a unified brand message across selected channels. Understanding the strategic, operational, and customer experience differences between these two approaches is essential for businesses seeking to optimize their marketing strategies and achieve sustained success in an increasingly complex marketplace.
Strategic Differences
- Omnichannel Marketing: Focuses on the entire customer journey, creating a seamless and personalized experience across all touchpoints. It prioritizes real-time data utilization and personalized interactions, making it highly responsive to individual customer needs.
- Integrated Marketing: Emphasizes consistency and coherence in messaging across selected channels. It is centered around well-planned campaigns that target broad audience segments, with a strong focus on maintaining a unified brand presence.
Operational Differences
- Omnichannel Marketing: Relies on advanced technology like CRM systems, AI, and automation tools to integrate and optimize customer interactions in real-time. It involves cross-functional teams that collaborate closely to enhance the overall customer experience and make continuous, real-time adjustments.
- Integrated Marketing: Utilizes traditional and digital marketing tools to execute well-coordinated campaigns. The team structure is often more traditional, with a focus on campaign execution and periodic evaluations to make future adjustments.
Customer Experience Differences
- Omnichannel Marketing: Delivers highly personalized experiences by integrating real-time feedback and continuously adapting to customer behavior. It ensures that every touchpoint is connected, providing a seamless and consistent journey tailored to individual preferences.
- Integrated Marketing: Focuses on delivering consistent messaging tailored to broad audience segments. Customer feedback is typically gathered post-campaign, with adjustments made in future campaigns. While this ensures coherence, it may lack the immediacy and personalization offered by omnichannel marketing.
In summary, omnichannel marketing is characterized by its dynamic, customer-centric approach, leveraging real-time data and advanced technology to create a personalized and seamless customer experience. Integrated marketing, while more structured and consistent, emphasizes campaign coordination and long-term strategic planning, making it effective for maintaining brand coherence across multiple channels. The choice between these two approaches depends on a business’s specific goals, whether prioritizing personalized customer engagement or consistent brand messaging.
Implementation Strategies for Omnichannel Marketing
Planning and Strategy Development
Assessing Current Marketing Efforts and Identifying Gaps
The first step in developing an effective omnichannel marketing strategy is to conduct a detailed assessment of the current marketing efforts. This involves reviewing all existing marketing channels and tactics to determine how well they are performing individually and collectively. The goal is to gain a clear understanding of how each channel contributes to the overall customer experience and to identify any gaps or inconsistencies that may exist.
For example, a business might find that while its email marketing campaigns are highly effective, its social media presence is inconsistent or lacks engagement. Alternatively, the company might discover that while its in-store experience is strong, the online shopping experience is disjointed or difficult to navigate. Identifying these gaps is essential for creating a more integrated and seamless customer journey, as it highlights the areas that need improvement or better coordination.

In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, this assessment phase is particularly important because it lays the groundwork for creating a truly interconnected strategy. Unlike integrated marketing, which may focus more on ensuring consistency within individual campaigns, omnichannel marketing requires a holistic view that considers how all channels work together to support the customer journey. By identifying gaps in the current marketing efforts, businesses can prioritize the areas that need the most attention and develop strategies to bridge these gaps, ensuring a more cohesive and effective omnichannel approach.
Defining Clear Objectives, KPIs, and Customer Personas
Once the current marketing efforts have been assessed and gaps identified, the next step in planning and strategy development for omnichannel marketing is to define clear objectives, KPIs, and customer personas. These elements serve as the guiding framework for the entire strategy, ensuring that all marketing efforts are aligned with the business’s goals and tailored to meet the specific needs of its target audience.
- Defining Clear Objectives: The objectives of an omnichannel marketing strategy should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). These objectives might include goals such as increasing customer retention rates, boosting average order value, enhancing brand loyalty, or improving the overall customer satisfaction score. Clear objectives provide direction and focus, helping the marketing team to prioritize initiatives and allocate resources effectively. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing comparison, omnichannel objectives are typically more customer-centric, focusing on enhancing the customer experience across all touchpoints rather than simply achieving campaign-specific goals.
- Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): KPIs are essential for measuring the success of an omnichannel marketing strategy. These metrics should be closely tied to the defined objectives and provide actionable insights into how well the strategy is performing. For example, KPIs might include metrics such as customer lifetime value (CLV), customer acquisition cost (CAC), conversion rates across different channels, and the percentage of customers engaging with multiple touchpoints. By tracking these KPIs, businesses can monitor progress, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to optimize the strategy. In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, omnichannel KPIs often emphasize cross-channel interactions and the overall customer journey, rather than focusing solely on the performance of individual campaigns.
- Developing Customer Personas: Customer personas are fictional representations of a brand’s ideal customers, based on real data and insights. These personas help businesses to better understand their target audience’s needs, preferences, behaviors, and pain points. In an omnichannel marketing strategy, customer personas are particularly important because they guide the development of personalized experiences across all touchpoints. By understanding who the customers are, what motivates them, and how they interact with different channels, businesses can tailor their messaging, content, and offers to resonate more effectively with each segment of their audience.
- For example, a business might develop distinct personas for different customer segments, such as busy professionals, tech-savvy millennials, and value-conscious shoppers. Each persona would have its own set of characteristics, including preferred communication channels, typical purchasing behaviors, and key factors influencing their buying decisions. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing framework, omnichannel personas are often more detailed and dynamic, reflecting the complexity of the customer journey across multiple touchpoints. These personas are used to create personalized marketing strategies that engage customers in a more meaningful and relevant way, ultimately driving higher levels of engagement and loyalty.
Technology and Tools
Selecting the Right CRM and Marketing Automation Tools
One of the foundational aspects of implementing an effective omnichannel marketing strategy is choosing the right CRM and marketing automation tools. These tools are essential for managing customer data, automating marketing processes, and personalizing interactions across various channels. In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, the CRM and marketing automation tools used in omnichannel strategies must be robust, flexible, and capable of handling complex, real-time data.

- CRM Tools: The CRM system serves as the central hub for all customer data in an omnichannel marketing strategy. It is where data from various touchpoints—such as online purchases, social media interactions, in-store visits, and customer service inquiries—converge to create a comprehensive view of each customer. When selecting a CRM for omnichannel marketing, businesses should prioritize systems that offer advanced data analytics, real-time data processing, and integration capabilities with other tools and platforms.
- A powerful CRM system in an omnichannel strategy not only tracks customer interactions but also helps in segmenting audiences, identifying patterns, and predicting future behavior. For example, a CRM might analyze purchase history and online behavior to suggest relevant products to customers via personalized email campaigns or targeted ads. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing comparison, the CRM in an omnichannel strategy is more dynamic and interactive, providing a continuous flow of insights that inform real-time decision-making and customer engagement.
- Marketing Automation Tools: Marketing automation tools are another critical component of an omnichannel marketing strategy. These tools enable businesses to automate repetitive tasks, such as sending emails, posting on social media, or managing ad campaigns, allowing marketers to focus on more strategic activities. In an omnichannel environment, marketing automation tools must be capable of managing campaigns across multiple channels, ensuring that messaging is consistent and timely.
- For instance, marketing automation tools can be used to trigger specific actions based on customer behavior. If a customer abandons their shopping cart, the automation tool can automatically send a follow-up email with a personalized offer to encourage them to complete the purchase. Additionally, these tools can segment audiences based on real-time data, ensuring that each customer receives content that is relevant to their current needs and preferences. The key difference in omnichannel vs integrated marketing lies in the level of personalization and immediacy that marketing automation tools can provide in an omnichannel strategy.
Ensuring Seamless Data Integration and Accessibility
Once the right CRM and marketing automation tools have been selected, the next crucial step in implementing an omnichannel marketing strategy is ensuring seamless data integration and accessibility. In an omnichannel environment, data flows continuously between different systems and channels, providing a unified view of the customer. Seamless data integration is essential for maintaining the accuracy and relevance of customer information, which in turn drives the effectiveness of personalized marketing efforts.
- Data Integration: Data integration in an omnichannel marketing strategy involves connecting various data sources—such as CRM systems, eCommerce platforms, social media channels, and in-store point-of-sale systems—so that information can be shared and accessed across the entire marketing ecosystem. This integration allows businesses to consolidate customer data into a single, unified profile, which can then be used to deliver personalized experiences.
- For example, if a customer interacts with a brand on social media, makes a purchase on the website, and later visits a physical store, data from all these interactions should be integrated into their profile. This enables the brand to recognize the customer across all touchpoints and provide a consistent, personalized experience. The ability to integrate data from multiple sources is one of the key differentiators in omnichannel vs integrated marketing, where omnichannel marketing requires a higher level of integration to achieve seamless customer experiences.
- Data Accessibility: In addition to integration, data accessibility is a critical factor in the success of an omnichannel marketing strategy. Marketers, sales teams, and customer service representatives must have easy access to up-to-date customer information to engage effectively with customers. This means that data should be readily available in real-time, allowing teams to respond quickly to customer inquiries, preferences, and behaviors.
- For instance, if a customer contacts customer service with a question about an online order, the representative should be able to access the customer’s entire interaction history, including previous purchases, website visits, and social media engagements. This level of accessibility ensures that the representative can provide informed and personalized assistance, enhancing the overall customer experience. In omnichannel vs integrated marketing, omnichannel strategies place a greater emphasis on real-time data accessibility, ensuring that all customer-facing teams are equipped with the information they need to deliver exceptional service.
The selection of CRM and marketing automation tools, along with seamless data integration and accessibility, are critical components of a successful omnichannel marketing strategy. These technologies enable businesses to manage complex customer data, automate personalized marketing efforts, and ensure that all touchpoints are connected to deliver a cohesive and seamless customer experience.
Team Structure and Collaboration
Building a Cross-Functional Team with Diverse Expertise
The implementation of an effective omnichannel marketing strategy begins with assembling a cross-functional team that brings together individuals with diverse skills and expertise. In the context of omnichannel vs integrated marketing, this team structure is essential because omnichannel marketing encompasses a wide range of activities, from data analytics and customer experience design to content creation and technology management. A cross-functional team ensures that all aspects of the customer journey are addressed, allowing the brand to deliver a cohesive and personalized experience across all touchpoints.
A cross-functional team typically includes members from various departments such as marketing, sales, customer service, IT, and product development. Each team member brings a unique perspective and set of skills to the table, contributing to a holistic approach to marketing. For example, marketing professionals might focus on crafting compelling content and campaigns, while IT specialists ensure that the necessary technology infrastructure is in place to support seamless data integration and automation. Similarly, customer service representatives provide insights into customer needs and preferences, which can inform the development of more effective engagement strategies.

In an omnichannel marketing strategy, the collaboration between these diverse team members is crucial. For instance, the marketing and IT teams must work closely together to implement CRM systems and marketing automation tools that enable real-time data analysis and personalized customer interactions. Likewise, sales and customer service teams need to coordinate with the marketing team to ensure that the messaging and offers are consistent across all channels and tailored to meet the specific needs of different customer segments.
The cross-functional nature of the team also allows for more agile decision-making and problem-solving. In the fast-paced world of omnichannel marketing, where customer expectations and market conditions can change rapidly, having a team that can quickly adapt and respond to new challenges is invaluable. By leveraging the diverse expertise within the team, businesses can develop more innovative and effective strategies that drive customer engagement and loyalty.
Promoting Collaboration and Continuous Learning
In addition to building a cross-functional team, promoting collaboration and continuous learning is a key component of a successful omnichannel marketing strategy. Collaboration within the team is essential for ensuring that all members are aligned with the overall marketing objectives and are working together to deliver a consistent and seamless customer experience. In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing comparison, omnichannel marketing places a greater emphasis on cross-departmental collaboration, as the integration of multiple channels and touchpoints requires close coordination between different areas of the business.
Promoting a culture of collaboration involves creating an environment where team members feel empowered to share ideas, insights, and feedback. Regular team meetings, brainstorming sessions, and collaborative tools such as project management software can facilitate open communication and help ensure that everyone is on the same page. For example, a weekly meeting might bring together representatives from marketing, IT, sales, and customer service to discuss ongoing campaigns, review performance metrics, and identify opportunities for improvement. This collaborative approach not only fosters a sense of shared ownership but also helps to identify potential issues or gaps in the strategy before they become significant problems.
Continuous learning is another critical aspect of successful collaboration in an omnichannel marketing strategy. The rapidly evolving nature of digital marketing means that team members must stay up-to-date with the latest trends, tools, and technologies. Encouraging continuous learning through professional development opportunities, such as workshops, webinars, and certifications, ensures that the team remains equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to excel in their roles.

For instance, marketing team members might attend training sessions on the latest CRM software or participate in a webinar on AI-driven marketing strategies. IT specialists might pursue certifications in data integration platforms or learn about the latest developments in cybersecurity. By fostering a culture of continuous learning, businesses can ensure that their teams are always at the forefront of industry best practices, which is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in the omnichannel vs integrated marketing landscape.
Furthermore, continuous learning supports innovation within the team. As team members gain new knowledge and skills, they are better equipped to experiment with new ideas and approaches, leading to more creative and effective marketing strategies. This focus on innovation is particularly important in omnichannel marketing, where the ability to adapt to new technologies and consumer behaviors can significantly impact the success of the overall strategy.
Continuous Optimization and Innovation
Omnichannel marketing thrives on its ability to adapt quickly to changing consumer behaviors and This section explores the importance of emphasizing data-driven decision-making and agility, as well as staying updated with technological advancements and market trends, which are critical for the successful implementation of an omnichannel marketing strategy.
Emphasizing Data-Driven Decision-Making and Agility
At the core of an effective omnichannel marketing strategy is the ability to make informed, data-driven decisions. In the comparison between omnichannel vs integrated marketing, omnichannel marketing places a stronger emphasis on leveraging data to optimize marketing efforts continuously. This approach requires a robust infrastructure for collecting, analyzing, and acting on data in real-time, allowing businesses to respond quickly to changes in customer behavior and market conditions.
Data-driven decision-making in omnichannel marketing involves collecting data from various touchpoints, such as website interactions, social media engagement, in-store purchases, and customer service inquiries. This data is then integrated into a centralized system, often within a CRM platform, where it can be analyzed to gain insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and trends. By understanding these patterns, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to meet the specific needs and expectations of their customers, leading to more personalized and effective campaigns.
For example, if data analysis reveals that a particular customer segment prefers to shop online during specific hours, the marketing team can optimize email campaigns or targeted ads to reach these customers at the most opportune times. Similarly, if a product is trending on social media, the team can quickly adjust its promotional strategy to capitalize on the increased interest. This level of agility is a hallmark of omnichannel marketing, enabling businesses to make real-time adjustments that enhance the customer experience and drive better results.

In addition to optimizing current campaigns, data-driven decision-making also supports long-term strategic planning. By continuously monitoring KPIs such as customer lifetime value, conversion rates, and engagement levels, businesses can identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about where to allocate resources. This ongoing process of optimization ensures that the marketing strategy remains aligned with the company’s objectives and responsive to evolving customer needs.
Agility is another crucial component of omnichannel marketing. In the fast-paced digital environment, where consumer behaviors and market conditions can shift rapidly, the ability to pivot quickly is essential. Omnichannel marketing strategies are designed to be flexible and adaptive, allowing businesses to respond to new opportunities or challenges as they arise. For example, if a new social media platform gains popularity, an agile omnichannel strategy would allow the marketing team to quickly incorporate this platform into their overall strategy, ensuring that the brand remains relevant and engaged with its audience.
This emphasis on agility also extends to customer feedback and interaction. Unlike integrated marketing, which often relies on post-campaign analysis, omnichannel marketing continuously integrates customer feedback to refine and enhance the customer experience. Whether through social media interactions, online reviews, or direct customer inquiries, real-time feedback is used to make immediate adjustments, ensuring that the marketing strategy remains aligned with customer expectations.
Staying Updated with Technological Advancements and Market Trends
In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing landscape, staying updated with technological advancements and market trends is critical for maintaining a competitive edge. Omnichannel marketing, by its very nature, is deeply intertwined with the latest technologies that enable seamless integration, personalization, and real-time interaction across multiple channels. As technology continues to evolve, businesses must stay ahead of the curve to ensure that their omnichannel strategies are not only effective but also innovative.
One of the key technological advancements driving omnichannel marketing is the rise of AI and machine learning. These technologies enable more sophisticated data analysis, allowing businesses to predict customer behavior, automate personalized interactions, and optimize marketing efforts on the fly. For instance, AI-powered recommendation engines can analyze a customer’s browsing and purchase history to suggest products they are most likely to be interested in, thereby enhancing the shopping experience and increasing the likelihood of conversion.
Another important trend is the increasing use of mobile technology. As more consumers rely on smartphones and tablets for their shopping and browsing needs, businesses must ensure that their omnichannel strategies are mobile-friendly. This includes optimizing websites and apps for mobile use, leveraging mobile-specific marketing channels such as SMS and push notifications, and ensuring that mobile and desktop experiences are seamlessly integrated. The ability to provide a consistent and personalized experience across all devices is a critical aspect of omnichannel marketing that sets it apart from more traditional, channel-specific approaches.

Staying updated with market trends also involves understanding changes in consumer behavior and preferences. For example, the growing demand for sustainable and ethically produced products has prompted many businesses to incorporate these values into their omnichannel marketing strategies. By highlighting sustainable practices in their messaging and offering eco-friendly options, businesses can align themselves with the values of their target audience, thereby strengthening brand loyalty and engagement.
In addition to technological advancements, businesses must also be aware of regulatory changes that may impact their omnichannel strategies. For instance, increasing concerns about data privacy and security have led to stricter regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Businesses must ensure that their data collection and marketing practices comply with these regulations while still delivering a personalized and effective customer experience.
To stay ahead in the omnichannel vs integrated marketing landscape, businesses must adopt a mindset of continuous learning and innovation. This involves regularly evaluating and updating their technology stack, staying informed about emerging trends, and being willing to experiment with new approaches. By fostering a culture of innovation, businesses can ensure that their omnichannel strategies remain effective and relevant in an ever-changing market.
Conclusion
In the omnichannel vs integrated marketing debate, the choice between these two approaches ultimately depends on a business’s specific goals and the nature of its customer interactions. Omnichannel marketing is ideal for businesses that prioritize a customer-centric approach, where personalized experiences and real-time engagement are critical to success. This strategy is particularly effective in today’s fast-paced digital environment, where consumer expectations are high, and the ability to adapt quickly can make a significant difference.
Integrated marketing, on the other hand, is well-suited for businesses that value consistency and long-term planning, where the focus is on delivering a cohesive brand message across multiple channels. This approach provides a reliable framework for executing campaigns that are aligned with the brand’s overall strategy, ensuring that all marketing efforts reinforce the desired brand identity.
In conclusion, both omnichannel and integrated marketing have their merits, and the decision to adopt one over the other—or to blend elements of both—should be based on a thorough understanding of the business’s objectives and the needs of its customers. By carefully considering the strategic, operational, and customer experience factors discussed in this blog post, businesses can make informed decisions that will enhance their marketing effectiveness and drive sustained success in an increasingly complex marketplace.