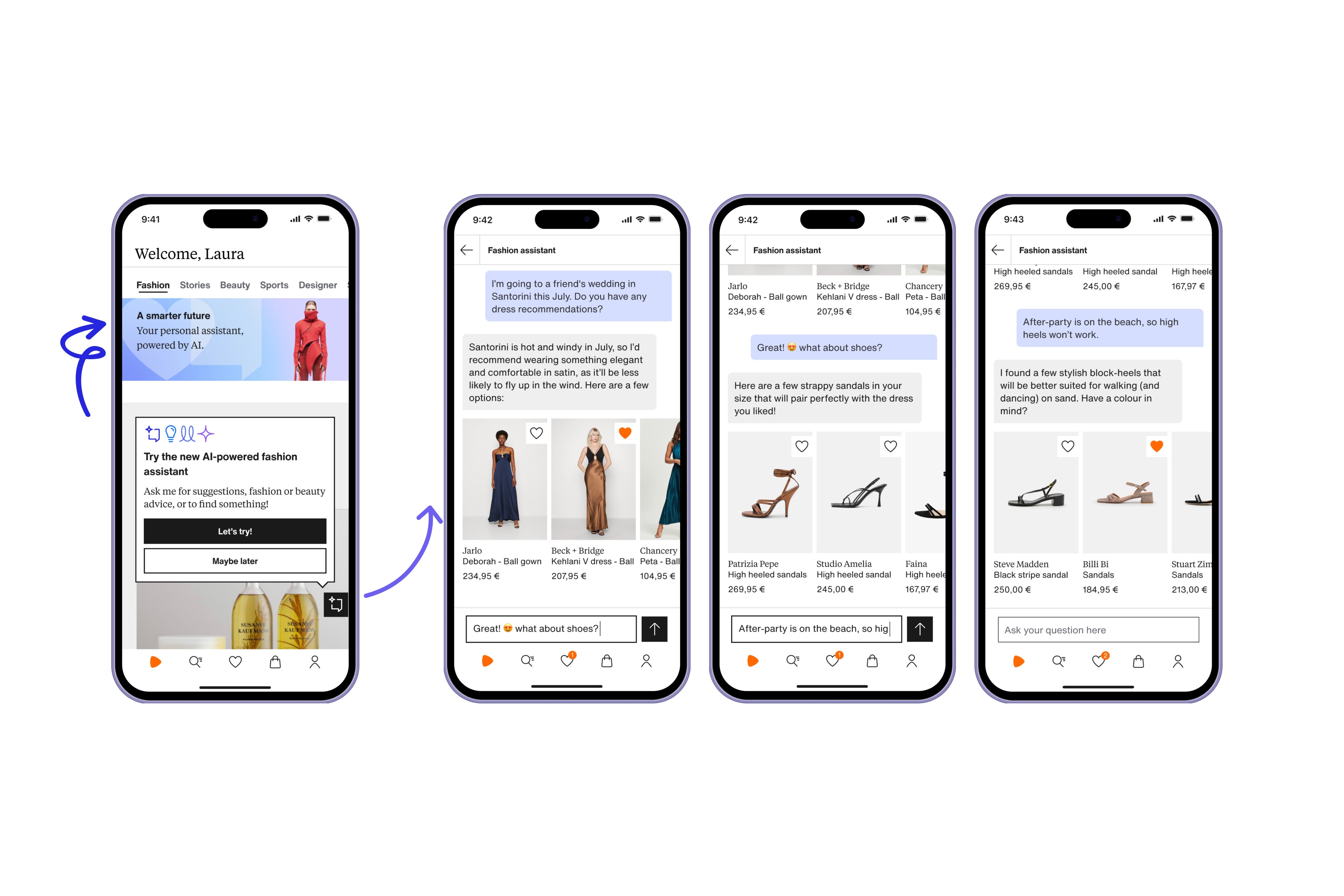
This section highlights how AI is transforming the front-end experience of eCommerce. From personalization and tailored content to conversational support and intuitive search, AI is redefining how customers interact with brands. Instead of generic promotions or one-size-fits-all interfaces, businesses now deliver shopping journeys that adapt to each individual in real time. Customers benefit from smarter recommendations, faster support, and more relevant experiences, while businesses see higher engagement and stronger loyalty.
These applications matter because they turn data into meaningful interactions that drive measurable results. AI in eCommerce examples at this stage show that personalization and discovery are no longer optional features—they are competitive necessities. Yet, customer-facing intelligence cannot stand alone. As Part 2 will show, these innovations are only sustainable when supported by an equally strong back-end AI ecosystem in pricing, logistics, fraud detection, and sustainability. Together, these layers ensure that the experiences customers see upfront are reliable, scalable, and profitable for the business behind them.
Table of Contents
AI in Personalization & Recommendations
AI in eCommerce examples of personalization come in many forms. Some are highly visible, such as a “You may also like” carousel on Amazon or Netflix-style recommendation lists adapted for retail. Others work silently in the background, like personalized pricing models or product sort orders that adjust to reflect the browsing history of a shopper. What unites all of these AI in eCommerce examples is the use of massive data inputs—past purchases, search behavior, demographic details, and contextual signals like device or location—processed by machine learning algorithms that predict what a customer will want next.
General examples
Amazon’s Collaborative Filtering System And Its Revenue Impact
Among the most iconic AI in eCommerce examples, Amazon’s recommendation engine stands as a benchmark for the industry. Amazon pioneered the use of collaborative filtering, a machine learning approach that analyzes the behaviors of millions of shoppers to uncover patterns. The system doesn’t just look at what one customer has purchased; it examines what others with similar behavior have also bought or viewed. From this, it generates suggestions that are both highly relevant and context-sensitive. Whether it’s “customers who bought this item also bought” or “recommended for you,” these prompts are rooted in deep data analysis rather than guesswork.
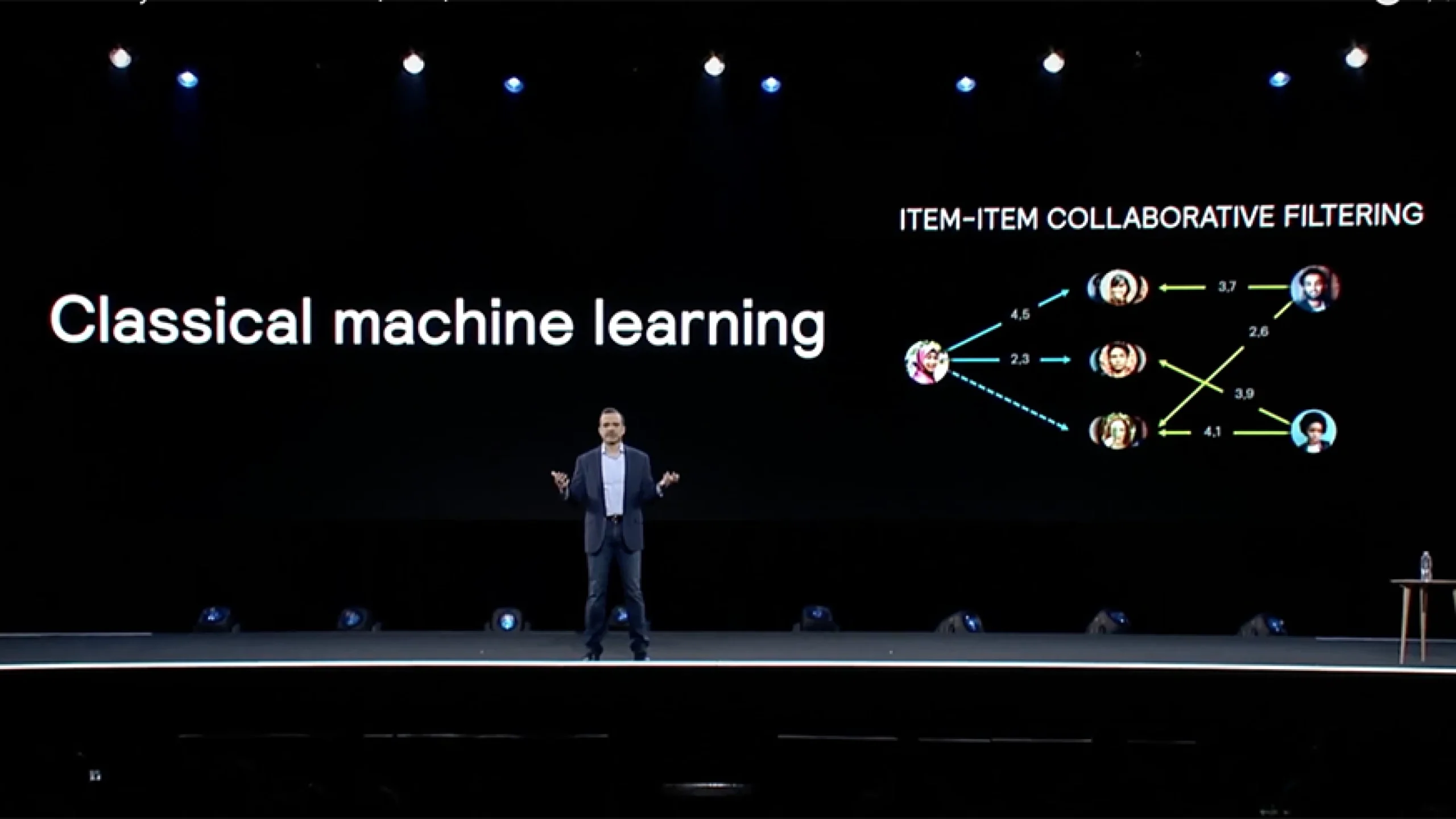
The business implications of this system are staggering. Industry analysts estimate that 30–35% of Amazon’s revenue is directly tied to its recommendation engine. This means that nearly a third of Amazon’s sales come not from initial customer intent, but from AI-driven nudges that increase order value. These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how personalization can move from being a helpful feature to a primary revenue driver. They also prove that investing in AI is not just about improving customer experience but about unlocking massive financial returns at scale.
Netflix-Inspired Personalization Applied In Retail
Another fascinating group of AI in eCommerce examples comes from the adaptation of recommendation systems developed in the entertainment industry. Netflix, for instance, invested heavily in algorithms that could predict what movies or shows a user would want to watch next, based on prior viewing behavior and the preferences of similar users. This logic has now been applied to retail, where it helps customers discover products that align with their style, size, or lifestyle.
One particularly strong adaptation is seen in Stitch Fix, a fashion retailer that integrates AI-powered personalization into its subscription service. The system analyzes customer feedback, body measurements, and historical purchase data to create tailored fashion selections. Similarly, Spotify’s recommendation logic, though rooted in music, has inspired AI solutions in apparel and lifestyle retail. These AI in eCommerce examples show how personalization models from one industry can successfully migrate to another, shifting consumer expectations in the process. Customers now assume that online retailers should “know them” just as well as their favorite streaming platforms do, raising the bar for personalization across the entire eCommerce ecosystem.
Business Benefits: Higher AOV and Improved Discovery
Beyond the technological achievement, the ultimate value of these AI in eCommerce examples lies in their measurable business benefits. Personalized product recommendations directly increase Average Order Value (AOV). By showing customers items that complement their intended purchase or higher-value alternatives, retailers encourage shoppers to spend more per transaction. This not only boosts short-term revenue but also introduces customers to a wider range of products within the brand’s catalog.

Another significant benefit is improved product discovery. In large online marketplaces, choice overload can paralyze shoppers, leading to indecision and abandoned carts. AI-driven personalization simplifies this process by narrowing down the options to those most relevant for each individual. Even niche products gain visibility when AI detects a match between a customer’s profile and the product’s attributes. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how recommendation systems reduce friction, streamline the shopping journey, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Long-Term Loyalty And Accessibility For All Retailers
The benefits of personalized product recommendations extend well beyond immediate sales. When customers consistently find items that match their preferences, they develop trust in the retailer. This trust translates into repeat purchases, stronger engagement with marketing campaigns, and long-term brand loyalty. AI in eCommerce examples from Zalando, eBay, and Alibaba show that well-designed recommendation systems are powerful tools for nurturing customer lifetime value rather than just generating one-time transactions.

Importantly, AI-powered recommendation systems are no longer limited to global giants. Small and medium-sized businesses can now access recommendation tools through platforms like Shopify, Magento, or third-party applications. These accessible AI in eCommerce examples prove that personalization is not an exclusive advantage for Amazon-sized companies. Instead, it is a democratized capability that allows businesses of all sizes to compete effectively in the crowded online marketplace. By integrating these tools, even niche retailers can offer personalized experiences that rival those of global leaders, ensuring that customers feel valued and understood.
Dynamic content personalization
While product recommendations often grab the spotlight in discussions of personalization, some of the most transformative AI in eCommerce examples can be found in dynamic content personalization. This approach goes beyond simply suggesting items to buy. It involves reshaping the entire digital storefront—banners, navigation menus, search results, promotions, and even page layouts—based on the unique preferences, behaviors, and contexts of each individual shopper. Dynamic personalization powered by AI adapts in real time, creating an experience where no two customers see exactly the same version of a website or app.

AI in eCommerce examples of dynamic personalization highlight how deeply machine learning models can analyze behavioral data. Instead of treating all visitors as a homogenous group, these systems continuously adjust content based on browsing history, purchase intent, demographic information, and even subtle signals like time of day or device type. For instance, a returning customer browsing from a smartphone during commuting hours may be shown a streamlined interface with quick-purchase options, while a first-time visitor exploring from a desktop at home might see more detailed product information and educational content. These AI in eCommerce examples show how personalization evolves from recommendations to full-scale content orchestration.
Sephora Tailoring App And Website Experiences Per User Profile
Among the most notable AI in eCommerce examples of dynamic content personalization is Sephora’s approach to tailoring its digital platforms. Sephora collects data through its Beauty Insider loyalty program, online surveys, and app interactions, building detailed customer profiles. AI algorithms then analyze skin type, product preferences, purchase history, and even browsing time to deliver individualized content. This might include displaying skincare tutorials for customers with sensitive skin, featuring curated makeup collections for those who purchase premium brands, or recommending personalized beauty routines. By ensuring that customers see content that aligns with their specific needs, Sephora creates a digital shopping experience that feels uniquely designed for each individual.
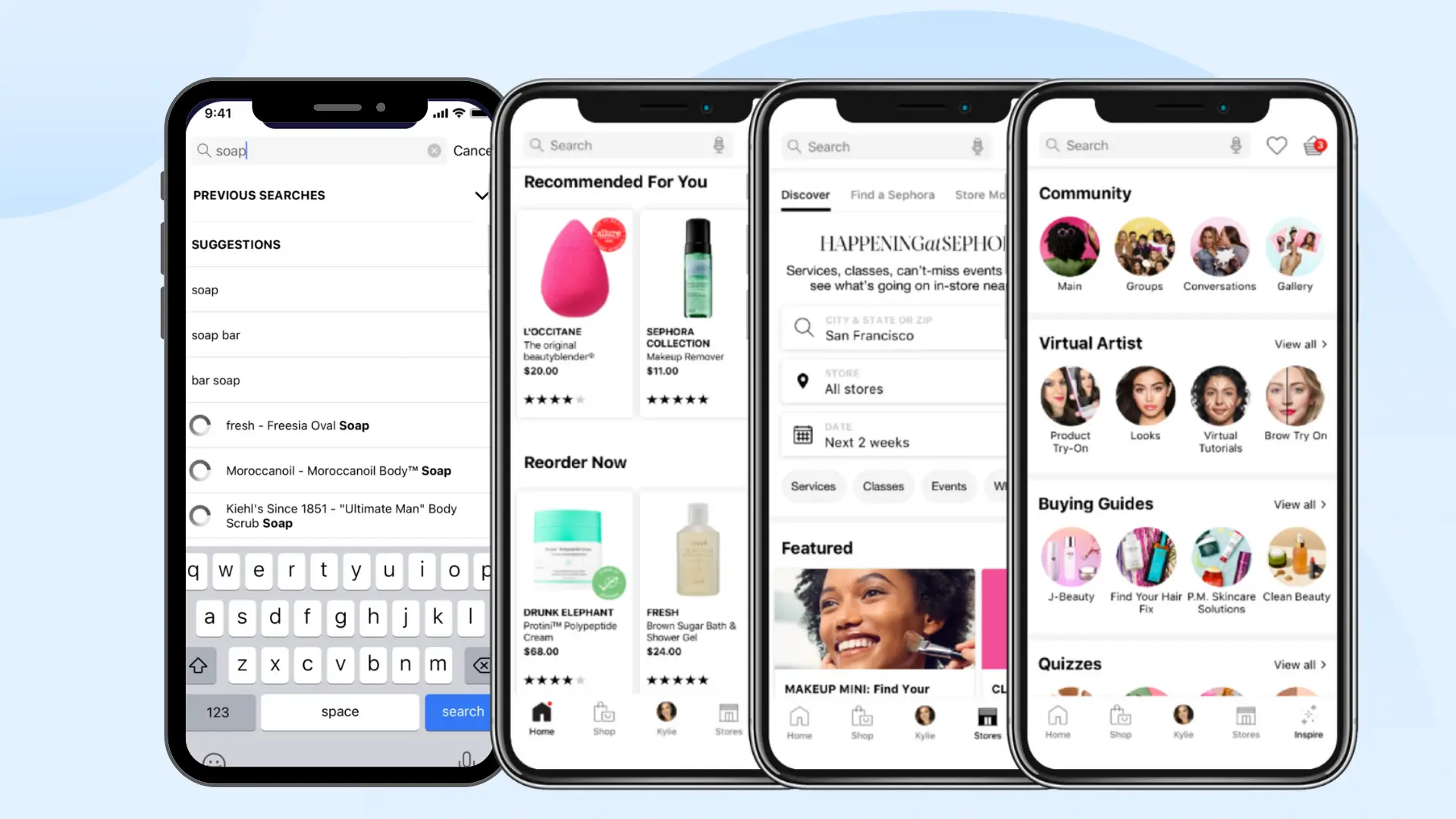
These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate the power of going beyond product recommendations to transform the entire storefront experience. Instead of navigating through a generic website, Sephora’s customers encounter content, promotions, and visuals that reflect their profile. This personalization builds trust, increases time spent on the platform, and ultimately drives higher conversion rates. More importantly, Sephora proves that personalization is not limited to eCommerce giants like Amazon but can also be deeply integrated into niche verticals such as beauty and cosmetics.
Booking.com Using AI to Change Page Layouts in Real Time
Another fascinating set of AI in eCommerce examples comes from Booking.com, which leverages AI not only for content targeting but also for real-time page layout optimization. The company serves millions of users worldwide, each with unique travel preferences and decision-making styles. To ensure maximum relevance, Booking.com uses AI to test and adapt page structures dynamically. For instance, some users may see customer reviews highlighted more prominently, while others encounter urgency cues like “only two rooms left” or “booked five times today” pushed to the top of the page.
These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how AI extends personalization into the domain of user experience (UX) design. Rather than creating one fixed interface, Booking.com allows AI to decide what version of the site is most effective for each visitor. The result is a highly adaptive platform that reduces friction in the decision-making process, increases bookings, and boosts customer satisfaction. By applying machine learning to layout decisions, Booking.com shows how AI can blur the line between marketing personalization and interface design, setting a new benchmark for other eCommerce businesses.
Impact on Customer Engagement and Retention
The broader impact of these AI in eCommerce examples lies in their ability to increase customer engagement and retention. When users encounter platforms that adapt to their needs in real time, they are more likely to explore additional products, spend more time browsing, and return for repeat purchases. Personalized content reduces the sense of choice overload, making it easier for customers to find relevant products without effort. This creates a smoother journey that translates into higher engagement metrics such as session duration, click-through rates, and conversion rates.
Over the long term, these AI in eCommerce examples also demonstrate significant retention benefits. Customers who feel recognized and valued by a platform are more likely to remain loyal. By providing tailored experiences rather than generic interactions, retailers strengthen emotional connections with their customers. This loyalty translates into improved customer lifetime value, reduced churn, and a sustainable competitive edge. Dynamic personalization, as seen in Sephora and Booking.com, proves that AI in eCommerce examples are not just about increasing short-term sales but about building enduring customer relationships.
AI-driven upselling & cross-selling
AI in eCommerce examples show that upselling and cross-selling are no longer limited to manual merchandising or static “customers also bought” sections. Today, machine learning models detect purchase intent signals in real time and generate personalized suggestions that increase basket size and customer lifetime value (CLV). The shift from guesswork to data-driven precision is one of the clearest demonstrations of how artificial intelligence has reshaped eCommerce profitability.
Walmart’s Cross-Sell Engine At Checkout
Walmart provides one of the most widely discussed AI in eCommerce examples of cross-selling at scale. With millions of SKUs and a diverse customer base, Walmart cannot rely on static product pairings to drive basket expansion. Instead, its AI-powered cross-sell engine leverages purchase history, seasonal demand, and regional preferences to determine which products are most relevant to a shopper at checkout. For example, a customer adding a laptop to their cart might be presented with complementary accessories such as a protective case, external mouse, or software package. In grocery, someone buying pasta may see sauce, cheese, or wine suggestions. These prompts are calculated in real time, ensuring that recommendations feel natural rather than forced.
The impact of Walmart’s strategy is significant. By embedding personalization into the checkout process, Walmart not only increases average order value but also enhances customer satisfaction by offering timely, useful suggestions. These AI in eCommerce examples illustrate how even a single moment—checkout—can be transformed into a powerful opportunity to boost revenue while adding genuine value for the shopper. More importantly, Walmart demonstrates that AI-driven cross-selling can be scaled effectively across categories as broad as electronics, fashion, and groceries, proving the adaptability of the technology in diverse contexts.
Shopify Apps with AI-Powered Product Bundles
Smaller retailers may not have the massive infrastructure of Walmart, but AI in eCommerce examples show that platforms like Shopify have leveled the playing field. Through specialized apps, Shopify merchants can deploy AI-driven upsell and cross-sell features without developing in-house systems. These apps analyze browsing behavior, past purchases, and cart contents to create dynamic product bundles. For example, a store selling fitness gear might suggest a bundle of leggings, a sports bra, and a reusable water bottle, all tailored to the customer’s browsing patterns and price sensitivity.

These AI in eCommerce examples highlight the accessibility of sophisticated personalization for businesses of all sizes. Instead of static “frequently bought together” bundles, Shopify apps adapt in real time, updating recommendations as customers add or remove products from their carts. This ensures that offers remain relevant, increasing the chances of conversion. For independent merchants, this functionality not only boosts revenue but also creates a professional shopping experience that rivals global brands. By democratizing access to advanced upsell and cross-sell strategies, Shopify’s AI-powered ecosystem proves that intelligent personalization is no longer reserved for retail giants.
ROI: Boosting CLV through Smarter Cross-Sell Strategies
The return on investment from these AI in eCommerce examples is compelling. Studies have shown that AI-powered upselling and cross-selling can increase average order value by double-digit percentages. More importantly, the long-term impact lies in boosting customer lifetime value (CLV). By consistently presenting relevant product suggestions, retailers encourage customers to explore more of their catalog, deepening their relationship with the brand. This leads to repeat purchases and increased loyalty, turning occasional shoppers into long-term customers.

Smarter cross-sell strategies also benefit retailers beyond immediate revenue gains. AI in eCommerce examples show how insights from purchase combinations can guide product development, inventory management, and marketing campaigns. For instance, if AI detects that customers who purchase eco-friendly cleaning products often also buy sustainable storage solutions, a retailer might expand its product line in that direction. These insights ensure that every upsell or cross-sell recommendation is not just a transaction but also a data point that strengthens strategic decision-making. In this way, AI in eCommerce examples reveal upselling and cross-selling as tools for both revenue generation and business intelligence.
Email & push personalization
Another critical dimension of personalization lies in how businesses communicate with their customers beyond the digital storefront. Among the most impactful AI in eCommerce examples are those that involve email and push notification personalization. These channels have long been staples of eCommerce marketing, but in their traditional form they often relied on broad segmentation and one-size-fits-all messaging. Today, AI systems can tailor the timing, content, and format of each message to align with the behavior and preferences of individual users, making every interaction more relevant and effective.
EBay Tailoring Triggered Email Campaigns
Among the most widely recognized AI in eCommerce examples of email personalization is eBay’s use of triggered campaigns. Rather than sending out generic weekly newsletters, eBay applies AI to analyze browsing history, bidding behavior, and incomplete purchases to generate emails that are highly specific to each customer. For instance, if a user has recently viewed a pair of headphones but not purchased them, eBay’s system automatically sends a reminder email highlighting that product along with similar alternatives or limited-time offers. The messages are not mass-produced but tailored in real time, ensuring relevance for the recipient.
These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how triggered campaigns improve customer experience while simultaneously driving conversions. Instead of feeling like spam, emails become timely nudges that reflect actual shopping interests. This approach reduces cart abandonment, increases click-through rates, and boosts sales. For eBay, personalization has been particularly effective because its marketplace includes both common items and unique, hard-to-find products. By leveraging AI, the platform ensures that customers do not lose track of the exact items they wanted, creating a shopping experience that feels attentive and responsive.
Zalando Personalized Push Notifications
Push notifications represent another rich category of AI in eCommerce examples, and Zalando’s strategy illustrates their potential. As a leading fashion retailer, Zalando faces the challenge of keeping customers engaged in a competitive industry where trends change rapidly. Its AI-powered system analyzes individual browsing patterns, past purchases, and style preferences to determine which notifications to send. A customer who has frequently browsed sneakers might receive an alert about a new sneaker drop, while another interested in dresses might be notified about a flash sale on evening wear.
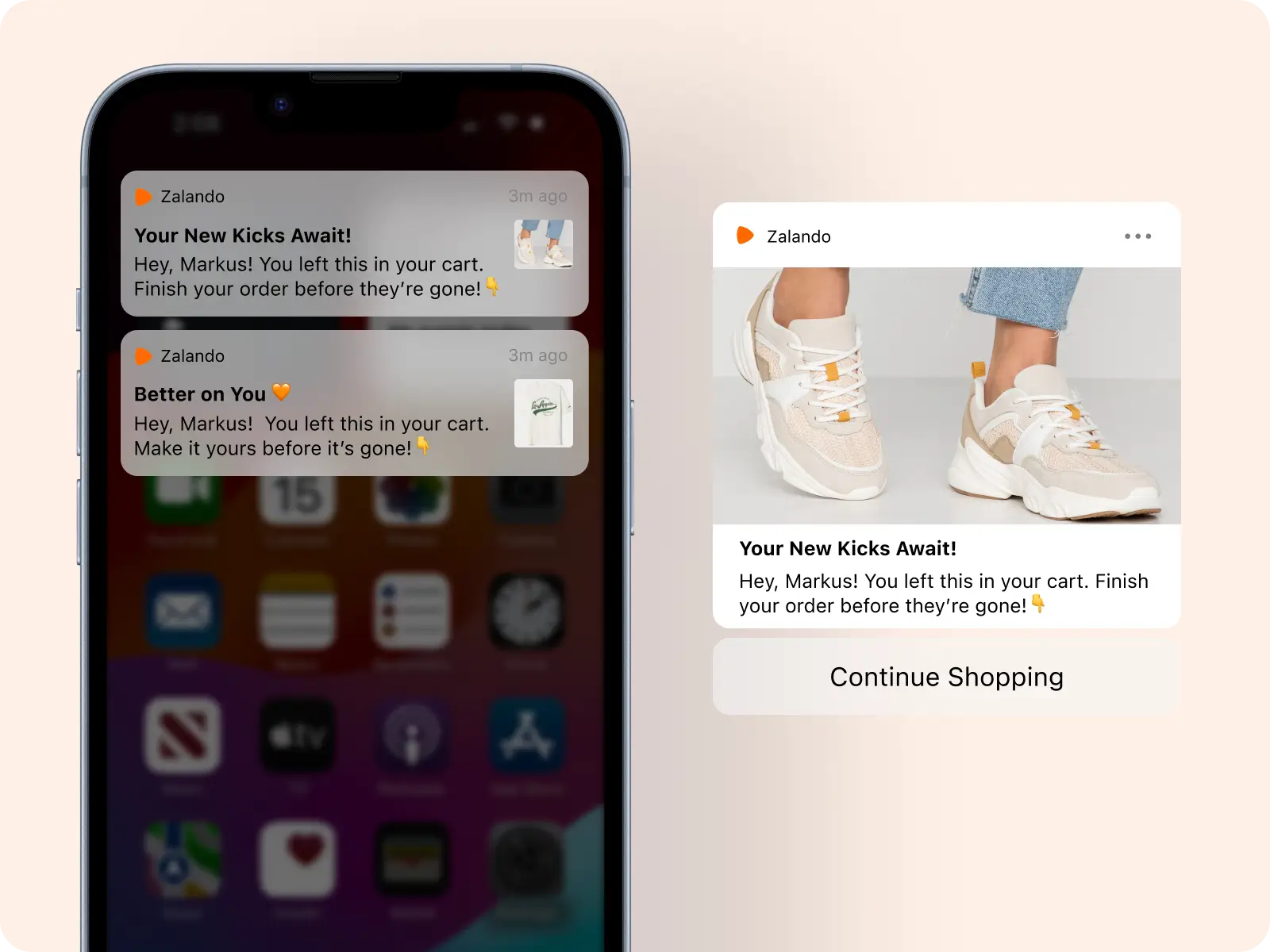
These AI in eCommerce examples show that personalization in push notifications is about more than just timing; it’s about relevance and context. Sending a notification that aligns perfectly with customer intent increases the likelihood of engagement, while irrelevant messages risk being ignored or even prompting users to disable notifications. Zalando demonstrates how machine learning can strike this balance, ensuring that every push notification is seen as a useful service rather than an interruption. This builds trust and strengthens the relationship between retailer and customer, fostering loyalty over the long term.
Results: Higher Open Rates and Conversions
The impact of these AI in eCommerce examples is evident in measurable outcomes. Personalized emails and push notifications consistently outperform generic campaigns in terms of open rates, click-throughs, and conversions. Customers are more likely to engage with content that speaks directly to their needs, whether it’s a reminder about an abandoned product, a personalized discount, or an alert about a relevant new arrival. These improved metrics translate directly into increased sales, making AI-driven personalization a high-ROI strategy for retailers of all sizes.
Beyond immediate revenue gains, these AI in eCommerce examples highlight the long-term benefits of customer retention and loyalty. When shoppers see that a brand understands their preferences and respects their time by delivering relevant messages, they are more inclined to maintain an ongoing relationship with the platform. This builds trust and encourages repeat business, boosting customer lifetime value (CLV). From eBay’s triggered emails to Zalando’s intelligent push notifications, the evidence is clear: AI in eCommerce examples of communication personalization are not optional enhancements but essential strategies for success in a crowded digital marketplace.
AI in Customer Service
AI in eCommerce examples of customer service cover a wide spectrum of use cases. Some are focused on real-time support, such as answering frequently asked questions or guiding shoppers through a purchase. Others operate behind the scenes, analyzing sentiment, predicting support needs, or escalating complex cases to human agents. Across all of these use cases, the unifying theme is that AI allows customer service teams to scale support without compromising quality. Whether for global giants like Amazon, fashion retailers like H&M, or marketplace platforms like Zalando, these AI in eCommerce examples illustrate how businesses can meet rising consumer expectations in a digital-first world.
Chatbots & Virtual Assistants
One of the most visible and widely adopted AI in eCommerce examples is the use of chatbots and virtual assistants. As online shopping has grown in complexity, customers expect immediate answers to their questions—whether about product availability, sizing, return policies, or delivery timelines. Traditional customer service channels such as email or phone support cannot keep pace with the demand for real-time assistance. Chatbots powered by artificial intelligence fill this gap by offering instant, context-aware support. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how brands can provide fast, scalable service while reducing the pressure on human customer service teams.

Chatbots are no longer limited to answering simple FAQs. Modern AI-driven virtual assistants use natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to understand intent, interpret complex questions, and provide relevant responses. They can guide customers through product searches, make personalized recommendations, and even handle transactions directly within the chat interface. These AI in eCommerce examples are redefining how consumers interact with online retailers, turning customer support from a reactive function into an integrated part of the shopping journey.
H&M’s Chatbot Offering Styling And Shopping Help
A standout among AI in eCommerce examples is H&M’s use of chatbots to provide styling assistance. Integrated into platforms such as Kik, the H&M chatbot asks customers about their fashion preferences, favorite colors, and occasion-specific needs. Based on the responses, it curates outfits and recommends items that fit the customer’s personal style. This goes beyond traditional support by blending customer service with product discovery, turning a functional chatbot into a personal stylist.
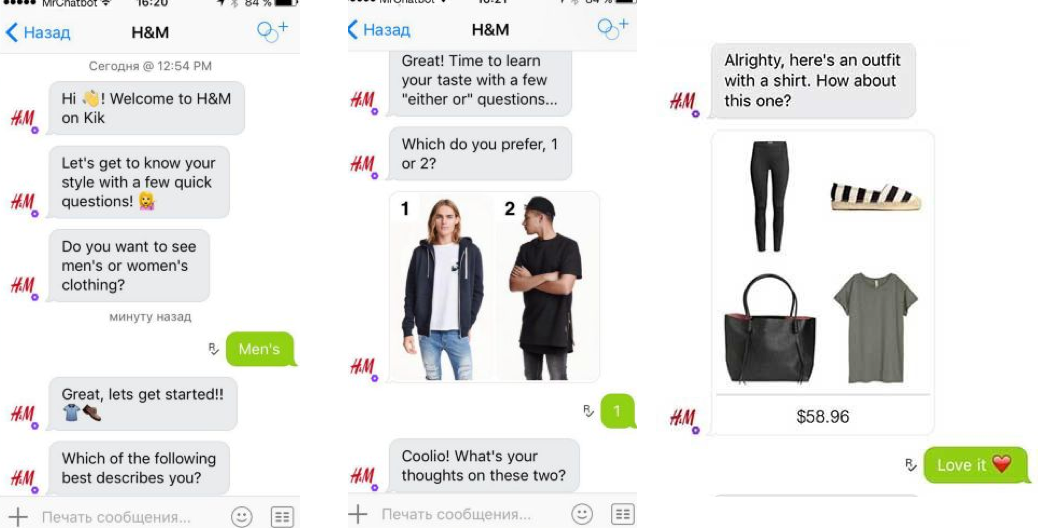
These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how chatbots can evolve from problem-solvers into brand ambassadors. By offering fashion guidance, H&M’s chatbot strengthens customer trust and engagement while encouraging higher-value purchases. The system not only provides instant service but also enriches the customer experience by making shopping fun, interactive, and tailored. For H&M, the chatbot reduces the workload on human agents while simultaneously driving sales through AI-powered personalization.
Levi’s Chatbot Providing Sizing Guidance
Another strong case among AI in eCommerce examples is Levi’s chatbot, which helps shoppers find the right size and fit. One of the biggest challenges in online fashion retail is that customers cannot try on products before purchasing. This often leads to uncertainty, abandoned carts, or high return rates. Levi’s chatbot addresses this issue by asking users a few simple questions about their body type and preferred fit style. Using AI-powered logic, it then recommends the most suitable jeans size and model.
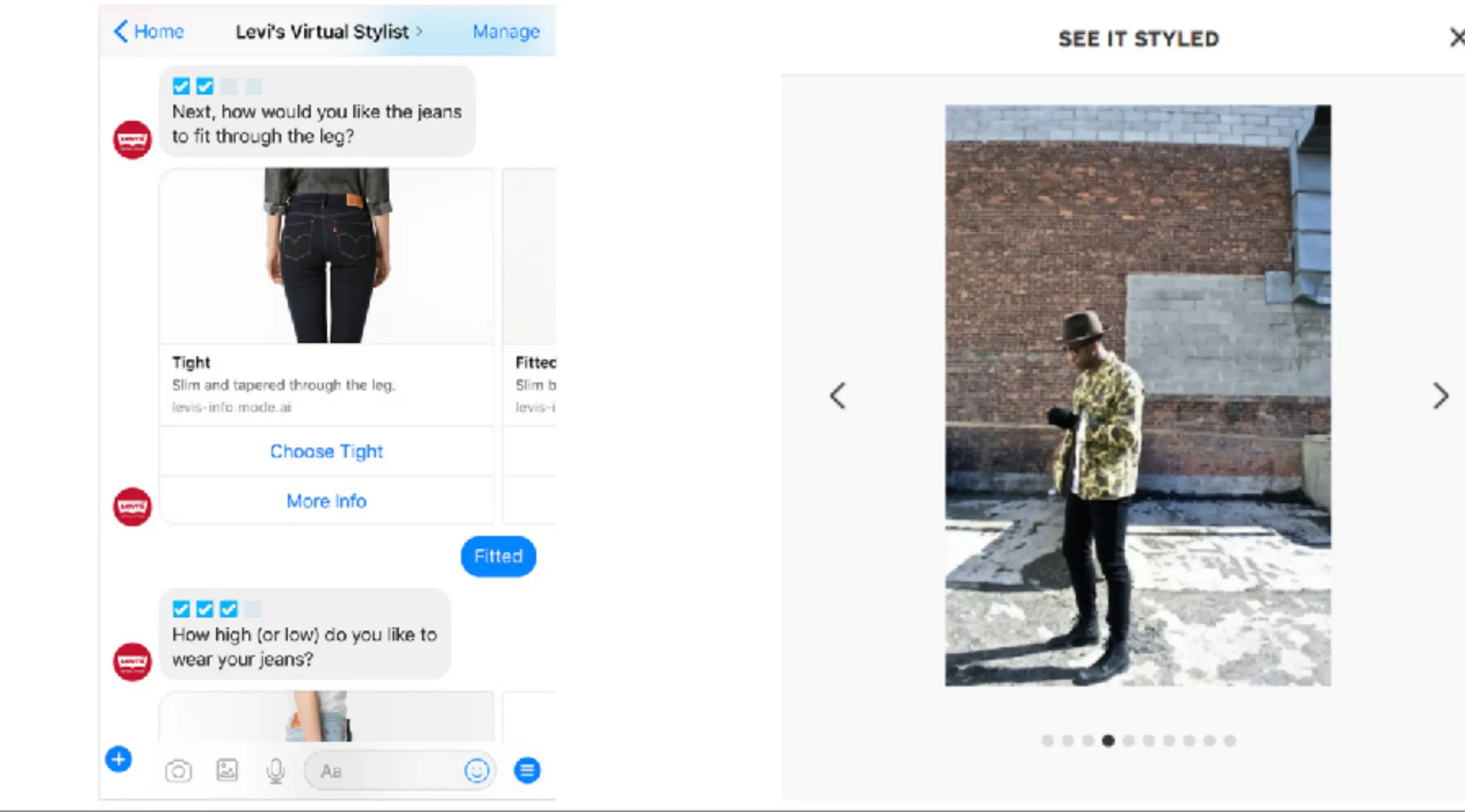
These AI in eCommerce examples show how virtual assistants can solve specific pain points in the customer journey. By offering accurate sizing advice, Levi’s reduces return rates and increases customer confidence in making a purchase. The chatbot’s ability to handle such a complex yet common problem demonstrates how AI can directly improve operational efficiency while delivering value to customers. It turns a potential friction point into an opportunity for engagement and satisfaction, proving that chatbots are far more than basic question-answer tools.
Result: 24/7 Support And Reduced Human Agent Load
The most consistent advantage across these AI in eCommerce examples is the ability to provide round-the-clock support. Unlike human agents constrained by working hours and time zones, AI-powered chatbots are available 24/7. This ensures that customers shopping late at night, during weekends, or from different regions can always get assistance. For global eCommerce platforms, this level of availability is no longer a luxury but a necessity to meet customer expectations.

Another major benefit highlighted in AI in eCommerce examples is the reduced workload on human support teams. By handling repetitive inquiries such as “Where is my order?” or “What is your return policy?”, chatbots free human agents to focus on complex or high-value interactions. This not only improves operational efficiency but also reduces costs. Retailers can scale their support functions without hiring large customer service teams, making chatbots a cost-effective solution that enhances both customer satisfaction and profitability.
Voice Assistants & Conversational AI
Voice assistants, powered by advanced natural language processing (NLP) and conversational AI, can interpret complex customer requests, understand context, and deliver relevant results. Unlike early chatbots with rigid, rule-based responses, conversational AI can adapt to variations in speech, accents, and customer intent. These AI in eCommerce examples show how retailers can make interactions more human-like, reducing frustration and building trust. For busy customers who want fast and convenient shopping, voice interfaces represent a major step forward.
Amazon Alexa Integrated Into Shopping
One of the most prominent AI in eCommerce examples is Amazon Alexa’s integration into shopping. Alexa allows customers to add products to their cart, reorder frequently purchased items, and even complete transactions using simple voice commands.

For instance, a shopper can say, “Alexa, order more paper towels,” and the assistant automatically selects the customer’s preferred brand and quantity based on past behavior. This removes friction from the shopping process and turns replenishment purchases into a seamless, one-step experience.

The success of Alexa demonstrates the potential of conversational AI to reshape customer service. These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how a voice assistant can do more than execute commands—it can also act as a proactive partner. Alexa can notify customers about relevant promotions, provide delivery updates, or suggest complementary products. By embedding AI deeply into the shopping journey, Amazon sets the standard for voice-driven commerce, showing how natural interactions can boost both customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Domino’s “Dom” Assistant For Quick Reorders
Another compelling case among AI in eCommerce examples is Domino’s “Dom” assistant, which enables customers to place pizza orders through voice commands. With Dom, users can simply say, “Order my usual pizza,” and the assistant retrieves past order data to replicate the experience. This eliminates the need to browse menus or input customization details manually, making the process faster and more enjoyable. For a company like Domino’s, where convenience is part of the brand promise, conversational AI aligns perfectly with customer expectations.
These AI in eCommerce examples emphasize how voice assistants can personalize experiences by leveraging historical data. Dom does not just take orders—it recognizes customer preferences, adapts to repeat patterns, and builds continuity across transactions. This personalization enhances customer satisfaction while driving repeat sales. The case of Domino’s shows how even outside traditional retail, voice and conversational AI can create competitive advantages by simplifying interactions and reducing barriers to purchase.
Result: Enabling Hands-Free Commerce
The overarching role of these AI in eCommerce examples is enabling hands-free commerce. Voice assistants and conversational AI make it possible for customers to shop while multitasking—cooking dinner, driving a car, or managing other activities. This level of convenience expands the situations in which eCommerce becomes accessible, allowing retailers to capture more transactions throughout the day. By reducing reliance on screens, voice commerce also appeals to demographics who may find traditional interfaces less intuitive, such as older shoppers.

These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate that hands-free shopping is not a novelty but a meaningful extension of digital commerce. Retailers that adopt conversational AI position themselves to meet evolving consumer behaviors where convenience is king. The ability to deliver seamless, natural, and fast interactions builds stronger emotional connections with customers while driving measurable business outcomes. As voice technology continues to advance, it will play a central role in the next wave of AI in eCommerce examples, shaping how customers shop and how brands serve them in an increasingly connected world.
Multilingual AI Service
As eCommerce becomes increasingly global, one of the most important challenges retailers face is language. A shopper in Spain may want to buy from a seller in China, or a customer in Indonesia might be browsing an American brand’s store. Without multilingual support, these opportunities often fall through due to misunderstandings, mistranslations, or the lack of localized customer service agents. Among the most transformative AI in eCommerce examples are those focused on multilingual AI services, which use artificial intelligence to automatically translate text, voice, and even images in real time. By breaking down language barriers, these technologies unlock cross-border trade and allow businesses to scale globally without the massive cost of hiring multilingual human teams.

Multilingual AI services represent some of the most practical AI in eCommerce examples because they address a universal friction point: communication. Online shoppers expect clarity when making a purchase decision. They want product descriptions they can understand, customer service in their native language, and confidence that their questions will be answered accurately. AI-driven translation and localization tools provide this assurance. Unlike older machine translation tools that often produced awkward or inaccurate results, modern AI systems use deep learning and natural language processing to capture context, idioms, and tone. These AI in eCommerce examples ensure that cross-border shopping feels as seamless as buying from a local store.
Alibaba’s Instant Translation For Cross-Border Trade
One of the most impressive AI in eCommerce examples is Alibaba’s instant translation service – Tongyi Qianwen (Qwen), which plays a central role in supporting its global marketplace. With millions of buyers and sellers from different countries, Alibaba faced the enormous challenge of enabling communication between people who often do not share a common language. To solve this, the company deployed AI-powered instant translation that supports dozens of languages. Whether a buyer is negotiating with a seller, asking about shipping details, or clarifying product specifications, the AI system translates both sides of the conversation in real time.

These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how multilingual services not only facilitate transactions but also build trust. When customers and sellers can communicate effortlessly, the likelihood of misunderstandings decreases, and the chances of completing a sale increase. For Alibaba, this capability has been crucial to expanding its presence outside of China, particularly in Europe, North America, and Southeast Asia. By removing linguistic barriers, AI transforms the platform into a truly global marketplace, proving how multilingual solutions can drive international growth.
Shopee Expanding Customer Support In Multiple Languages
Shopee, one of Southeast Asia’s leading eCommerce platforms, provides another strong case among AI in eCommerce examples. Operating across countries such as Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, and the Philippines, Shopee needed to deliver customer support in multiple languages while keeping operational costs manageable. To achieve this, it integrated AI-powered multilingual support into its chat and helpdesk systems. Customers can now submit queries in their native language, and the AI system automatically translates and routes responses accordingly.

These AI in eCommerce examples show how Shopee uses multilingual AI to scale across diverse markets without hiring massive teams of local agents. For customers, the experience feels personal and localized, even though it is powered by AI in the background. For the business, it represents an efficient way to provide consistent, high-quality support across countries. By combining machine translation with customer intent recognition, Shopee ensures that issues are resolved quickly and accurately, strengthening its reputation as a customer-first platform.
Result: Breaking Language Barriers In eCommerce
The advantage of these AI in eCommerce examples is clear: they break down one of the most persistent barriers in online retail. Language is not just a communication tool—it is also an emotional connector. Customers are more likely to trust a brand that speaks to them in their own language, and they are more comfortable making purchases when they fully understand product details and policies. By using AI for multilingual services, retailers can expand their reach to entirely new markets without prohibitive costs.

Moreover, these AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how breaking language barriers improves customer engagement and retention. Shoppers who can navigate a platform in their preferred language are more likely to return, recommend the service to others, and develop loyalty. For businesses, this translates into higher sales, greater international visibility, and sustainable growth. Multilingual AI services ensure that eCommerce is no longer bound by geography or language, making it one of the most impactful and inclusive categories of AI in eCommerce examples.
AI in Search & Discovery
The traditional search bar, once limited to exact (or near exact) keyword matching, has evolved into a sophisticated AI-powered engine that understands intent, context, and even visual cues. Customers now expect search systems that recognize natural speech, deliver results instantly, and adapt recommendations to their personal preferences. These AI in eCommerce examples not only improve convenience but also drive higher conversions by ensuring that the right product is shown to the right customer at the right moment.
Visual Search
Visual search belongs to a class of AI in eCommerce examples that enhance both convenience and engagement. Traditional keyword-based search often fails when customers lack the exact vocabulary to describe what they want. For instance, a shopper might not know the specific term for a patterned dress style or the technical name of a furniture finish.

In these cases, typing into a search bar can yield irrelevant results or none at all. Visual search solves this problem by allowing customers to simply show what they mean, turning an image into the key to discovery.
ASOS “Style Match” for finding similar clothing
A leading AI in eCommerce example of visual search comes from ASOS, one of the most innovative online fashion retailers. ASOS launched “Style Match,” a tool within its mobile app that enables users to upload photos of outfits or items they admire. The AI system then analyzes the visual attributes—colors, patterns, shapes, and textures—and searches the retailer’s catalog for products that look similar. This eliminates the guesswork of typing in keywords like “striped blue summer dress” or “boho floral blouse.” Instead, customers can instantly find matches that reflect the exact visual inspiration they had in mind.
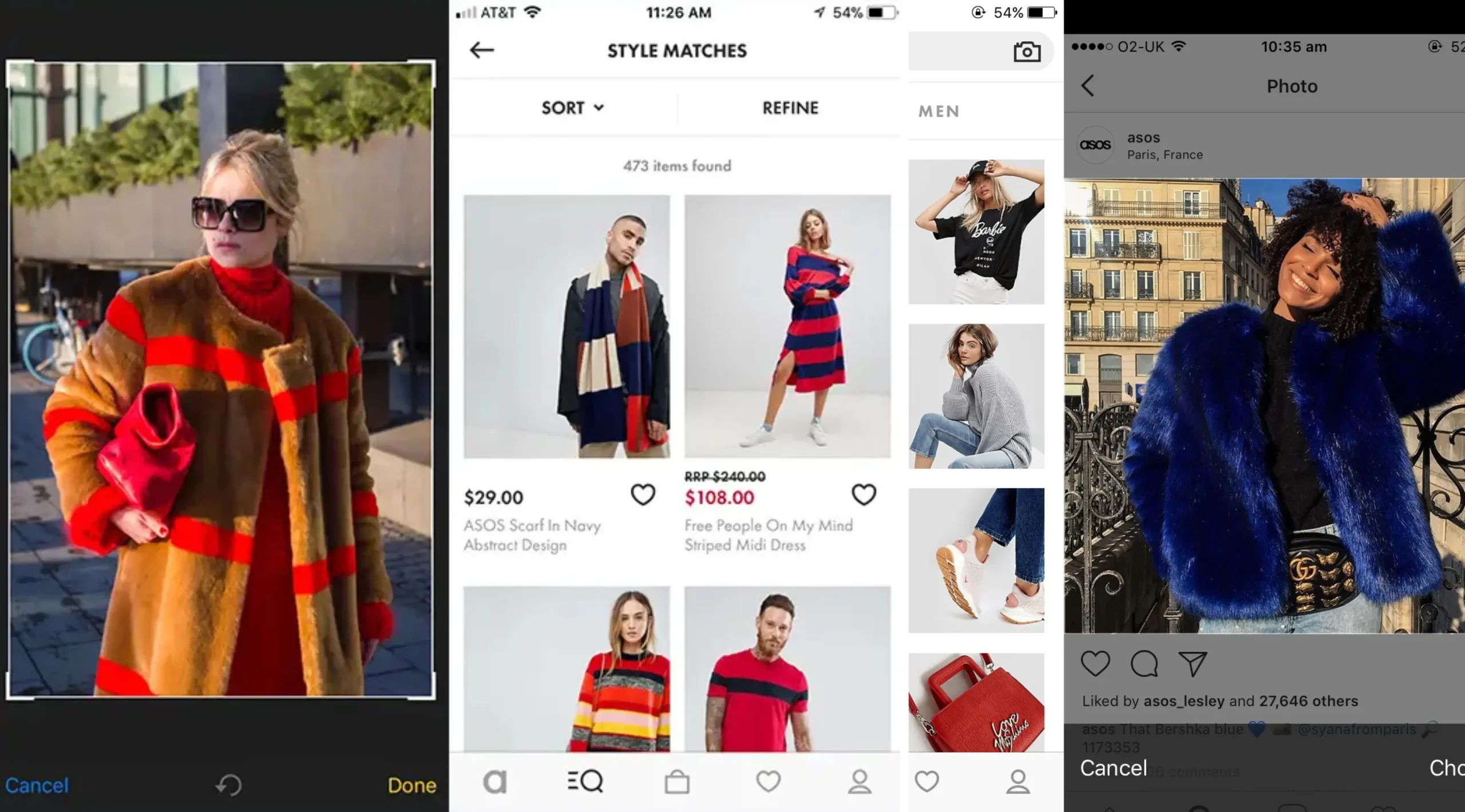
These AI in eCommerce examples from ASOS demonstrate how visual search drives both customer satisfaction and business growth. By offering an easy way to replicate looks seen on social media, in magazines, or on the street, ASOS bridges the gap between aspiration and purchase. Customers are more likely to convert because they are presented with items that match their preferences precisely, while ASOS benefits from increased engagement, reduced friction, and higher conversion rates.
Pinterest Lens partnered with retailers
Another compelling case among AI in eCommerce examples is Pinterest Lens, which has redefined how users engage with products on the platform. Pinterest Lens allows users to point their camera at an object—anything from a handbag to a piece of furniture—and instantly see visually similar items along with suggestions for purchase. What makes Pinterest Lens particularly powerful is its integration with retailer partnerships. When users discover an item they like, they can click through to buy it from participating merchants, turning inspiration into a seamless shopping journey.
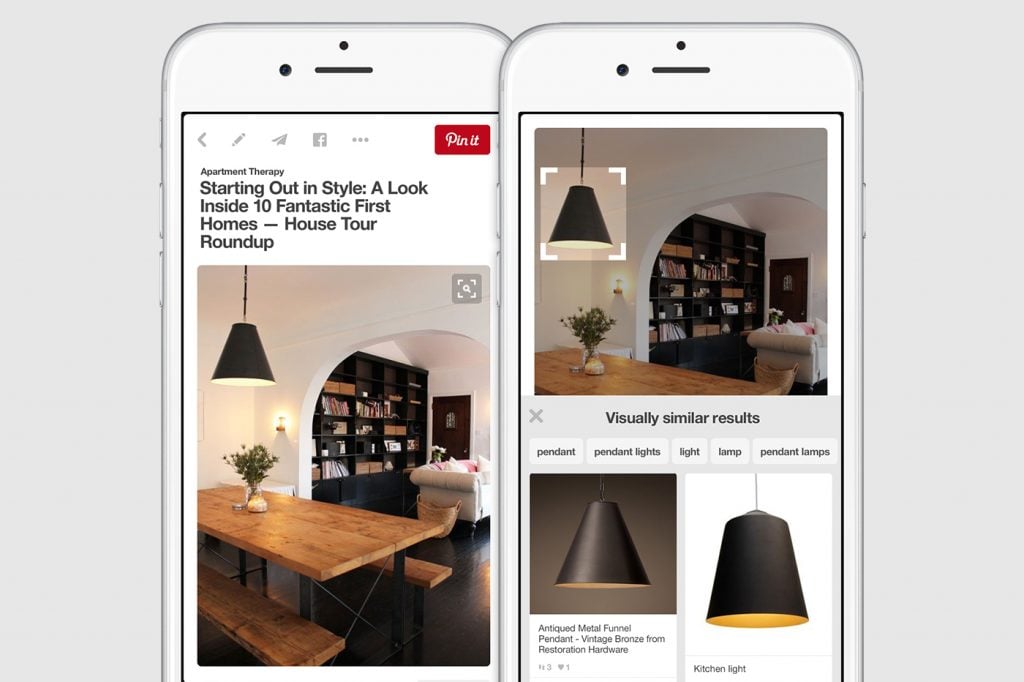
These AI in eCommerce examples illustrate how platforms can position themselves at the intersection of discovery and commerce. For retailers, Pinterest’s Lens integration provides a new customer acquisition channel, connecting shoppers with products they may not have searched for explicitly. For consumers, it transforms Pinterest from a source of inspiration into an actionable shopping tool. By using visual cues rather than words, Lens breaks down barriers between desire and purchase, making discovery more natural and engaging.
Result: Shop with images, not words
The most significant advantage of these AI in eCommerce examples is the ability for consumers to shop with images instead of words. This shift aligns with how people increasingly interact with digital platforms, where visual content dominates. Social media, influencer culture, and lifestyle photography drive much of today’s purchase inspiration, and visual search allows customers to act on that inspiration instantly. Instead of struggling to describe a product, users can simply show it, making shopping both faster and more enjoyable.
These AI in eCommerce examples also expand inclusivity in digital retail. Not all customers are equally fluent in the terminology of fashion, home design, or electronics. By lowering the need for precise vocabulary, visual search empowers a wider range of shoppers to discover products that fit their needs. For businesses, the payoff is clear: higher engagement, greater product visibility, and increased sales. Visual search doesn’t just improve usability—it fundamentally redefines how people connect with products, proving why it stands out as one of the most important AI in eCommerce examples in today’s marketplace.
Natural Language Search
Search is one of the most important parts of the eCommerce customer journey. If shoppers cannot find what they are looking for quickly and accurately, they are likely to abandon the site and look elsewhere. Among the most impactful AI in eCommerce examples is the adoption of natural language search, which uses artificial intelligence and natural language processing (NLP) to interpret human language in a more flexible and intuitive way. Unlike traditional keyword-based search systems, which often require exact phrasing, natural language search understands context, intent, synonyms, and even incomplete phrases.

These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how retailers are addressing a long-standing pain point. In the past, a customer searching for “black running shoes for marathon” might only see results that matched each keyword literally, excluding relevant items tagged differently such as “men’s lightweight trainers.” With natural language search, the system interprets the full intent of the query, recognizing that the customer is looking for a particular type of athletic shoe. By narrowing results intelligently, AI eliminates frustration and increases the likelihood of conversion.
Shopify AI semantic search for small merchants
One of the most significant AI in eCommerce examples of natural language search comes from Shopify, which has built semantic search capabilities into its platform to empower small and medium-sized businesses. Shopify’s AI engine can understand conversational queries typed by customers, such as “gifts for Mother’s Day under $50” or “eco-friendly kitchen storage.” Instead of relying on exact keyword matches, the system interprets these requests in terms of meaning, returning products that best fit the shopper’s intent.
These AI in eCommerce examples are especially valuable for independent merchants, who may not have the resources to build advanced search systems themselves. By leveraging Shopify’s built-in AI tools, small retailers can compete with larger players by offering a seamless discovery experience. The ability to process natural language queries not only improves customer satisfaction but also helps merchants increase visibility for products that might otherwise remain hidden. This democratization of advanced search demonstrates how AI can level the playing field in digital commerce.
Etsy applying NLP to improve search intent understanding
Another strong case among AI in eCommerce examples comes from Etsy, the global marketplace known for its handmade and vintage products. With millions of unique listings, search functionality is critical for connecting buyers with sellers. Etsy employs natural language processing to interpret search queries more accurately, particularly when shoppers use vague or creative terms. For example, a customer searching for “rustic wedding decorations” might be presented with mason jar centerpieces, burlap table runners, and hand-painted wooden signs, even if those specific keywords were not included in the seller’s listing.
These AI in eCommerce examples reveal how NLP helps Etsy bridge the gap between buyer language and seller descriptions. By focusing on intent rather than exact matches, Etsy reduces the number of irrelevant results and enhances product discovery. This not only benefits buyers, who find what they are looking for more quickly, but also helps sellers reach a broader audience. The success of Etsy’s natural language search shows how AI can be applied to marketplaces with diverse, user-generated inventories where consistency in product tagging is often a challenge.
Result: Fewer “no results found” and higher conversion
The measurable impact of these AI in eCommerce examples is clear. Natural language search significantly reduces the number of “no results found” errors, which are among the most frustrating experiences for online shoppers. When customers see relevant results for their queries—even if their language is unconventional—they are more likely to stay engaged, browse further, and ultimately make a purchase. This improvement directly translates into higher conversion rates, making natural language search not just a usability enhancement but a revenue-generating tool.

Moreover, these AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how natural language search contributes to long-term customer satisfaction. Shoppers who consistently find relevant results are more likely to return to the same platform, recommend it to others, and build loyalty over time. For retailers, this means reduced bounce rates, better engagement metrics, and improved customer lifetime value. By interpreting human language in all its complexity, natural language search proves why it is one of the most valuable AI in eCommerce examples driving innovation in digital retail today.
Personalized search ranking
Another important area where artificial intelligence is reshaping digital retail is personalized search ranking. While natural language search ensures that customer queries are understood, the next step is to determine the order in which products are displayed. Among the most impactful AI in eCommerce examples are those where machine learning algorithms re-rank search results based on each customer’s unique preferences, browsing history, and purchase intent. Instead of showing every customer the same list of results, AI tailors the ranking to maximize relevance and conversion.

These AI in eCommerce examples are particularly powerful because they address a common frustration in online shopping: irrelevant or overwhelming results. A shopper might type “wireless headphones,” but the most relevant product for one customer may be a budget-friendly option, while another is looking for premium noise-canceling technology. By analyzing signals such as past purchases, time spent browsing specific categories, and even device type, AI-powered search ranking systems deliver results that feel personalized rather than generic. This personalization reduces friction in discovery and ensures that shoppers spend less time searching and more time purchasing.
EBay re-ranking search results with AI
One of the most well-documented AI in eCommerce examples of personalized search ranking is eBay’s application of machine learning to optimize search result order. eBay hosts hundreds of millions of listings, many of which are for similar products. Without personalization, customers might be forced to scroll through dozens of irrelevant items before finding something that matches their preferences. To solve this, eBay developed AI systems that consider factors like a user’s previous searches, purchasing history, and engagement behavior to re-rank results in real time.
These AI in eCommerce examples show how eBay leverages personalization to improve the buyer experience. A customer who previously purchased video game consoles, for instance, will see game-related listings prioritized higher in their search results, while another customer who often buys home goods will see those items featured more prominently. By tailoring results dynamically, eBay not only enhances customer satisfaction but also boosts seller visibility, ensuring that relevant items connect with the right buyers. This approach demonstrates how AI-driven ranking is essential for marketplaces with vast inventories.
Amazon tailoring product results by browsing history
Another compelling case among AI in eCommerce examples is Amazon’s personalized ranking of search results. Amazon’s recommendation engine is already famous, but its search algorithm also uses browsing and purchase history to prioritize results. For instance, a customer who frequently shops for eco-friendly products may see sustainable options ranked higher, while a customer who often purchases electronics might see tech accessories surface more quickly. By incorporating personalization into search ranking, Amazon ensures that each customer’s experience feels unique.
These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how Amazon combines real-time behavioral signals with long-term historical data to predict intent. Even factors like whether a shopper is browsing from a mobile device or desktop can influence which products are shown first. The result is a highly adaptive search experience where relevance is maximized, frustration is minimized, and the path to purchase is streamlined. For Amazon, this translates into higher conversion rates, greater customer loyalty, and increased revenue. For shoppers, it means finding what they want faster, without having to sift through irrelevant products.
Result: Reduced friction in discovery
The broader impact of these AI in eCommerce examples is the dramatic reduction of friction in the discovery process. In traditional search, customers often abandon their sessions if results feel irrelevant or require too much effort to filter. Personalized ranking ensures that the most relevant items are displayed first, making the shopping journey more efficient and enjoyable. By aligning results with intent, AI minimizes the gap between desire and discovery, increasing the likelihood of conversion.

These AI in eCommerce examples also emphasize how personalization fosters trust and loyalty. Customers are more inclined to return to a platform where they consistently find products that match their needs and tastes. For retailers, this means not only higher short-term revenue but also improved customer lifetime value. Personalized search ranking transforms product discovery from a frustrating task into a curated experience, proving why it stands out as one of the most important AI in eCommerce examples, driving success in digital retail today.
AI in Marketing & Advertising
What makes AI in eCommerce examples in marketing particularly powerful is the ability to transform marketing from broad, guesswork-driven strategies into highly personalized, data-driven campaigns. Traditional marketing methods relied heavily on demographic segments and basic behavioral data, but these approaches often lacked precision. AI allows marketers to analyze millions of data points in real time, detecting patterns invisible to human teams. The result is not only more efficient campaigns but also advertising experiences that feel tailored to each consumer.
Predictive customer targeting
Predictive targeting works by analyzing large volumes of structured and unstructured data—browsing history, cart abandonment patterns, time spent on product pages, purchase frequency, social media interactions, and even responses to past campaigns. Machine learning algorithms process these data points to build highly accurate forecasts about customer intent.

These AI in eCommerce examples show how predictive targeting enables businesses to anticipate needs before customers explicitly express them, creating campaigns that feel timely and relevant rather than intrusive.
Stitch Fix predicting fashion needs using AI
One of the most widely discussed AI in eCommerce examples of predictive targeting is Stitch Fix, the subscription-based fashion retailer that has built its business model around personalization. Stitch Fix collects a vast array of data from its customers, including body measurements, style preferences, budget ranges, and detailed feedback on each item received in a “fix.” This feedback loop allows Stitch Fix to continuously refine its understanding of each customer’s fashion identity.
AI algorithms then analyze this data not just to recommend products but to predict future needs. For example, if a customer frequently buys workwear but begins browsing casual wear more often, Stitch Fix’s predictive models will adjust recommendations accordingly. The system also takes into account external factors such as seasonality, upcoming holidays, or regional weather conditions to anticipate when a customer might need specific clothing items. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how predictive targeting moves beyond basic personalization to proactive anticipation of customer demand.
The business impact is significant. By predicting fashion needs, Stitch Fix reduces the likelihood of returns, increases customer satisfaction, and builds long-term loyalty. Customers feel that the brand “gets them,” while the company benefits from reduced waste in inventory and marketing. These AI in eCommerce examples show how predictive targeting creates a win-win: customers enjoy curated experiences, and retailers gain higher efficiency in campaign execution and inventory management.
Zalando AI audience modeling for campaigns
Another strong case among AI in eCommerce examples comes from Zalando, Europe’s leading online fashion platform. Zalando faces the challenge of marketing to millions of customers across diverse markets with varying tastes, budgets, and cultural preferences. To address this, Zalando uses AI-powered audience modeling that segments customers not by simple demographic factors but by behavioral signals and predicted intent.
For instance, Zalando’s AI analyzes browsing activity, clickstream data, purchase frequency, and interaction with promotional campaigns to predict which customers are most likely to buy during a sales event. These customers can then be targeted with personalized ads, while those less likely to purchase may receive lighter, brand-building messaging or be excluded from costlier ad placements altogether. These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how Zalando optimizes ad spend by focusing resources where they will have the greatest impact.
Zalando also applies predictive targeting to test campaign variations. AI systems can predict which creative assets—such as ad copy, product imagery, or discount offers—will resonate most with specific audiences. By automating this process, Zalando avoids the inefficiencies of A/B testing at scale and delivers more relevant content to customers. These AI in eCommerce examples reveal the strategic advantage of AI in managing complex, multi-market campaigns with precision and efficiency.
Result: Reduced ads waste and higher ROI
The ultimate value of predictive targeting, as seen in these AI in eCommerce examples, lies in its ability to reduce advertising waste and drive higher ROI. Traditional digital marketing often involves casting a wide net, paying for impressions or clicks that may never convert. Predictive AI systems, by contrast, ensure that ads are shown primarily to those with the highest likelihood of engagement and purchase. This precision minimizes wasted spend while increasing the effectiveness of each campaign.

Retailers using predictive targeting also benefit from shorter sales cycles. Because AI delivers the right message to the right customer at the right time, shoppers are more likely to move quickly from consideration to conversion. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate that predictive targeting does not just improve efficiency—it accelerates revenue generation and improves campaign profitability.
Another critical outcome is long-term customer value. By consistently delivering relevant messages and offers, retailers build trust and deepen relationships with their customers. Instead of bombarding users with irrelevant ads that cause fatigue or irritation, predictive targeting fosters engagement and loyalty. These AI in eCommerce examples prove that higher ROI is not just about cutting waste but about creating campaigns that resonate authentically with consumers.
AI ads optimization
Advertising has always been one of the most resource-intensive aspects of running an eCommerce business. Brands must decide where to place their ads, how much to bid, which creative assets to use, and how to measure success. In the past, marketing teams had to manually test combinations of targeting options, budgets, and creatives, often relying on trial and error. Among the most impactful AI in eCommerce examples is AI ad optimization, where machine learning automates many of these decisions, continuously improving campaigns to maximize conversions and reduce wasted spend.

AI ads optimization belongs to a group of AI in eCommerce examples that fundamentally change how campaigns are managed. Instead of marketers making dozens of manual adjustments each day, AI algorithms analyze thousands of signals in real time—such as user behavior, demographics, device usage, and time of day—to determine the best way to allocate resources. These systems learn quickly, adapting strategies that would be impossible for humans to calculate at scale. For retailers, this means more efficient advertising with better results and fewer resources dedicated to manual campaign management.
Facebook/Meta Advantage+ Shopping Campaigns
One of the most prominent AI in eCommerce examples of ad optimization comes from Meta’s Advantage+ Shopping Campaigns. Traditionally, running an ad on Facebook or Instagram required marketers to manually configure targeting options, placements, and creative testing. Advantage+ automates much of this process using AI. The system automatically identifies the best-performing audiences, creative variations, and placements across Meta’s ecosystem, ensuring that ads reach the people most likely to convert.
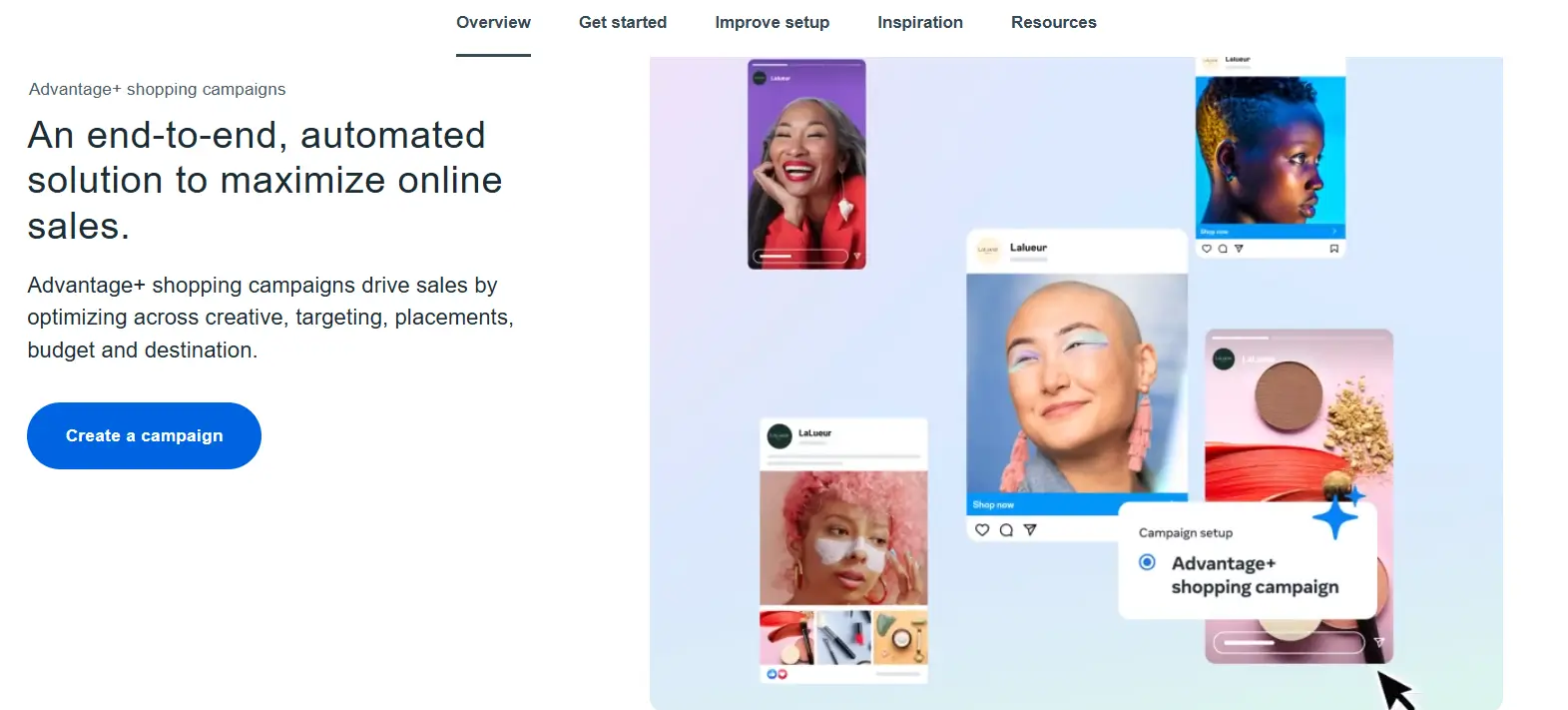
These AI in eCommerce examples show how automation reduces friction in advertising. For example, instead of a retailer manually testing whether carousel ads perform better than single-image ads for a new shoe line, Advantage+ can run multiple variations simultaneously, learn from performance data, and prioritize the format and message that delivers the highest ROI. The system continuously updates in real time, adjusting bids and placements based on changing consumer behavior.
For small and medium-sized businesses, these AI in eCommerce examples are especially valuable. Many merchants lack the resources or expertise to run complex, segmented campaigns. Advantage+ provides them with enterprise-level optimization by default. It democratizes advanced advertising, allowing even small eCommerce shops to compete with larger players. The results are evident: retailers using Advantage+ often see improved conversion rates, reduced cost per acquisition, and faster learning cycles compared to manual campaign setups.
Meta’s approach also highlights another key benefit of AI in eCommerce examples: scalability. As businesses grow and expand into new markets, manual campaign management becomes increasingly unmanageable. AI systems like Advantage+ scale seamlessly, handling millions of impressions and conversions while ensuring that the most relevant audiences are reached at the right time.
Google Ads Smart Bidding strategies
Another leading case among AI in eCommerce examples is Google Ads Smart Bidding. Paid search has always been one of the most competitive digital marketing channels, requiring advertisers to set precise bids for keywords, placements, and audiences. Smart Bidding automates this process by using machine learning to set bids in real time, optimizing for specific goals such as maximizing conversions, targeting a desired return on ad spend (ROAS), or increasing overall traffic.
These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how Google uses signals far beyond keywords to optimize campaigns. Smart Bidding considers factors like device type, time of day, location, remarketing lists, and even browser behavior to determine the optimal bid for each auction. This level of granularity is impossible for human marketers to replicate consistently. By letting AI handle the complexity, advertisers achieve better results with less manual effort.
For example, an eCommerce retailer running ads for a seasonal product such as winter coats may see higher demand in colder regions and at specific times of day. Smart Bidding automatically adjusts bids to ensure that ads appear prominently to high-intent shoppers in those regions and times. These AI in eCommerce examples prove how real-time optimization directly impacts campaign efficiency, ensuring that ad spend is allocated to the audiences most likely to convert.
Another advantage is adaptability. Consumer behavior is never static, and what works today may not work tomorrow. Google’s AI systems continuously learn from new data, adjusting strategies accordingly. These AI in eCommerce examples show how Smart Bidding ensures campaigns remain effective even as market dynamics shift, whether due to seasonality, competitor activity, or broader economic trends.
Result: Maximizing conversions with less manual tuning
The overarching benefit of these AI in eCommerce examples is the ability to maximize conversions with minimal manual intervention. Advertising platforms once required teams of marketers and analysts to constantly monitor performance and adjust campaigns. Now, AI takes over much of that labor-intensive work, freeing human teams to focus on strategy, creative direction, and customer engagement.
These AI in eCommerce examples highlight the efficiency gains from automation. Instead of spending hours analyzing spreadsheets to determine which audience segments perform best, marketers can rely on AI to handle the data analysis and optimization in real time. This not only saves time but also produces more accurate results, since AI systems process far more data than human teams could ever manage.

For businesses, this translates into higher ROI. Campaigns optimized by AI reduce wasted impressions, focus spending on high-value audiences, and generate more conversions per dollar spent. For customers, the experience also improves, as they are served ads that are more relevant to their interests and intent. These AI in eCommerce examples illustrate a win-win: businesses achieve better performance, while consumers encounter ads that feel personalized rather than intrusive.
Another major outcome is accessibility. These AI in eCommerce examples show that even smaller eCommerce businesses can now access advanced advertising capabilities that were once the domain of large enterprises with big budgets. Tools like Meta’s Advantage+ and Google’s Smart Bidding bring enterprise-level optimization to merchants of all sizes, making the competitive digital advertising landscape more level.
Content creation
Marketing and advertising have always depended on compelling content. From product descriptions and catalog copy to blog articles and ad creatives, content is the vehicle through which retailers communicate with their customers. But in the fast-moving world of online commerce, the demand for content has grown exponentially. Retailers must update thousands of product pages, launch campaigns across multiple channels, and adapt messaging to different regions, all while keeping quality consistent. Among the most important AI in eCommerce examples are those in content creation, where artificial intelligence is helping businesses scale content at unprecedented speed and efficiency.

AI in eCommerce examples of content creation involve systems that automatically generate product descriptions, craft catalog copy, write headlines, and even design personalized ad messaging. Instead of requiring teams of copywriters to manually produce every piece of text, machine learning and natural language generation (NLG) tools can create content instantly, often tailored to customer preferences or SEO goals. This not only saves time and resources but also ensures that retailers can keep up with the relentless pace of digital retail.
Shopify Magic auto-writing product descriptions
One of the most prominent AI in eCommerce examples of content creation comes from Shopify Magic, the AI tool integrated directly into the Shopify platform. For merchants, writing unique product descriptions is one of the most time-consuming tasks. Each new product requires a description that is not only accurate but also persuasive, keyword-rich, and aligned with the brand’s tone of voice. For small and medium-sized businesses managing hundreds or even thousands of SKUs, this can quickly become overwhelming.

Shopify Magic solves this problem by automatically generating product descriptions based on simple prompts or product details provided by the merchant. For instance, a seller might input basic information such as “red cotton T-shirt, casual wear, unisex” and Shopify Magic will generate a polished product description that highlights comfort, durability, and style. These AI in eCommerce examples show how merchants can instantly populate their stores with professional, engaging copy without hiring additional staff or spending countless hours writing manually.
The advantage of Shopify Magic goes beyond efficiency. Because the AI is trained to understand customer psychology and eCommerce best practices, the generated descriptions are not only grammatically correct but also optimized for conversion. Phrases that emphasize benefits, highlight urgency, or showcase social proof are integrated naturally into the copy. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how Shopify Magic helps merchants not only save time but also improve sales performance. For many small retailers, this tool is a game-changer, allowing them to compete with larger businesses that have dedicated marketing teams.
Wayfair AI catalog copy generation
Another compelling case among AI in eCommerce examples is Wayfair’s use of AI to generate catalog copy. As one of the world’s largest online furniture and home décor retailers, Wayfair manages millions of SKUs across a constantly expanding catalog. Manually creating and updating descriptions for every item is nearly impossible. To address this challenge, Wayfair implemented AI-driven content creation systems that automatically generate detailed, persuasive copy for its catalog.
These AI in eCommerce examples show how Wayfair uses artificial intelligence to analyze product specifications, material details, and design attributes to create descriptions that appeal to customers. For example, an AI-generated description for a sofa might emphasize the softness of the fabric, the durability of the frame, and the suitability for modern living spaces. Instead of presenting dry technical data, the AI transforms structured information into engaging narratives that highlight both functional and emotional benefits.
Wayfair’s approach also ensures consistency across its vast catalog. With millions of items coming from different suppliers, there is often a risk of fragmented or inconsistent descriptions. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how AI standardizes tone, style, and quality, ensuring that customers receive a seamless brand experience no matter what product they are browsing. For Wayfair, this consistency translates into stronger trust, fewer returns due to unclear product descriptions, and higher overall sales.
Result: Scaling content at speed
Perhaps the most important takeaway from these AI in eCommerce examples is the ability to scale content creation at a speed that matches the demands of digital retail. Modern eCommerce businesses must constantly add new products, adapt to seasonal campaigns, and localize content for international audiences. Human teams alone cannot keep pace without significant investment. AI, however, allows retailers to create, update, and optimize content in real time.

Scaling content with AI offers several key advantages. First, it reduces the time to market for new products. Instead of waiting days or weeks for descriptions and campaign copy to be written, retailers can launch new items almost instantly. Second, it enables continuous testing and optimization. These AI in eCommerce examples show how content can be generated in multiple variations, tested for performance, and refined automatically based on engagement metrics. This kind of agility ensures that campaigns remain fresh and effective without draining creative resources.
Localization is another critical benefit of scaling content with AI. Global retailers must provide product descriptions and advertising in multiple languages, tailored to cultural nuances. Manual translation and rewriting are expensive and time-consuming, but AI-driven systems can instantly generate localized content that feels natural to each market. These AI in eCommerce examples prove how retailers can expand internationally without being slowed down by the challenges of language and cultural adaptation.
AI in influencer & affiliate marketing
Among the most powerful AI in eCommerce examples are those in influencer and affiliate marketing, where artificial intelligence transforms guesswork into a data-driven process. Instead of relying on intuition, manual research, or vanity metrics like follower counts, AI platforms now analyze vast amounts of data to connect brands with influencers who align with their goals. These systems also measure potential return on investment (ROI) before a campaign even begins, ensuring that marketing budgets are spent effectively. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate that influencer and affiliate marketing no longer have to be risky bets—they can be optimized with the same precision as programmatic advertising.
AI platforms matching brands with influencers
One of the most direct AI in eCommerce examples in this space is the use of AI-powered platforms that match brands with influencers. Traditional influencer selection was time-intensive: marketers had to sift through hundreds of profiles, evaluate engagement metrics manually, and hope the influencer’s audience aligned with their target customers. AI platforms like Heepsy AI have revolutionized this process by automating influencer discovery and analysis.

Heepsy AI, for instance, scans millions of influencer profiles across social media platforms, evaluating metrics such as audience demographics, engagement rates, content themes, and follower authenticity. By doing so, it helps brands identify influencers whose audiences closely mirror their target customers. For example, a sustainable fashion retailer can use AI to filter influencers with environmentally conscious audiences, ensuring that marketing messages reach receptive consumers. These AI in eCommerce examples show how artificial intelligence removes the guesswork from influencer discovery, making partnerships more strategic and effective.
The efficiency gains are significant. What once took weeks of manual research can now be achieved in minutes. Beyond speed, AI-driven platforms also reduce the risk of fraud by detecting suspicious patterns such as inflated follower counts or inauthentic engagement. These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how brands can protect themselves while ensuring that partnerships are built on genuine influence.
Predicting influencer ROI using machine learning
Another critical category of AI in eCommerce examples is predictive modeling for influencer ROI. Marketers often struggle to justify investments in influencer marketing because results can vary widely between creators. While one influencer partnership may drive significant sales, another might generate little more than brand impressions. Machine learning addresses this challenge by analyzing past campaign data, audience engagement patterns, and influencer content performance to forecast ROI.

For example, predictive AI systems can examine an influencer’s historical performance across campaigns—measuring not only likes and comments but also click-through rates, conversion data, and long-term engagement. These AI in eCommerce examples show that machine learning models can predict whether an influencer is likely to deliver tangible results for a brand. Retailers can then allocate budgets more effectively, focusing on influencers with the highest likelihood of generating revenue rather than wasting resources on underperforming partnerships.
This predictive capability also extends to campaign strategy. By analyzing when an influencer’s audience is most active, which types of content formats resonate best, and what product categories have historically performed well, AI systems can recommend the optimal timing, creative style, and product focus for each campaign. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how machine learning not only identifies the right influencers but also provides actionable insights to maximize campaign success.
Result: Data-driven influencer selection
The rise of data-driven influencer selection represents one of the most practical AI in eCommerce examples in marketing. Traditional influencer campaigns often relied on superficial criteria like follower counts or personal connections between brands and influencers. However, these factors rarely correlated with actual performance. AI transforms influencer selection into a data-first process, where every decision is backed by measurable insights.
Data-driven selection begins with analyzing the demographics of an influencer’s audience: age, gender, location, income level, and even lifestyle preferences. These AI in eCommerce examples show how AI ensures that brands target influencers whose followers match their desired customer profile. For instance, a luxury skincare brand targeting women aged 30–45 in urban markets can use AI to filter out influencers whose audiences skew younger or more price-sensitive.

Beyond demographics, AI evaluates engagement quality. It distinguishes between genuine comments and automated spam, examines patterns of follower growth, and assesses the consistency of engagement across posts. These AI in eCommerce examples ensure that partnerships are built with influencers who have authentic, active audiences rather than inflated numbers. This precision minimizes risks and increases the likelihood of achieving strong ROI.
Affiliate marketing also benefits from data-driven selection. AI systems analyze affiliate performance data, including click-through rates, conversion rates, and average order values, to identify which affiliates deliver the highest returns. These AI in eCommerce examples show how AI helps brands prioritize top-performing affiliates, negotiate better terms, and expand relationships strategically. By focusing on evidence-based selection, businesses ensure that every partnership contributes meaningfully to growth.
AI in Visual & AR/VR Commerce
As online shopping becomes more immersive and interactive, visuals have taken center stage in shaping the customer journey. Consumers no longer want to rely on static images and generic product descriptions; they want to see, experience, and even virtually “try on” products before making a purchase. This shift has driven retailers to explore visual search, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) experiences. Among the most innovative AI in eCommerce examples are those that combine artificial intelligence with AR/VR commerce, enabling highly personalized, interactive, and engaging shopping experiences that reduce uncertainty and increase conversion.

Traditional eCommerce presented a gap between the physical and digital worlds: customers could see an image but not fully visualize how a sofa might look in their living room or whether a pair of glasses would suit their face shape. AI bridges this gap by powering visual recognition systems, enabling AR product visualization, and delivering VR shopping environments that replicate or even enhance in-store experiences. These AI in eCommerce examples show how computer vision, deep learning, and generative AI are being applied to create new standards for product discovery and consumer engagement.
Virtual try-ons
One of the most transformative innovations in digital retail is the concept of virtual try-ons, where artificial intelligence and augmented reality combine to allow shoppers to test products virtually before committing to a purchase. In categories like fashion, beauty, and footwear, the inability to try before buying has long been a barrier in eCommerce. Customers often hesitate because they cannot visualize how a lipstick shade might look on their skin, how a pair of sneakers will fit their feet, or how sunglasses will suit their face shape. Among the most practical and exciting AI in eCommerce examples are virtual try-on tools, which reduce uncertainty, build confidence, and significantly cut down on return rates.

Traditional product images and size charts are no longer enough for today’s consumers. Shoppers demand immersive experiences that replicate the advantages of in-store shopping while maintaining the convenience of digital commerce. Artificial intelligence, particularly computer vision and deep learning, makes this possible by analyzing facial features, body shapes, and environmental contexts to deliver realistic, interactive product simulations. These AI in eCommerce examples show how brands like L’Oréal, ModiFace, and Nike are pioneering virtual try-ons, changing how consumers engage with products online.
L’Oréal & ModiFace virtual makeup trials
One of the most widely recognized AI in eCommerce examples of virtual try-ons comes from L’Oréal, which acquired ModiFace, a company specializing in AR beauty technology. ModiFace uses AI-powered facial recognition and computer vision to simulate how different shades of lipstick, eyeshadow, foundation, or hair color will look on a customer’s face in real time through their smartphone or computer camera.
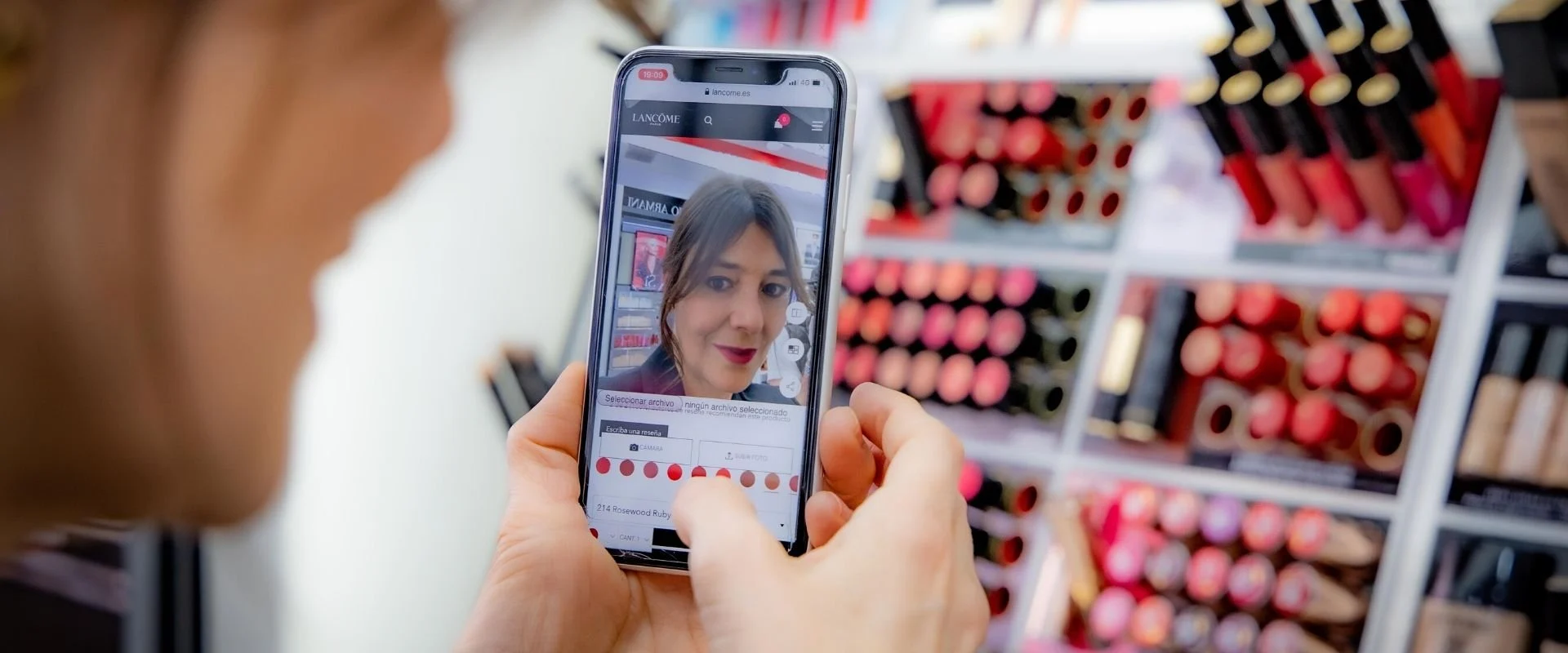

The system maps facial features with remarkable accuracy, adjusting for lighting conditions, skin tone, and movement. Customers can tilt their heads, smile, or change expressions, and the AI dynamically adapts the makeup visualization to maintain realism. These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how artificial intelligence creates highly personalized experiences that give shoppers confidence in their purchase decisions.

L’Oréal’s integration of ModiFace across its brand websites and retail apps has had a profound business impact. Shoppers who use virtual try-ons are more likely to complete purchases because they can preview products with greater confidence. Returns also decline because customers have a clearer expectation of how products will look in real life. These AI in eCommerce examples illustrate how virtual try-ons address one of the beauty industry’s greatest challenges: product mismatch leading to dissatisfaction and returns.
The innovation also supports inclusivity. With AI-driven try-ons, customers can test hundreds of shades and styles regardless of their skin tone or face shape, ensuring that product options feel accessible to all. These AI in eCommerce examples prove that virtual try-ons are not only about convenience but also about building stronger emotional connections between brands and diverse consumer groups.
Nike AI-powered shoe try-ons
Another powerful case among AI in eCommerce examples is Nike’s adoption of AI-powered shoe try-on technology. Buying footwear online has always been tricky because of size discrepancies, fit variations, and the inability to physically test comfort. To solve this, Nike developed tools like Nike Fit, which use AI and computer vision to scan a customer’s feet using a smartphone camera.
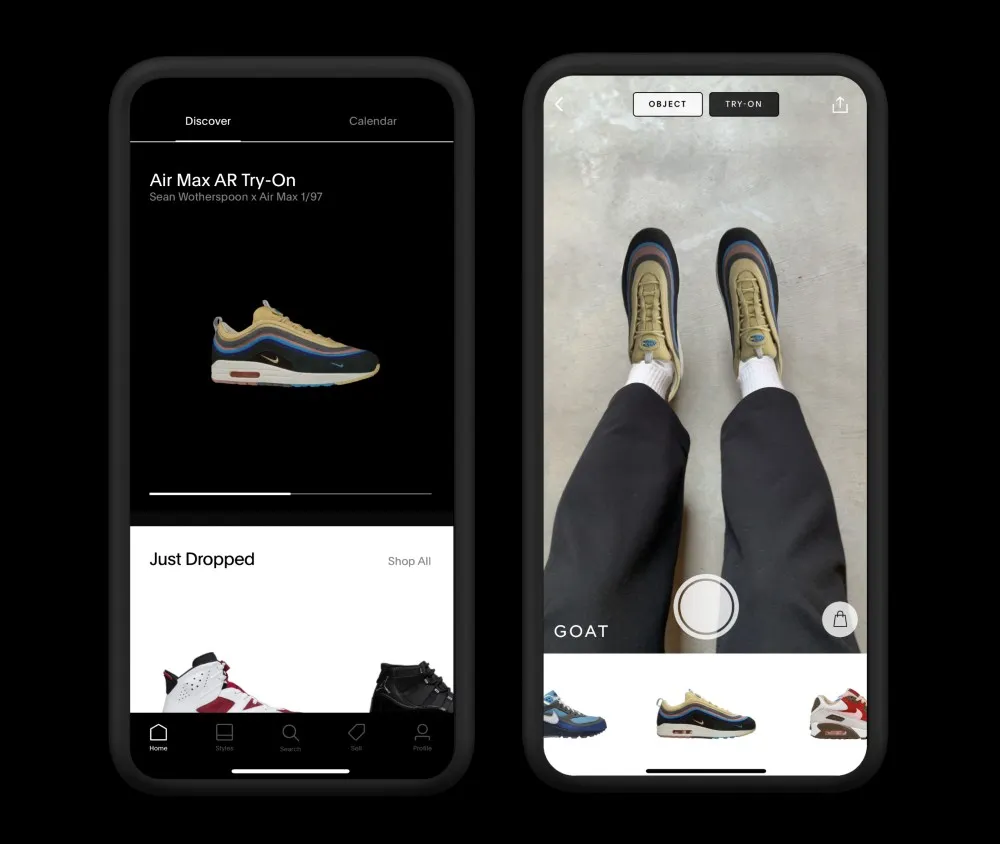
The AI system captures precise measurements of foot length, width, and shape, then recommends the most suitable shoe size for different Nike models. This is particularly valuable because sizes can vary even within the same brand depending on the shoe’s design. These AI in eCommerce examples show how artificial intelligence eliminates guesswork, making online shoe shopping more accurate and enjoyable.
Nike has also experimented with AR try-ons, allowing customers to point their phone cameras at their feet to see how different sneakers will look in real time. This combines the practical benefits of sizing accuracy with the fun of visual experimentation. Shoppers can quickly switch between models, colors, and styles, creating an interactive browsing experience that keeps them engaged longer. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how try-ons not only drive conversions but also strengthen brand engagement through gamified shopping experiences.
The business benefits are clear. With AI guiding size selection and visualization, Nike has reduced return rates caused by poor fit, one of the most common issues in online footwear sales. At the same time, customer satisfaction and loyalty have increased, as shoppers trust that their purchases will meet expectations. These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how virtual try-ons combine functional accuracy with engaging digital experiences to redefine online footwear shopping.
Result: Reducing returns and boosting confidence
The ultimate outcome of these AI in eCommerce examples is their ability to reduce returns while boosting customer confidence. Returns are one of the most expensive challenges in eCommerce, particularly in fashion and beauty, where mismatched expectations are common. Virtual try-ons address this directly by giving customers realistic previews of products before purchase. When shoppers know how a product will look or fit, they are less likely to return it, saving retailers significant costs in reverse logistics, restocking, and markdowns.
Beyond cost savings, virtual try-ons build trust and confidence in the buying process. Customers who can experiment with products virtually feel empowered to make informed decisions. This creates a sense of ownership before the purchase even occurs, increasing satisfaction and reducing buyer’s remorse. These AI in eCommerce examples show how artificial intelligence transforms hesitation into confidence, directly improving conversion rates and long-term loyalty.

The technology also enhances customer engagement. Virtual try-ons are interactive and often entertaining, encouraging shoppers to spend more time exploring products. This additional engagement not only increases the likelihood of purchase but also strengthens the emotional connection between customers and brands. These AI in eCommerce examples underline how the intersection of AI, AR, and personalization can transform shopping into a more meaningful experience.
From a strategic perspective, virtual try-ons also provide retailers with valuable data. By analyzing which products customers experiment with most frequently, AI systems can identify trends, optimize inventory, and personalize recommendations. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate that try-on technology benefits both customers and businesses, creating a feedback loop that improves product development and marketing strategies.
AI-generated imagery
High-quality imagery has always been the backbone of eCommerce. Customers cannot physically touch or test products online, so visuals must do the heavy lifting in building confidence, inspiring desire, and closing sales. However, creating professional product photography is expensive, time-consuming, and often inflexible. Retailers must organize photoshoots, coordinate models or stylists, and re-shoot whenever designs or catalog updates are required. Among the most transformative AI in eCommerce examples is the use of AI-generated imagery, which replaces or supplements traditional photography with AI-created visuals that are faster, cheaper, and highly customizable.

Artificial intelligence, powered by deep learning and generative adversarial networks (GANs), can now generate photorealistic images of products, models, and even complete room settings. These images are nearly indistinguishable from traditional photography but require only a fraction of the resources. Beyond speed and cost savings, AI-generated imagery offers unmatched flexibility: retailers can instantly create product visuals in different colors, contexts, or styles, tailoring catalogs for different markets or customer segments. These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing visual content creation, making it smarter, more efficient, and more engaging.
Zalando AI fashion design experiments
One of the most striking AI in eCommerce examples of AI-generated imagery comes from Zalando, the European online fashion giant. Zalando has been experimenting with AI tools that generate fashion designs and product imagery. The company’s AI systems use deep learning to analyze fashion trends, customer preferences, and design patterns, then create new garment visuals and outfit combinations that appeal to shoppers.
Zalando’s experiments go beyond just generating static visuals. The AI can simulate how clothing will look on different body types, skin tones, and in varied settings. This creates inclusive product imagery that resonates with a broader customer base without requiring hundreds of photoshoots. These AI in eCommerce examples show how artificial intelligence democratizes fashion imagery, enabling greater personalization and inclusivity at scale.

The AI-generated visuals also accelerate Zalando’s design and catalog workflows. Instead of waiting weeks for prototypes and photoshoots, designers and marketers can preview and launch collections virtually within days. This agility is particularly valuable in fast fashion, where trends shift rapidly and speed is critical. These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how AI-generated imagery supports both creativity and operational efficiency.
Zalando’s initiatives also reflect a sustainability angle. By reducing the need for physical samples and large-scale photoshoots, the company lowers its environmental footprint. These AI in eCommerce examples illustrate how artificial intelligence not only creates efficiency but also supports greener retail practices—a growing priority for consumers.
IKEA AI furniture renders in home settings
Another powerful case among AI in eCommerce examples comes from IKEA, which has been experimenting with AI-generated imagery to create realistic furniture renders in home environments. IKEA already pioneered virtual visualization with its AR-based IKEA Place app, allowing customers to “place” digital furniture in their living rooms through their smartphones. The next evolution involves AI-generated renders that simulate not just products, but entire lifestyle scenes.
Using AI, IKEA can generate photorealistic images of furniture placed in different types of homes—urban apartments, suburban houses, or minimalist studios. The AI adjusts lighting, textures, and scale to make the images indistinguishable from real photography. Customers browsing IKEA’s catalog can therefore see how a sofa, bed, or dining table might look in a variety of settings without the company having to stage multiple photoshoots. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how AI-generated imagery makes product catalogs more immersive, versatile, and relatable.
Customization is another major benefit. AI can render the same furniture item in multiple color schemes or materials, allowing customers to visualize personalized options instantly. Instead of photographing every single variation of a product, IKEA can generate the visuals on demand. These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how artificial intelligence saves costs while simultaneously expanding customer choice.
The scalability of AI-generated renders is critical for a company with as large and diverse a catalog as IKEA. With thousands of SKUs and countless variations, traditional product photography is impractical at scale. AI-generated imagery provides a solution that is both efficient and flexible, ensuring that customers always have accurate, engaging visuals to guide their purchasing decisions.
Result: Faster catalog building and customization
The broader business impact of these AI in eCommerce examples is most evident in faster catalog building and customization. Traditional catalog creation is one of the costliest and most resource-intensive parts of eCommerce operations. From photographing each product variation to editing and formatting images for multiple platforms, the process consumes time and money that could otherwise be invested in innovation or marketing.

AI-generated imagery changes this equation entirely. Retailers can generate product visuals automatically, reducing production times from weeks to hours. For instance, a fashion retailer launching a new collection can generate hundreds of outfit combinations instantly, covering multiple colors, sizes, and contexts. These AI in eCommerce examples show how artificial intelligence accelerates time-to-market, enabling businesses to react quickly to trends or customer demand.
Customization also becomes seamless. Instead of offering one-size-fits-all imagery, retailers can generate visuals tailored to different demographics or markets. For example, a furniture retailer could showcase the same product in minimalist settings for European markets and in more colorful, family-oriented spaces for Asian customers. These AI in eCommerce examples highlight how imagery becomes a strategic tool for personalization, directly influencing customer engagement and conversion.

Another major outcome is improved customer confidence. Shoppers often abandon purchases because they cannot visualize products clearly. AI-generated imagery provides highly realistic previews that reduce uncertainty and buyer hesitation. This leads to higher conversion rates and fewer returns, as customers have a more accurate sense of what they are purchasing. These AI in eCommerce examples demonstrate how imagery is not just about aesthetics—it is about driving revenue and reducing operational inefficiencies.
The sustainability implications are equally significant. By reducing reliance on physical samples, travel for photoshoots, and large production teams, AI-generated imagery lowers the environmental impact of eCommerce. These AI in eCommerce examples prove that artificial intelligence can align business goals with sustainability initiatives, addressing both profitability and social responsibility.
Conclusion
AI is no longer just a tool—it is the experience customers remember. From hyper-personalized recommendations to seamless multilingual support and AR-powered shopping, businesses are proving that intelligent engagement is the real differentiator in today’s market. Part 1 of these AI in eCommerce examples demonstrates how innovation on the customer-facing side can capture attention, build loyalty, and set brands apart in an increasingly competitive landscape. These examples also show accessibility: while global leaders like Amazon or Sephora scale advanced models, smaller businesses can leverage off-the-shelf AI solutions to compete effectively without massive resources.
Yet, as engaging as these customer-facing features are, their long-term success depends on what Part 2 explores—operational intelligence. Without AI in pricing, logistics, and fraud detection, even the most personalized journeys would collapse under inefficiency or lack of trust. Together, the lessons from Part 1 and Part 2 illustrate that AI in eCommerce examples are not just about delighting customers on the surface but about creating a complete, intelligent value chain that works seamlessly from front to back.